A síndrome de Sturge-Weber (SSW) é um distúrbio neurocutâneo congénito que se apresenta com uma marca de nascença facial chamada mancha vinho do porto ( MVP MVP Mitral valve prolapse (MVP) is the most common cardiac valvular defect, and is characterized by bulging of the mitral valve (MV) cusps into the left atrium (LA) during systole. Mitral valve prolapse is most commonly due to idiopathic myxomatous degeneration. Patients are typically asymptomatic. Mitral Valve Prolapse), alterações neurológicas, como convulsões, e alterações oculares, como glaucoma Glaucoma Glaucoma is an optic neuropathy characterized by typical visual field defects and optic nerve atrophy seen as optic disc cupping on examination. The acute form of glaucoma is a medical emergency. Glaucoma is often, but not always, caused by increased intraocular pressure (IOP). Glaucoma. Nem todos estes sintomas precisam de estar presentes num indivíduo afetado, e alguns podem desenvolver-se mais MAIS Androgen Insensitivity Syndrome tarde. Embora a condição seja congénita, não é herdada, pois a mutação causadora no gene Gene A category of nucleic acid sequences that function as units of heredity and which code for the basic instructions for the development, reproduction, and maintenance of organisms. Basic Terms of Genetics GNAQ é somática e esporádica. A suspeita do diagnóstico ocorre com base nos sintomas e na neuroimagem e é confirmada com testes Testes Gonadal Hormones genéticos. O tratamento é direcionado ao controlo dos sintomas e prevenção de convulsões e hemiparésia.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
A incidência é de aproximadamente 1 em 20.000 a 50.000 recém-nascidos vivos.
Os sintomas são geralmente causados pelo efeito da malformação capilar-venosa no cérebro, na pele e no olho. Nem todos os sintomas precisam de estar presentes num indivíduo para que seja diagnosticado com SSW, e alguns sintomas podem desenvolver-se mais MAIS Androgen Insensitivity Syndrome tarde.
Mancha de vinho do Porto ( MVP MVP Mitral valve prolapse (MVP) is the most common cardiac valvular defect, and is characterized by bulging of the mitral valve (MV) cusps into the left atrium (LA) during systole. Mitral valve prolapse is most commonly due to idiopathic myxomatous degeneration. Patients are typically asymptomatic. Mitral Valve Prolapse):
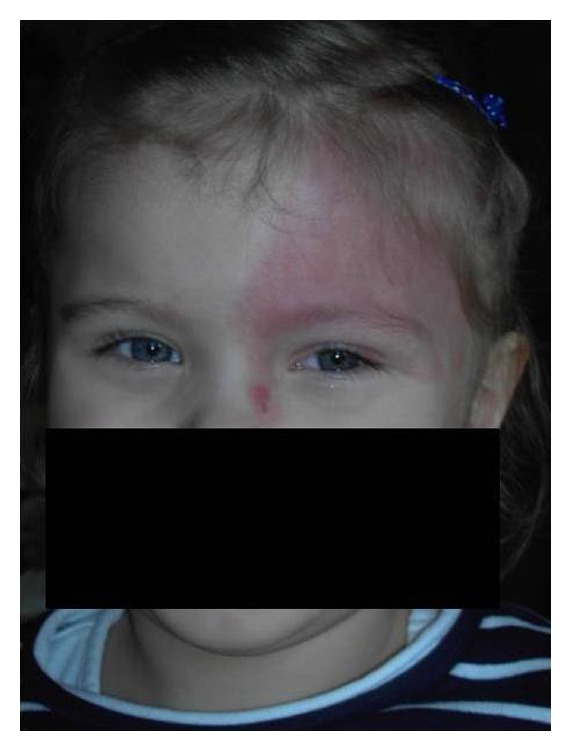
Mancha de vinho do Porto (MVP):
Nevus flammeus difuso a envolver a pálpebra superior esquerda e a testa
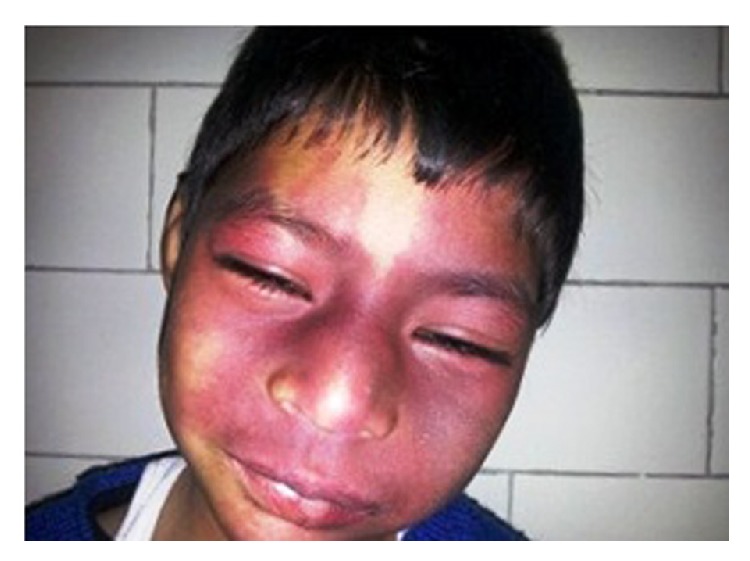
Mancha de vinho do Porto (MVP):
Nevus flammeus bilateral sobre a face
Uma forma fácil de lembrar é usando a mnemónica STURGE:
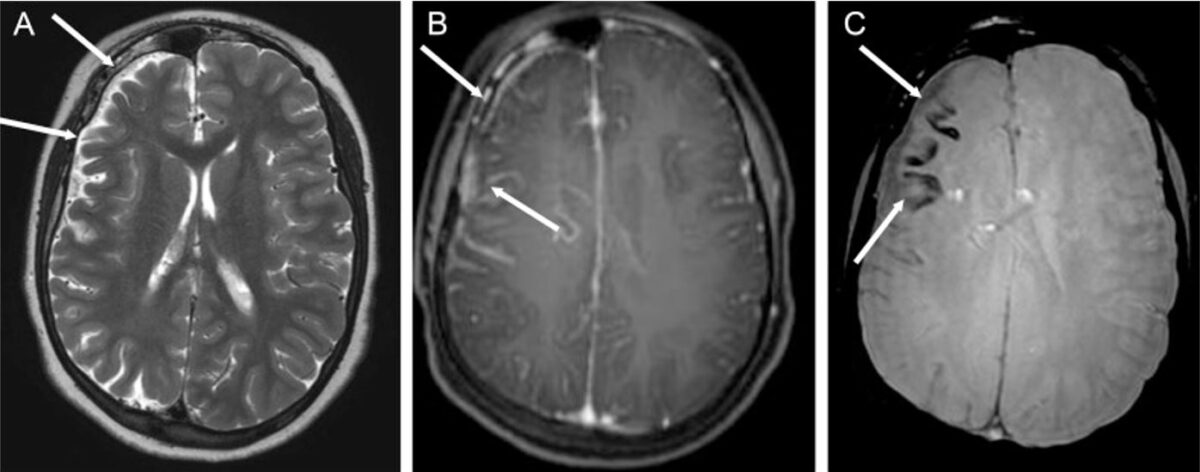
Epilepsia associada à síndrome de Sturge-Weber (SSW): síndrome de Sturge-Weber num menino de 14 anos com múltiplos focos epiléticos no hemisfério cerebral direito e epilepsia parcial crónica
A: imagem axial ponderada em T2 a demonstrar hemiatrofia cerebral direita (setas brancas)
B: sequência axial ponderada em T1 após injeção de gadolínio, a demonstrar realce leptomeníngeo da região frontoparietal (setas brancas)
C: As setas brancas apontam para calcificação cortical no lobo frontal, aparecendo como ausência de sinal nas imagens ponderadas obtidas.