El virus Virus Viruses are infectious, obligate intracellular parasites composed of a nucleic acid core surrounded by a protein capsid. Viruses can be either naked (non-enveloped) or enveloped. The classification of viruses is complex and based on many factors, including type and structure of the nucleoid and capsid, the presence of an envelope, the replication cycle, and the host range. Virology de la hepatitis E Hepatitis E Acute inflammation of the liver in humans; caused by hepatitis E virus, a non-enveloped single-stranded RNA virus. Similar to hepatitis a, its incubation period is 15-60 days and is enterically transmitted, usually by fecal-oral transmission. Hepatitis E Virus ( HEV HEV The hepatitis E virus (HEV) is a small nonenveloped virus that contains linear, single-stranded, positive-sense RNA, making it similar to norovirus. Transmission of HEV is via the fecal-oral route and is clinically similar to that of hepatitis A. However, unlike hepatitis A, hepatitis E is quite severe, especially in pregnant women, and may cause fulminant hepatitis. Hepatitis E Virus, por sus siglas en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum inglés) es un pequeño virus Virus Viruses are infectious, obligate intracellular parasites composed of a nucleic acid core surrounded by a protein capsid. Viruses can be either naked (non-enveloped) or enveloped. The classification of viruses is complex and based on many factors, including type and structure of the nucleoid and capsid, the presence of an envelope, the replication cycle, and the host range. Virology no envuelto de ARN lineal, monocatenario positivo, por lo que es similar al AL Amyloidosis norovirus Norovirus Norovirus is a nonenveloped, single-stranded, positive-sense RNA virus belonging to the Caliciviridae family. Norovirus infections are transmitted via the fecal-oral route or by aerosols from vomiting. The virus is one of the most common causes of nonbacterial gastroenteritis epidemic worldwide. Symptoms include watery and nonbloody diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, and low-grade fever. Norovirus. La transmisión del HEV HEV The hepatitis E virus (HEV) is a small nonenveloped virus that contains linear, single-stranded, positive-sense RNA, making it similar to norovirus. Transmission of HEV is via the fecal-oral route and is clinically similar to that of hepatitis A. However, unlike hepatitis A, hepatitis E is quite severe, especially in pregnant women, and may cause fulminant hepatitis. Hepatitis E Virus es por vía fecal-oral y es clínicamente similar a la de la hepatitis A Hepatitis A Hepatitis A is caused by the hepatitis A virus (HAV), a nonenveloped virus of the Picornaviridae family with single-stranded RNA. HAV causes an acute, highly contagious hepatitis with unspecific prodromal symptoms such as fever and malaise followed by jaundice and elevated liver transaminases. Hepatitis A Virus. Sin embargo, a diferencia de la hepatitis A Hepatitis A Hepatitis A is caused by the hepatitis A virus (HAV), a nonenveloped virus of the Picornaviridae family with single-stranded RNA. HAV causes an acute, highly contagious hepatitis with unspecific prodromal symptoms such as fever and malaise followed by jaundice and elevated liver transaminases. Hepatitis A Virus, la hepatitis E Hepatitis E Acute inflammation of the liver in humans; caused by hepatitis E virus, a non-enveloped single-stranded RNA virus. Similar to hepatitis a, its incubation period is 15-60 days and is enterically transmitted, usually by fecal-oral transmission. Hepatitis E Virus es bastante grave, especialmente en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum mujeres embarazadas, y puede causar una hepatitis fulminante junto con una encefalopatía hepática en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum un periodo de aproximadamente 8 semanas. El tratamiento es principalmente preventivo e incluye evitar el consumo de agua contaminada, un buen saneamiento y una higiene personal adecuada.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025

Identificación de los virus ARN:
Los virus pueden clasificarse de muchas maneras. Sin embargo, la mayoría de los virus tienen un genoma formado por ADN o ARN. Los virus con genoma ARN pueden caracterizarse además por tener ARN monocatenario o bicatenario. Los virus “envueltos” están cubiertos por una fina capa de membrana celular (normalmente tomada de la célula huésped). Si la capa está ausente, los virus se denominan “desnudos”. Los virus con genomas monocatenarios son “positivos” si el genoma se emplea directamente como ARN mensajero (ARNm), que se traduce en proteínas. Los virus monocatenarios negativos emplean la ARN polimerasa dependiente de ARN, una enzima viral, para transcribir su genoma en ARN mensajero.
Replicación primaria:
Tabla: Comparación de los LOS Neisseria virus Virus Viruses are infectious, obligate intracellular parasites composed of a nucleic acid core surrounded by a protein capsid. Viruses can be either naked (non-enveloped) or enveloped. The classification of viruses is complex and based on many factors, including type and structure of the nucleoid and capsid, the presence of an envelope, the replication cycle, and the host range. Virology de la hepatitis A Hepatitis A Hepatitis A is caused by the hepatitis A virus (HAV), a nonenveloped virus of the Picornaviridae family with single-stranded RNA. HAV causes an acute, highly contagious hepatitis with unspecific prodromal symptoms such as fever and malaise followed by jaundice and elevated liver transaminases. Hepatitis A Virus–E
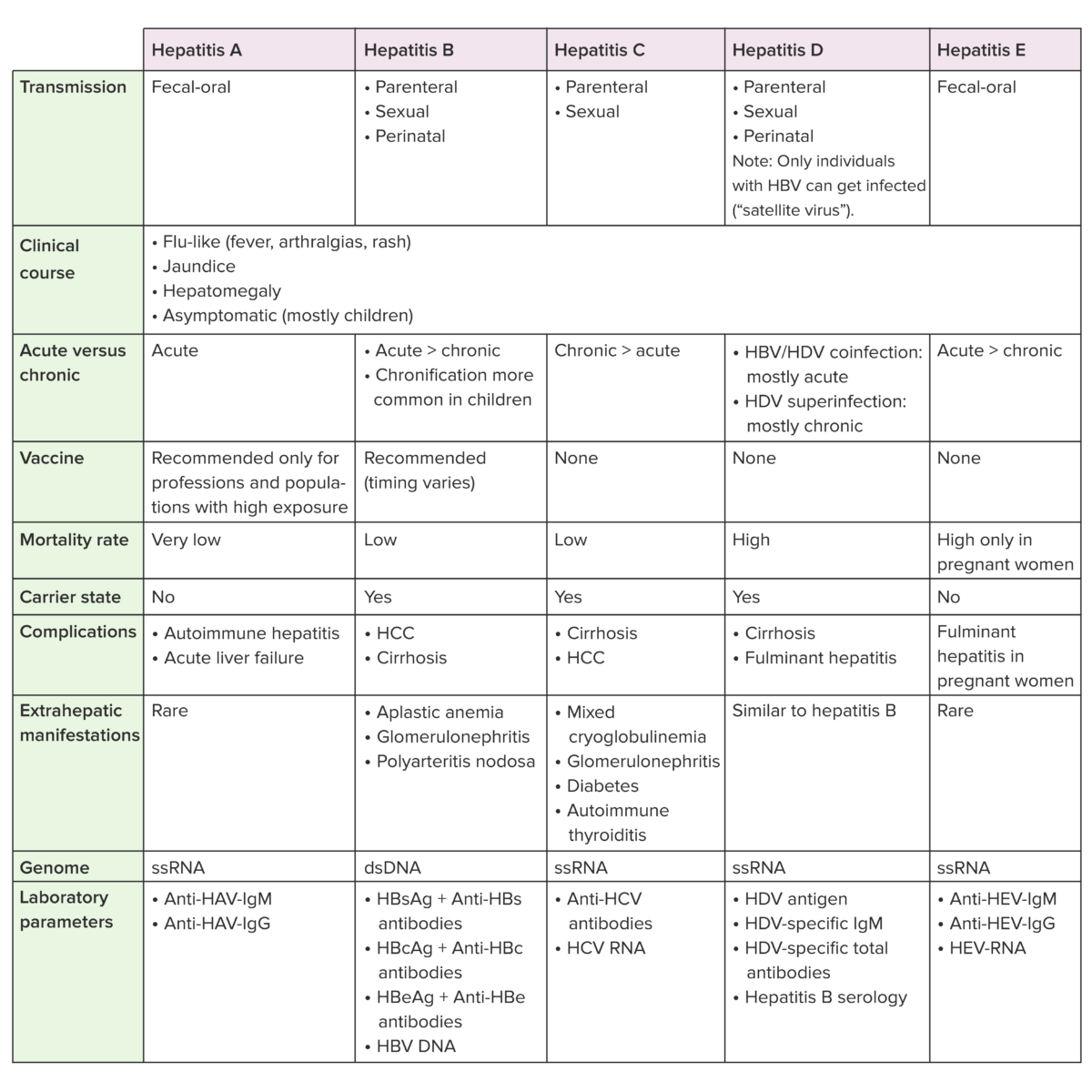
Anti-HBc antibodies: anticuerpos del núcleo de la hepatitis B
Anti-HBs antibodies: anticuerpos de superficie contra la hepatitis B
HBcAg: antígeno del núcleo de la hepatitis B
HBsAg: antígeno de superficie de la hepatitis B
HBV: virus de la hepatitis B
HCC: carcinoma hepatocelular
HCV: virus de la hepatitis C
HDV: virus de la hepatitis D