Mycobacterium Mycobacterium Mycobacterium is a genus of the family Mycobacteriaceae in the phylum Actinobacteria. Mycobacteria comprise more than 150 species of facultative intracellular bacilli that are mostly obligate aerobes. Mycobacteria are responsible for multiple human infections including serious diseases, such as tuberculosis (M. tuberculosis), leprosy (M. leprae), and M. avium complex infections. Mycobacterium é um género da família Mycobacteriaceae Mycobacteriaceae A family of gram-positive bacteria found in soil and dairy products and as parasites on animals and man. Several are important pathogens. Mycobacterium do filo Actinobacteria Actinobacteria Class of bacteria with diverse morphological properties. Strains of actinobacteria show greater than 80% 16s rDNA/rRNA sequence similarity among each other and also the presence of certain signature nucleotides. Mycobacterium. As micobactérias compreendem mais MAIS Androgen Insensitivity Syndrome de 150 espécies de bacilos intracelulares facultativos, que são principalmente aeróbios obrigatórios. As micobactérias são responsáveis por múltiplas infeções humanas, incluindo doenças graves, como a tuberculose (M. tuberculosis Tuberculosis Tuberculosis (TB) is an infectious disease caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex bacteria. The bacteria usually attack the lungs but can also damage other parts of the body. Approximately 30% of people around the world are infected with this pathogen, with the majority harboring a latent infection. Tuberculosis spreads through the air when a person with active pulmonary infection coughs or sneezes. Tuberculosis), a lepra (M. leprae) e infeções do complexo M. avium. Embora os pulmões sejam o local mais MAIS Androgen Insensitivity Syndrome comum de infeção, as micobactérias podem colonizar e infetar outros sistemas de órgãos, incluindo os nódulos linfáticos, pele, seios da face, olhos, ouvidos, ossos, SNC e trato urinário.
Last updated: May 17, 2022
Morfologia e propriedades:
Propriedades da coloração:
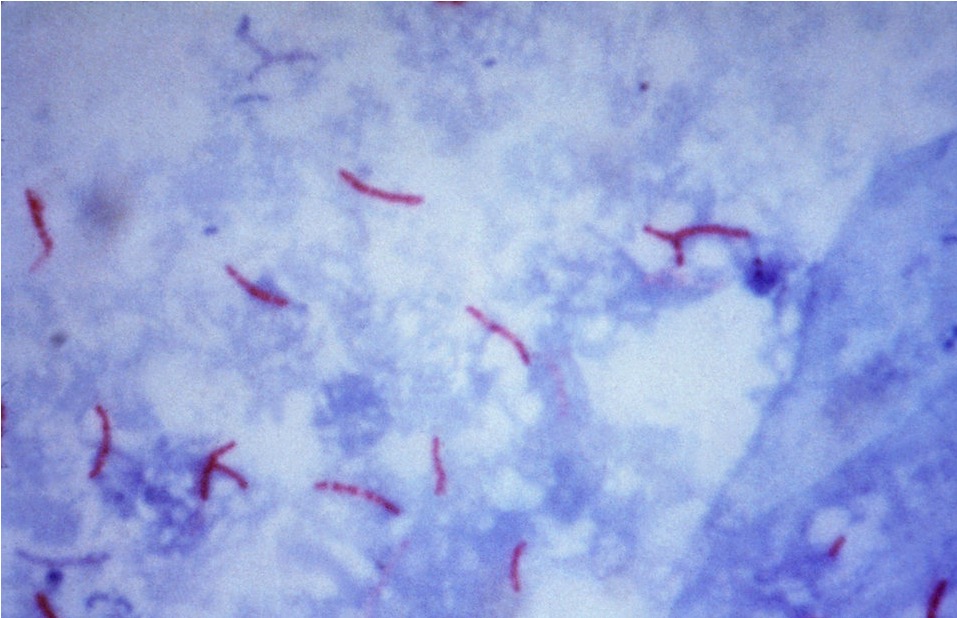
Coloração ácido-resistente de Mycobacterium tuberculosis
Imagem: “Mycobacterium tuberculosis bacteria” por CDC/Dr. George P. Kubica. Licença: Domínio Público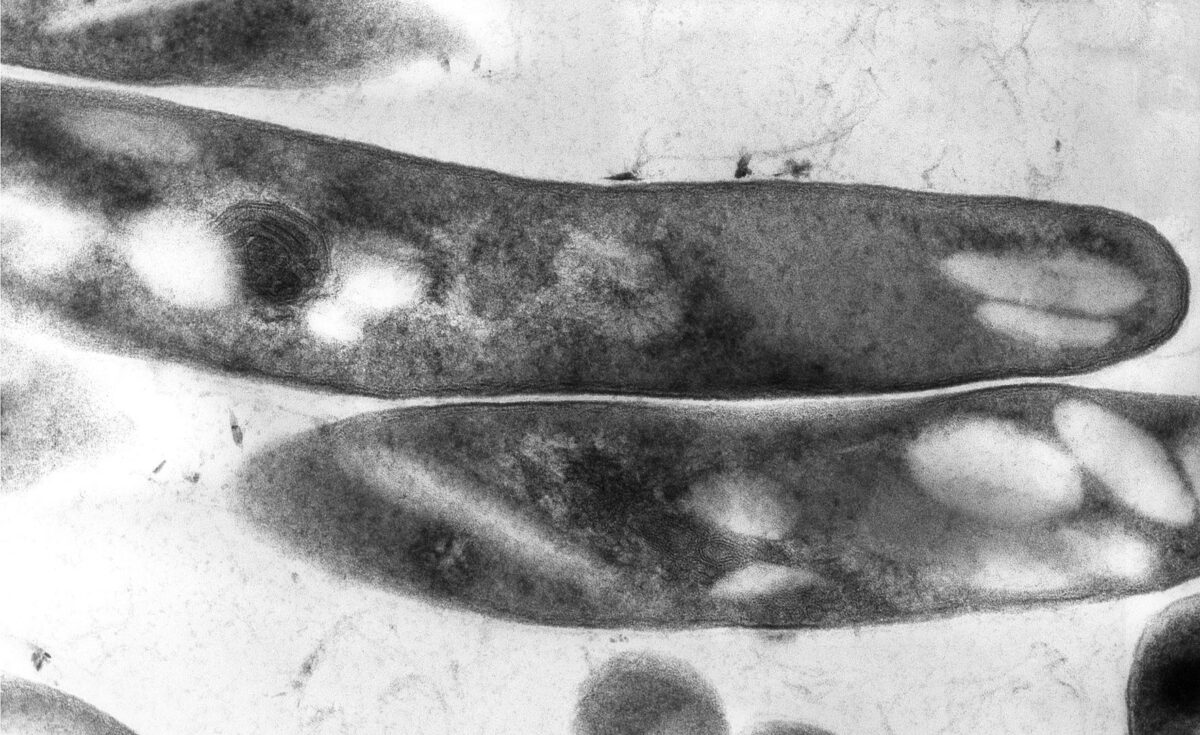
Micrografia eletrónica de Mycobacterium tuberculosis
Imagem: “Mycobacterium tuberculosis 01” por Elizabeth White. Licença: Domínio PúblicoMicobactérias:
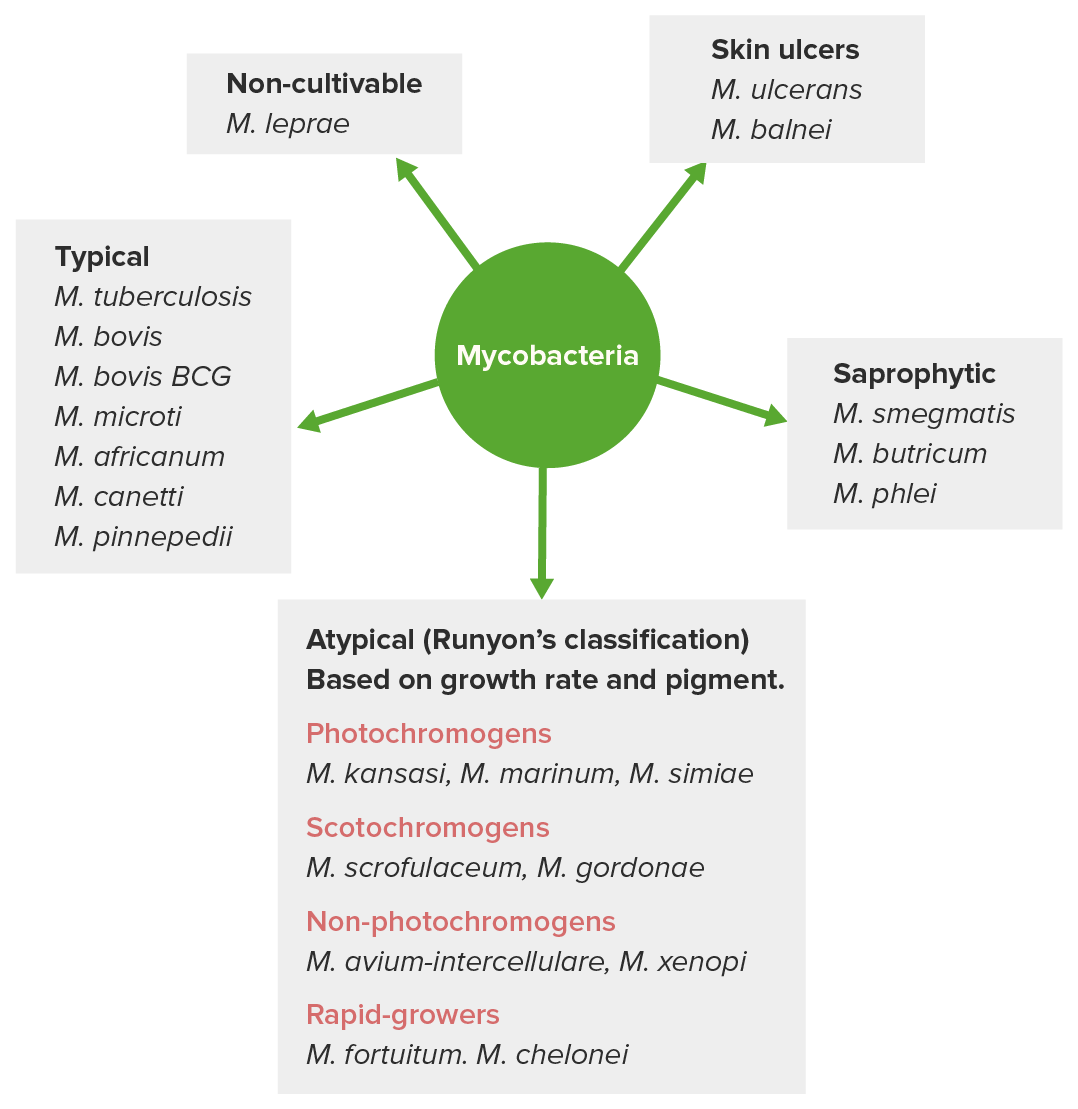
Classificação das micobactérias
Imagem por Lecturio. Licença: CC BY-NC-SA 4.0Espécies patogénicas mais MAIS Androgen Insensitivity Syndrome importantes:
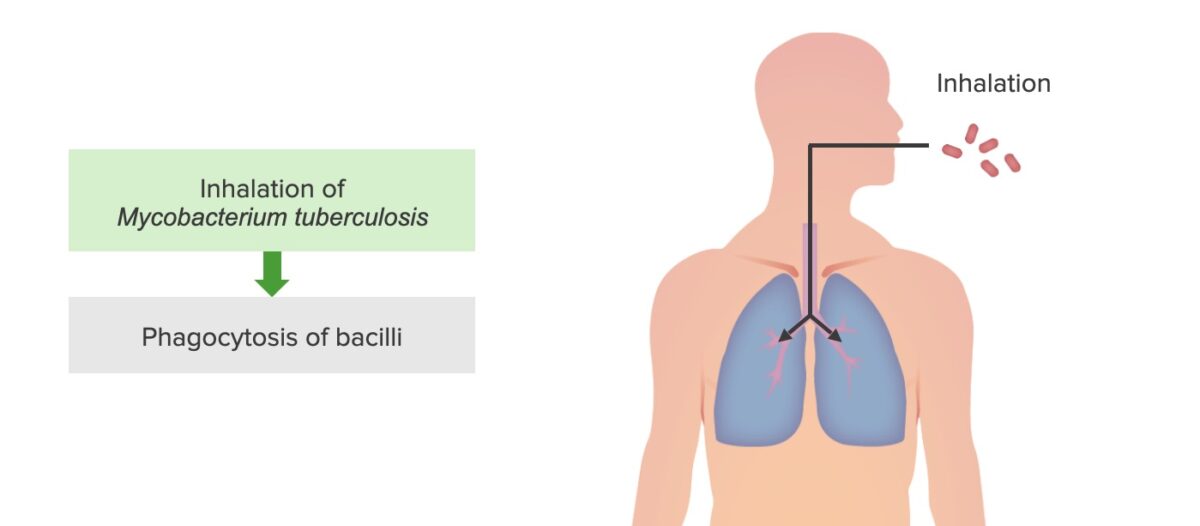
Etapa 1 da infeção por tuberculose: Inalação e fagocitose de M. tuberculosis por macrófagos alveolares
Imagem por Lecturio. Licença: CC BY-NC-SA 4.0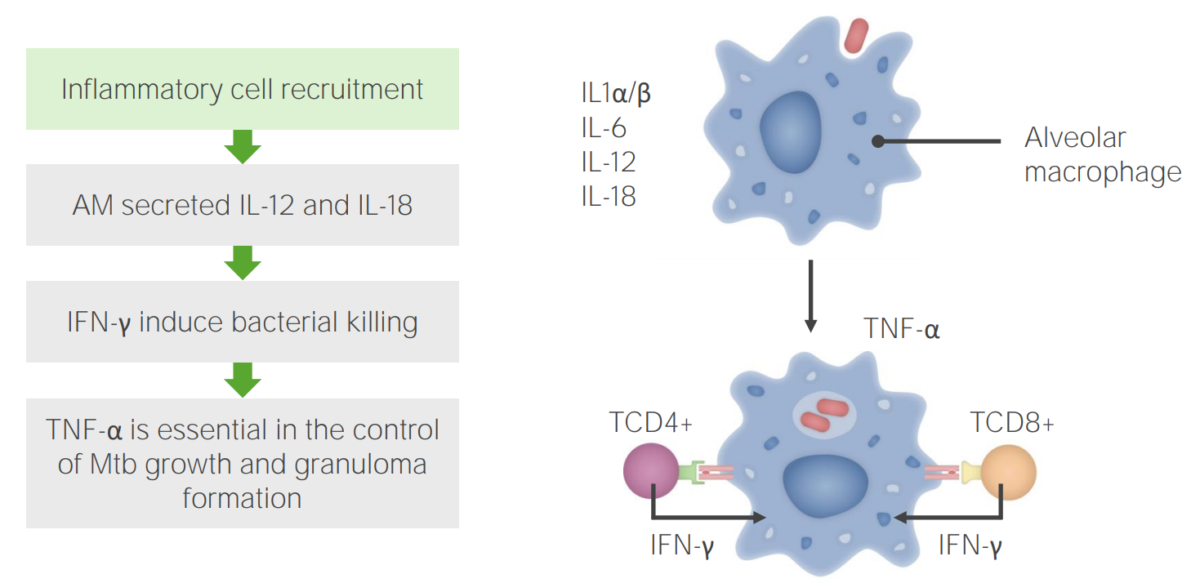
Etapa 2 da infeção por tuberculose: Recrutamento de células inflamatórias
MA: macrófagos alveolares
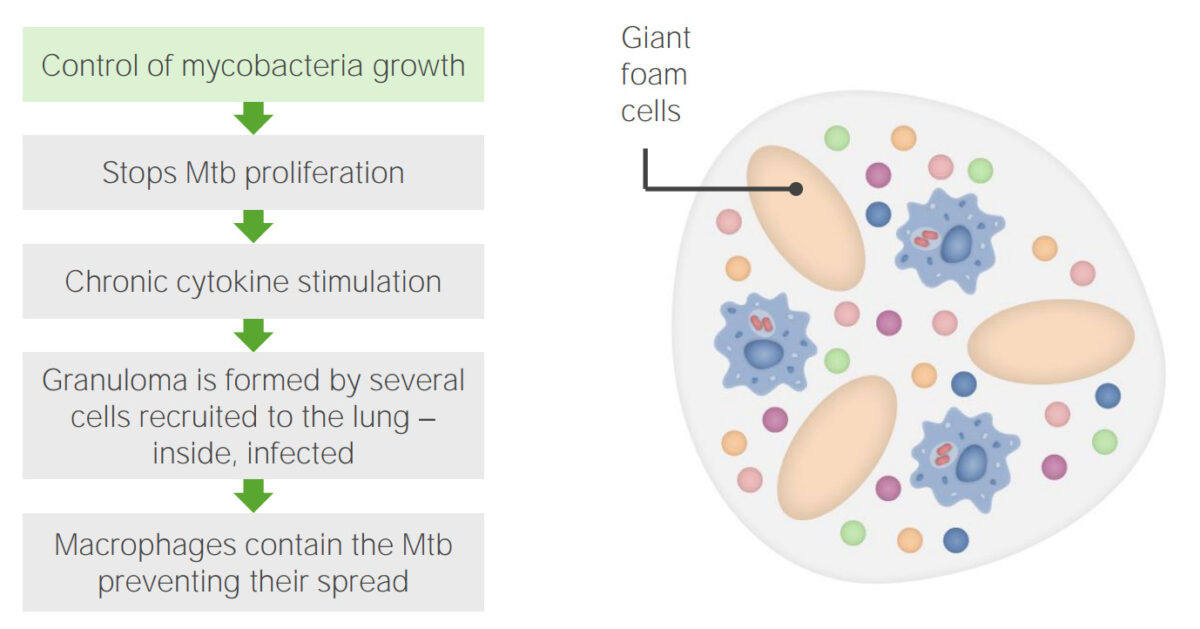
Etapa 3 da infeção da tuberculose: Formação do granuloma
Imagem por Lecturio. Licença: CC BY-NC-SA 4.0| Tuberculose primária | Tuberculose secundária | TB TB Tuberculosis (TB) is an infectious disease caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex bacteria. The bacteria usually attack the lungs but can also damage other parts of the body. Approximately 30% of people around the world are infected with this pathogen, with the majority harboring a latent infection. Tuberculosis spreads through the air when a person with active pulmonary infection coughs or sneezes. Tuberculosis extrapulmonar (miliar) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Apresentação clínica | Início até 2 anos de infeção em 5%–10% dos casos | Reativação da infeção em pacientes imunodeprimidos | Indivíduos imunodeprimidos |
| Localização |
|
|
|
| Sintomas |
|
Recorrência dos sintomas |
|
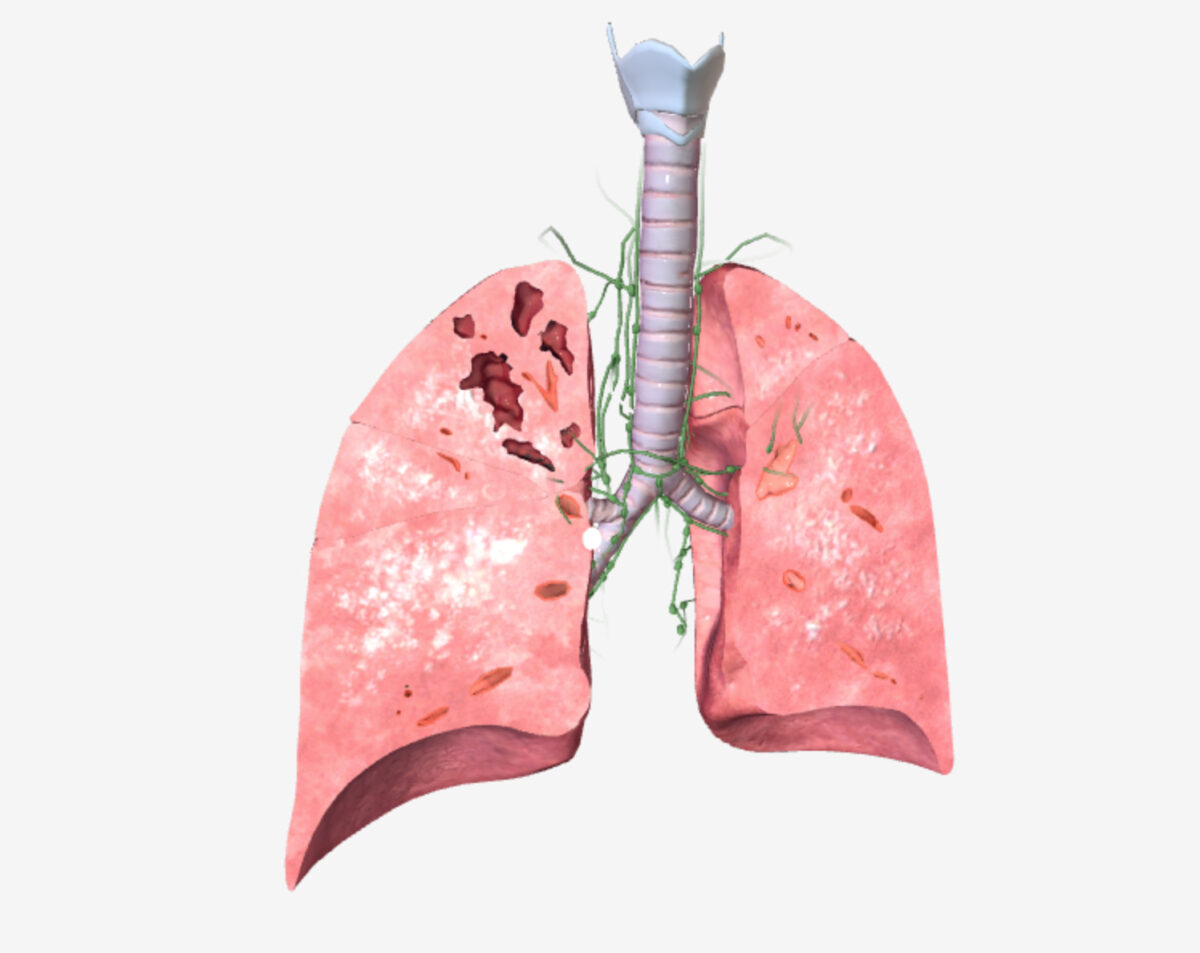
Tuberculose pulmonar (TB): manifestações primárias e secundárias da doença
Imagem por BioDigital, editada por Lecturio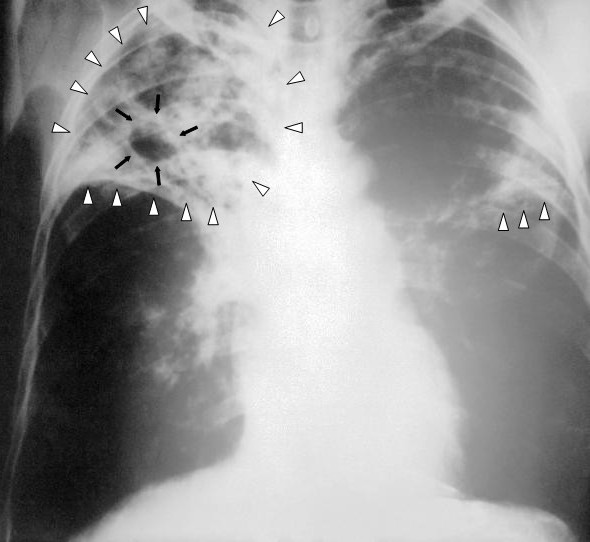
Radiografia de um paciente com tuberculose:
Radiografia do tórax com visualização de infiltrados reticulares bilaterais (triângulos brancos) e lesão cavitária (setas pretas) no lobo superior direito
Expetoração:
Cultura micobacteriana de sangue ou urina: em pacientes com VIH ou indivíduos imunodeprimidos
Teste tuberculínico (TST; PPD (derivado de proteína purificada) ou teste de Mantoux):
Ensaio de libertação de interferão gama-γ ( IGRA IGRA The assay of interferon-gamma released from lymphocytes after their exposure to a specific test antigen, to check for immunologic memory resulting from a previous exposure to the antigen. The amount of interferon-gamma released is usually assayed by an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Tuberculosis – Interferon-Gamma Release Assays): não faz distinção entre TB TB Tuberculosis (TB) is an infectious disease caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex bacteria. The bacteria usually attack the lungs but can also damage other parts of the body. Approximately 30% of people around the world are infected with this pathogen, with the majority harboring a latent infection. Tuberculosis spreads through the air when a person with active pulmonary infection coughs or sneezes. Tuberculosis ativa e inativa

Resposta imune à lepra
Imagem por Lecturio. Licença: CC BY-NC-SA 4.0| Tuberculoide | Lepromatosa | |
|---|---|---|
| Apresentação clínica | Indivíduos imunocompetentes | Indivíduos imunodeprimidos |
| Localização | Pele e nervos | Pele e nervos |
| Sintomas |
|
|
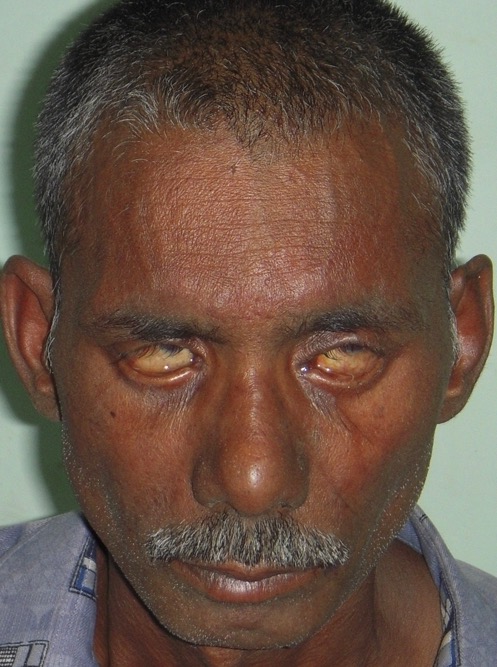
Lagoftalmo num paciente com lepra lepromatosa:
O paciente tenta fechar as pálpebras, mas não consegue.
