El bazo desempeña un papel crucial en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la función inmunitaria, filtración de la sangre y almacenamiento de las plaquetas. La asplenia Asplenia Asplenia is the absence of splenic tissue or function and can stem from several factors ranging from congenital to iatrogenic. There is a distinction between anatomic asplenia, which is due to the surgical removal of the spleen, and functional asplenia, which is due to a condition that leads to splenic atrophy, infarct, congestion, or infiltrative disease. Asplenia es la ausencia de tejido o función esplénica y puede deberse a varios factores, desde congénitos hasta iatrogénicos. Existe una distinción entre la asplenia Asplenia Asplenia is the absence of splenic tissue or function and can stem from several factors ranging from congenital to iatrogenic. There is a distinction between anatomic asplenia, which is due to the surgical removal of the spleen, and functional asplenia, which is due to a condition that leads to splenic atrophy, infarct, congestion, or infiltrative disease. Asplenia anatómica, que se debe a la extirpación quirúrgica del bazo, y la asplenia Asplenia Asplenia is the absence of splenic tissue or function and can stem from several factors ranging from congenital to iatrogenic. There is a distinction between anatomic asplenia, which is due to the surgical removal of the spleen, and functional asplenia, which is due to a condition that leads to splenic atrophy, infarct, congestion, or infiltrative disease. Asplenia funcional, que se debe a una afección que provoca atrofia esplénica, infarto, congestión o enfermedad infiltrativa. Los LOS Neisseria cuerpos de Howell-Jolly se observan habitualmente en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el frotis de sangre periférica. Para el diagnóstico se utilizan imágenes abdominales y gammagrafías. El alto riesgo de sepsis Sepsis Systemic inflammatory response syndrome with a proven or suspected infectious etiology. When sepsis is associated with organ dysfunction distant from the site of infection, it is called severe sepsis. When sepsis is accompanied by hypotension despite adequate fluid infusion, it is called septic shock. Sepsis and Septic Shock por bacterias encapsuladas requiere el cumplimiento de un estricto calendario de vacunación y un tratamiento antibiótico temprano cuando se sospecha una infección. Los LOS Neisseria eventos tromboembólicos son comunes.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
El bazo es uno de los LOS Neisseria órganos linfáticos secundarios fundamentales para la función inmunitaria, que desempeña un papel en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el filtrado de la sangre y la eliminación de eritrocitos viejos o dañados. La asplenia Asplenia Asplenia is the absence of splenic tissue or function and can stem from several factors ranging from congenital to iatrogenic. There is a distinction between anatomic asplenia, which is due to the surgical removal of the spleen, and functional asplenia, which is due to a condition that leads to splenic atrophy, infarct, congestion, or infiltrative disease. Asplenia se define como la ausencia de bazo o de función esplénica.
La epidemiología difiere según la etiología.
| Categoría | Enfermedad/condición |
|---|---|
| Congénito |
|
| Iatrogénica |
|
| Circulatorias |
|
| Hematológicas/oncológicas |
|
| Hepáticas |
|
| Autoinmune |
|
| Gastrointestinales |
|
| Infecciosa |
|
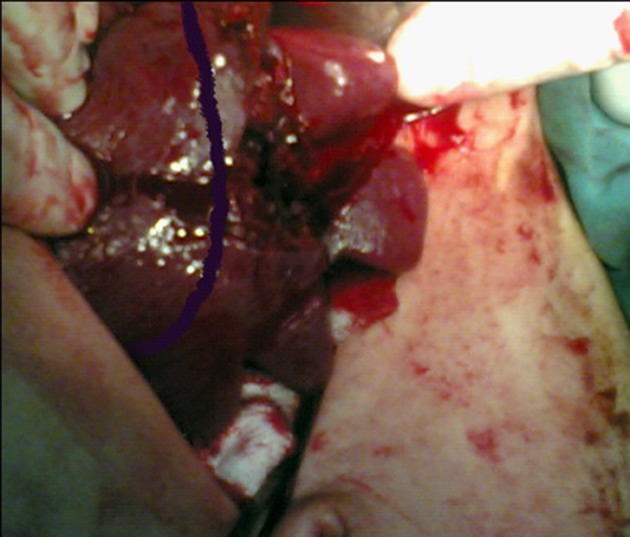
Lesión esplénica en estadio IV en un paciente de 34 años
Imagen: “Stage IV Splenic injury in a 34 Year Old Patient” por Eskandarlou, M., Derakhshanfar, A. Licencia: CC BY 3.0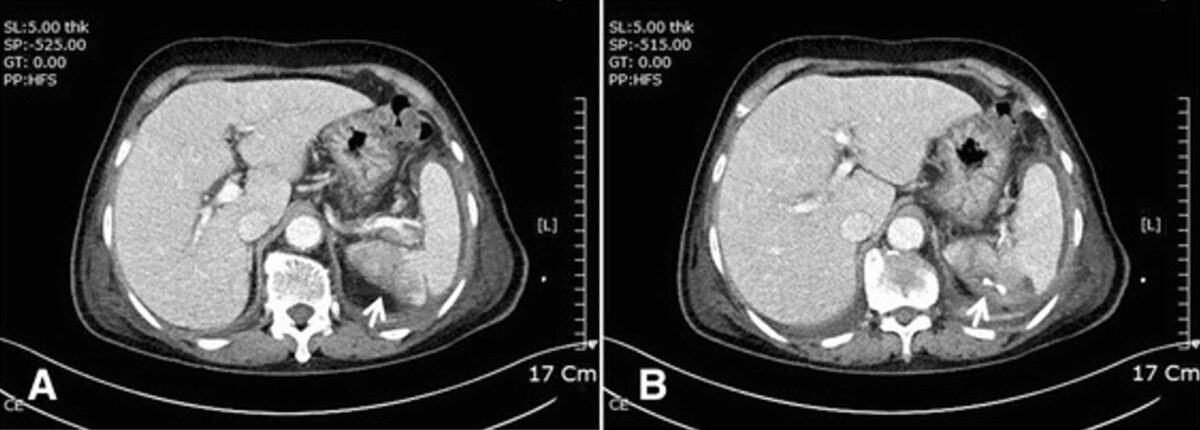
La TC muestra un infarto esplénico (A: flecha blanca) y un absceso con drenaje percutáneo (B: flecha blanca).
Image: “Complicated infective endocarditis: a case series” por Journal de Medical Case Reports. Licencia: CC BY 4.0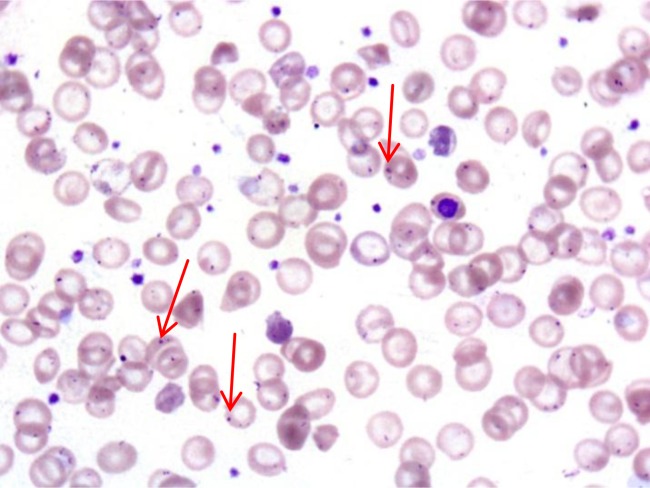
Cuerpos de Howell-Jolly:
Cuerpos de Howell-Jolly (flechas rojas) en los glóbulos rojos circulantes de un paciente con síndrome de sepsis grave post-esplenectomía (OPSI, por sus siglas en inglés)
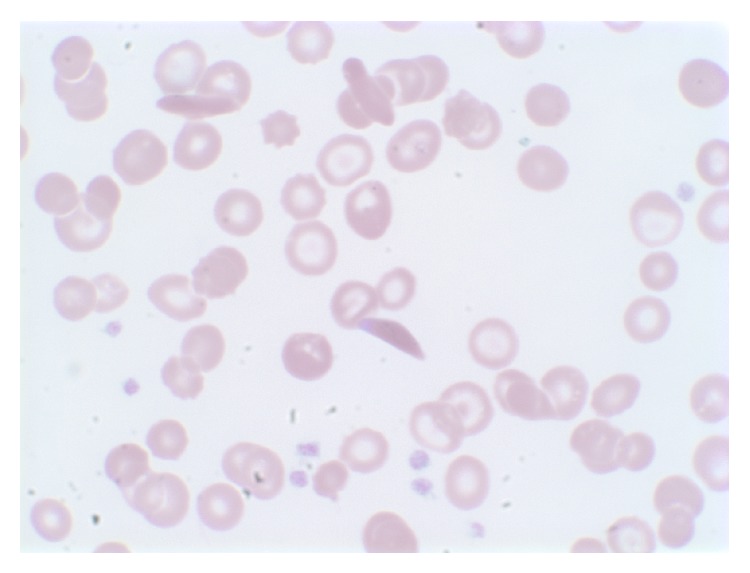
El frotis de sangre periférica del paciente a gran aumento muestra células falciformes irreversibles, anisocitosis, poiquilocitosis y células en diana.
Imagen: “Peripheral blood smear” por Shemisa K, Jafferjee N, Thomas D, Jacobs G, Meyerson HJ. Licencia: CC BY 3.0El tratamiento depende de la causa subyacente, el grado de asplenia Asplenia Asplenia is the absence of splenic tissue or function and can stem from several factors ranging from congenital to iatrogenic. There is a distinction between anatomic asplenia, which is due to the surgical removal of the spleen, and functional asplenia, which is due to a condition that leads to splenic atrophy, infarct, congestion, or infiltrative disease. Asplenia y la edad. Los LOS Neisseria pacientes > 5 años tienen un mejor pronóstico. La prevención de infecciones es la piedra angular de los LOS Neisseria cuidados a largo plazo, debido al AL Amyloidosis mayor riesgo de septicemia de rápida evolución, que es mortal en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el 50% de los LOS Neisseria pacientes.
Septicemia de inicio rápido: