El raquitismo y la osteomalacia Osteomalacia Disorder caused by an interruption of the mineralization of organic bone matrix leading to bone softening, bone pain, and weakness. It is the adult form of rickets resulting from disruption of vitamin d; phosphorus; or calcium homeostasis. Osteomalacia and Rickets son trastornos de la disminución de la mineralización ósea. El raquitismo afecta al AL Amyloidosis tejido cartilaginoso de los LOS Neisseria cartílagos de crecimiento epifisarios en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria niños, mientras que la osteomalacia Osteomalacia Disorder caused by an interruption of the mineralization of organic bone matrix leading to bone softening, bone pain, and weakness. It is the adult form of rickets resulting from disruption of vitamin d; phosphorus; or calcium homeostasis. Osteomalacia and Rickets afecta a los LOS Neisseria lugares de recambio óseo en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum niños y adultos. Aunque la mayoría de los LOS Neisseria casos de raquitismo y osteomalacia Osteomalacia Disorder caused by an interruption of the mineralization of organic bone matrix leading to bone softening, bone pain, and weakness. It is the adult form of rickets resulting from disruption of vitamin d; phosphorus; or calcium homeostasis. Osteomalacia and Rickets se deben a la deficiencia de vitamina D, otros trastornos genéticos y nutricionales, así como los LOS Neisseria medicamentos, pueden causar este tipo de trastornos. El raquitismo suele presentarse con deformidades esqueléticas y anomalías del crecimiento, mientras que la osteomalacia Osteomalacia Disorder caused by an interruption of the mineralization of organic bone matrix leading to bone softening, bone pain, and weakness. It is the adult form of rickets resulting from disruption of vitamin d; phosphorus; or calcium homeostasis. Osteomalacia and Rickets puede presentarse con dolor Dolor Inflammation óseo, dificultad para caminar y fracturas patológicas. El diagnóstico se realiza basándose en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum una combinación de hallazgos clínicos, estudios de laboratorio e imagen. El tratamiento incluye la administración de suplementos de vitamina D, calcio y fósforo.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
El raquitismo y la osteomalacia Osteomalacia Disorder caused by an interruption of the mineralization of organic bone matrix leading to bone softening, bone pain, and weakness. It is the adult form of rickets resulting from disruption of vitamin d; phosphorus; or calcium homeostasis. Osteomalacia and Rickets son trastornos de la disminución de la mineralización ósea. El raquitismo afecta al AL Amyloidosis tejido cartilaginoso de los LOS Neisseria cartílagos del crecimiento epifisarios en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria niños, mientras que la osteomalacia Osteomalacia Disorder caused by an interruption of the mineralization of organic bone matrix leading to bone softening, bone pain, and weakness. It is the adult form of rickets resulting from disruption of vitamin d; phosphorus; or calcium homeostasis. Osteomalacia and Rickets afecta a los LOS Neisseria lugares de recambio óseo en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum niños y adultos.
Raquitismo:
Osteomalacia Osteomalacia Disorder caused by an interruption of the mineralization of organic bone matrix leading to bone softening, bone pain, and weakness. It is the adult form of rickets resulting from disruption of vitamin d; phosphorus; or calcium homeostasis. Osteomalacia and Rickets:
El raquitismo y la osteomalacia Osteomalacia Disorder caused by an interruption of the mineralization of organic bone matrix leading to bone softening, bone pain, and weakness. It is the adult form of rickets resulting from disruption of vitamin d; phosphorus; or calcium homeostasis. Osteomalacia and Rickets pueden estar causados por deficiencias de vitamina D, calcio o fósforo. Estas afecciones pueden ser causadas por anomalías en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la deposición de la matriz ósea.
Relacionadas con la vitamina D (más comunes):
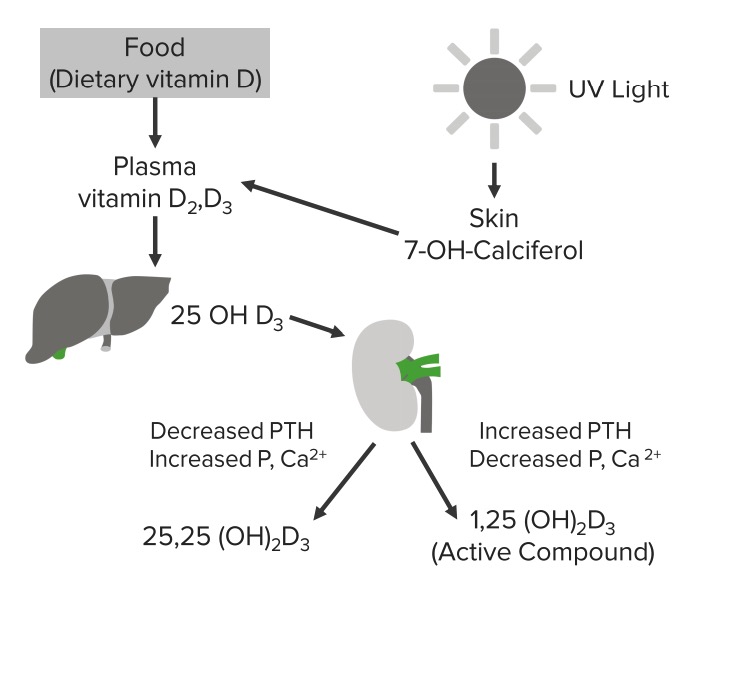
Diagrama esquemático del ciclo de la vitamina D
Imagen por Lecturio.Relacionados con la hipofosfatemia:
Inhibidores de la mineralización:
Misceláneos:
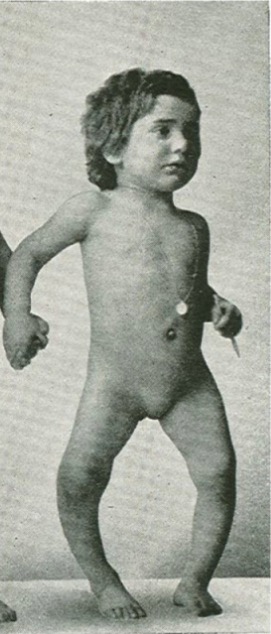
El niño con raquitismo presenta el arqueo característico de los huesos largos de las extremidades inferiores (Genu varum).
Imagen: “Sister” por Vitamin D, Skin and Bone Research Laboratory, Section of Endocrinology, Nutrition, and Diabetes, Department of Medicine, Boston University Medical Center, 85 East Newton Street, M-1013, Boston, MA 02118, USA. Licencia: CC BY 3.0, recortada por Lecturio.
Deformación en genu valgum en raquitismo
Imagen: “Showing genu valgum” por Department of Pedodontics and Preventive Dentistry, Sharad Pawar Dental College, Sawangi (M), Mahartashtra State, Wardha 442102, India. Licencia: CC BY 4.0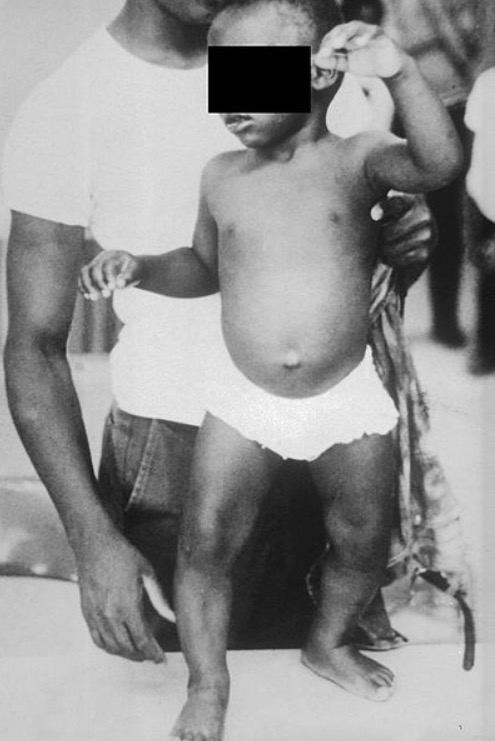
Raquitismo:
Observe las piernas arqueadas y la muñeca derecha ensanchada. El raquitismo nutricional es una enfermedad en la que los huesos de los niños son demasiado blandos y no se desarrollan correctamente debido a una deficiencia de vitamina D.
Historia clínica:
Examen físico: Deformidades esqueléticas típicas del raquitismo
Estudios de laboratorio:
Imágenes de rayos X:
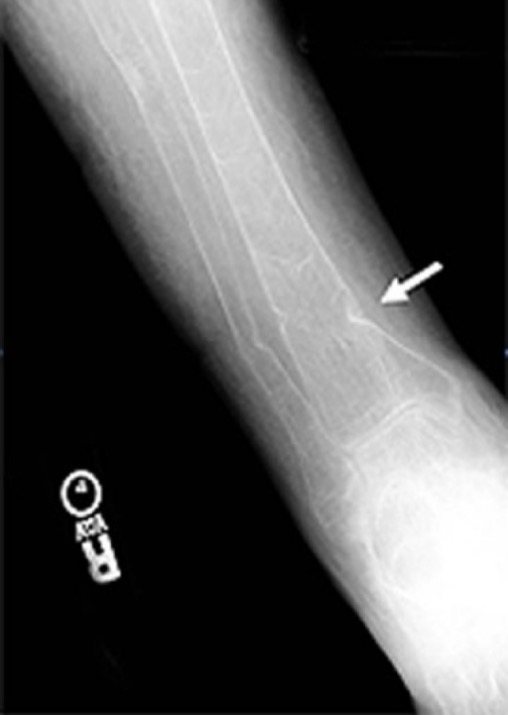
Radiografía de la tibia y el peroné derechos de un paciente con osteomalacia:
Obsérvense las múltiples pseudofracturas y la fractura de Colles de la tibia (flecha).
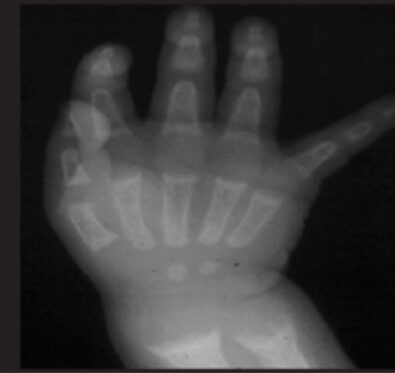
La radiografía de la muñeca de un niño con raquitismo muestra un hueco metafisario.
Imagen: “Radiological appearance” por Atatürk University, Faculty of Medicine, Department of Pediatric Endocrinology, Erzurum, Turkey. Licencia: CC BY 2.5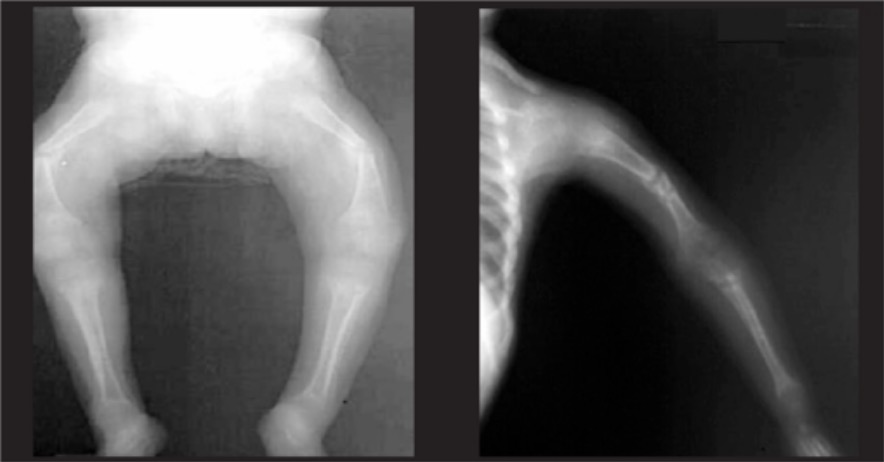
La radiografía anteroposterior de las extremidades de un niño con raquitismo muestra el arqueamiento de los huesos largos.
Imagen: “Radiological findings in nutritional rickets (NR)” por Atatürk University, Faculty of Medicine, Department of Pediatric Endocrinology, Erzurum, Turkey. Licencia: CC BY 2.5