Os herpesvírus humanos (HHV)-6 e HHV-7 HHV-7 Human herpesvirus (HHV)-6 and HHV-7 are similar double-stranded DNA viruses belonging to the Herpesviridae family. Human herpesviruses are ubiquitous and infections are commonly contracted during childhood. Human Herpesvirus 6 and 7 são vírus de DNA DNA A deoxyribonucleotide polymer that is the primary genetic material of all cells. Eukaryotic and prokaryotic organisms normally contain DNA in a double-stranded state, yet several important biological processes transiently involve single-stranded regions. DNA, which consists of a polysugar-phosphate backbone possessing projections of purines (adenine and guanine) and pyrimidines (thymine and cytosine), forms a double helix that is held together by hydrogen bonds between these purines and pyrimidines (adenine to thymine and guanine to cytosine). DNA Types and Structure de cadeia dupla semelhantes, pertencentes à família Herpesviridae Herpesviridae A family of enveloped, linear, double-stranded DNA viruses infecting a wide variety of animals. Subfamilies, based on biological characteristics, include: alphaherpesvirinae; betaherpesvirinae; and gammaherpesvirinae. Herpes Simplex Virus 1 and 2. Os herpesvírus humanos são onipresentes e as infeções são frequentemente contraídas na infância. Tanto o HHV-6B como o HHV-7 HHV-7 Human herpesvirus (HHV)-6 and HHV-7 are similar double-stranded DNA viruses belonging to the Herpesviridae family. Human herpesviruses are ubiquitous and infections are commonly contracted during childhood. Human Herpesvirus 6 and 7 causam uma doença comum conhecida como roséola infantil (também conhecida como roséola ou 6ª doença). A roséola é uma doença autolimitada que se apresenta com febre alta, seguida de uma erupção maculopapular Maculopapular Dermatologic Examination de cor rosada difusa. O diagnóstico é clínico e o tratamento é apenas de suporte.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
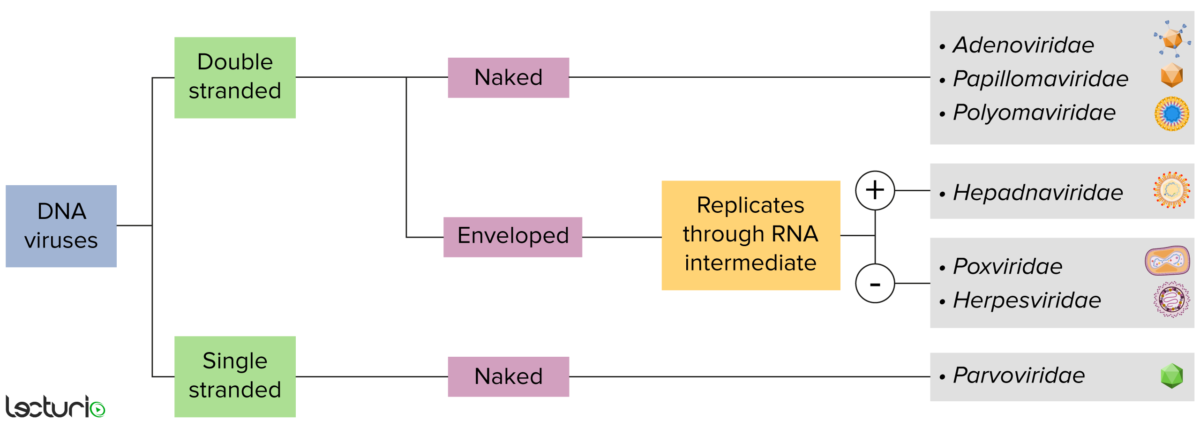
Identificação de vírus de DNA:
Os vírus podem ser classificados de várias formas. Contudo, a maioria dos vírus possui um genoma formado por DNA ou RNA. Os vírus com genoma de DNA podem ainda ser caracterizados como de cadeia simples ou dupla. Os vírus com envelope são revestidos por uma camada fina de membrana celular, que geralmente é retirada da célula hospedeira. Os vírus sem envelope são apelidados de vírus “nus”. Alguns vírus com envelope traduzem DNA em RNA antes de serem incorporados no genoma da célula hospedeira.
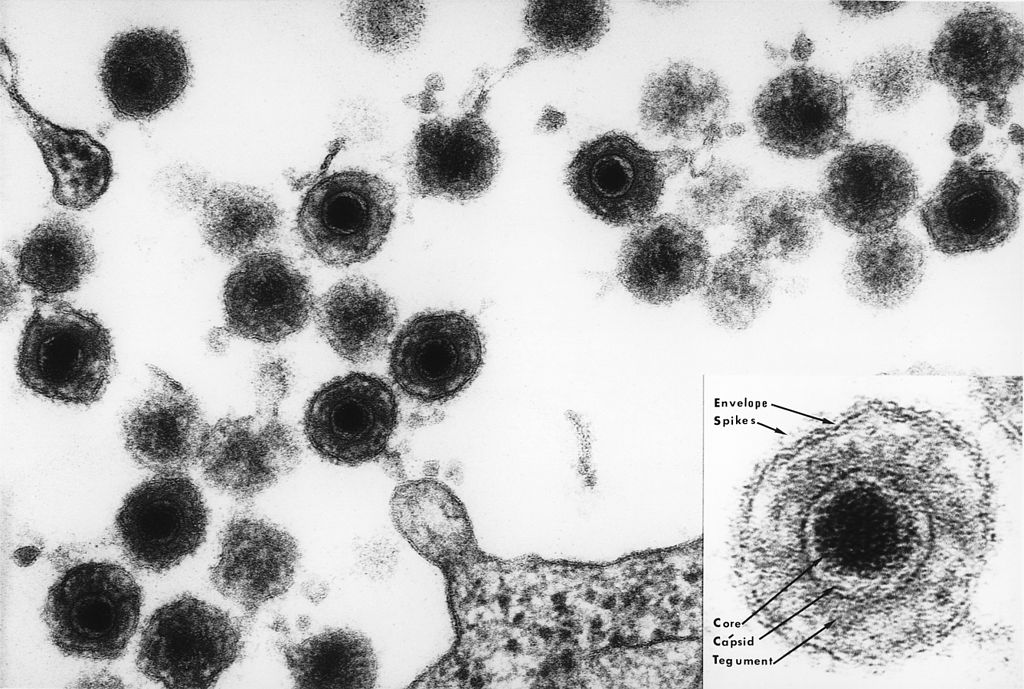
Micrografia eletrónica do vírus HHV-6
Imagem: “Electron micrograph of one of the HHV6 species” por Bernard Kramarsky. Licença: Domínio PúblicoA relevância clínica do HHV-6A não é totalmente conhecida.
Os seres humanos são o reservatório de HHV-6 HHV-6 Human herpesvirus (HHV)-6 and HHV-7 are similar double-stranded DNA viruses belonging to the Herpesviridae family. Human herpesviruses are ubiquitous and infections are commonly contracted during childhood. Human Herpesvirus 6 and 7 e HHV-7 HHV-7 Human herpesvirus (HHV)-6 and HHV-7 are similar double-stranded DNA viruses belonging to the Herpesviridae family. Human herpesviruses are ubiquitous and infections are commonly contracted during childhood. Human Herpesvirus 6 and 7.
HHV-6 HHV-6 Human herpesvirus (HHV)-6 and HHV-7 are similar double-stranded DNA viruses belonging to the Herpesviridae family. Human herpesviruses are ubiquitous and infections are commonly contracted during childhood. Human Herpesvirus 6 and 7 e HHV-7 HHV-7 Human herpesvirus (HHV)-6 and HHV-7 are similar double-stranded DNA viruses belonging to the Herpesviridae family. Human herpesviruses are ubiquitous and infections are commonly contracted during childhood. Human Herpesvirus 6 and 7 são transmitidos através do contacto com a saliva Saliva The clear, viscous fluid secreted by the salivary glands and mucous glands of the mouth. It contains mucins, water, organic salts, and ptyalin. Salivary Glands: Anatomy.
As infeções por herpesvírus humano-6 são maioritariamente ligeiras e ocorrem durante a infância. A maioria das infeções por HHV-7 HHV-7 Human herpesvirus (HHV)-6 and HHV-7 are similar double-stranded DNA viruses belonging to the Herpesviridae family. Human herpesviruses are ubiquitous and infections are commonly contracted during childhood. Human Herpesvirus 6 and 7 são assintomáticas.
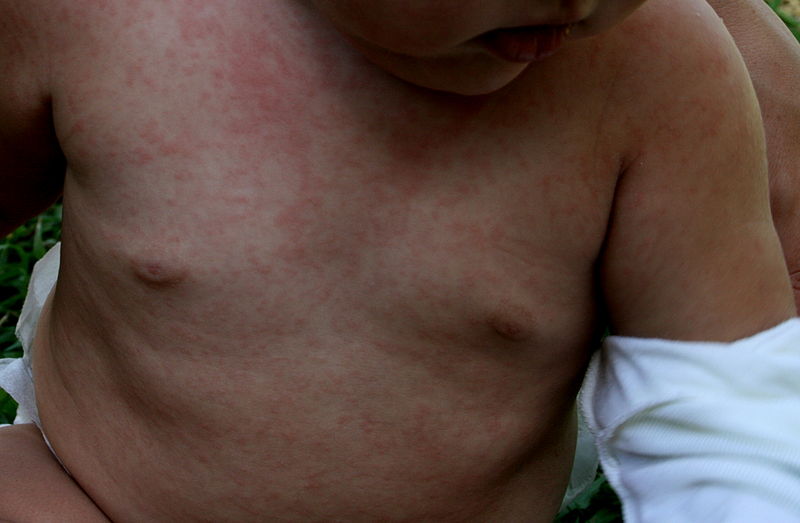
Erupção maculopapular eritematosa observada na roséola:
Esta erupção é habitualmente causada pelo HHV-6B humano e, menos frequentemente, pelo HHV-7.
O diagnóstico é clínico e raramente há indicação para realização de exames, exceto em casos de doença grave em indivíduos imunodeprimidos (por exemplo, encefalite, miocardite).
O tratamento por norma não é necessário,uma vez que os sintomas são autolimitados. os pacientes com doença grave podem ser tratados com:
A tabela abaixo compara os 9 herpesvírus considerados endémicos em humanos; existem 115 espécies diferentes de herpesvírus no total, agrupadas em 3 famílias:
| HHV | Nome comum | Principais células-alvo | Local de latência | Apresentação clínica* |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
1 (grupo alfa) |
HSV-1 | Células mucoepiteliais | Gânglios da raiz dorsal |
|
|
2 (grupo alfa) |
HSV-2 |
|
||
|
3 (grupo alfa) |
VZV |
|
||
|
4 (grupo gama) |
EBV EBV Epstein-barr virus (EBV) is a linear, double-stranded DNA virus belonging to the herpesviridae family. This highly prevalent virus is mostly transmitted through contact with oropharyngeal secretions from an infected individual. The virus can infect epithelial cells and B lymphocytes, where it can undergo lytic replication or latency. Epstein-Barr Virus |
|
Células B de memória |
|
|
5 (grupo beta) |
CMV |
|
Células progenitoras hematopoiéticas da medula óssea |
|
|
6A, 6B (grupo beta) |
HHV-6 HHV-6 Human herpesvirus (HHV)-6 and HHV-7 are similar double-stranded DNA viruses belonging to the Herpesviridae family. Human herpesviruses are ubiquitous and infections are commonly contracted during childhood. Human Herpesvirus 6 and 7 | células T | Monócitos | Roséola |
|
7 (grupo beta) |
HHV-7 HHV-7 Human herpesvirus (HHV)-6 and HHV-7 are similar double-stranded DNA viruses belonging to the Herpesviridae family. Human herpesviruses are ubiquitous and infections are commonly contracted during childhood. Human Herpesvirus 6 and 7 | células T | ||
|
8 (grupo gama) |
Herpesvírus associado ao sarcoma de Kaposi Kaposi A multicentric, malignant neoplastic vascular proliferation characterized by the development of bluish-red cutaneous nodules, usually on the lower extremities, most often on the toes or feet, and slowly increasing in size and number and spreading to more proximal areas. The tumors have endothelium-lined channels and vascular spaces admixed with variably sized aggregates of spindle-shaped cells, and often remain confined to the skin and subcutaneous tissue, but widespread visceral involvement may occur. Hhv-8 is the suspected cause. There is also a high incidence in AIDS patients. AIDS-defining Conditions |
|
células B | Sarcoma de Kaposi Kaposi A multicentric, malignant neoplastic vascular proliferation characterized by the development of bluish-red cutaneous nodules, usually on the lower extremities, most often on the toes or feet, and slowly increasing in size and number and spreading to more proximal areas. The tumors have endothelium-lined channels and vascular spaces admixed with variably sized aggregates of spindle-shaped cells, and often remain confined to the skin and subcutaneous tissue, but widespread visceral involvement may occur. Hhv-8 is the suspected cause. There is also a high incidence in AIDS patients. AIDS-defining Conditions |
| Número | Outros nomes para a doença | Etiologia | Descrição |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1ª doença |
|
Morbillivirus Morbillivirus A genus of the family paramyxoviridae (subfamily paramyxovirinae) where the virions of most members have hemagglutinin but not neuraminidase activity. All members produce both cytoplasmic and intranuclear inclusion bodies. Measles virus is the type species. Measles Virus do sarampo |
|
| 2ª doença |
|
Streptococcus Streptococcus Streptococcus is one of the two medically important genera of gram-positive cocci, the other being Staphylococcus. Streptococci are identified as different species on blood agar on the basis of their hemolytic pattern and sensitivity to optochin and bacitracin. There are many pathogenic species of streptococci, including S. pyogenes, S. agalactiae, S. pneumoniae, and the viridans streptococci. Streptococcus pyogenes |
|
| 3ª doença |
|
Vírus da rubéola |
|
| 4ª doença |
|
Devido às estirpes de Staphylococcus aureus Staphylococcus aureus Potentially pathogenic bacteria found in nasal membranes, skin, hair follicles, and perineum of warm-blooded animals. They may cause a wide range of infections and intoxications. Brain Abscess que produzem toxina epidermolítica (esfoliativa) |
|
| 5ª doença | Eritema infecioso | Eritrovírus ou parvovírus B19 (primata eritroparvovírus 1) |
|
| 6ª doença |
|
Herpesvírus humano 6B ou 7 |
|