La parte inferior de la pierna, o simplemente “pierna” en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum términos anatómicos, es la parte del miembro inferior entre la rodilla y la articulación del tobillo. La estructura ósea está compuesta por los LOS Neisseria huesos de la tibia Tibia The second longest bone of the skeleton. It is located on the medial side of the lower leg, articulating with the fibula laterally, the talus distally, and the femur proximally. Knee Joint: Anatomy y el peroné, que se articulan entre sí en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum las articulaciones tibiofibulares proximal y distal. Los LOS Neisseria músculos de la pierna se agrupan en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria compartimentos anterior, lateral y posterior mediante extensiones de fascia Fascia Layers of connective tissue of variable thickness. The superficial fascia is found immediately below the skin; the deep fascia invests muscles, nerves, and other organs. Cellulitis, y ejercen su acción sobre el tobillo, el pie y los LOS Neisseria dedos.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
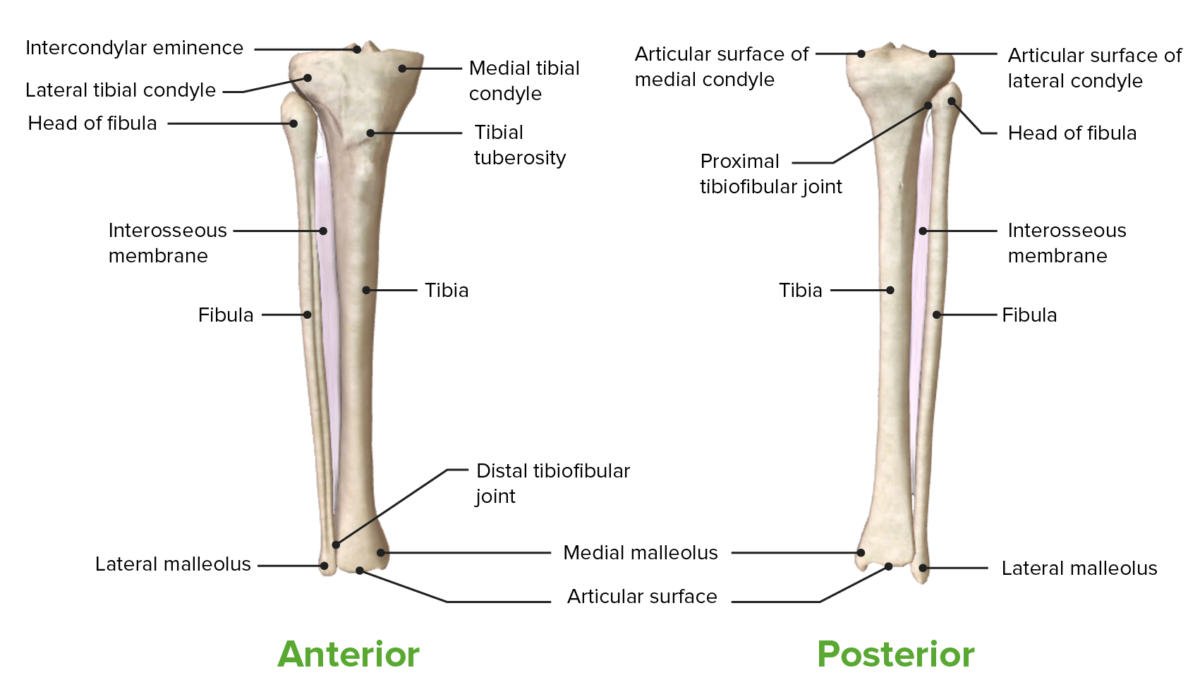
Vistas anterior y posterior de la tibia, el peroné y las articulaciones tibiofibulares
Imagen por BioDigital, editado por Lecturio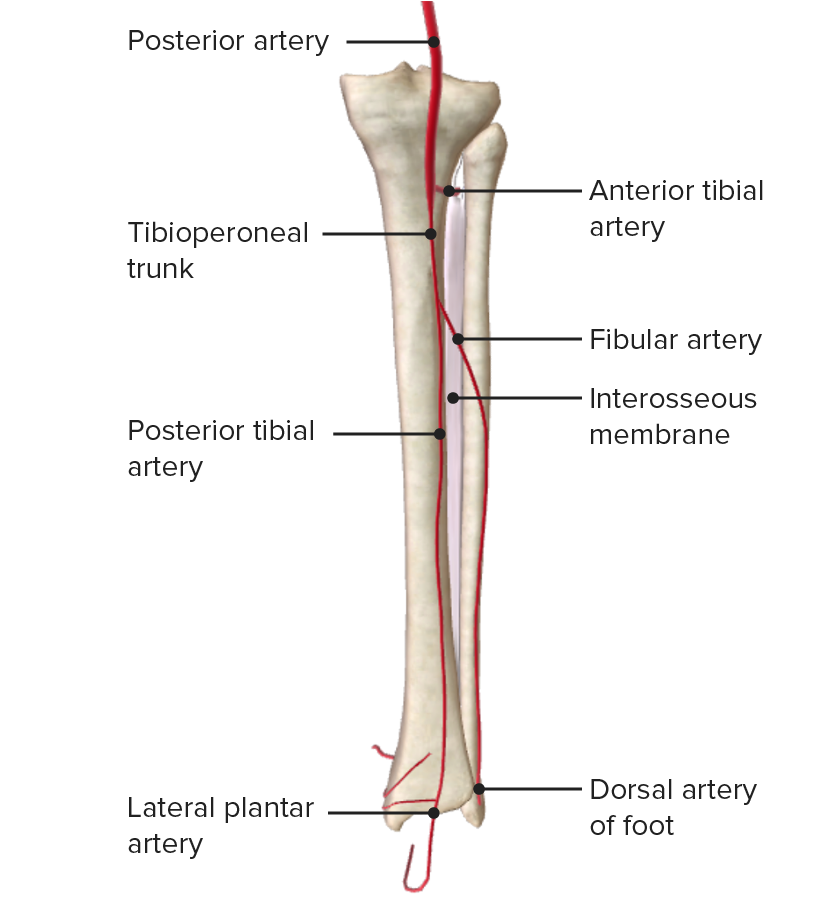
Vista posterior de la pierna, mostrando la abertura en la membrana interósea y el paso de la arteria tibial anterior
Imagen por BioDigital, editado por LecturioLa pierna está dividida en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum 4 compartimentos fasciales por la membrana interósea y los LOS Neisseria tabiques intermusculares anterior, posterior y transversal, como se indica a continuación:
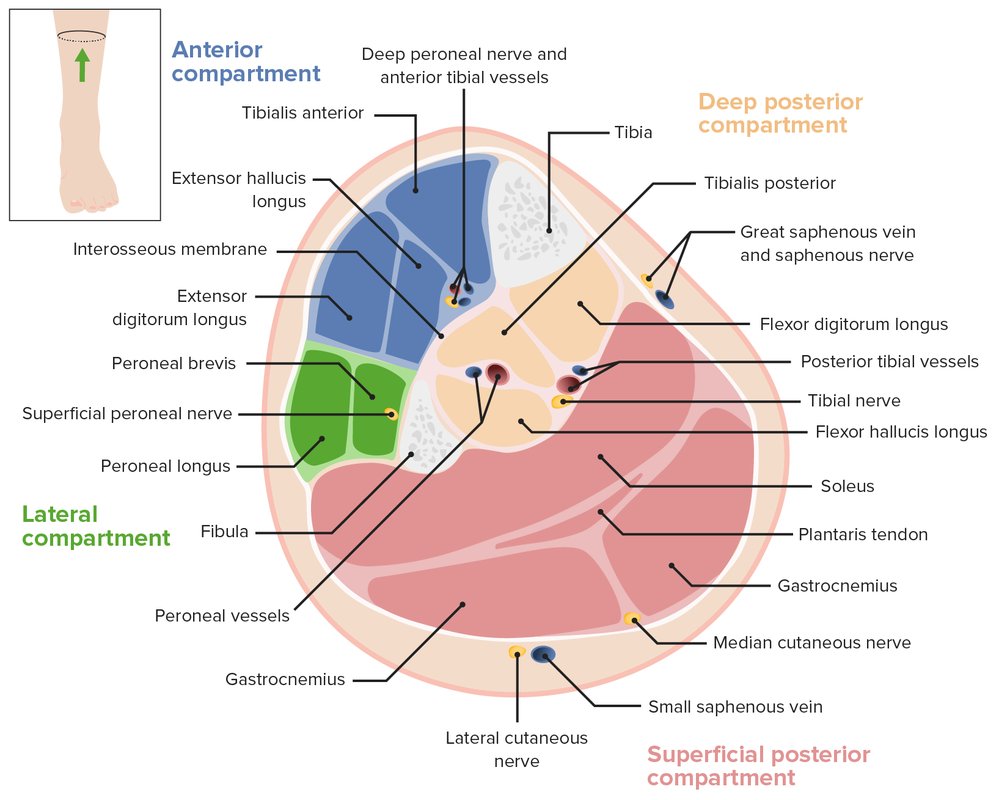
Corte transversal de la pierna, en el que se aprecian los compartimentos fasciales y la ubicación de los vasos principales
Imagen por Lecturio.| Músculo | Origen | Inserción | Inervación | Función |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tibial anterior | Cóndilo lateral, superficie lateral de la tibia Tibia The second longest bone of the skeleton. It is located on the medial side of the lower leg, articulating with the fibula laterally, the talus distally, and the femur proximally. Knee Joint: Anatomy proximal y membrana interósea | Cuneiforme medial y base del primer metatarsiano | Nervios peroneos profundos (L4, L5, S1 S1 Heart Sounds) |
|
| Extensor largo de los LOS Neisseria dedos | Cóndilo lateral de la tibia Tibia The second longest bone of the skeleton. It is located on the medial side of the lower leg, articulating with the fibula laterally, the talus distally, and the femur proximally. Knee Joint: Anatomy, superficie anterior del peroné y membrana interósea | Falanges medias y distales de los LOS Neisseria dedos 2–5 | ||
| Extensor largo del hallux | Superficie anterior y medial del peroné y membrana interósea | Falange distal del hallux (dedo 1) |
|
|
| Tercer peroneo | Superficie anterior del peroné inferior y membrana interósea | Base del 5to metatarsiano |
|
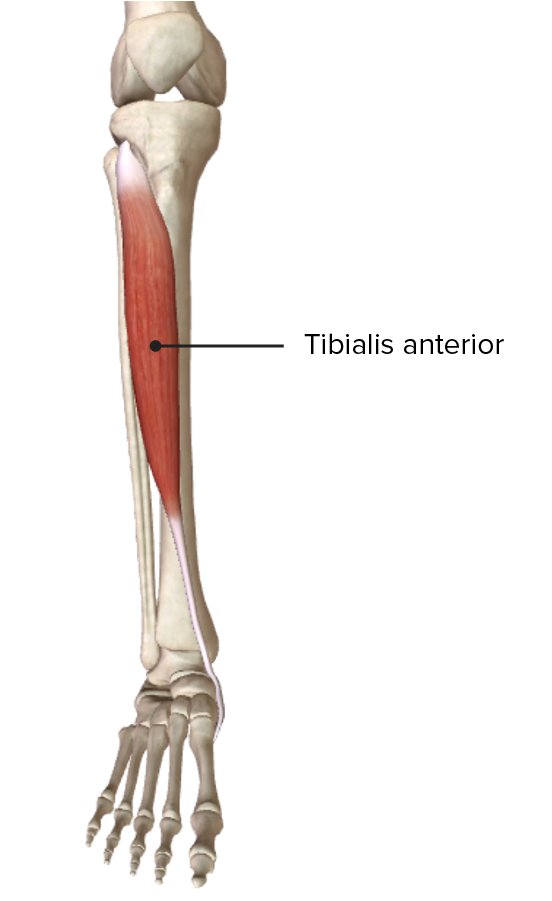
Origen e inserción del músculo tibial anterior en el compartimento anterior de la pierna
Imagen por BioDigital, editado por Lecturio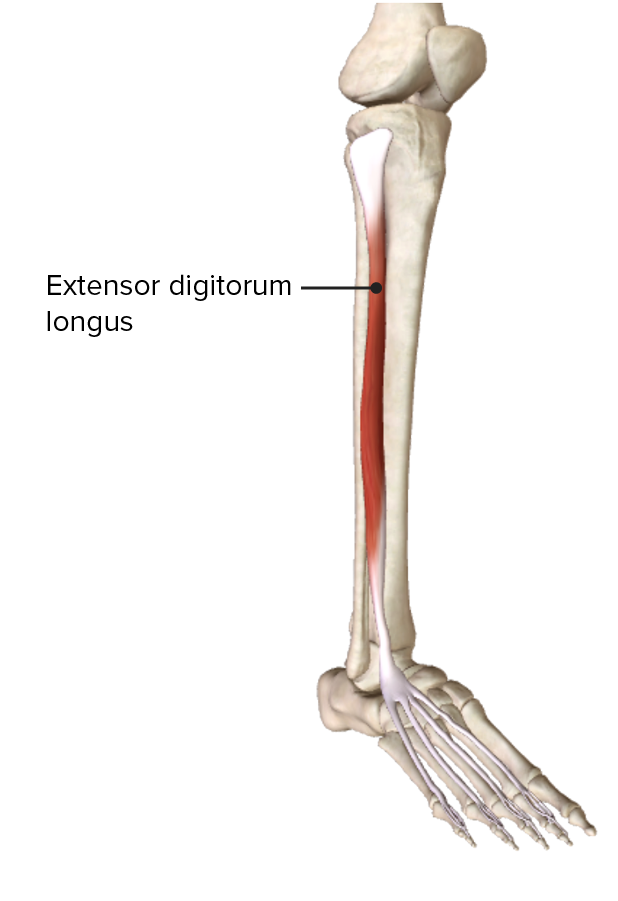
Origen e inserción del músculo extensor largo de los dedos en el compartimento anterior de la pierna
Imagen por BioDigital, editado por Lecturio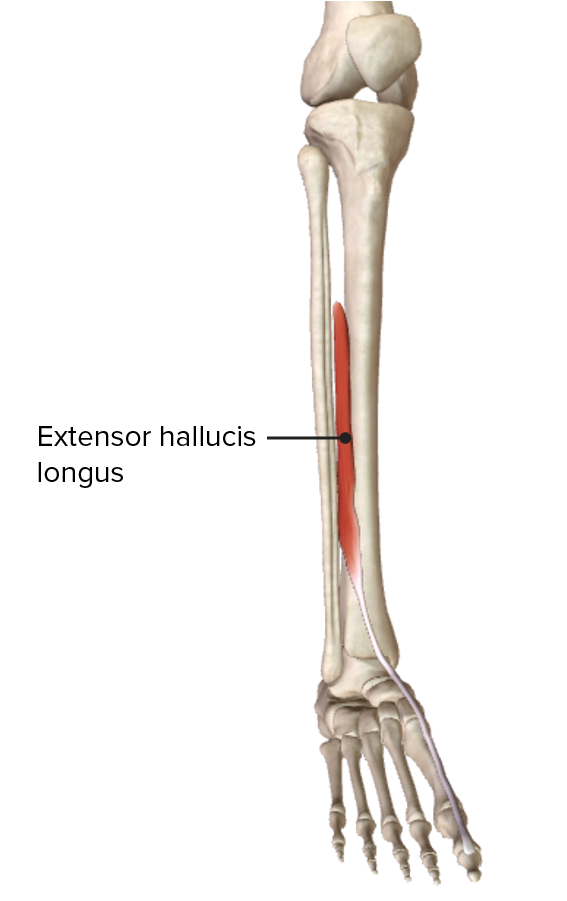
Origen e inserción del músculo extensor largo del hallux en el compartimento anterior de la pierna
Imagen por BioDigital, editado por Lecturio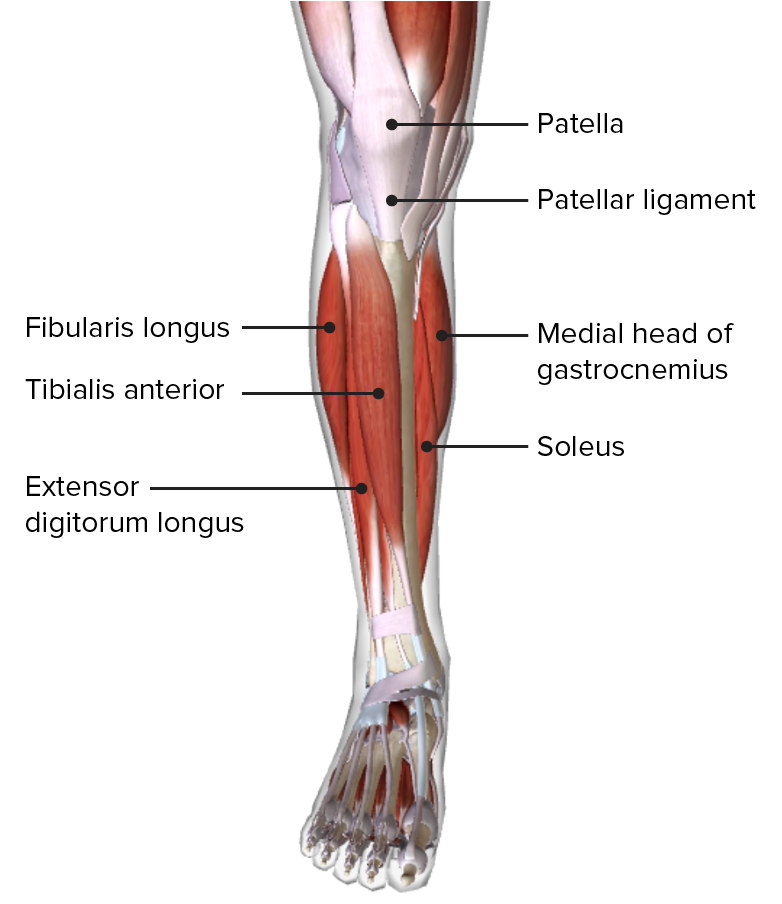
Vista anterior de la pierna, mostrando los músculos del compartimento anterior y sus relaciones con otros músculos y entre sí
Imagen por BioDigital, editado por Lecturio| Músculo | Origen | Inserción | Inervación | Función |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Peroneo largo | Cabeza y dos-tercios proximales del peroné lateral | 1er metatarsiano y cuneiforme medial | Nervios peroneos superficiales (L5, S1 S1 Heart Sounds) | |
| Peroneo corto | Cara lateral de la porción medial del peroné | Base del 5to metatarsiano | Eversión del pie; flexión plantar débil |
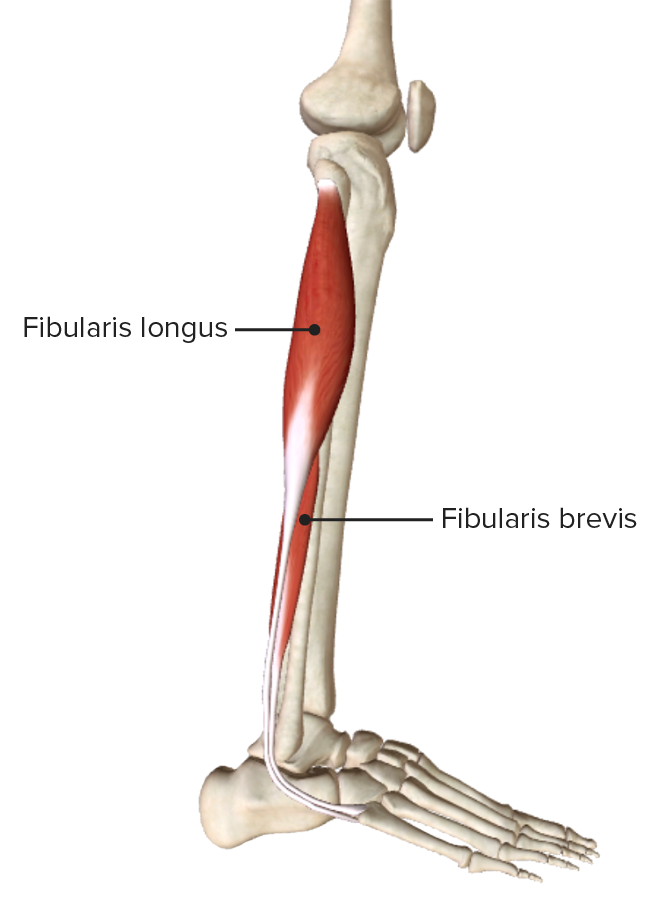
Vista lateral de la pierna, que muestra el origen y la inserción de los músculos que componen el compartimento lateral, o eversor, de la pierna
Imagen por BioDigital, editado por Lecturio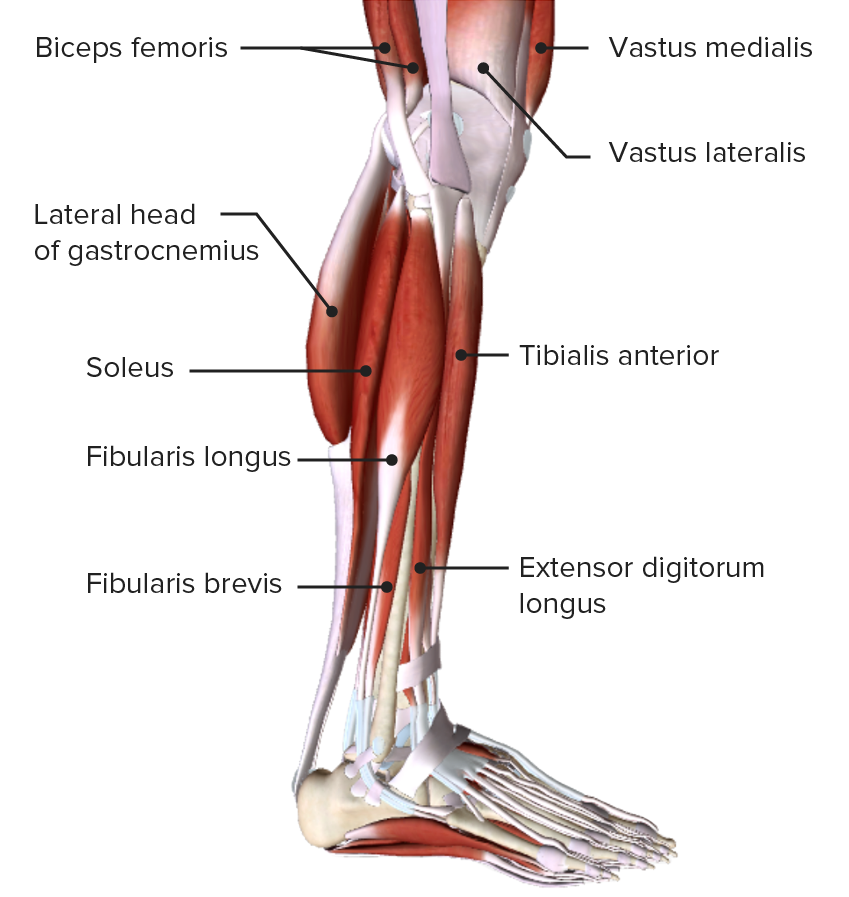
Vista lateral de la pierna, mostrando los músculos del compartimento lateral, o eversor, y sus relaciones con otros músculos y entre sí
Imagen por BioDigital, editado por Lecturio| Músculo | Origen | Inserción | Inervación | Función |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gastrocnemio |
|
Cara posterior del calcáneo a través del tendón del calcáneo | Nervios tibiales ( S1 S1 Heart Sounds, S2 S2 Heart Sounds) |
|
| Sóleo | Cara posterior del peroné y línea soleal de la tibia Tibia The second longest bone of the skeleton. It is located on the medial side of the lower leg, articulating with the fibula laterally, the talus distally, and the femur proximally. Knee Joint: Anatomy | Flexión plantar del tobillo | ||
| Plantar | Cresta supracondilar lateral inferior del fémur | Flexión plantar débil |
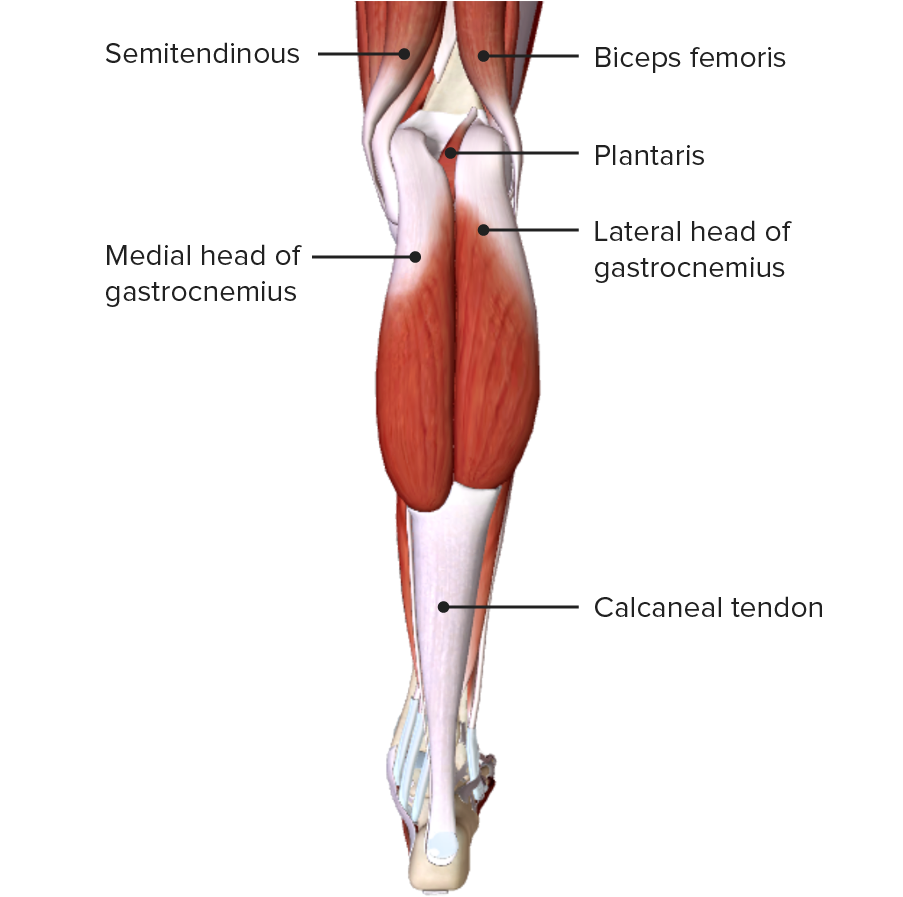
Vista posterior de la pierna, mostrando los músculos gastrocnemios de la capa superficial del compartimento posterior
Imagen por BioDigital, editado por Lecturio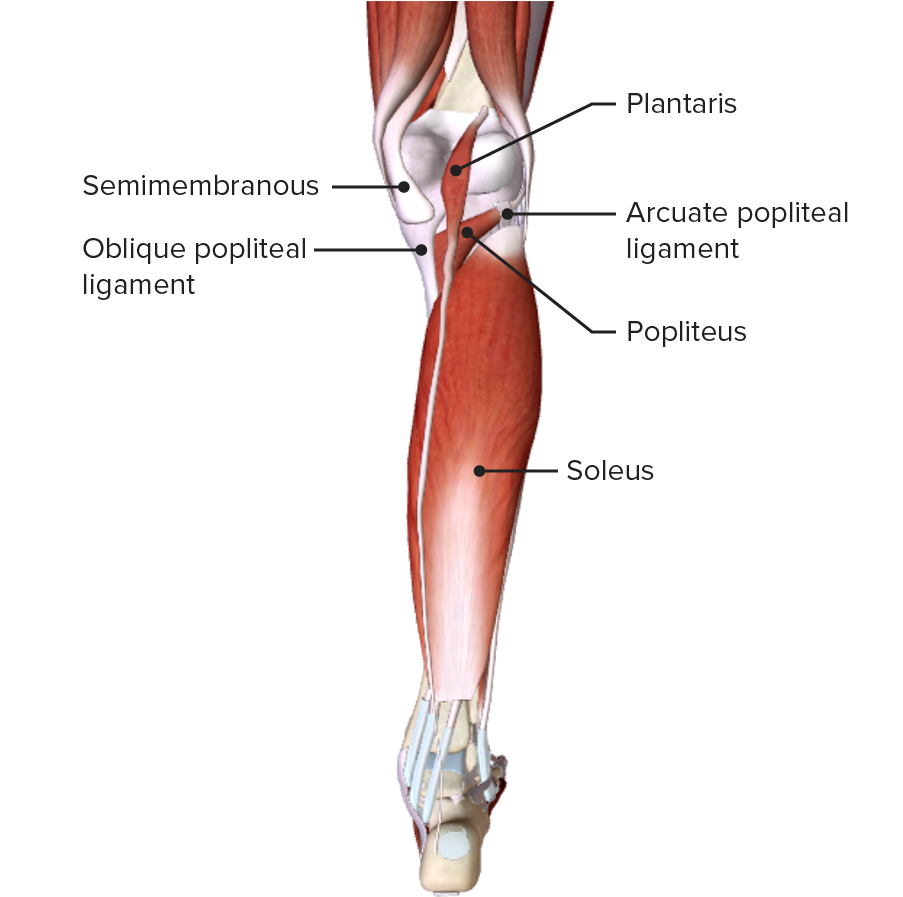
Vista posterior de la pierna, mostrando los músculos plantar y sóleo de la capa superficial del compartimento posterior
Imagen por BioDigital, editado por Lecturio| Músculo | Origen | Inserción | Inervación | Función |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Poplíteo | Cara lateral del cóndilo lateral del fémur y del menisco lateral | Tibia Tibia The second longest bone of the skeleton. It is located on the medial side of the lower leg, articulating with the fibula laterally, the talus distally, and the femur proximally. Knee Joint: Anatomy posterior por encima de la línea del sóleo | Nervios tibiales (L4, L5, S1 S1 Heart Sounds, S2 S2 Heart Sounds, S3 S3 Heart Sounds) |
|
| Flexor largo de los LOS Neisseria dedos | Superficie posterior de la tibia Tibia The second longest bone of the skeleton. It is located on the medial side of the lower leg, articulating with the fibula laterally, the talus distally, and the femur proximally. Knee Joint: Anatomy por debajo de la línea del sóleo | Falanges distales de los LOS Neisseria dedos 2–5 | ||
| Flexor largo del hallux | Dos-tercios inferiores del peroné posterior y membrana interósea | Falange distal del hallux |
|
|
| Tibial posterior | Membrana interósea y bordes posteriores de la tibia Tibia The second longest bone of the skeleton. It is located on the medial side of the lower leg, articulating with the fibula laterally, the talus distally, and the femur proximally. Knee Joint: Anatomy y el peroné | Tuberosidad del hueso navicular Navicular Foot: Anatomy, 1ro–3er huesos cuneiformes y 2do–4to huesos metatarsianos |
|
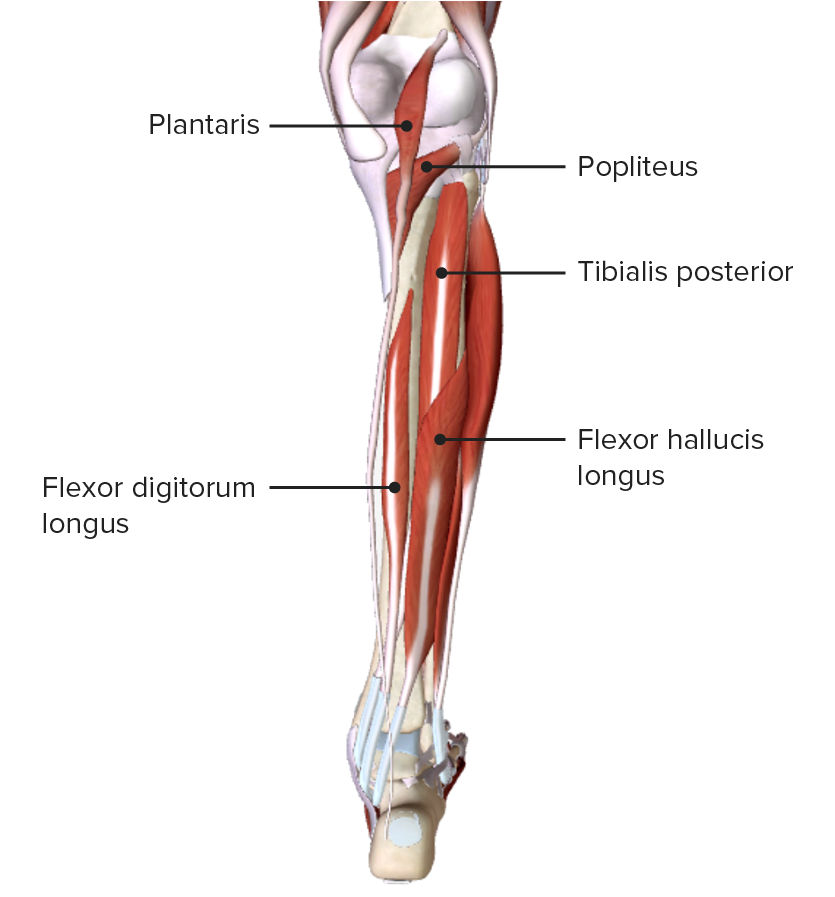
Vista posterior de la pierna, mostrando los músculos de la capa profunda del compartimento posterior y sus relaciones espaciales con otros músculos y entre sí
Imagen por BioDigital, editado por Lecturio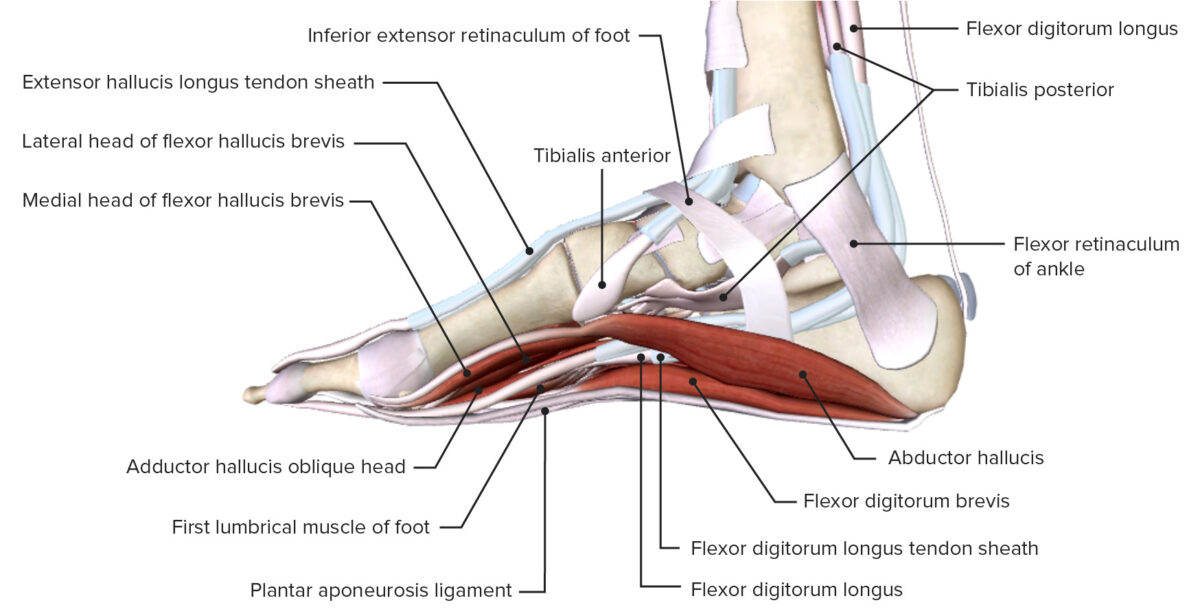
Vista medial de la articulación del tobillo, mostrando los retináculos del tobillo y las inserciones de los músculos de la pierna
Imagen por BioDigital, editado por LecturioUna continuación de la arteria poplítea suministra sangre a la parte inferior de la pierna. La arteria se bifurca en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el margen inferior de la fosa poplítea y envía ramas al AL Amyloidosis compartimento anterior, a la arteria tibial anterior y a los LOS Neisseria compartimentos posterior y lateral, formando el tronco tibioperoneo.
| Origen | Trayectoria | Ramas | Estructuras que irriga | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Arteria tibial anterior (acompañada del nervio peroneo profundo) | División de la arteria poplítea en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum arteria tibial anterior y tronco tibiofibular |
|
|
Compartimento anterior de la pierna |
| Arteria tibial posterior (acompañada del nervio tibial) | Rama terminal del tronco tibioperoneo |
|
|
|
| Arteria peronea | Rama terminal del tronco tibioperoneo |
|
Ramas musculares | Compartimento lateral y capa profunda del compartimento posterior de la pierna |
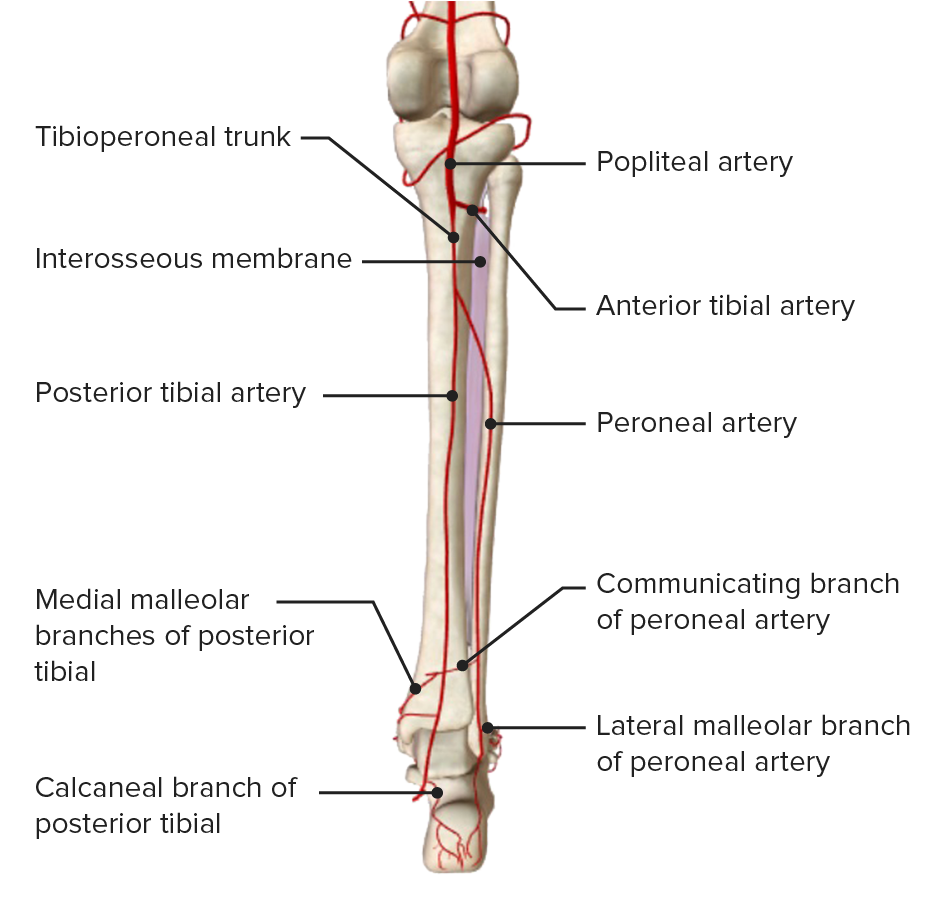
Vista posterior de la pierna, mostrando las vías de irrigación arterial derivadas de la arteria poplítea y sus ramas
Imagen por BioDigital, editado por Lecturio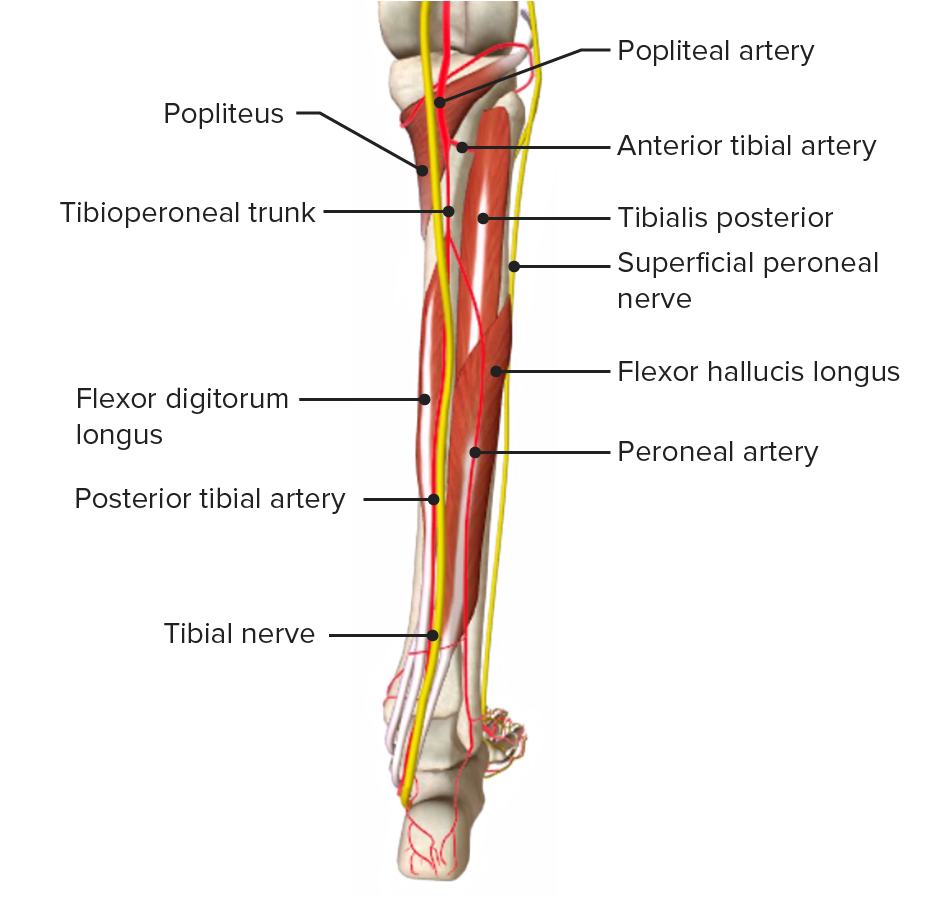
Vista posterior de la pierna, mostrando su irrigación arterial y los nervios acompañantes
Imagen por BioDigital, editado por Lecturio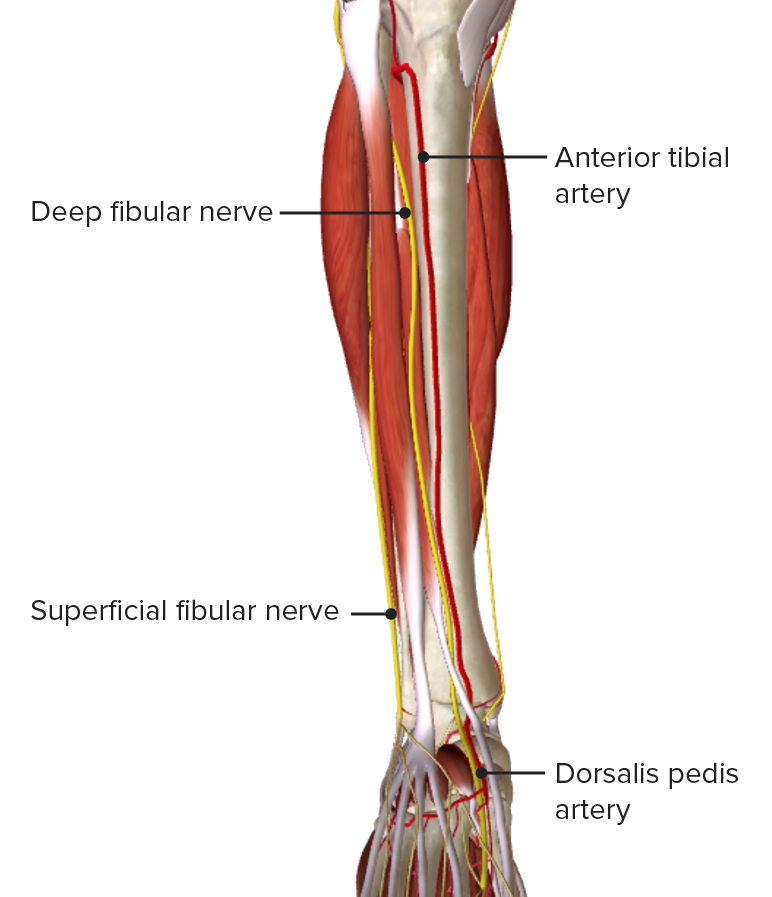
Vista anterior de la pierna, mostrando la irrigación arterial del compartimento anterior
Imagen por BioDigital, editado por LecturioExisten 2 redes de drenaje venoso en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la pierna:
| Origen | Trayectoria | Tributarias | Estructuras que drenan | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vena safena mayor (acompañada del nervio safeno) | Continuación del extremo medial del arco venoso dorsal del pie |
|
|
Cara anteromedial de la pierna y cara plantar del pie |
| Vena safena menor (acompañada del nervio sural) | Continuación del extremo lateral del arco venoso dorsal del pie |
|
Cara posterior de la pierna |
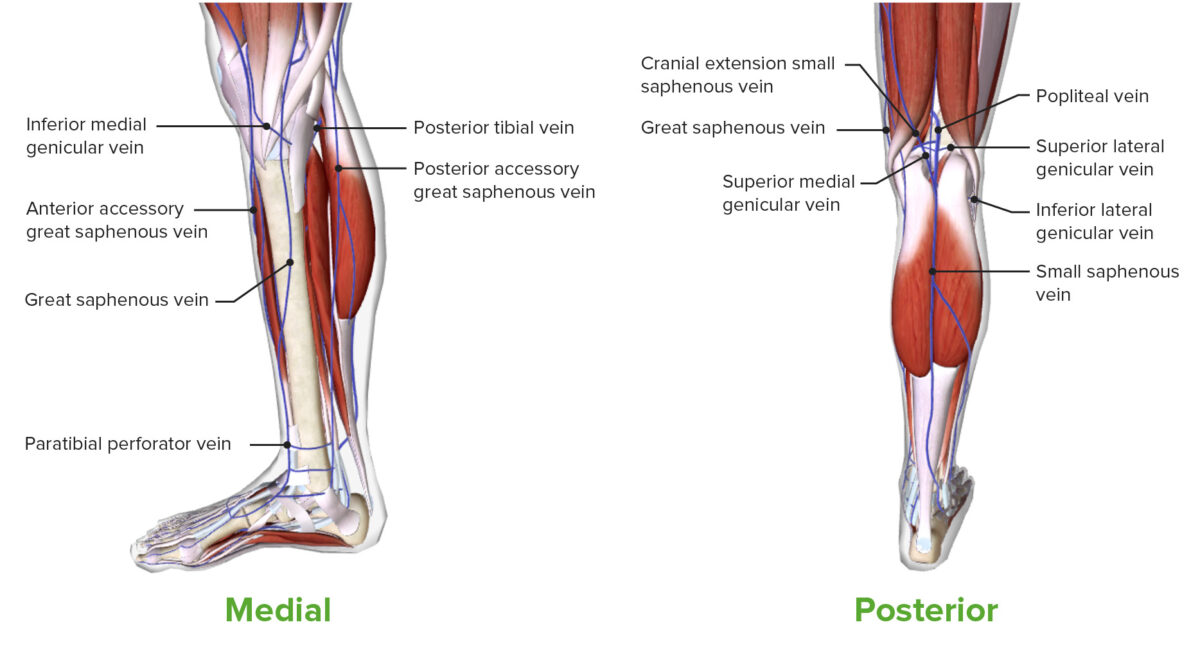
Vistas medial y posterior de la pierna, mostrando el drenaje venoso superficial
Imagen por BioDigital, editado por LecturioVenas profundas de la pierna:
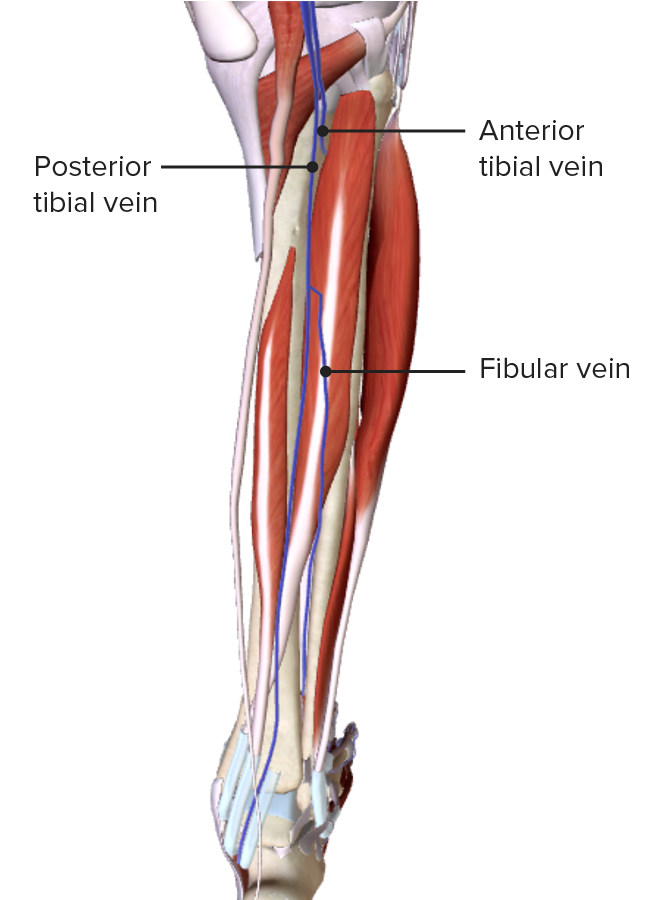
Vista posterior de la pierna, mostrando el drenaje venoso profundo
Imagen por BioDigital, editado por LecturioLa inervación sensorial y motora de la extremidad inferior procede del plexo lumbosacro (L1-S4).
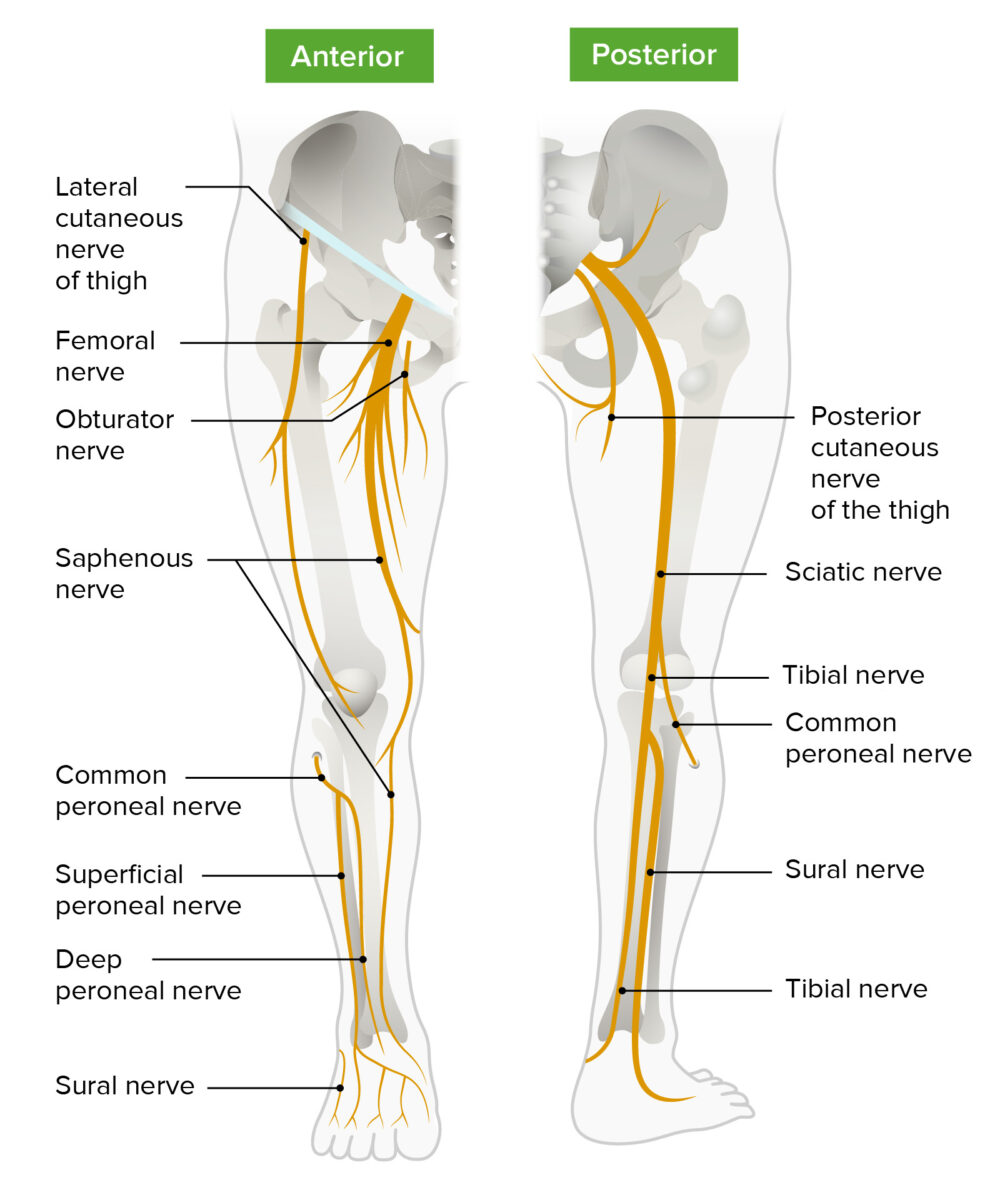
Diagrama esquemático del trayecto y las principales ramas del plexo lumbosacro que inervan los miembros inferiores
Imagen por Lecturio.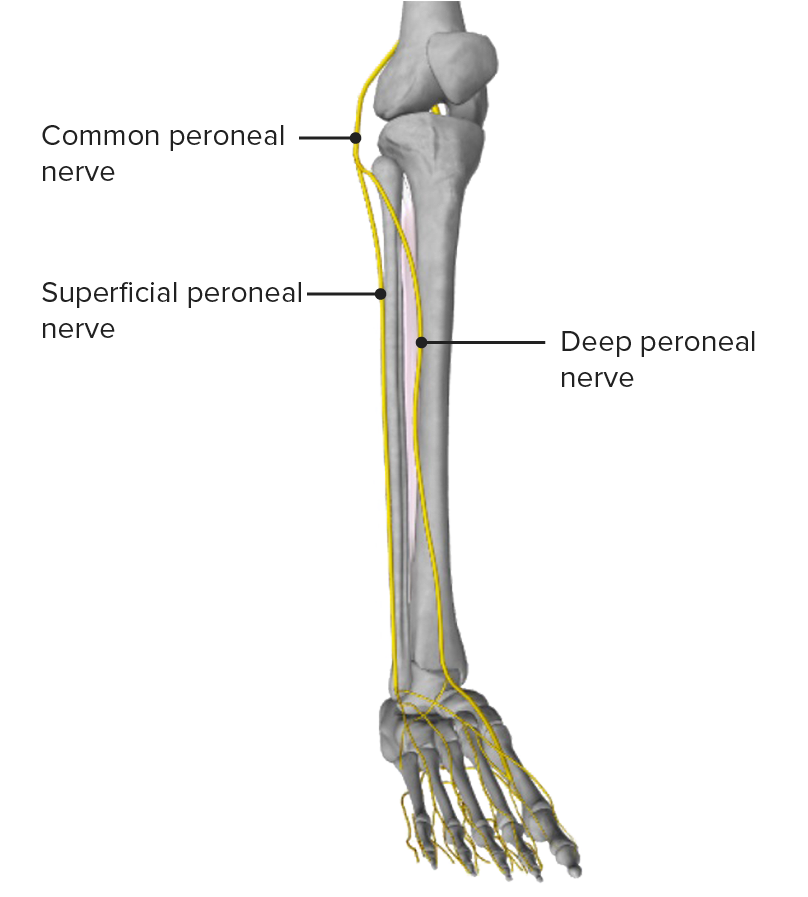
Vista anterior de la pierna, mostrando el nervio peroneo común y sus principales ramas
Imagen por BioDigital, editado por Lecturio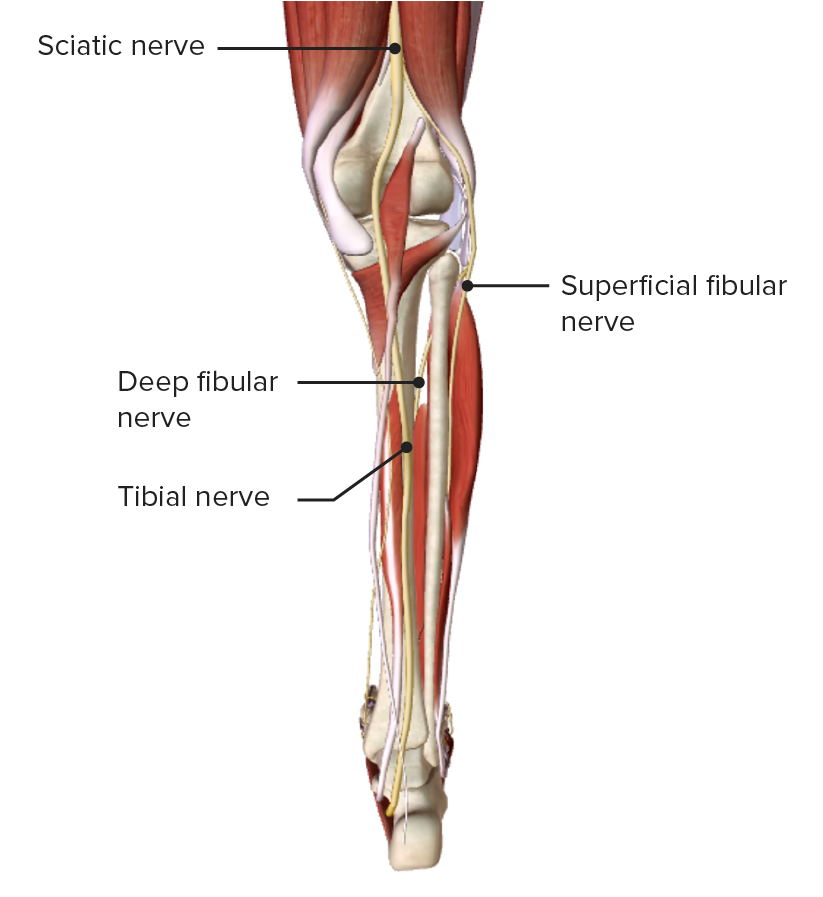
Vista posterior de la pierna, mostrando el nervio tibial a su paso por la cara medial de la fosa poplítea
Imagen por BioDigital, editado por Lecturio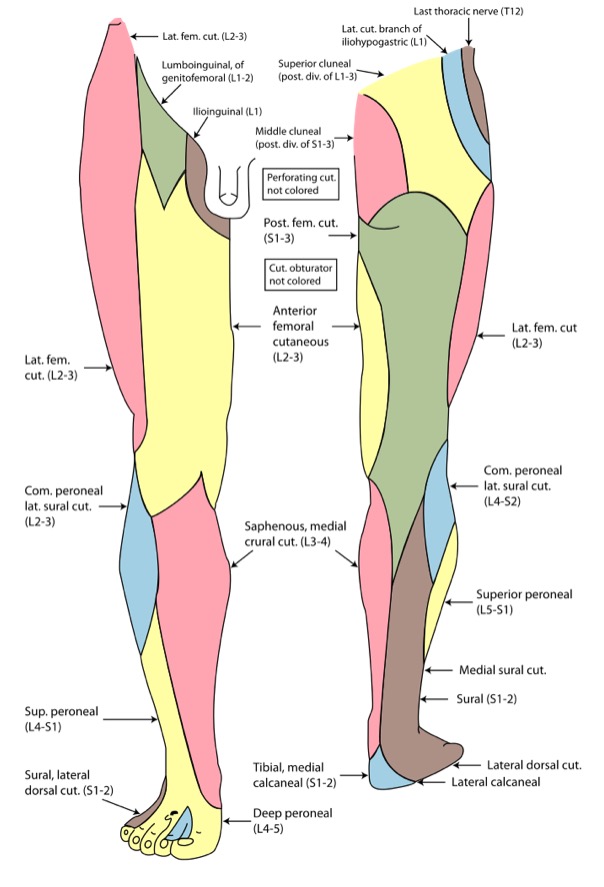
Inervación cutánea del miembro inferior
Imagen: “Gray826and831” por Henry Vandyke Carter. Licencia: Dominio PúblicoLos LOS Neisseria siguientes son trastornos comunes asociados a la parte inferior de la pierna: