El síndrome de dificultad respiratoria aguda se caracteriza por la aparición repentina de hipoxemia y edema Edema Edema is a condition in which excess serous fluid accumulates in the body cavity or interstitial space of connective tissues. Edema is a symptom observed in several medical conditions. It can be categorized into 2 types, namely, peripheral (in the extremities) and internal (in an organ or body cavity). Edema pulmonar bilateral sin insuficiencia cardíaca. La sepsis Sepsis Systemic inflammatory response syndrome with a proven or suspected infectious etiology. When sepsis is associated with organ dysfunction distant from the site of infection, it is called severe sepsis. When sepsis is accompanied by hypotension despite adequate fluid infusion, it is called septic shock. Sepsis and Septic Shock es la causa más común del SDRA. El mecanismo subyacente y la correlación histológica es el daño alveolar difuso. El daño alveolar difuso implica daños en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum las células endoteliales y epiteliales alveolares, y se asocia con inflamación y desarrollo de membranas hialinas que recubren las paredes alveolares internas. El estadio de reparación sigue después de semanas, con la posibilidad de que se desarrolle fibrosis Fibrosis Any pathological condition where fibrous connective tissue invades any organ, usually as a consequence of inflammation or other injury. Bronchiolitis Obliterans más adelante. Clínicamente, la siguiente tríada de hallazgos favorece el diagnóstico de SDRA: disnea aguda o rápidamente progresiva, insuficiencia respiratoria hipóxica (relación de presión parcial de O2/fracción de O2 inspirado < 300 mm Hg) y opacidades alveolares bilaterales en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la imagenología torácica. El tratamiento implica la determinación y el tratamiento de la causa mientras se proporciona el oxígeno adecuado, se reduce el daño pulmonar adicional y se evita la sobrecarga de líquidos. La mayoría de los LOS Neisseria pacientes requieren ventilación mecánica. El síndrome de dificultad respiratoria aguda se asocia a una elevada mortalidad o a complicaciones a largo plazo que pueden desarrollarse incluso después del tratamiento.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
El síndrome de dificultad respiratoria aguda es un síndrome clínico (no un diagnóstico patológico) caracterizado por una aparición repentina de hipoxemia y edema Edema Edema is a condition in which excess serous fluid accumulates in the body cavity or interstitial space of connective tissues. Edema is a symptom observed in several medical conditions. It can be categorized into 2 types, namely, peripheral (in the extremities) and internal (in an organ or body cavity). Edema pulmonar bilateral sin insuficiencia cardíaca.
El mecanismo subyacente del SDRA es el daño alveolar difuso:
El síndrome de dificultad respiratoria aguda se diagnostica clínicamente utilizando los LOS Neisseria criterios diagnósticos de Berlín.
El síndrome de dificultad respiratoria aguda es el resultado de trastornos clínicos que afectan a los LOS Neisseria pulmones directa o indirectamente.
Lesión pulmonar directa:
Lesión pulmonar indirecta:
Riesgo de SDRA:
El síndrome de dificultad respiratoria aguda comienza con una lesión inicial en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria neumocitos y el endotelio pulmonar, que inicia una reacción en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum cadena con aumento de la inflamación y el daño pulmonar que puede tener una distribución desigual o en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum parches.
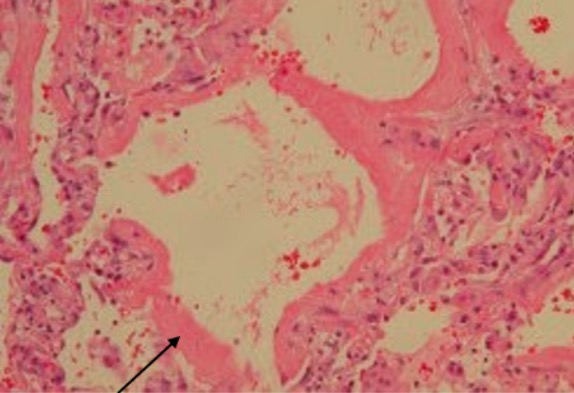
Síndrome de dificultad respiratoria aguda:
Un hombre de 68 años tenía un linfoma de células del manto y recibió quimioterapia. Fue ingresado en el hospital por fiebre e insuficiencia respiratoria. Se excluyó la afectación pulmonar por linfoma de células del manto. La biopsia pulmonar toracoscópica asistida por vídeo reveló un daño alveolar difuso con membranas hialinas que recubrían las superficies alveolares (flecha), consistente con el SDRA.
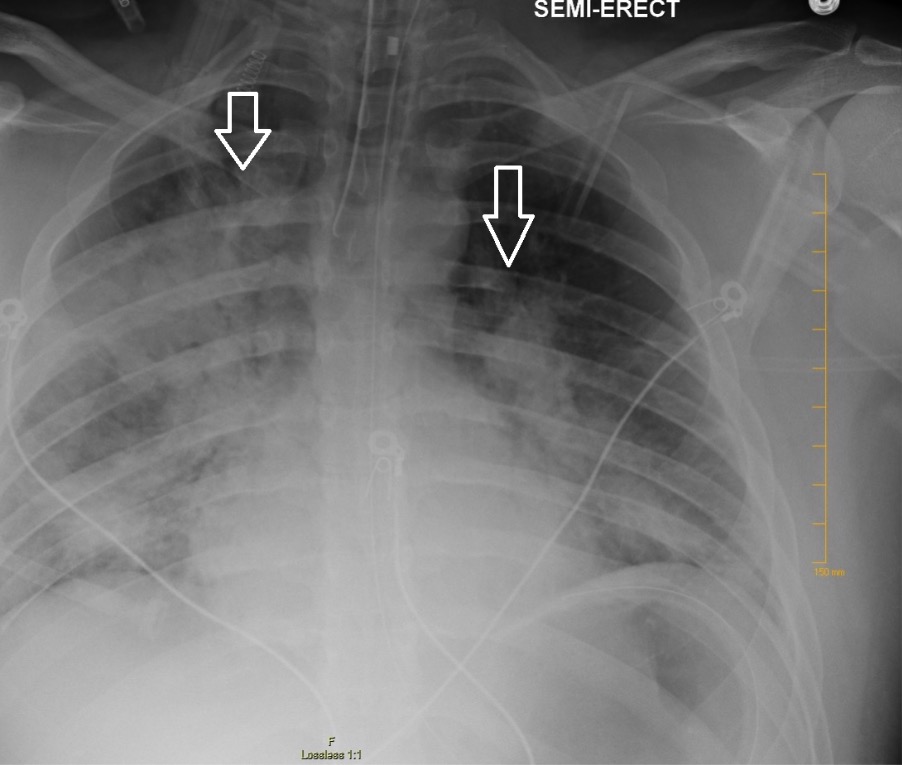
La radiografía de tórax que muestra infiltrados parcheados bilaterales sugestivos de SDRA
Imagen: “Chest radiography demonstrating bilateral hilar opacities” por Ologun G O, Ridley D, Chea N D, et al. (September 08, 2017). Severe ARDS after laparoscopic appendectomy in a young adult. Cureus 9(9):e1664. doi:10.7759/cureus.1664.1664. Licencia: CC BY 4.0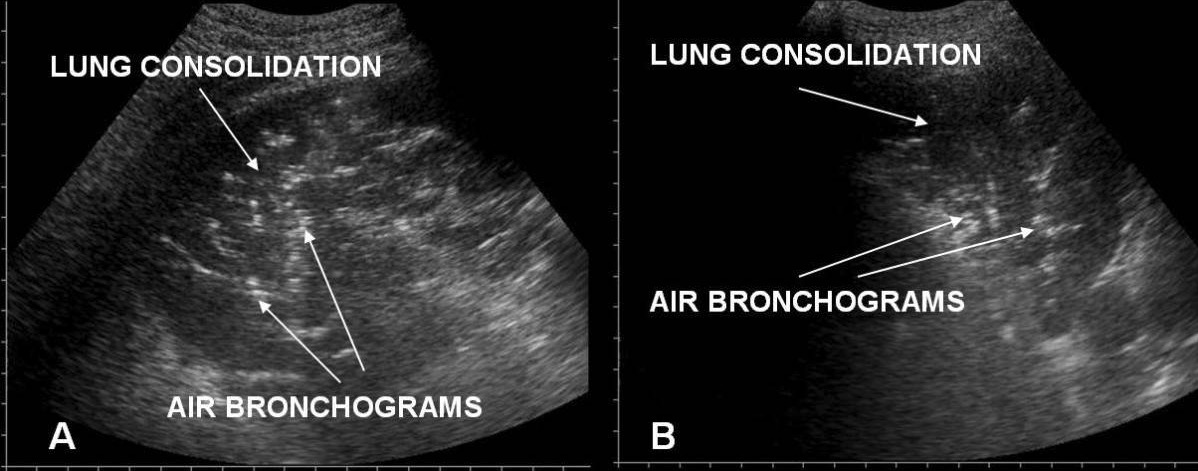
Síndrome de dificultad respiratoria aguda versus edema pulmonar cardiogénico agudo en el ultrasonido torácico/pulmonar:
A: línea pleural irregular en el SDRA
B: una línea pleural uniforme en el edema pulmonar agudo cardiogénico
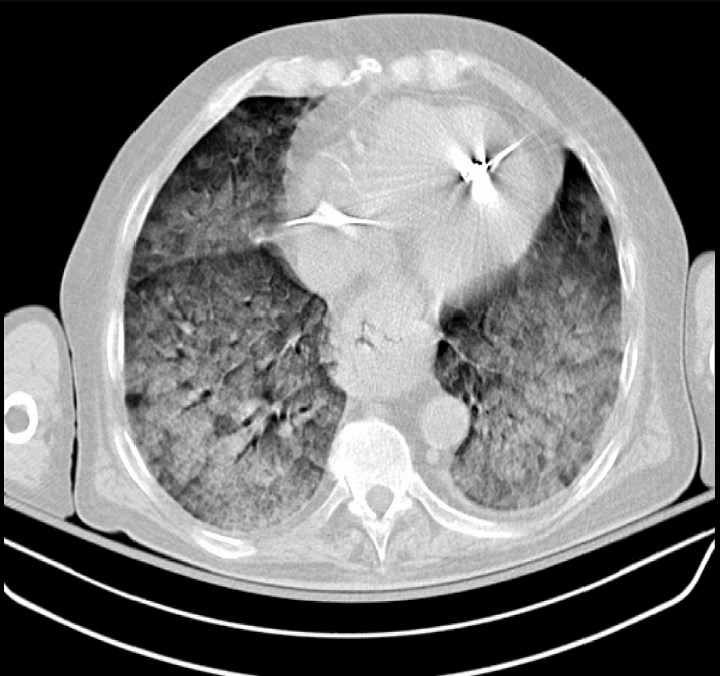
Una TC que muestra un SDRA grave: opacidades pulmonares difusas presentes bilateralmente
Imagen: “Chest CT scan indicative of severe ARDS” por Zagkotsis G, Markou M, Papanikolaou P, et al. (January 24, 2021). Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome Induced by Parathyroid Storm. Cureus 13(1): e12881. doi:10.7759/cureus.12881. Licencia: CC BY 4.0Casi todos los LOS Neisseria pacientes son tratados en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la UCI
El síndrome de dificultad respiratoria aguda es una enfermedad grave que suele estar asociada a una elevada mortalidad y morbilidad.
Se han identificado varios factores de riesgo que pueden estimar el pronóstico en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum un paciente con SDRA:
La mayoría de los LOS Neisseria pacientes recuperan la mayor parte de su función pulmonar, pero tardarán meses.
Complicaciones a largo plazo: