El síndrome de CHARGE es una afección genética rara de herencia autosómica dominante en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la que se ven afectados casi todos los LOS Neisseria sistemas corporales. El acrónimo CHARGE representa el conjunto de características clínicas que se observan en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum esta afección: Coloboma, Defectos cardíacos (Heart defects, en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum inglés), Atresia de coanas, Retraso del crecimiento, Anomalías Genitales y Anomalías del oído (E ar AR Aortic regurgitation (AR) is a cardiac condition characterized by the backflow of blood from the aorta to the left ventricle during diastole. Aortic regurgitation is associated with an abnormal aortic valve and/or aortic root stemming from multiple causes, commonly rheumatic heart disease as well as congenital and degenerative valvular disorders. Aortic Regurgitation abnormalities, en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum inglés). Las pruebas genéticas confirman el diagnóstico. El tratamiento es sintomático y las prioridades son el tratamiento de las vías respiratorias, los LOS Neisseria defectos cardíacos y la capacidad de alimentación en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria primeros años de vida. No existe una terapia curativa definitiva.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
CHARGE es un acrónimo para describir la presentación clínica de este síndrome:
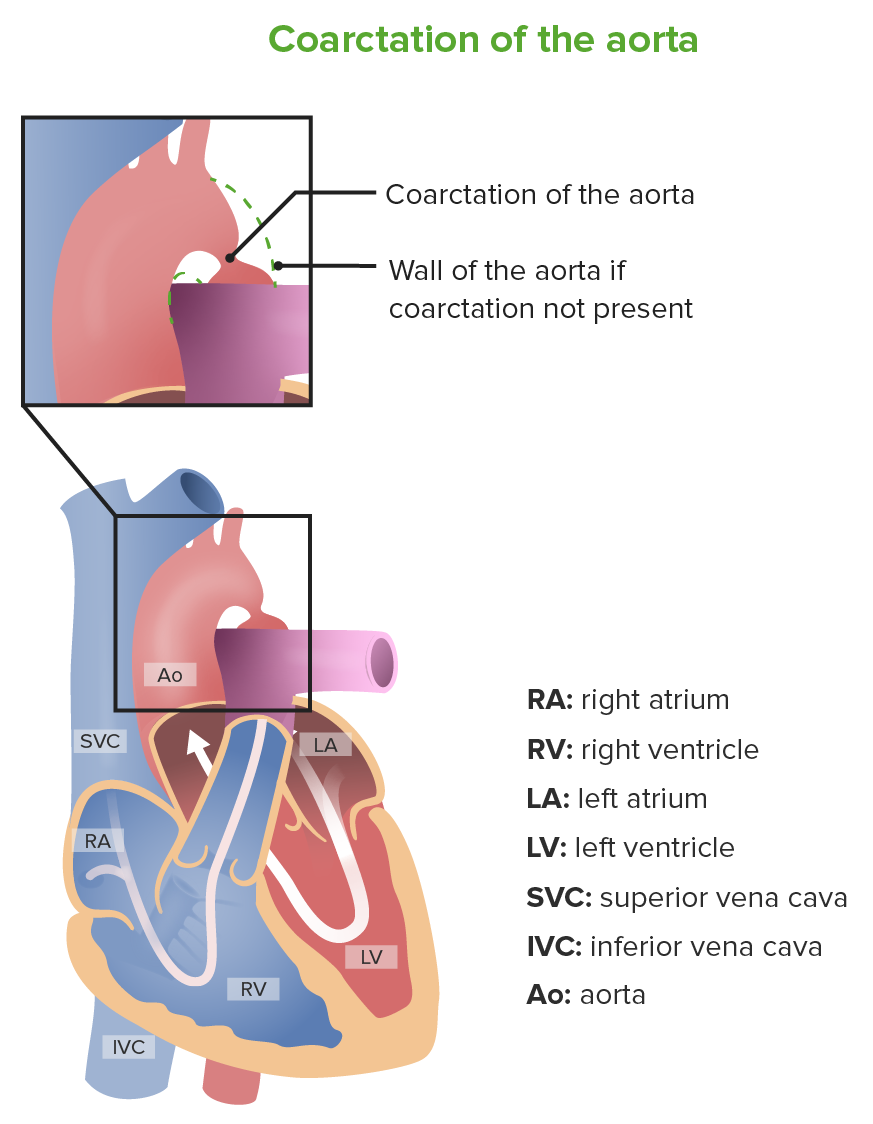
Coartación de la aorta
Imagen por Lecturio.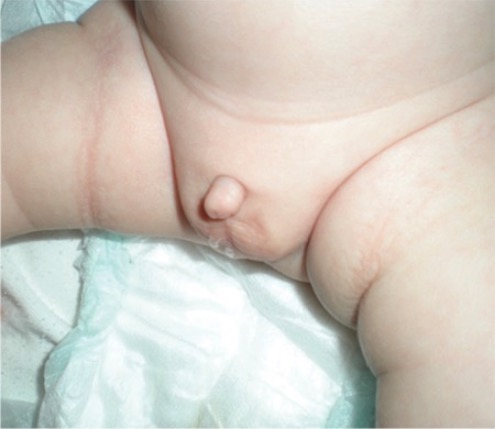
Lactante nacido con micropene
Imagen: “Micropenis in a newborn” por Erciyes University Faculty of Medicine, Department of Pediatric Endocrinology, Kayseri, Turkey. Licencia: CC BY 2.5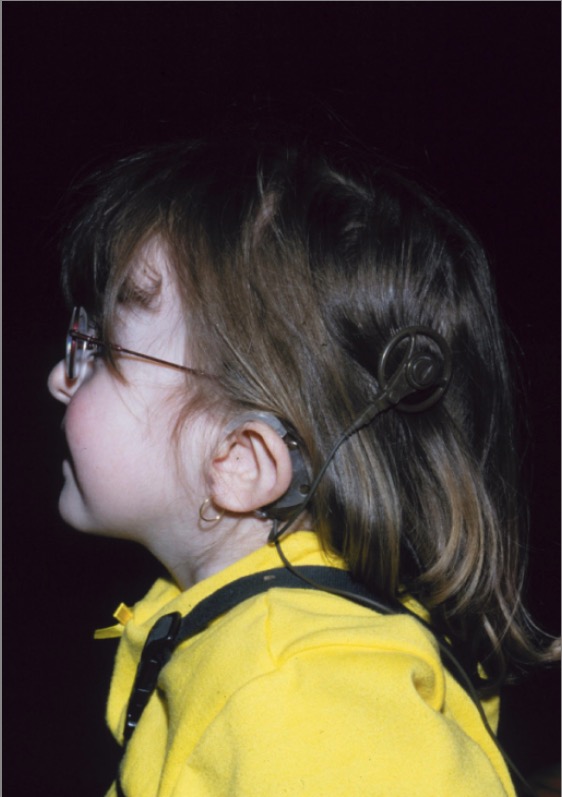
Una niña con síndrome CHARGE: Obsérvese la llamada “oreja caída” característica del síndrome CHARGE, junto con el implante coclear.
Imagen: “CHARGE syndrome” por Department of Pediatrics, IWK Health Centre, Dalhousie University, Canada. Licencia: CC BY 2.0El diagnóstico del síndrome de CHARGE puede establecerse si se dan 2 criterios principales más cualquier número de criterios menores.
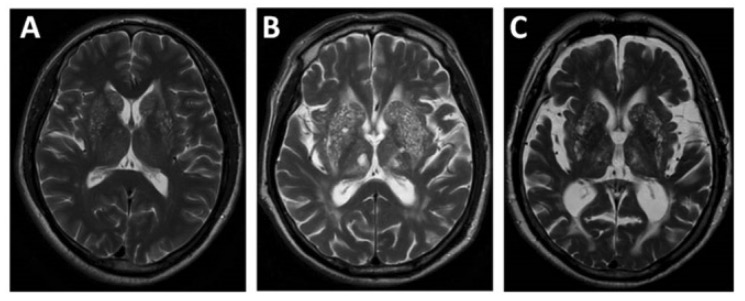
Resonancia magnética que muestra atrofia cerebral por etapas: leve (A) moderada (B) a grave (C)
Imagen: “EPVS” por Department of Neurology, Beijing Chaoyang Hospital, Capital Medical University, Beijing, China. Licencia: CC BY 4.0Existen varias opciones de tratamiento de soporte y correctivo. El tratamiento se adapta a los LOS Neisseria síntomas y a las anomalías presentes.