El neurinoma del acústico, también denominado schwannoma Schwannoma Schwannomas (also known as neurilemmomas) are benign nerve sheath tumors in the peripheral nervous system (PNS), arising from Schwann cells that encase the peripheral nerves. Schwannomas are the most common tumors in the PNS. Schwannoma vestibular, es un tumor Tumor Inflammation benigno que surge de las células de Schwann del componente vestibular del nervio craneal VIII. El neurinoma del acústico se forma dentro del meato auditivo interno y se extiende hasta el ángulo pontocerebeloso. El schwannoma Schwannoma Schwannomas (also known as neurilemmomas) are benign nerve sheath tumors in the peripheral nervous system (PNS), arising from Schwann cells that encase the peripheral nerves. Schwannomas are the most common tumors in the PNS. Schwannoma vestibular es mayormente unilateral. Los LOS Neisseria schwannomas vestibulares bilaterales están asociados a la neurofibromatosis tipo II. Los LOS Neisseria síntomas surgen debido a la compresión de los LOS Neisseria nervios craneales V, VII, VIII y del cerebelo. La queja más común es la pérdida de audición unilateral, pero el neurinoma del acústico también puede presentarse con vértigo, disminución de la sensibilidad facial, parálisis de Bell y ataxia Ataxia Impairment of the ability to perform smoothly coordinated voluntary movements. This condition may affect the limbs, trunk, eyes, pharynx, larynx, and other structures. Ataxia may result from impaired sensory or motor function. Sensory ataxia may result from posterior column injury or peripheral nerve diseases. Motor ataxia may be associated with cerebellar diseases; cerebral cortex diseases; thalamic diseases; basal ganglia diseases; injury to the red nucleus; and other conditions. Ataxia-telangiectasia. El diagnóstico del schwannoma Schwannoma Schwannomas (also known as neurilemmomas) are benign nerve sheath tumors in the peripheral nervous system (PNS), arising from Schwann cells that encase the peripheral nerves. Schwannomas are the most common tumors in the PNS. Schwannoma vestibular se realiza mediante una RM del cerebro con contraste. El tratamiento depende del tamaño del tumor Tumor Inflammation y de la gravedad de los LOS Neisseria síntomas. Los LOS Neisseria tumores grandes con pérdida de audición grave se tratan con escisión quirúrgica o radioterapia, mientras que los LOS Neisseria tumores pequeños con síntomas leves pueden mantenerse en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum observación con el tiempo.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
El neurinoma del acústico es un tumor Tumor Inflammation benigno de las células de Schwann que se encuentra con mayor frecuencia en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el nervio craneal VIII (nervio vestibulococlear).
| Categorías | Tumores específicos |
|---|---|
| Tumores neuroepiteliales en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el SNC |
|
| Tumores meníngeos |
|
| Tumores de la región selar |
|
| Linfoma primario del SNC | Linfoma primario del SNC |
| Metástasis al AL Amyloidosis cerebro (5 veces más común que los LOS Neisseria tumores cerebrales primarios) | Más comúnmente surgen de: |
| Tumores periféricos |
|
Los LOS Neisseria síntomas del neurinoma del acústico se divide en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum fase inicial y tardía.
Expansión tumoral en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el meato auditivo interno que ejerce presión sobre el nervio vestibulococlear (NC VIII):
Compresión de estructuras adyacentes en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el ángulo pontocerebeloso:
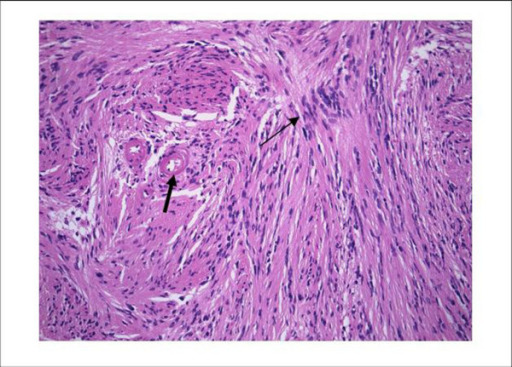
Schwannoma
histología:
Vista de bajo poder del
schwannoma
ilustrando el empalizamiento nuclear (flecha fina) y las paredes vasculares hialinas (flecha gruesa). Tinción H&E ×300
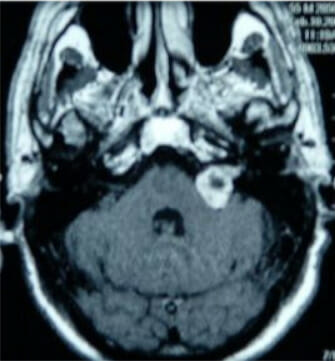
RM con contraste de gadolinio que muestra un neuroma acústico del ángulo pontocerebeloso izquierdo
Imagen: “Figure 1” por Sean P Collins et al. Licencia: CC BY 2.0Monitorización en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum serie: