El síndrome de Guillain-Barré, el cual alguna vez se pensó que era un proceso de una sola enfermedad, es una familia de polineuropatías inmunomediadas que ocurren después de infecciones (e.g., con Campylobacter jejuni Campylobacter jejuni A species of bacteria that resemble small tightly coiled spirals. Its organisms are known to cause abortion in sheep and fever and enteritis in man and may be associated with enteric diseases of calves, lambs, and other animals. Campylobacter). El síndrome de Guillain-Barré típico se caracteriza por una parálisis neuromuscular monofásica aguda, simétrica y de progresión ascendente. Si la parálisis alcanza los LOS Neisseria músculos respiratorios, el síndrome de Guillain-Barré puede progresar a insuficiencia respiratoria, lo que requiere una hospitalización prolongada. El tratamiento es principalmente de soporte y puede requerir plasmaféresis o inmunoglobulina IV.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
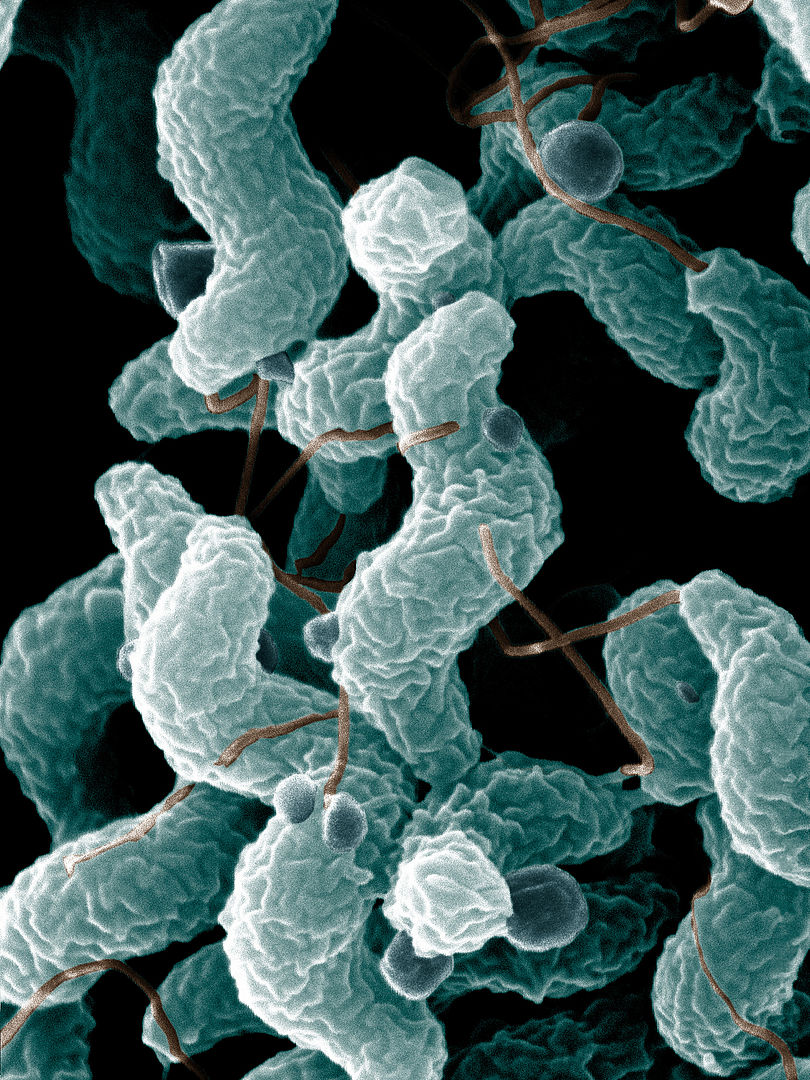
Campylobacter jejuni
Esta micrografía electrónica de barrido muestra el organismo en forma de S con un único flagelo polar.
Los LOS Neisseria síntomas clínicos varían según el subtipo de síndrome de Guillain-Barré. Las personas pueden tener antecedentes de síntomas respiratorios o gastrointestinales de 1–4 semanas previas a la aparición del síndrome de Guillain-Barré.
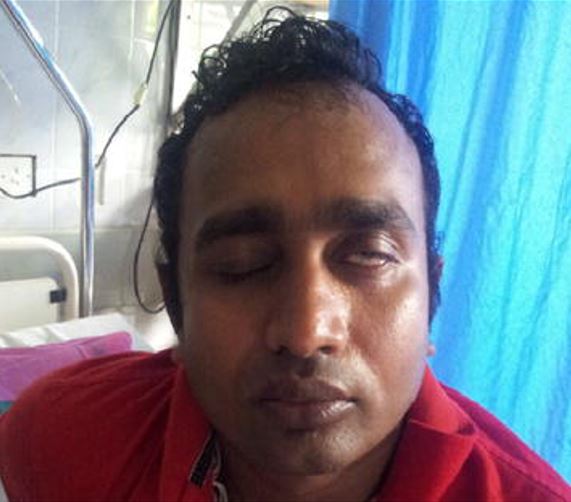
Síntomas clínicos del síndrome de Guillain-Barré:
Parálisis de Bell (parálisis del nervio facial) en una persona con síndrome de Guillain-Barré después de una infección aguda por dengue