Herpes zoster Herpes Zoster Varicella-zoster virus (VZV) is a linear, double-stranded DNA virus in the Herpesviridae family. Shingles (also known as herpes zoster) is more common in adults and occurs due to the reactivation of VZV. Varicella-Zoster Virus/Chickenpox (também conhecido como zona) é uma infeção viral de reativação causada pelo vírus varicela-zoster (VVZ). O VVZ latente permanece inativo no gânglio da raiz dorsal após a fase de infeção primária da varicela. Idade, “stress” ou estados de imunossupressão podem desencadear a reativação do vírus. O herpes zoster Herpes Zoster Varicella-zoster virus (VZV) is a linear, double-stranded DNA virus in the Herpesviridae family. Shingles (also known as herpes zoster) is more common in adults and occurs due to the reactivation of VZV. Varicella-Zoster Virus/Chickenpox apresenta-se clinicamente com uma distribuição por dermátomo única, como uma erupção cutânea unilateral dolorosa. O diagnóstico é efetuado principalmente a partir da história clínica e do exame físico. No entanto, testes Testes Gonadal Hormones laboratoriais (como PCR PCR Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is a technique that amplifies DNA fragments exponentially for analysis. The process is highly specific, allowing for the targeting of specific genomic sequences, even with minuscule sample amounts. The PCR cycles multiple times through 3 phases: denaturation of the template DNA, annealing of a specific primer to the individual DNA strands, and synthesis/elongation of new DNA molecules. Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR)) podem ser realizados se o diagnóstico não for claro. O tratamento inclui terapêutica antiviral Antiviral Antivirals for Hepatitis B e tratamento sintomático.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Herpes zoster Herpes Zoster Varicella-zoster virus (VZV) is a linear, double-stranded DNA virus in the Herpesviridae family. Shingles (also known as herpes zoster) is more common in adults and occurs due to the reactivation of VZV. Varicella-Zoster Virus/Chickenpox (também conhecido como zona) é uma infeção viral de reativação causada pelo vírus varicela-zoster (VVZ) que se manifesta como uma erupção vesicular unilateral, com distribuição ao longo do dermátomo e dolorosa.
Organismo causador: VVZ
Transmissão:
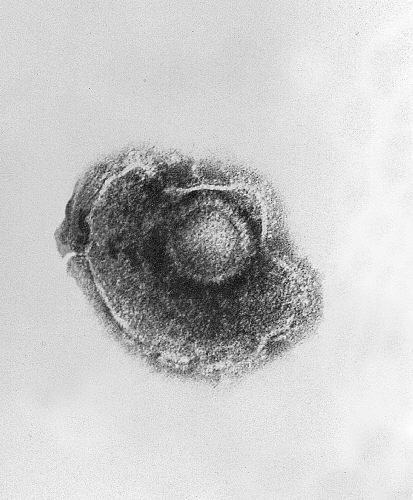
Imagem microscópica de transmissão de eletrões demonstrando um único vírus varicela-zoster (VVZ), também conhecido como herpesvírus humano 3, que causa a varicela
Imagem: “Ultrastructural features exhibited by a single varicella-zoster virus (VZV), also known as human herpesvirus 3 (HHV-3), the cause of chickenpox.” por CDC. Licença: Public DomainO vírus varicela-zoster causa 2 síndromes distintas:
Infeção primária (varicela):
Infeção secundária (zona):
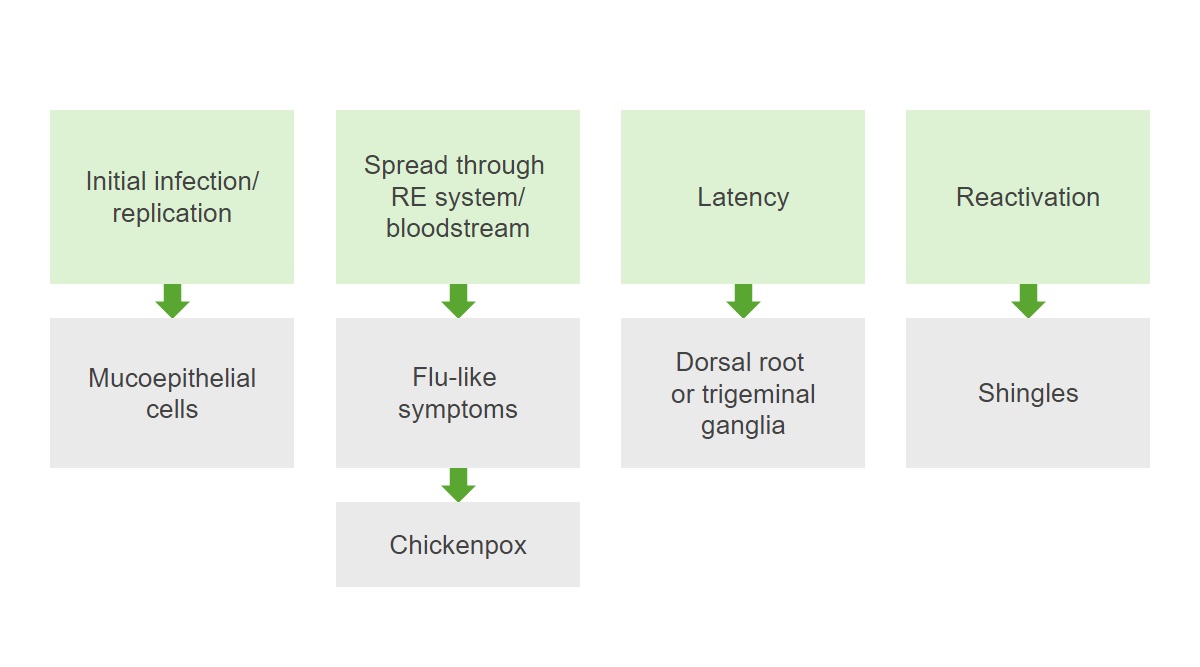
Patogénese do vírus varicela-zoster (VVZ):
A infeção replica os vírus nas células mucoepiteliais, espalha-se por todo o sistema reticuloendotelial (RE) e pela corrente sanguínea, causando sintomas semelhantes aos da gripe e da varicela. Após a resolução da infeção primária, ocorre um período de latência e o vírus permanece latente nos gânglios da raiz dorsal. A reativação da infeção resulta em herpes.
Neurite aguda:
Rash Rash Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever:
Sintomas sistémicos (< 20% dos casos):
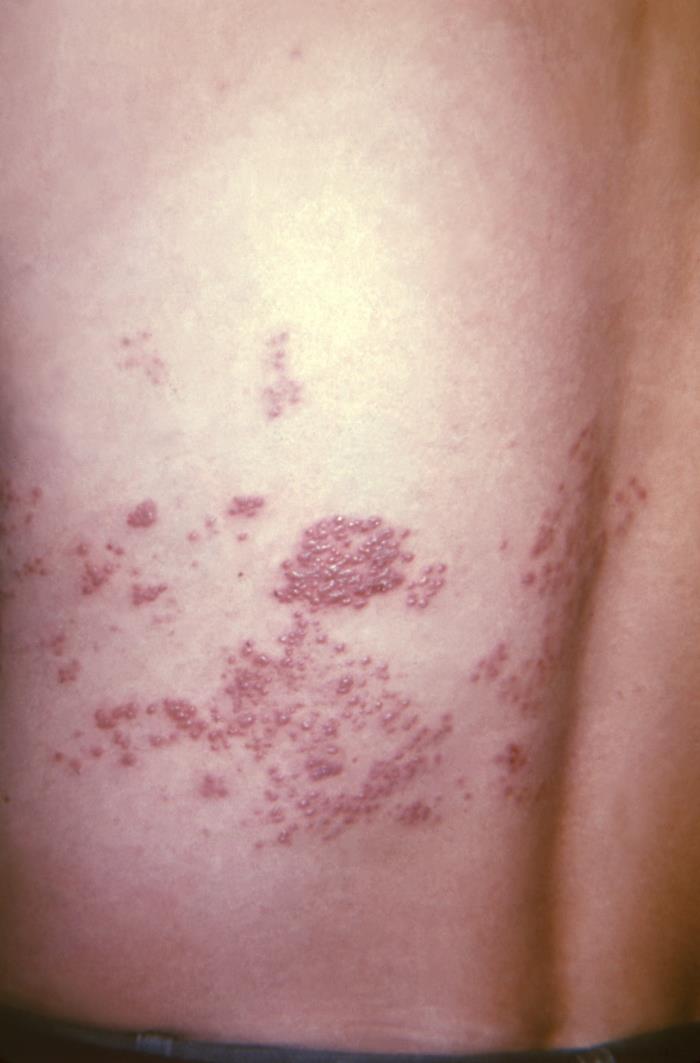
Erupção cutânea no dermátomo T10‒11 ao longo das costas de um doente
Imagem: “This view of a patient’s skin, revealed a maculopapular rash, which had been due to an outbreak of shingles.” por CDC. Licença: Public Domain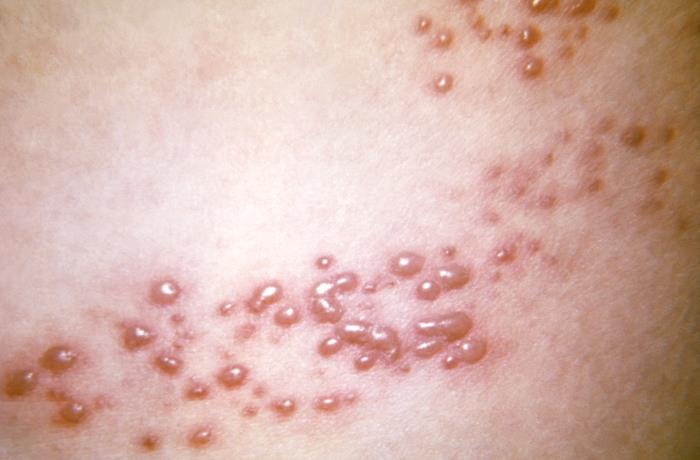
Visão de perto da erupção vesicular da zona
Imagem: “This view of a patient’s skin, revealed a maculopapular rash, which had been due to an outbreak of shingles.” por CDC. Licença: Public Domain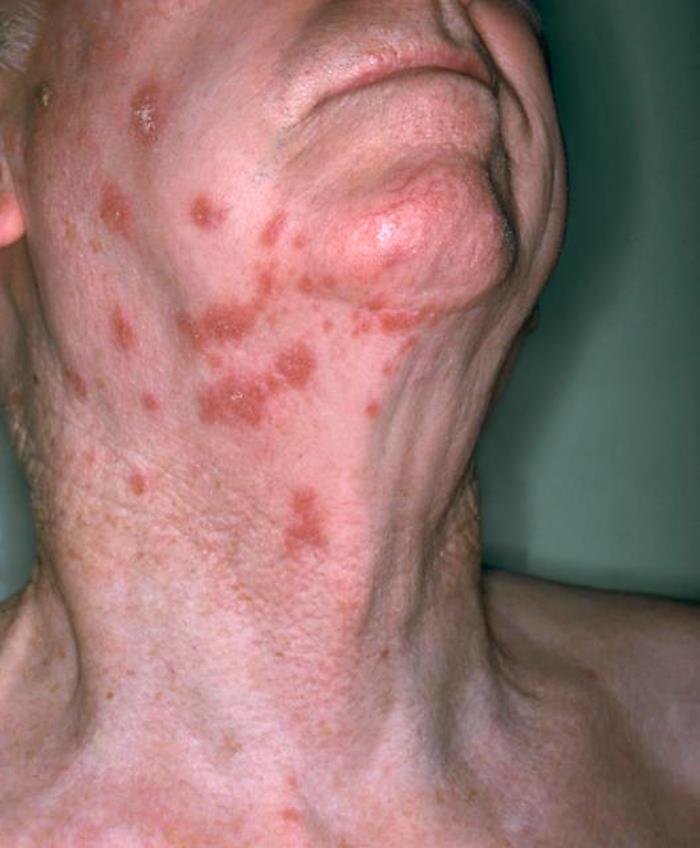
Visão anterolateral do pescoço de um paciente mostrando a presença de uma erupção cutânea eritematosa devido a zona
Imagem: “Anterolateral view of this patient’s neck showing the presence of an erythematous rash due to shingles” por NIAID. Licença: Public Domain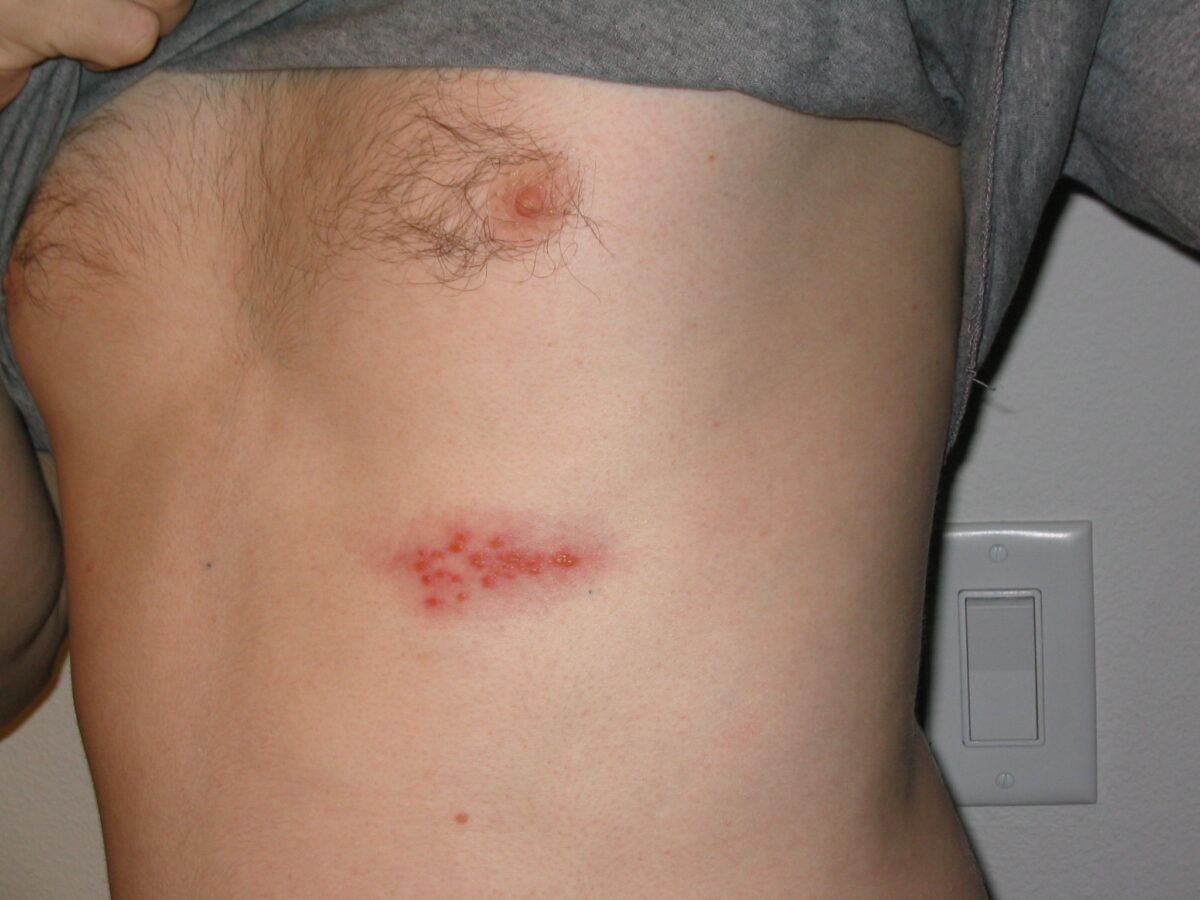
Imagem de um surto de zona no toráx
Imagem : “Imagem de um surto de herpes zoster no peito” por Preston Hunt. Licença: CC BY 3.0As seguintes são apresentações graves, que podem ocorrer em doentes imunocomprometidos:
Disseminação cutânea:
Envolvimento de órgão visceral:
Herpes zoster Herpes Zoster Varicella-zoster virus (VZV) is a linear, double-stranded DNA virus in the Herpesviridae family. Shingles (also known as herpes zoster) is more common in adults and occurs due to the reactivation of VZV. Varicella-Zoster Virus/Chickenpox oftálmico:
Síndrome de Ramsay Hunt ( herpes zoster oticus Herpes zoster oticus A syndrome characterized by facial palsy in association with a herpetic eruption of the external auditory meatus. This may occasionally be associated with tinnitus, vertigo, deafness, severe otalgia, and inflammation of the pinna. The condition is caused by reactivation of a latent herpesvirus 3, human infection which causes inflammation of the facial and vestibular nerves, and may occasionally involve additional cranial nerves. Herpes Zoster (Shingles)):
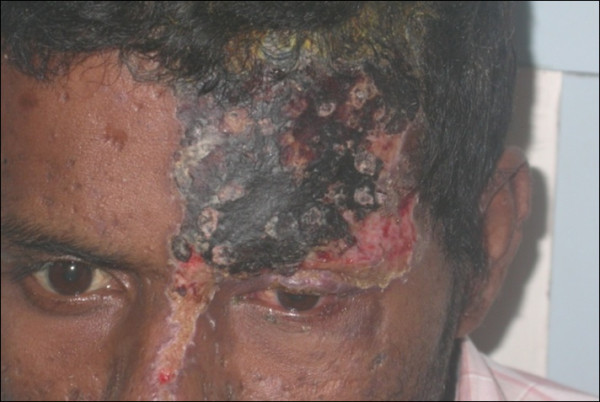
Herpes zoster oftálmico com envolvimento do olho esquerdo
Imagem: “External photograph showing herpes zoster ophthalmicus” por Sudharshan S et al. Licença: CC BY 2.0Neuralgia pós-herpética:
Necrose retinal aguda:
Outras complicações:
O diagnóstico da zona é baseado principalmente na apresentação clínica. Em doentes com apresentações atípicas, pode ser usado o seguinte:
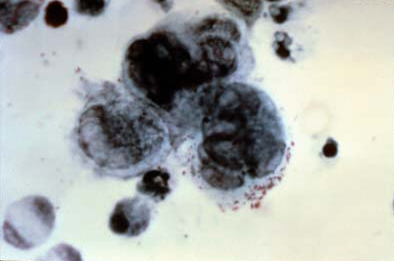
Esfregaço de Tzanck com 3 células gigantes multinucleadas
Imagem: “Positive Tzanck test, showing three multinucleated giant cells in center” por NIAID. Licença: Public DomainMedidas para prevenir a transmissão:
Vacinas: