A agamaglobulinemia ligada ao cromossoma X, também conhecida como agamaglobulinemia de Bruton ou doença de Bruton, é um distúrbio genético recessivo raro caracterizado pelo desenvolvimento inadequado de células B, levando ao défice de células B maduras, capazes de responder à estimulação de respostas imunes mediadas por células ou por certas células apresentadoras de antigénios. A agamaglobulinemia ligada ao X é mais MAIS Androgen Insensitivity Syndrome provável de ser encontrada em homens do que em mulheres e é causada por mutações no gene Gene A category of nucleic acid sequences that function as units of heredity and which code for the basic instructions for the development, reproduction, and maintenance of organisms. Basic Terms of Genetics da tirosina cinase de Bruton no cromossoma X. O resultado desta mutação é uma ausência completa ou quase completa de todos os anticorpos. A apresentação inclui infeções bacterianas recorrentes após os primeiros meses de vida. O tratamento consiste em imunoglobulinas IV e uso profilático de antibióticos.
Last updated: Feb 19, 2025
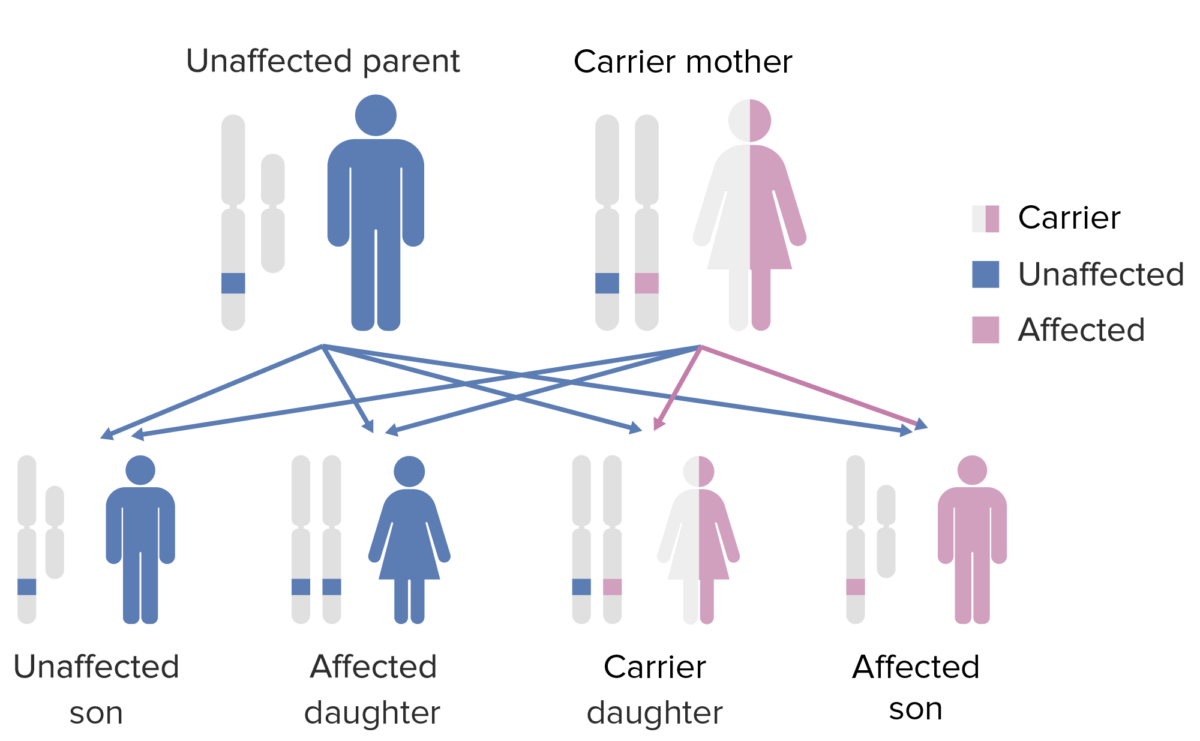
O padrão de hereditariedade da agamaglobulinemia ligada ao X:
Observar que a mãe deve contribuir com o gene X como defeito para o filho do sexo masculino para que este expresse esse fenótipo.
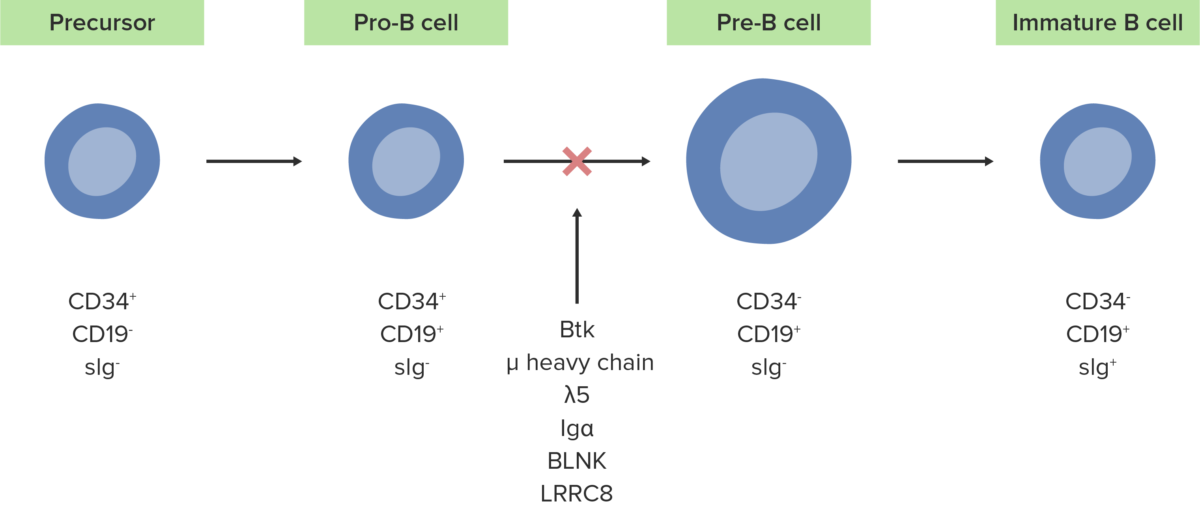
A ausência ou defeito da enzima Btk inibe o desenvolvimento normal de células pró-B em células pré-B.
Imagem por Lecturio.As seguintes condições são diagnósticos diferenciais da agamaglobulinemia ligada ao X.