El retinoblastoma Retinoblastoma Retinoblastoma is a rare tumor but the most common primary intraocular malignancy of childhood. It is believed that the condition arises from a neuronal progenitor cell. Retinoblastoma can be heritable or non-heritable. Retinoblastoma es un tumor Tumor Inflammation raro, pero es la neoplasia maligna intraocular primaria más común de la infancia. Se cree que la afección surge de una célula progenitora neuronal. El retinoblastoma Retinoblastoma Retinoblastoma is a rare tumor but the most common primary intraocular malignancy of childhood. It is believed that the condition arises from a neuronal progenitor cell. Retinoblastoma can be heritable or non-heritable. Retinoblastoma puede ser hereditario o no hereditario. La afección generalmente se presenta como leucocoria unilateral o bilateral (reflejo blanco anormal en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el ojo) en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum un niño menor de 2 años. El retinoblastoma Retinoblastoma Retinoblastoma is a rare tumor but the most common primary intraocular malignancy of childhood. It is believed that the condition arises from a neuronal progenitor cell. Retinoblastoma can be heritable or non-heritable. Retinoblastoma es fatal si no es tratado, pero el reconocimiento temprano representa una alta tasa de supervivencia en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum países ricos en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum recursos.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
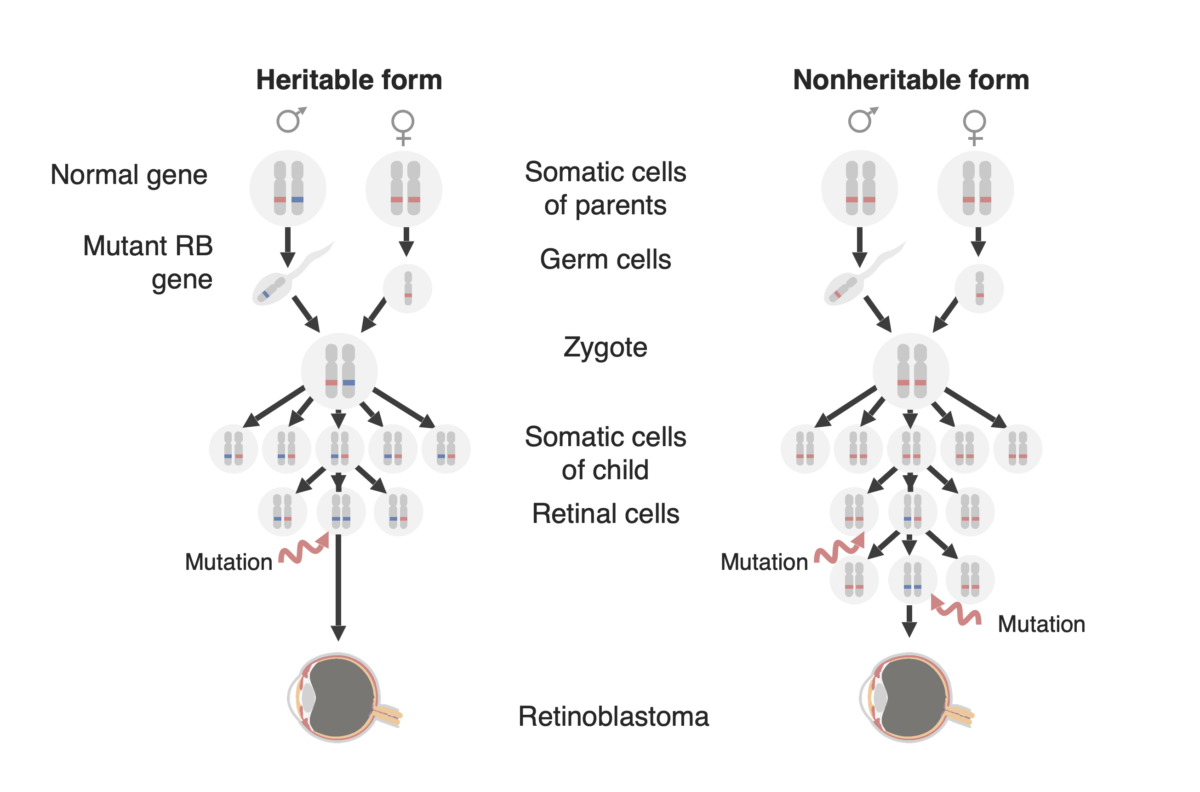
Diagrama de las dos formas de desarrollo del retinoblastoma: una forma familiar (ahora llamada “forma hereditaria”, a la izquierda y una ”forma esporádica” (ahora llamada ”forma no hereditaria”) a la derecha. En la forma hereditaria, se transmite al niño un gen RB1 mutado (en azul), y solo se necesita una mutación adicional en el alelo normal emparejado (en rojo) para desarrollar el tumor. En la forma no hereditaria, el gen RB1 puede mutar de novo en la línea germinal de la descendencia (no se muestra en esta figura) para luego comportarse como en la forma hereditaria, o una célula precursora de la retina puede adquirir una mutación RB1 en ambos alelos creando así un tumor de retinoblastoma.
Imagen por Lecturio.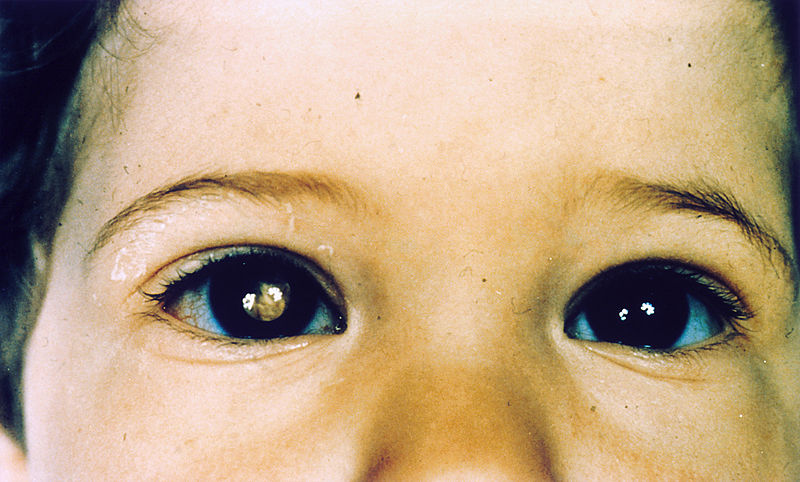
Niño con retinoblastoma del ojo derecho, que presenta leucocoria
Imagen : “Pathology: Patient: Retinoblastoma” por The National Cancer Institute. Licencia: Dominio Público
Niño que presenta celulitis orbitaria del ojo derecho causada por un retinoblastoma localmente avanzado
Imagen : “Orbital cellulitis” por The Pan African Medical Journal. Licencia: CC BY 2.0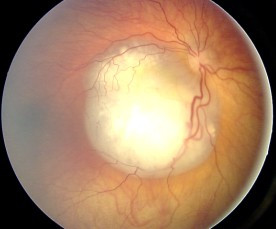
Aspecto del fondo de ojo del retinoblastoma
Imagen : “Fundus retinoblastoma” por Aerts, I, Lumbroso-Le Rouic. Licencia: CC BY 2.0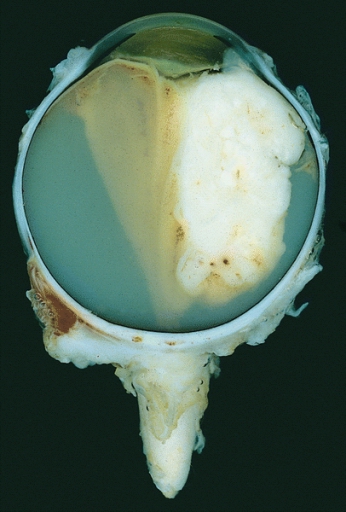
Ojo enucleado que muestra un gran retinoblastoma exofítico
Imagen : “Retinoblastoma” por The Armed Forces Institute of Pathology (AFIP). Licencia: Dominio Público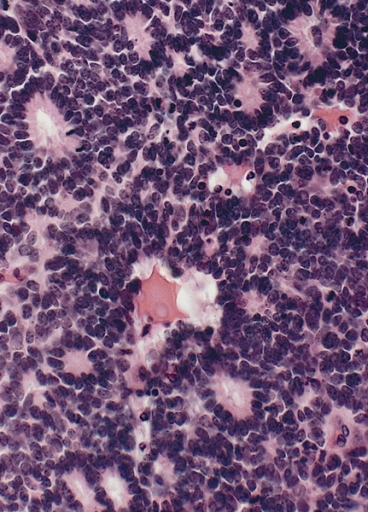
Retinoblastoma con rosetas Flexner-Wintersteiner características que presentan una alineación circular de células cilíndricas cortas alrededor de una luz central
Imagen : “Flexner-Wintersteiner rosettes” por The Armed Forces Institute of Pathology (AFIP). Licencia: Dominio PúblicoEl tratamiento depende de la etapa, con múltiples terapias “preservadoras de la visión” disponibles:
El diagnóstico diferencial incluye cualquier afección que pueda causar leucocoria.