Las infecciones intestinales por anquilostoma que afectan al AL Amyloidosis ser humano son causadas principalmente por Necator americanus Necator americanus A common parasite of humans in the moist tropics and subtropics. These organisms attach to villi in the small intestine and suck blood causing diarrhea, anorexia, and anemia. Hookworm Infections y Ancylostoma duodenale Ancylostoma Duodenale Hookworm Infections. Millones de personas a nivel mundial están infectadas, principalmente en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum las regiones tropicales, donde los LOS Neisseria ambientes cálidos y húmedos facilitan la supervivencia de las larvas en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el suelo. La transmisión se produce a través de la penetración dérmica de las larvas. Una vez adentro, el parásito realiza un pasaje transpulmonar, alcanzando la tráquea y la faringe, donde es deglutido. En EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el intestino delgado, los LOS Neisseria vermes maduran y se adhieren al AL Amyloidosis duodeno. La diarrea, las náuseas y los LOS Neisseria vómitos son síntomas gastrointestinales. Las complicaciones son la hemorragia (que produce anemia Anemia Anemia is a condition in which individuals have low Hb levels, which can arise from various causes. Anemia is accompanied by a reduced number of RBCs and may manifest with fatigue, shortness of breath, pallor, and weakness. Subtypes are classified by the size of RBCs, chronicity, and etiology. Anemia: Overview and Types) y posteriormente la desnutrición. El diagnóstico se realiza por microscopía de heces que muestra los LOS Neisseria huevos de anquilostoma y por PCR PCR Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is a technique that amplifies DNA fragments exponentially for analysis. The process is highly specific, allowing for the targeting of specific genomic sequences, even with minuscule sample amounts. The PCR cycles multiple times through 3 phases: denaturation of the template DNA, annealing of a specific primer to the individual DNA strands, and synthesis/elongation of new DNA molecules. Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR). El tratamiento preventivo se centra en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum un saneamiento adecuado y la desparasitación periódica en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria grupos de alto riesgo. El tratamiento consiste en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el uso de medicamentos antiparasitarios, con suplementos de hierro para la anemia Anemia Anemia is a condition in which individuals have low Hb levels, which can arise from various causes. Anemia is accompanied by a reduced number of RBCs and may manifest with fatigue, shortness of breath, pallor, and weakness. Subtypes are classified by the size of RBCs, chronicity, and etiology. Anemia: Overview and Types.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
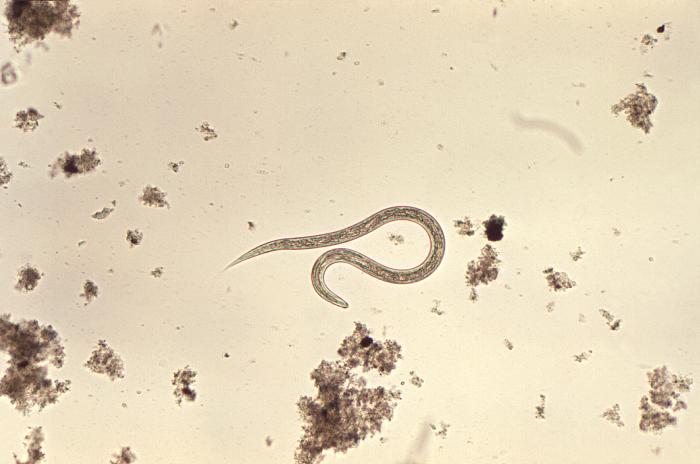
Microfotografía que muestra la morfología ultraestructural que presenta una larva filariforme de anquilostoma
Imagen: “1431” por Dr. Mae Melvin. Licencia: Dominio Público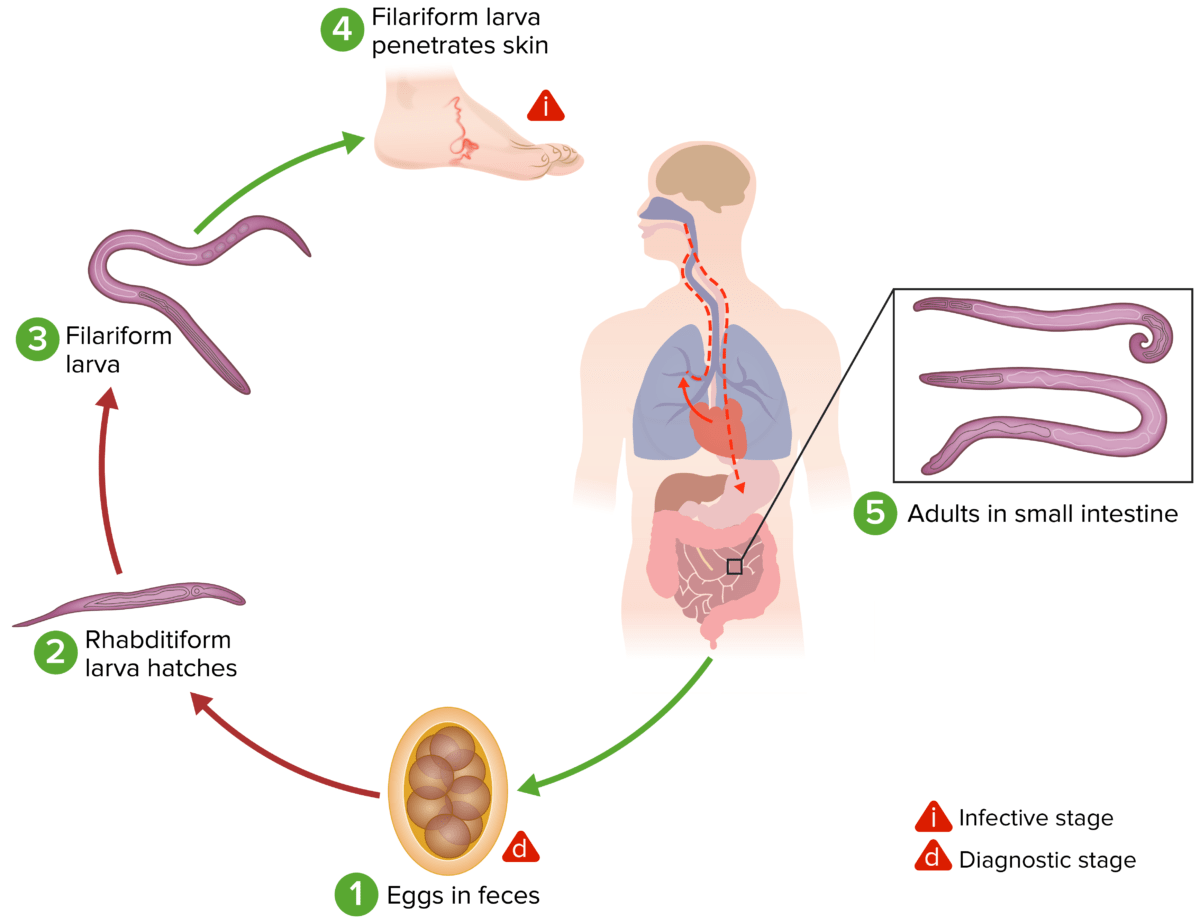
Ciclo vital de los anquilostomas:
(1) Los huevos de las heces contaminan el suelo. En condiciones favorables (humedad, calor, sombra), las larvas eclosionan en 1-2 días.
(2) Las larvas rabditiformes crecen en las heces y/o en el suelo, y (3) posteriormente se convierten en las larvas filariformes infecciosas.
(4) Un huésped humano entra en contacto con el suelo contaminado, las larvas penetran en la piel y, con la circulación, pasan a través del corazón y luego a los pulmones (alvéolos pulmonares). Las larvas ascienden por el árbol bronquial hasta la faringe y son deglutidas. A continuación, las larvas llegan al intestino delgado, donde maduran hasta convertirse en adultos.
(5) Los gusanos adultos se adhieren a la pared intestinal con la consiguiente pérdida de sangre por parte del huésped. La mayoría de los gusanos adultos viven hasta 1-2 años, incluso más en algunos huéspedes.
Algunas larvas de A. duodenale pueden quedar latentes (en el intestino o en el músculo) tras la penetración en la piel. Además, la infección por A. duodenale puede transmitirse por vía oral y transmamaria.
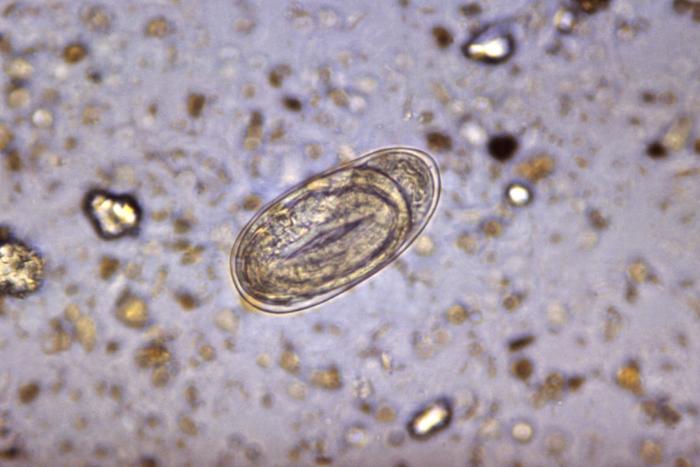
Las características diagnósticas de los huevos de anquilostoma incluyen una cáscara fina, de forma ovalada o elipsoidal.
Imagen: “4825” por CDC. Licencia: Dominio PúblicoTratamiento médico:
Prevención: