La púrpura trombótica trombocitopénica (PTT) es una enfermedad potencialmente mortal debida a una deficiencia congénita o adquirida de ADAMTS-13, una metaloproteinasa que escinde los LOS Neisseria multímeros del factor Von Willebrand (FVW). Los LOS Neisseria grandes multímeros agregan entonces un exceso de plaquetas, lo que provoca una trombosis microvascular y un aumento del consumo de plaquetas. La presentación clínica puede consistir en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum trombocitopenia, anemia Anemia Anemia is a condition in which individuals have low Hb levels, which can arise from various causes. Anemia is accompanied by a reduced number of RBCs and may manifest with fatigue, shortness of breath, pallor, and weakness. Subtypes are classified by the size of RBCs, chronicity, and etiology. Anemia: Overview and Types hemolítica, hematuria Hematuria Presence of blood in the urine. Renal Cell Carcinoma, síntomas gastrointestinales, síntomas neurológicos y afectación renal. El diagnóstico se establece sobre la base de una combinación de síntomas clínicos y pruebas de laboratorio. La púrpura trombótica trombocitopénica es una emergencia médica y casi siempre es mortal si no se inicia rápidamente el tratamiento adecuado. El tratamiento de emergencia incluye el intercambio de plasma Plasma The residual portion of blood that is left after removal of blood cells by centrifugation without prior blood coagulation. Transfusion Products y las terapias inmunosupresoras.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
La púrpura trombótica trombocitopénica es una microangiopatía trombótica causada por la deficiencia de ADAMTS-13, una proteasa que escinde el FVW.
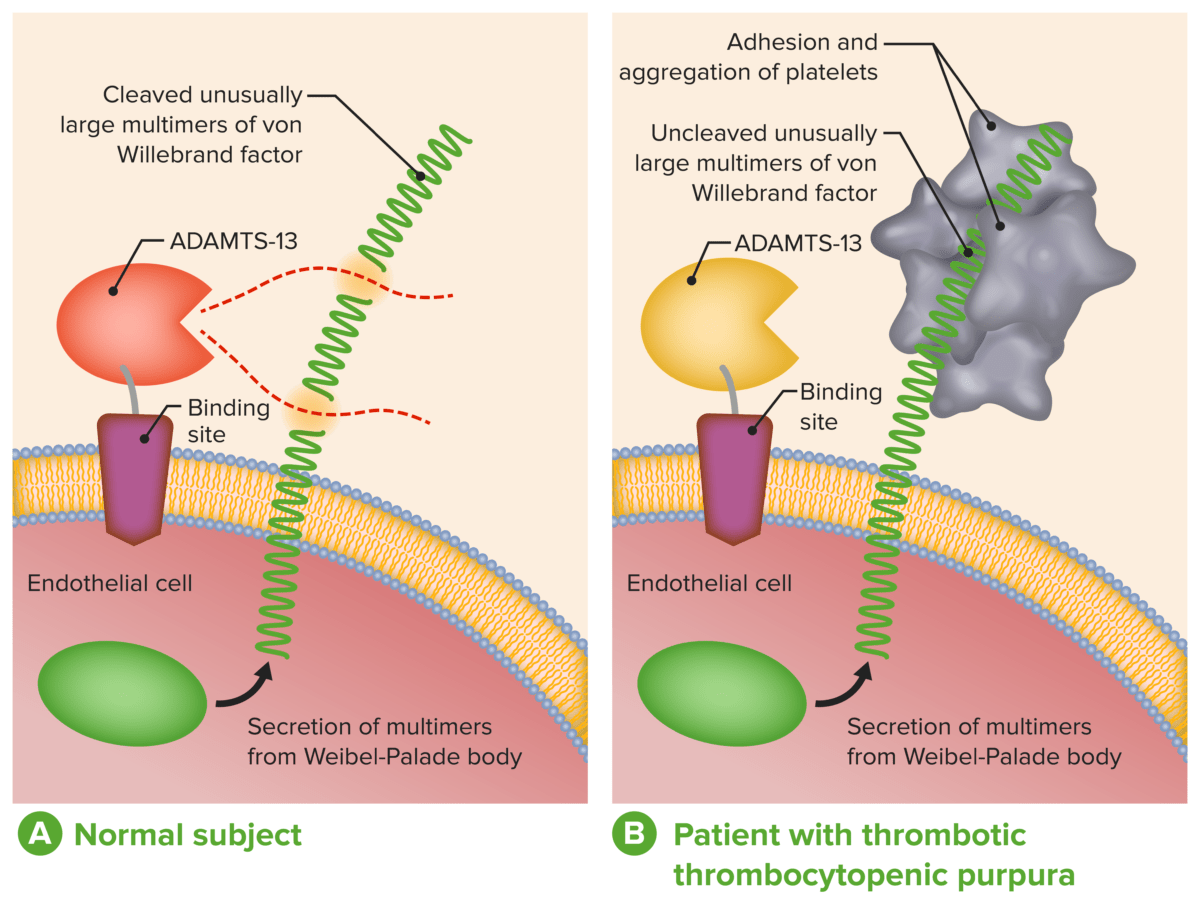
ADAMTS-13 en el diagnóstico y tratamiento de las microangiopatías trombóticas:
A: Función fisiológica normal de ADAMTS-13
B: La ausencia o la severa reducción de la actividad de ADAMTS-13 en pacientes con PTT impide el desdoblamiento oportuno de multímeros inusualmente grandes del FVW durante su secreción por las células endoteliales..
La clásica pentada de PTT:
Manifestaciones sistémicas-orgánicas:
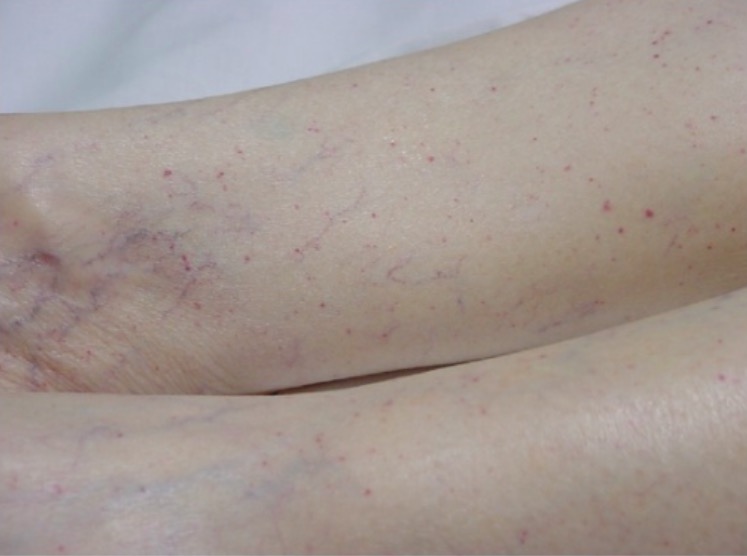
Típica erupción petequial en las extremidades inferiores del paciente
Imagen: “Typical petechial rash” por Department of Emergency Medicine, University of Florida, Gainesville, FL 32610, USA. Licencia: CC BY 3.0A diferencia de la PTT adquirida, la PTT congénita no se presenta con episodios agudos.
Los LOS Neisseria síntomas suelen ser leves, vagos y continuos:
Las exacerbaciones graves y potencialmente mortales son más probables durante 2 períodos de la vida:
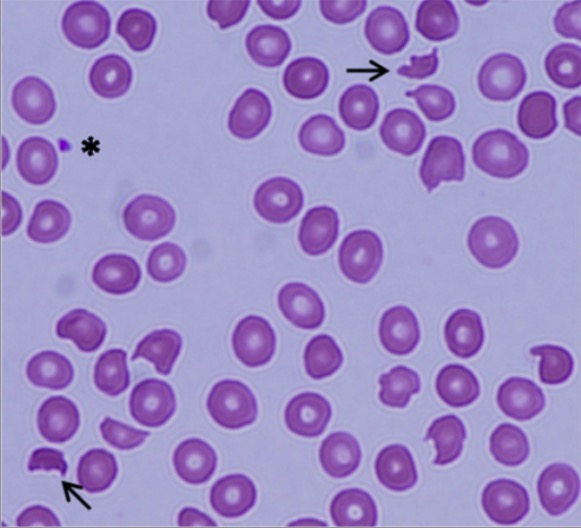
Púrpura trombótica trombocitopénica (PTT):
Frotis de sangre periférica que muestra esquistocitos (flechas) y una marcada disminución del número de plaquetas, lo que indica una anemia hemolítica microangiopática
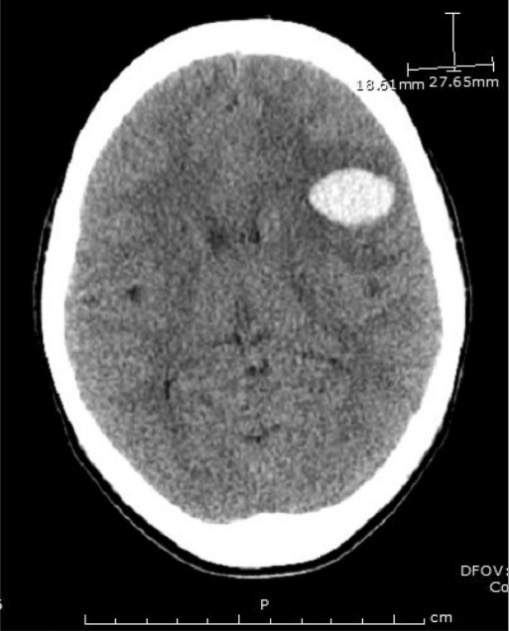
TC craneal en un paciente que muestra la mayor de dos hemorragias frontoparietales
Imagen: “Emergent head CT demonstrating the larger of two frontoparietal hemorrhages” por Divisions of Infectious Disease, The George Washington University, School of Medicine and Health Sciences, Washington, DC, USA. Licencia: CC BY 3.0La puntuación PLASMIC predice la probabilidad de PTT en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum presencia de esquistocitos en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el frotis de sangre.
Criterios PLASMIC (1 punto por cada uno):
Puntuación: