Os inibidores de microtúbulos e de topoisomerases têm como alvo estruturas e processos celulares para inibir a proliferação de células cancerígenas. Os inibidores de microtúbulos atuam no citoesqueleto, enquanto que os inibidores de topoisomerases atuam numa enzima importante na replicação e na transcrição do DNA. O sistema de microtúbulos, juntamente com os microfilamentos e os filamentos intermediários, formam o citoesqueleto celular. Estes componentes são essenciais para a divisão, movimento e sinalização celular. Os taxanos e os alcaloides da vinca interferem com a função dos microtúbulos, portanto, como efeito, inibem a mitose. A topoisomerase auxilia na replicação de DNA ao criar quebras nas cadeias duplas e simples para libertar "supercoils". A inibição da enzima causa o fim da replicação do DNA DNA A deoxyribonucleotide polymer that is the primary genetic material of all cells. Eukaryotic and prokaryotic organisms normally contain DNA in a double-stranded state, yet several important biological processes transiently involve single-stranded regions. DNA, which consists of a polysugar-phosphate backbone possessing projections of purines (adenine and guanine) and pyrimidines (thymine and cytosine), forms a double helix that is held together by hydrogen bonds between these purines and pyrimidines (adenine to thymine and guanine to cytosine). DNA Types and Structure e danos no DNA DNA A deoxyribonucleotide polymer that is the primary genetic material of all cells. Eukaryotic and prokaryotic organisms normally contain DNA in a double-stranded state, yet several important biological processes transiently involve single-stranded regions. DNA, which consists of a polysugar-phosphate backbone possessing projections of purines (adenine and guanine) and pyrimidines (thymine and cytosine), forms a double helix that is held together by hydrogen bonds between these purines and pyrimidines (adenine to thymine and guanine to cytosine). DNA Types and Structure. Existem vários agentes quimioterápicos em cada classe que normalmente produzem mielossupressão como um efeito adverso.
Last updated: Aug 29, 2025
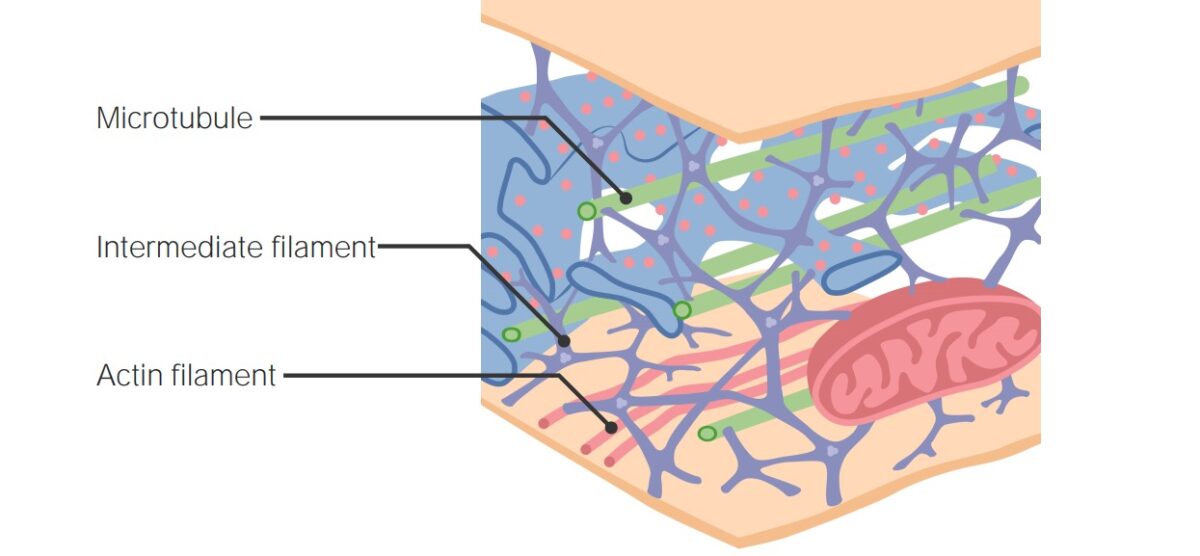
Filamentos do citoesqueleto
Imagem por Lecturio.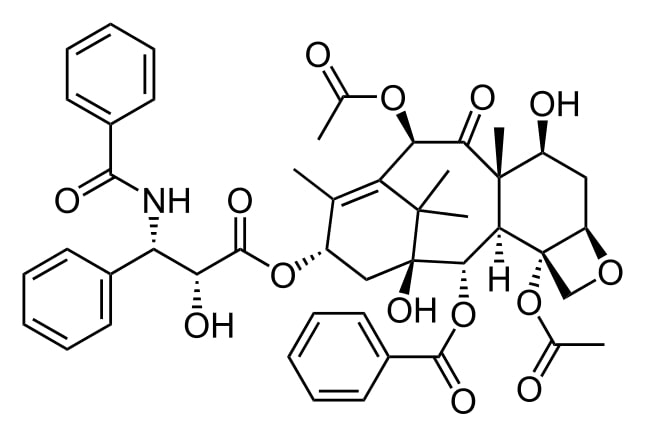
Estrutura do paclitaxel
Imagem: “Taxol” por Calvero. Licença: Public Domain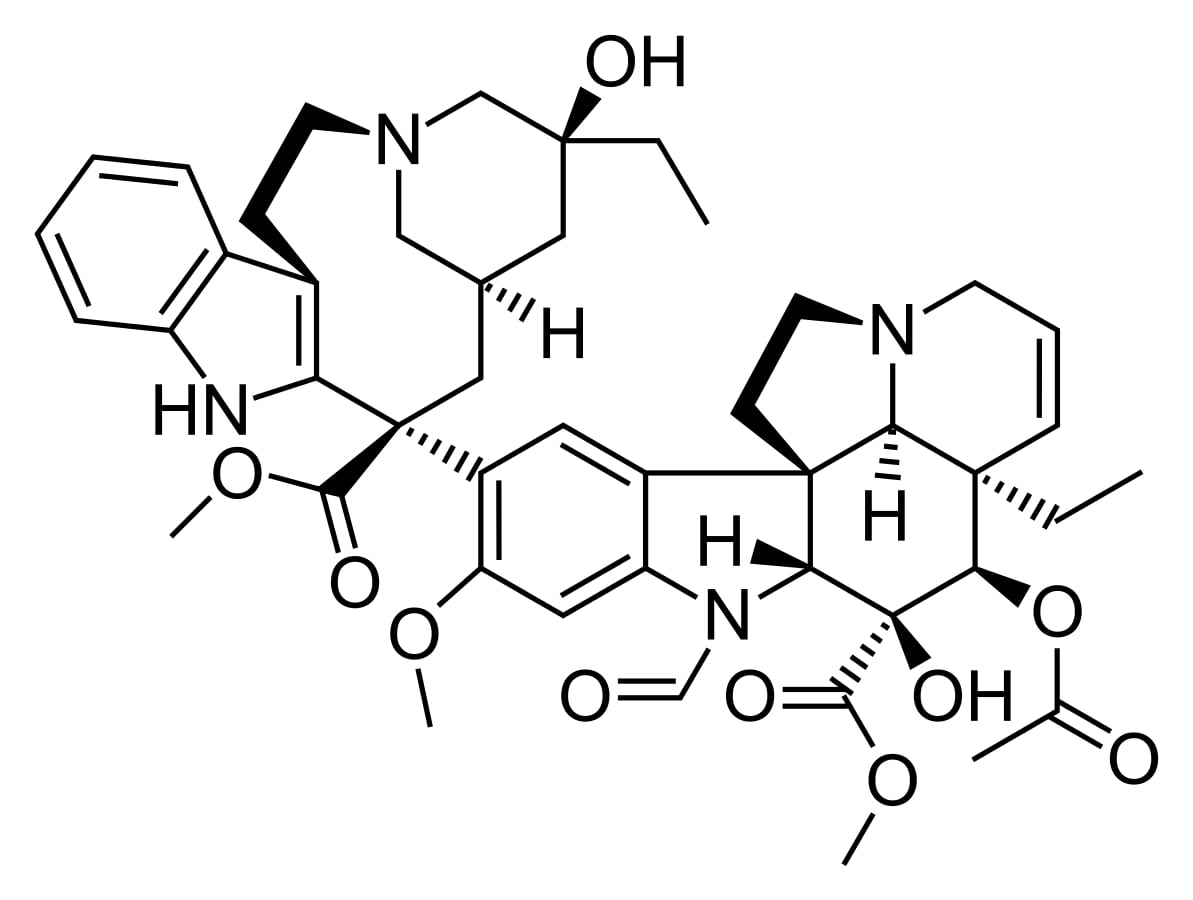
Estrutura da vincristina
Imagem: “Vincristine” por Fvasconcellos. Licença: Public Domain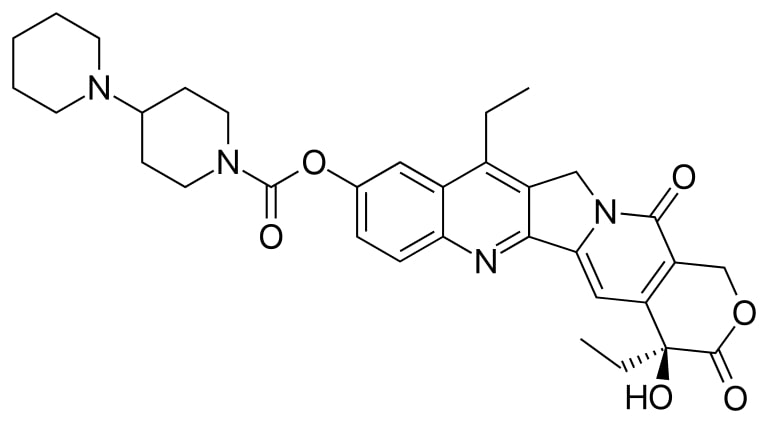
Estrutura do irinotecano
Imagem: “Irinotecan” por Fvasconcellos. Licença: Public Domain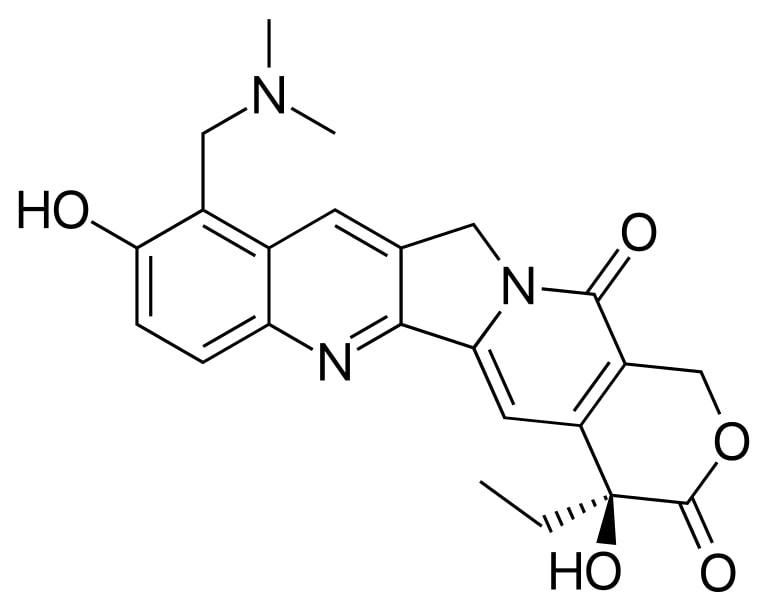
Estrutura do topotecano
Imagem: “Topotecan” por Fvasconcellos. Licença: Public Domain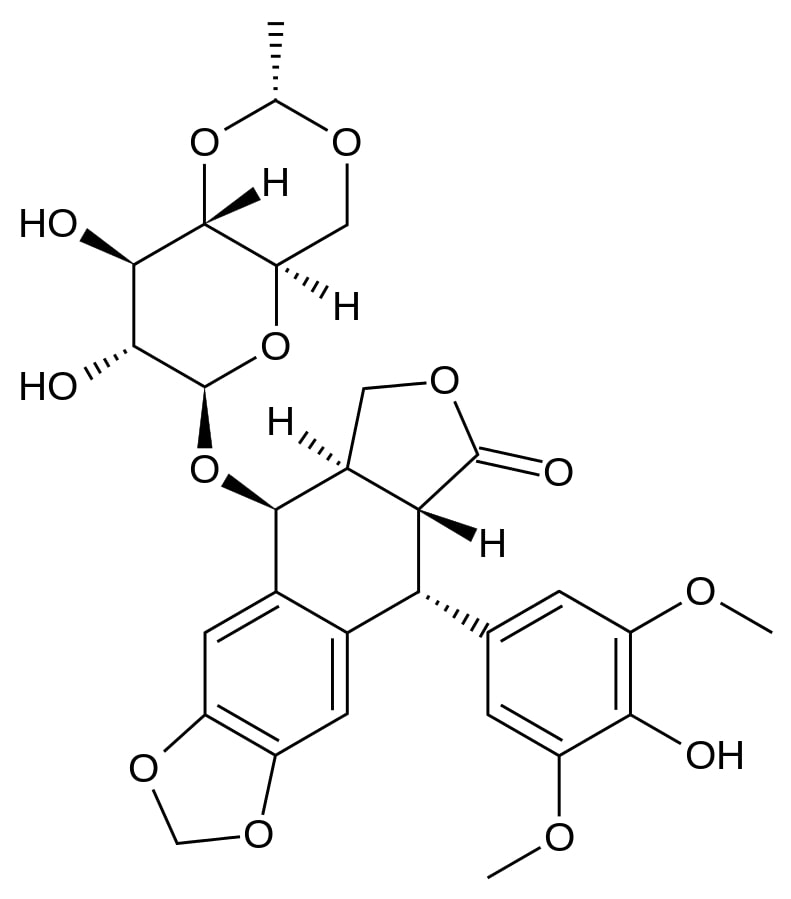
Estrutura do etoposido
Imagem: “Etoposide” por Fvasconcellos. Licença: Public Domain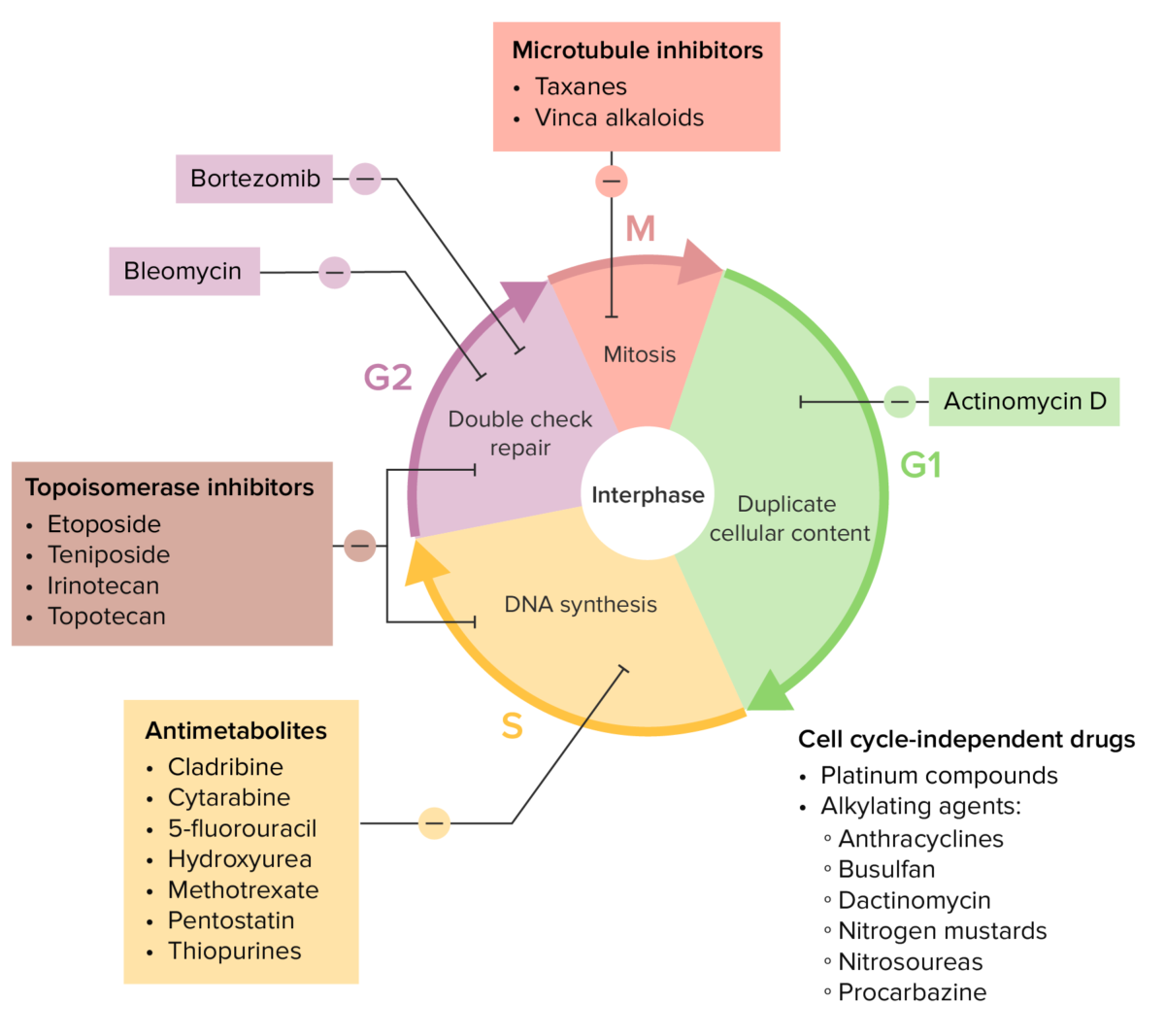
Vários fármacos de quimioterapia e os seus efeitos sobre o ciclo celular
Imagem por Lecturio.| Classe do fármaco | Mecanismo |
|---|---|
Antibióticos antitumorais:
|
Intercalam-se entre bases Bases Usually a hydroxide of lithium, sodium, potassium, rubidium or cesium, but also the carbonates of these metals, ammonia, and the amines. Acid-Base Balance, o que leva ao bloqueio da síntese de DNA DNA A deoxyribonucleotide polymer that is the primary genetic material of all cells. Eukaryotic and prokaryotic organisms normally contain DNA in a double-stranded state, yet several important biological processes transiently involve single-stranded regions. DNA, which consists of a polysugar-phosphate backbone possessing projections of purines (adenine and guanine) and pyrimidines (thymine and cytosine), forms a double helix that is held together by hydrogen bonds between these purines and pyrimidines (adenine to thymine and guanine to cytosine). DNA Types and Structure ou de RNA RNA A polynucleotide consisting essentially of chains with a repeating backbone of phosphate and ribose units to which nitrogenous bases are attached. RNA is unique among biological macromolecules in that it can encode genetic information, serve as an abundant structural component of cells, and also possesses catalytic activity. RNA Types and Structure e à prevenção da replicação de DNA DNA A deoxyribonucleotide polymer that is the primary genetic material of all cells. Eukaryotic and prokaryotic organisms normally contain DNA in a double-stranded state, yet several important biological processes transiently involve single-stranded regions. DNA, which consists of a polysugar-phosphate backbone possessing projections of purines (adenine and guanine) and pyrimidines (thymine and cytosine), forms a double helix that is held together by hydrogen bonds between these purines and pyrimidines (adenine to thymine and guanine to cytosine). DNA Types and Structure |
| Antraciclinas |
|
| Agentes alquilantes |
|
| Classe do fármaco | Fase do ciclo celular afetada | Mecanismo de ação |
|---|---|---|
| Antifolatos | Paragem do ciclo celular na fase S | Inibem:
|
| Bleomicina | Paragem do ciclo celular na fase G2 | Liga-se ao DNA DNA A deoxyribonucleotide polymer that is the primary genetic material of all cells. Eukaryotic and prokaryotic organisms normally contain DNA in a double-stranded state, yet several important biological processes transiently involve single-stranded regions. DNA, which consists of a polysugar-phosphate backbone possessing projections of purines (adenine and guanine) and pyrimidines (thymine and cytosine), forms a double helix that is held together by hydrogen bonds between these purines and pyrimidines (adenine to thymine and guanine to cytosine). DNA Types and Structure, levando a quebras nas cadeias duplas e simples |
| Fluoropirimidinas | Paragem do ciclo celular na fase S | Inibem a timidilato sintase |
| Análogos de desoxicitidina | Paragem do ciclo celular na fase S | Inibem:
|
| Análogos de purina | Paragem do ciclo celular na fase S | Inibição da síntese de novo de purinas |
| Inibidores da topoisomerase II Topoisomerase II DNA topoisomerases that catalyze ATP-dependent breakage of both strands of DNA, passage of the unbroken strands through the breaks, and rejoining of the broken strands. These enzymes bring about relaxation of the supercoiled DNA and resolution of a knotted circular DNA duplex. Fluoroquinolones | Paragem do ciclo celular nas fases S e G2 | Inibem a topoisomerase II Topoisomerase II DNA topoisomerases that catalyze ATP-dependent breakage of both strands of DNA, passage of the unbroken strands through the breaks, and rejoining of the broken strands. These enzymes bring about relaxation of the supercoiled DNA and resolution of a knotted circular DNA duplex. Fluoroquinolones |
| Taxanos | Paragem do ciclo celular na metáfase da fase M | Hiperestabilização dos microtúbulos |
| Alcaloides da vinca | Paragem do ciclo celular durante a metáfase da fase M | Liga-se à beta-tubulina e previne a polimerização de microtúbulos |