O hipopituitarismo é uma condição que se caracteriza pelo défice de hormonas hipofisárias. Ocorre maioritariamente por doença da hipófise, mas pode também surgir por disfunção hipotalâmica. Os tumores hipofisários são uma das causas mais MAIS Androgen Insensitivity Syndrome comuns. A maioria dos casos afeta o lobo anterior da hipófise (adenohipófise), que representa 80% da glândula. As hormonas produzidas neste lobo são a hormona do crescimento, a hormona folículo-estimulante, a hormona luteinizante, a hormona estimuladora da tiróide (TSH, pela sigla em inglês), a hormona adrenocorticotrófica e a prolactina. Quando o lobo posterior (neurohipófise) também é lesado, ocorre défice de hormona antidiurética e ocitocina. Todas estas hormonas regulam atividades de diferentes órgãos, logo, os efeitos da hipofunção hipofisária são multissistémicos. O diagnóstico é realizado através de uma combinação de achados clínicos, níveis hormonais, testes Testes Gonadal Hormones de provocação e imagiologia cerebral. O tratamento consiste na reposição hormonal e na abordagem etiológica.
Last updated: Jan 28, 2026
O hipopituitarismo é a condição que resulta da produção inadequada de hormonas hipofisárias:
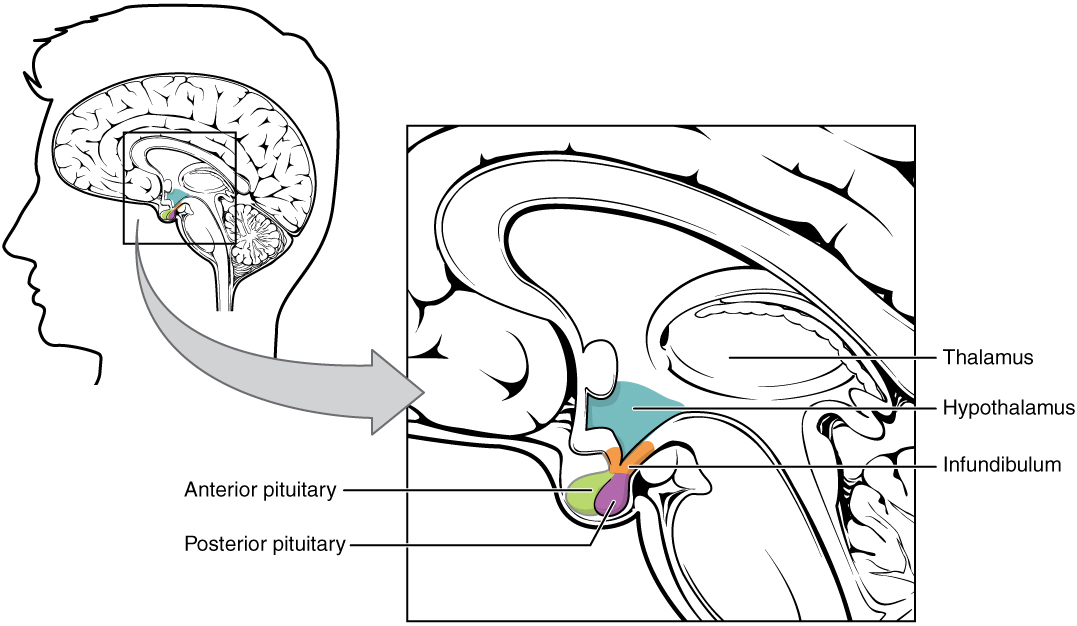
Complexo hipotálamo-hipófise:
A imagem mostra a hipófise, composta pelos lobos anterior e posterior, em relação com o hipotálamo.
| Hormona | Tipo de célula hipofisária | Orgão alvo | Função | Diminuição da produção |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ACTH | Corticotrófica | Córtex adrenal | Estimulação:
|
Insuficiência adrenal secundária |
| GH | Somatotrófica | Fígado e outros tecidos | Estimulação da síntese de proteínas e crescimento geral da maioria das células e tecidos |
|
| Prolactina | Lactotrófica | Glândulas mamárias |
|
Incapacidade de produzir leite (hipoprolactinemia) |
| TSH | Tirotrófica | Glândula tiroideia | Estimulação da glândula tiroideia para a síntese e secreção de hormonas tiroideias | Hipotiroidismo |
| LH LH A major gonadotropin secreted by the adenohypophysis. Luteinizing hormone regulates steroid production by the interstitial cells of the testis and the ovary. The preovulatory luteinizing hormone surge in females induces ovulation, and subsequent luteinization of the follicle. Luteinizing hormone consists of two noncovalently linked subunits, alpha and beta. Within a species, the alpha subunit is common in the three pituitary glycoprotein hormones (TSH, LH, and FSH), but the beta subunit is unique and confers its biological specificity. Menstrual Cycle | Gonadotrófica |
|
|
|
| FSH FSH A major gonadotropin secreted by the adenohypophysis. Follicle-stimulating hormone stimulates gametogenesis and the supporting cells such as the ovarian granulosa cells, the testicular sertoli cells, and leydig cells. Fsh consists of two noncovalently linked subunits, alpha and beta. Within a species, the alpha subunit is common in the three pituitary glycoprotein hormones (TSH, LH, and FSH), but the beta subunit is unique and confers its biological specificity. Menstrual Cycle | Gonadotrófica |
|
|
|
| Hormona | Tipo de célula hipofisária | Orgão alvo | Função | Diminuição da produção |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ADH | Núcleo supraótico do hipotálamo |
|
|
Diabetes Diabetes Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a metabolic disease characterized by hyperglycemia and dysfunction of the regulation of glucose metabolism by insulin. Type 1 DM is diagnosed mostly in children and young adults as the result of autoimmune destruction of β cells in the pancreas and the resulting lack of insulin. Type 2 DM has a significant association with obesity and is characterized by insulin resistance. Diabetes Mellitus insípida |
| Ocitocina | Núcleo paraventricular do hipotálamo |
|
Estimulação:
|
Causa poucos sintomas, com efeitos limitados |
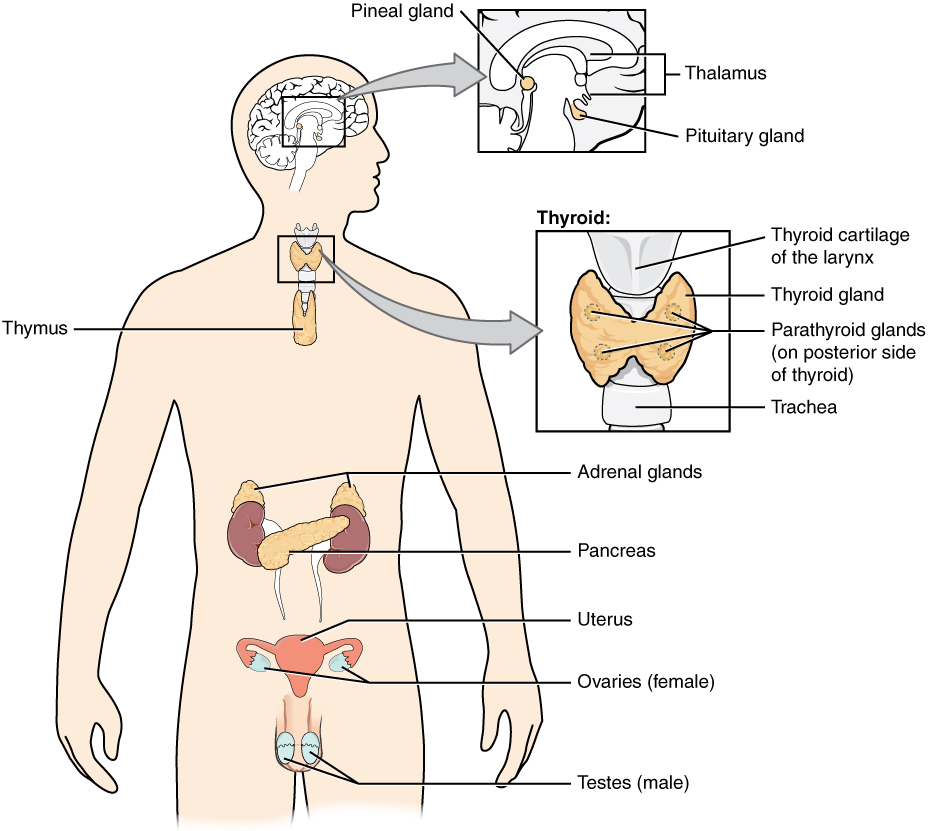
Glândula pituitária e órgãos alvo:
As hormonas hipofisárias ajudam a regular a atividade das glândulas endócrinas no organismo e desempenham um papel importante na homeostase.
Os sinais e sintomas dependem da patologia subjacente, da velocidade de início e da gravidade do hipopituitarismo (parcial ou total).
Défice de ACTH:
Défice de GH:
Défice de TSH:
Défice de LH LH A major gonadotropin secreted by the adenohypophysis. Luteinizing hormone regulates steroid production by the interstitial cells of the testis and the ovary. The preovulatory luteinizing hormone surge in females induces ovulation, and subsequent luteinization of the follicle. Luteinizing hormone consists of two noncovalently linked subunits, alpha and beta. Within a species, the alpha subunit is common in the three pituitary glycoprotein hormones (TSH, LH, and FSH), but the beta subunit is unique and confers its biological specificity. Menstrual Cycle/ FSH FSH A major gonadotropin secreted by the adenohypophysis. Follicle-stimulating hormone stimulates gametogenesis and the supporting cells such as the ovarian granulosa cells, the testicular sertoli cells, and leydig cells. Fsh consists of two noncovalently linked subunits, alpha and beta. Within a species, the alpha subunit is common in the three pituitary glycoprotein hormones (TSH, LH, and FSH), but the beta subunit is unique and confers its biological specificity. Menstrual Cycle:
Défice de ADH:
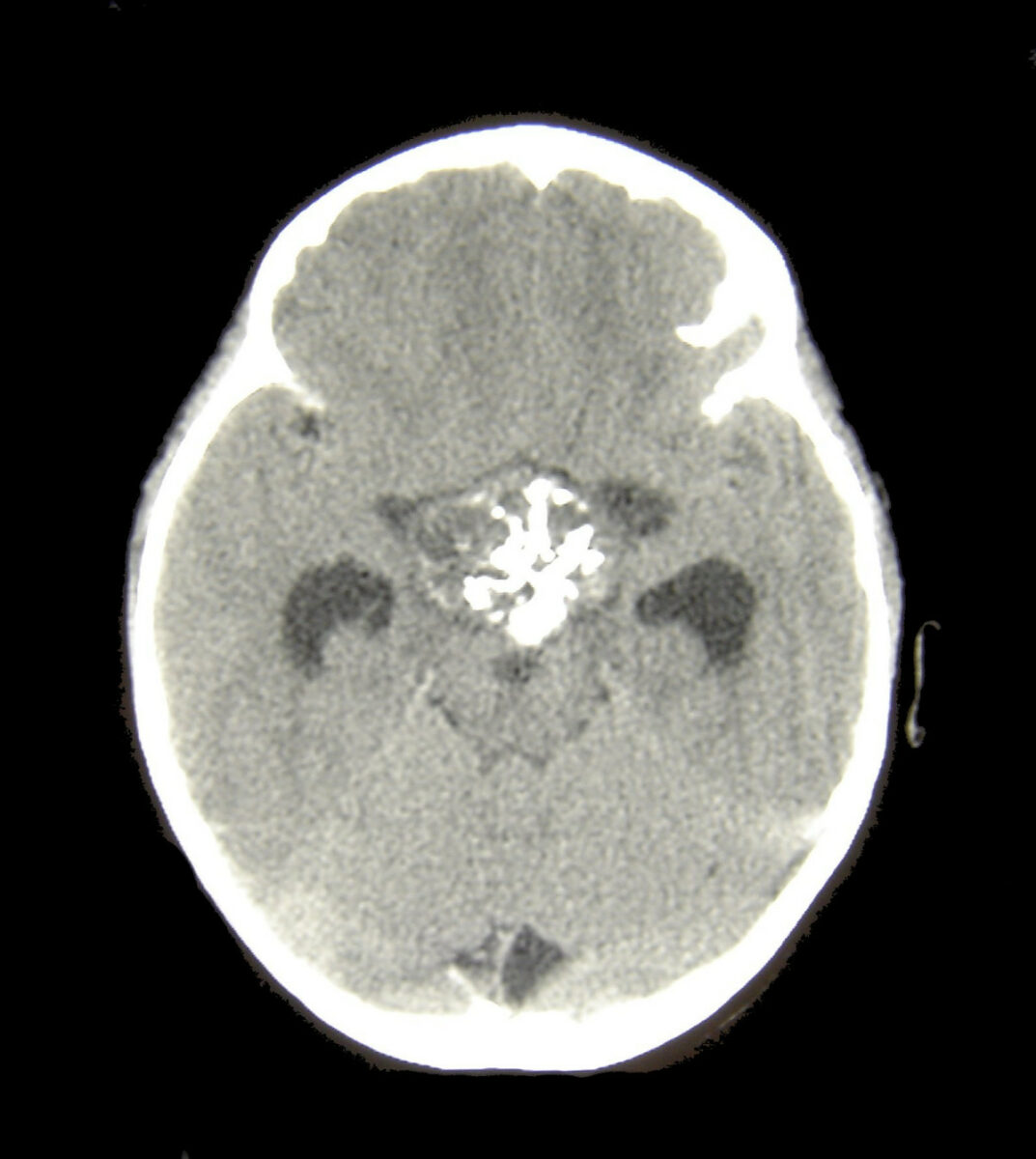
TC de crânio de paciente com craniofaringioma
Imagem: “Craniopharyngioma1” por Matthew R Garnett, Stéphanie Puget, Jacques Grill, Christian Sainte-Rose. Licença: CC BY 2.0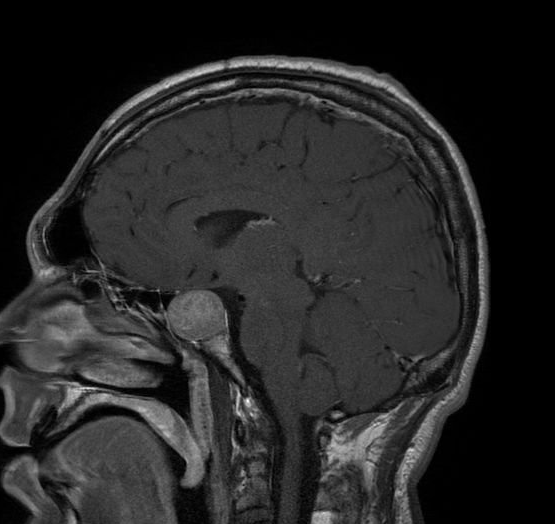
Ressonância magnética de paciente com adenoma hipofisário extenso
Imagen: “Acromegaly” por Elgee. Licença: CC BY 3.0, editado por Lecturio.