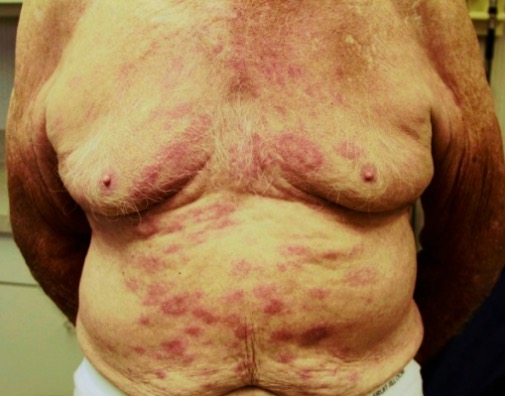
Lepra:
Manchas eritematosas cutâneas
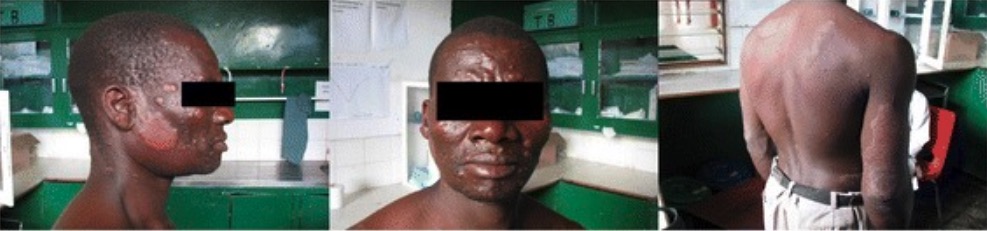
Lesões cutâneas generalizadas consistentes com lepra lepromatosa:
O paciente desenvolve uma fácies “leonina”, com numerosas pápulas e nódulos que acometem a face, tórax, tronco, membros inferiores e virilhas. Placas de grandes dimensões bem circunscritas sobre o tricípite braquial direito, ombro esquerdo e flanco direito.
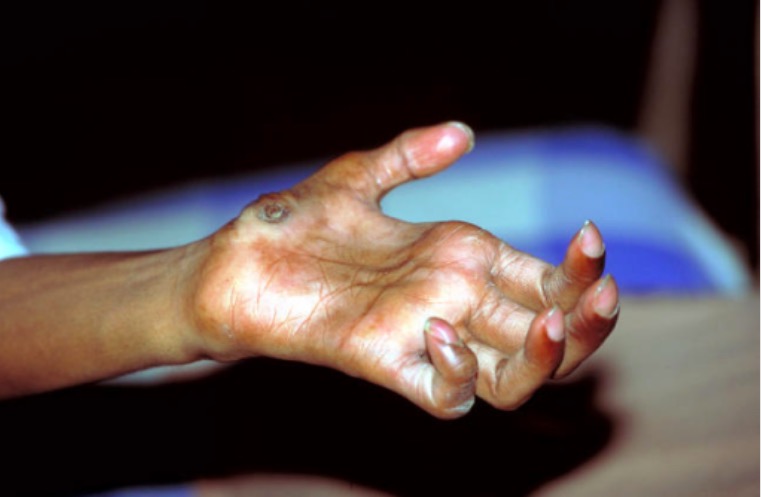
Dedos em garra:
Deformidade típica num paciente com lepra avançada
O microorganismo é identificado através de biópsia da pele:
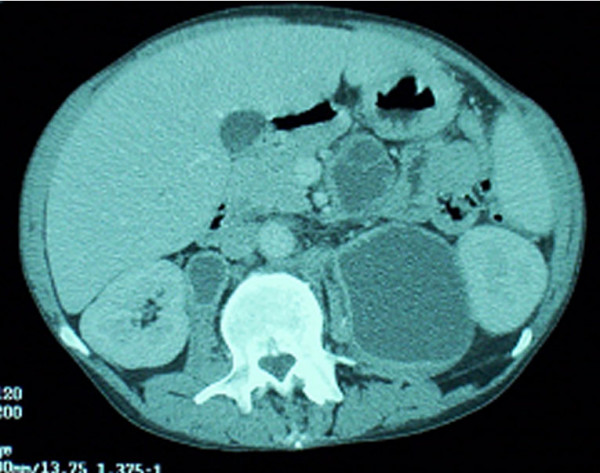
Infeção pelo MAC: TC abdominal com múltiplos abcessos intra-abdominais nos nódulos linfáticos
Imagem: “Mycobacterium avium complex immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome: long term outcomes” por Riddell J, Kaul DR, Karakousis PC, Gallant JE, Mitty J, Kazanjian PH. Licença: CC BY 2.0