La poliposis adenomatosa familiar es un trastorno genético hereditario autosómico dominante que se presenta con numerosos pólipos adenomatosos en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el colon Colon The large intestines constitute the last portion of the digestive system. The large intestine consists of the cecum, appendix, colon (with ascending, transverse, descending, and sigmoid segments), rectum, and anal canal. The primary function of the colon is to remove water and compact the stool prior to expulsion from the body via the rectum and anal canal. Colon, Cecum, and Appendix: Anatomy. La poliposis adenomatosa familiar es el síndrome de poliposis más común, que es un grupo de condiciones hereditarias o adquiridas caracterizadas por el crecimiento de pólipos en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el tracto gastrointestinal, asociados a otras características extracolónicas. Estos síndromes son causados por mutaciones en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum genes Genes A category of nucleic acid sequences that function as units of heredity and which code for the basic instructions for the development, reproduction, and maintenance of organisms. DNA Types and Structure específicos asociados a la supresión de tumores o a la regulación del ciclo celular. Todos los LOS Neisseria pacientes con poliposis adenomatosa familiar desarrollarán cáncer de colon Colon The large intestines constitute the last portion of the digestive system. The large intestine consists of the cecum, appendix, colon (with ascending, transverse, descending, and sigmoid segments), rectum, and anal canal. The primary function of the colon is to remove water and compact the stool prior to expulsion from the body via the rectum and anal canal. Colon, Cecum, and Appendix: Anatomy a la edad de 35–40 años si no reciben tratamiento. El tratamiento es con un programa de vigilancia y colectomía.
Last updated: Dec 26, 2025
La poliposis adenomatosa familiar es un trastorno autosómico dominante que se asocia al AL Amyloidosis desarrollo de numerosos adenomas colorrectales.
Mutaciones patogénicas en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el gen supresor de tumores APC APC A polyposis syndrome due to an autosomal dominant mutation of the apc genes on chromosome 5. The syndrome is characterized by the development of hundreds of adenomatous polyps in the colon and rectum of affected individuals by early adulthood. Familial Adenomatous Polyposis ( adenomatous polyposis coli Adenomatous polyposis coli A polyposis syndrome due to an autosomal dominant mutation of the APC genes on chromosome 5. The syndrome is characterized by the development of hundreds of adenomatous polyps in the colon and rectum of affected individuals by early adulthood. Familial Adenomatous Polyposis) en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el cromosoma 5 en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la banda 5q21:
Riesgo de tumores relacionados con poliposis adenomatosa familiar
Existen 4 síndromes derivados de la mutación de la línea germinal en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el gen APC APC A polyposis syndrome due to an autosomal dominant mutation of the apc genes on chromosome 5. The syndrome is characterized by the development of hundreds of adenomatous polyps in the colon and rectum of affected individuals by early adulthood. Familial Adenomatous Polyposis:
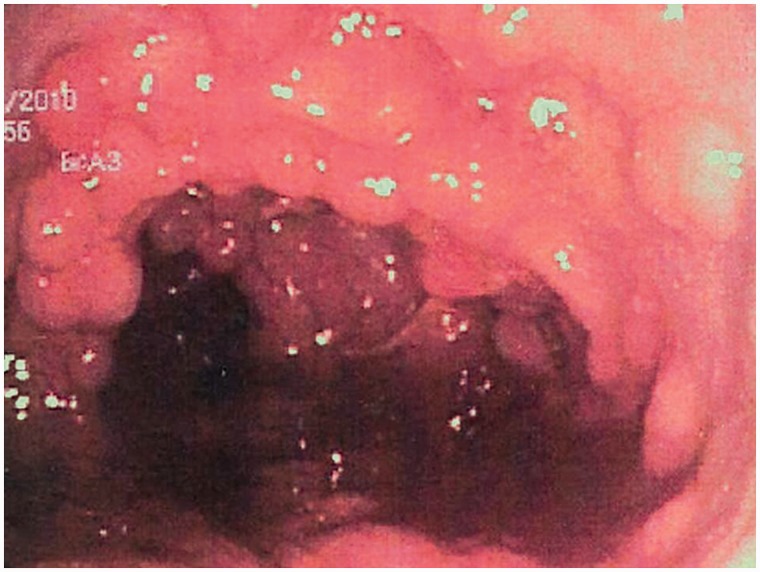
Mucosa colónica tapizada de pólipos adenomatosos en la poliposis adenomatosa familiar
Imagen: “Colonic mucosa carpeted with adenomatous polyps in a patient with familial adenomatous polyposis” por Shussman, N., Wexner, S.D. Licencia: CC BY 3.0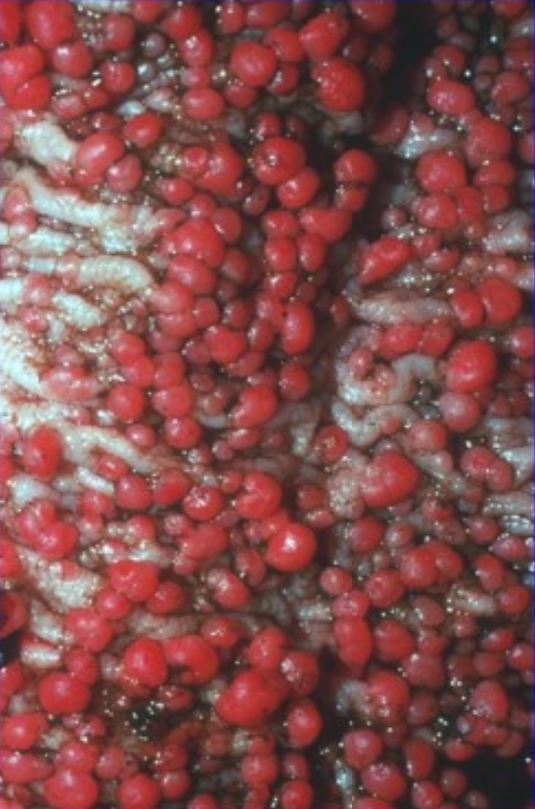
Vista endoscópica de múltiples adenomas en un caso de poliposis adenomatosa familiar establecido
Imagen: “Familial adenomatous polyposis” por Half, E., Bercovich, D., Rozen, P. Licencia: CC BY 2.0, editado por Lecturio.