O angioedema Angioedema Angioedema is a localized, self-limited (but potentially life-threatening), nonpitting, asymmetrical edema occurring in the deep layers of the skin and mucosal tissue. The common underlying pathophysiology involves inflammatory mediators triggering significant vasodilation and increased capillary permeability. Angioedema hereditário (AEH), também conhecido como deficiência do inibidor de C1 esterase (C1-INH, pela sigla em inglês), é uma doença autossómica dominante caracterizada por episódios recorrentes de edema Edema Edema is a condition in which excess serous fluid accumulates in the body cavity or interstitial space of connective tissues. Edema is a symptom observed in several medical conditions. It can be categorized into 2 types, namely, peripheral (in the extremities) and internal (in an organ or body cavity). Edema grave ( angioedema Angioedema Angioedema is a localized, self-limited (but potentially life-threatening), nonpitting, asymmetrical edema occurring in the deep layers of the skin and mucosal tissue. The common underlying pathophysiology involves inflammatory mediators triggering significant vasodilation and increased capillary permeability. Angioedema). O angioedema Angioedema Angioedema is a localized, self-limited (but potentially life-threatening), nonpitting, asymmetrical edema occurring in the deep layers of the skin and mucosal tissue. The common underlying pathophysiology involves inflammatory mediators triggering significant vasodilation and increased capillary permeability. Angioedema hereditário frequentemente afeta os membros, face, trato intestinal e vias aéreas superiores. O edema Edema Edema is a condition in which excess serous fluid accumulates in the body cavity or interstitial space of connective tissues. Edema is a symptom observed in several medical conditions. It can be categorized into 2 types, namely, peripheral (in the extremities) and internal (in an organ or body cavity). Edema nas vias aéreas pode restringir a respiração e levar a uma obstrução das vias aéreas com risco de vida. O angioedema Angioedema Angioedema is a localized, self-limited (but potentially life-threatening), nonpitting, asymmetrical edema occurring in the deep layers of the skin and mucosal tissue. The common underlying pathophysiology involves inflammatory mediators triggering significant vasodilation and increased capillary permeability. Angioedema hereditário tem 3 subtipos distinguidos pelas suas etiologias subjacentes e níveis de inibidor de C1 no sangue. O tratamento inclui tratamento com danazol Danazol A synthetic steroid with antigonadotropic and anti-estrogenic activities that acts as an anterior pituitary suppressant by inhibiting the pituitary output of gonadotropins. It possesses some androgenic properties. Danazol has been used in the treatment of endometriosis and some benign breast disorders. Antiestrogens, inibidores de calicreína e C1-INHs. O angioedema Angioedema Angioedema is a localized, self-limited (but potentially life-threatening), nonpitting, asymmetrical edema occurring in the deep layers of the skin and mucosal tissue. The common underlying pathophysiology involves inflammatory mediators triggering significant vasodilation and increased capillary permeability. Angioedema hereditário é autolimitado, mas pode ser fatal se as vias aéreas forem comprometidas.
Last updated: Mar 28, 2025
O angioedema Angioedema Angioedema is a localized, self-limited (but potentially life-threatening), nonpitting, asymmetrical edema occurring in the deep layers of the skin and mucosal tissue. The common underlying pathophysiology involves inflammatory mediators triggering significant vasodilation and increased capillary permeability. Angioedema hereditário (AEH) é uma condição hereditária caracterizada por episódios recorrentes de edema Edema Edema is a condition in which excess serous fluid accumulates in the body cavity or interstitial space of connective tissues. Edema is a symptom observed in several medical conditions. It can be categorized into 2 types, namely, peripheral (in the extremities) and internal (in an organ or body cavity). Edema ( angioedema Angioedema Angioedema is a localized, self-limited (but potentially life-threatening), nonpitting, asymmetrical edema occurring in the deep layers of the skin and mucosal tissue. The common underlying pathophysiology involves inflammatory mediators triggering significant vasodilation and increased capillary permeability. Angioedema), geralmente da mucosa dos sistemas respiratório e gastrointestinal (GI), sem urticária ou prurido.
Mutações genéticas são a causa do AEH:
A fisiopatologia básica do edema Edema Edema is a condition in which excess serous fluid accumulates in the body cavity or interstitial space of connective tissues. Edema is a symptom observed in several medical conditions. It can be categorized into 2 types, namely, peripheral (in the extremities) and internal (in an organ or body cavity). Edema no AEH relaciona-se com a sobreprodução de bradicinina.
| AEH tipo I | AEH tipo II | AEH tipo III | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Prevalência | 80%–85% dos casos | 15%–20% | Muito raro; geralmente em mulheres |
| Causa | Secreção reduzida de C1-INHs | Produção de C1-INH não funcional |
|
| Fisiopatologia | Excesso de produção de anafilatoxinas inflamatórias que afetam o fluxo de fluidos corporais entre o sistema vascular e os tecidos corporais | Excesso de produção de anafilatoxinas inflamatórias que afetam o fluxo de fluidos corporais entre o sistema vascular e os tecidos corporais |
|
Doentes com AEH têm crises recorrentes:
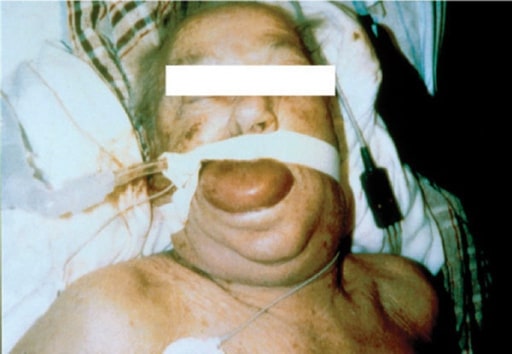
Edema grave de face, língua e faringe em doente tratado com inibidor da enzima conversora de angiotensina (ECA)
Imagem : “F3” por the National Allergy, Asthma, and Urticaria Centers of Charleston, Charleston, SC. Licença: CC BY 2.0.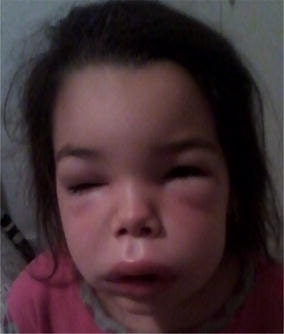
Angioedema da face
Imagem : “Angioedema of the face” por S. Tolga Yavuz et al. Licença: CC BY 4.0.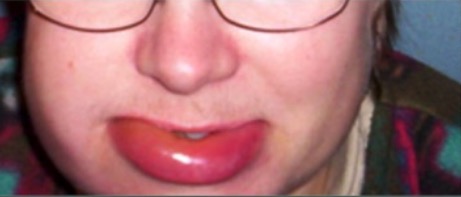
Angioedema hereditário
Imagem : “Typical features” por Department of Bacteriology and Immunology, Haartman Institute, University of Helsinki, Helsinki, Finland. Licença: CC BY 4.0.Reconhecer o AEH muitas vezes é difícil devido a uma ampla variabilidade na expressão da doença:
Análises sanguíneas frequentemente usadas para confirmar o diagnóstico:
| Tipo de angioedema Angioedema Angioedema is a localized, self-limited (but potentially life-threatening), nonpitting, asymmetrical edema occurring in the deep layers of the skin and mucosal tissue. The common underlying pathophysiology involves inflammatory mediators triggering significant vasodilation and increased capillary permeability. Angioedema sem urticária | Proteína C1-INH | C1q | C4 e C2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| AEH tipo I | ↓ | Normal | ↓ |
| AEH tipo II | N ou ↑ (mas disfuncional) | Normal | ↓ |
| Angioedema Angioedema Angioedema is a localized, self-limited (but potentially life-threatening), nonpitting, asymmetrical edema occurring in the deep layers of the skin and mucosal tissue. The common underlying pathophysiology involves inflammatory mediators triggering significant vasodilation and increased capillary permeability. Angioedema adquirido com deficiência de C1-INH (tipo I) | ↓ | ↓ | ↓ |
| Angioedema Angioedema Angioedema is a localized, self-limited (but potentially life-threatening), nonpitting, asymmetrical edema occurring in the deep layers of the skin and mucosal tissue. The common underlying pathophysiology involves inflammatory mediators triggering significant vasodilation and increased capillary permeability. Angioedema adquirido com deficiência de C1-INH (tipo II) | ↓ | ↓ | ↓ |
Concentra-se no tratamento de crises com base em sintomas específicos: