El páncreas es un órgano compuesto que contiene una combinación distintiva de linajes celulares. El tejido exocrino comprende células acinares, que secretan enzimas digestivas en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el intestino. La función endocrina la realizan los LOS Neisseria islotes de Langerhans, que consisten en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum distintos tipos de células que secretan 4 hormonas diferentes a la circulación (células α, glucagón; células β, insulina; células δ, somatostatina; y células γ, polipéptido pancreático). Las hormonas endocrinas, así como algunas enzimas exocrinas, se pueden medir en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria fluidos corporales y proporcionan información diagnóstica importante en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la enfermedad pancreática aguda y crónica.
Last updated: Jan 11, 2024
El páncreas es un órgano ubicado en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la parte posterior del abdomen, detrás del estómago y tiene 2 funciones principales:
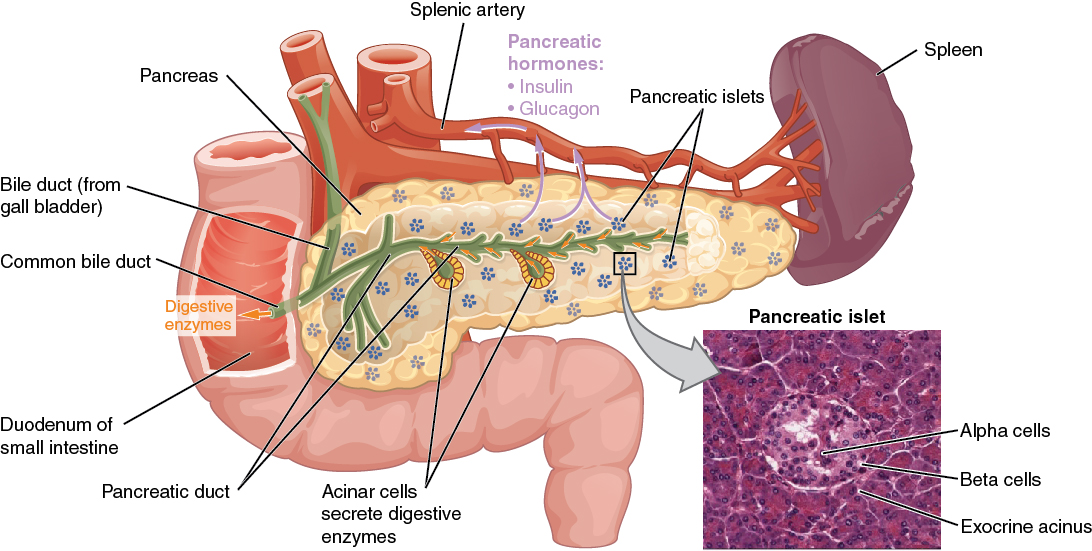
El páncreas
Imagen: “The pancreas” por CDC. Licencia: CC BY 3.0Los LOS Neisseria islotes de Langerhans, dispersos por todo el páncreas, tienen diferentes tipos de células, que corresponden a las siguientes hormonas:
Las funciones y los LOS Neisseria estímulos difieren para cada hormona.
| Parámetro | Pruebas asociadas | Condiciones |
|---|---|---|
| Insulina |
|
Aumentados
en
EN
Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins.
Erythema Nodosum:
|
| Somatostatina | Somatostatina plasmática | Aumentada
en
EN
Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins.
Erythema Nodosum:
|
| Glucagón | Glucagón plasmático | Aumentado
en
EN
Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins.
Erythema Nodosum:
|
| Polipéptido pancreático | Polipéptido pancreático plasmático | Aumentado
en
EN
Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins.
Erythema Nodosum:
|
| Amilasa pancreática | Amilasa sérica/plasmática | Aumentada
en
EN
Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins.
Erythema Nodosum:
|
| Lipasa pancreática | Lipasa sérica | Aumentada
en
EN
Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins.
Erythema Nodosum:
|
| Elastasa pancreatic | Elastasa-1 (heces) | Aumentada
en
EN
Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins.
Erythema Nodosum:
pancreatitis
Pancreatitis
Inflammation of the pancreas. Pancreatitis is classified as acute unless there are computed tomographic or endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatographic findings of chronic pancreatitis. The two most common forms of acute pancreatitis are alcoholic pancreatitis and gallstone pancreatitis.
Acute Pancreatitis aguda Disminuida en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum:
|
| Tripsinógeno | Tripsinógeno sérico | Aumentado en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum: pancreatitis Pancreatitis Inflammation of the pancreas. Pancreatitis is classified as acute unless there are computed tomographic or endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatographic findings of chronic pancreatitis. The two most common forms of acute pancreatitis are alcoholic pancreatitis and gallstone pancreatitis. Acute Pancreatitis aguda |
| Quimiotripsina | Quimiotripsina (heces) | Insuficiencia pancreática: prueba negativa |