Mycoplasma Mycoplasma Mycoplasma is a species of pleomorphic bacteria that lack a cell wall, which makes them difficult to target with conventional antibiotics and causes them to not gram stain well. Mycoplasma bacteria commonly target the respiratory and urogenital epithelium. Mycoplasma pneumoniae (M. pneumoniae), the causative agent of atypical or "walking" pneumonia. Mycoplasma es una especie de bacteria Bacteria Bacteria are prokaryotic single-celled microorganisms that are metabolically active and divide by binary fission. Some of these organisms play a significant role in the pathogenesis of diseases. Bacteriology pleomórfica que carece de pared celular, lo que hace HACE Altitude Sickness que sean difíciles de tratar con antibióticos convencionales ( en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum particular, las penicilinas y otros antibióticos betalactámicos que afectan la síntesis de la pared celular) y hace HACE Altitude Sickness que no se tiñan bien con tinción de Gram. Las bacterias Mycoplasma Mycoplasma Mycoplasma is a species of pleomorphic bacteria that lack a cell wall, which makes them difficult to target with conventional antibiotics and causes them to not gram stain well. Mycoplasma bacteria commonly target the respiratory and urogenital epithelium. Mycoplasma pneumoniae (M. pneumoniae), the causative agent of atypical or "walking" pneumonia. Mycoplasma comúnmente afectan el epitelio respiratorio y urogenital. Mycoplasma pneumoniae Mycoplasma pneumoniae Short filamentous organism of the genus mycoplasma, which binds firmly to the cells of the respiratory epithelium. It is one of the etiologic agents of non-viral primary atypical pneumonia in man. Mycoplasma (M. pneumoniae), el agente causal de la neumonía atípica o “errante”, es la especie clínicamente más relevante. Los LOS Neisseria antibióticos, particularmente los LOS Neisseria macrólidos, son el método de terapia más eficaz.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
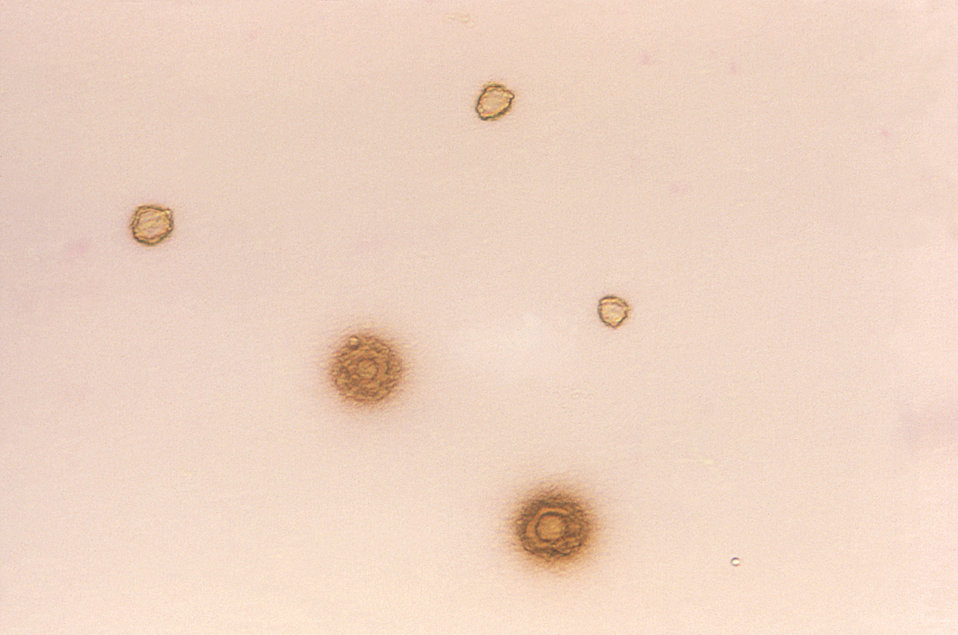
Aspecto de “huevo frito” de las colonias de Mycoplasma hominis
Imagen: “Gram-negative Mycoplasma hominis” por CDC/ Dr. E. Arum. Licencia: Dominio Público.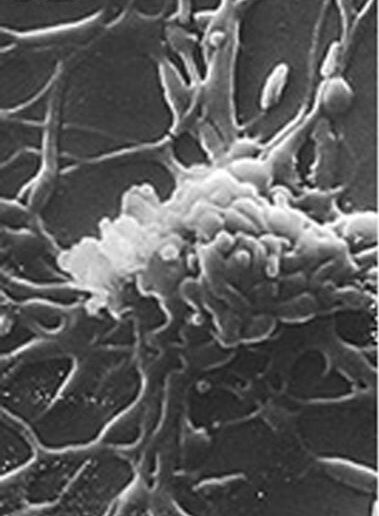
Imagen de microscopio electrónico de barrido de M. pneumoniae, una bacteria pleomórfica que carece de pared celular, vista aquí en su forma filamentosa
Imagen: “Mycoplasma pneumoniae” por Rottem et al. Licencia: CC BY 3.0, editada por Lecturio.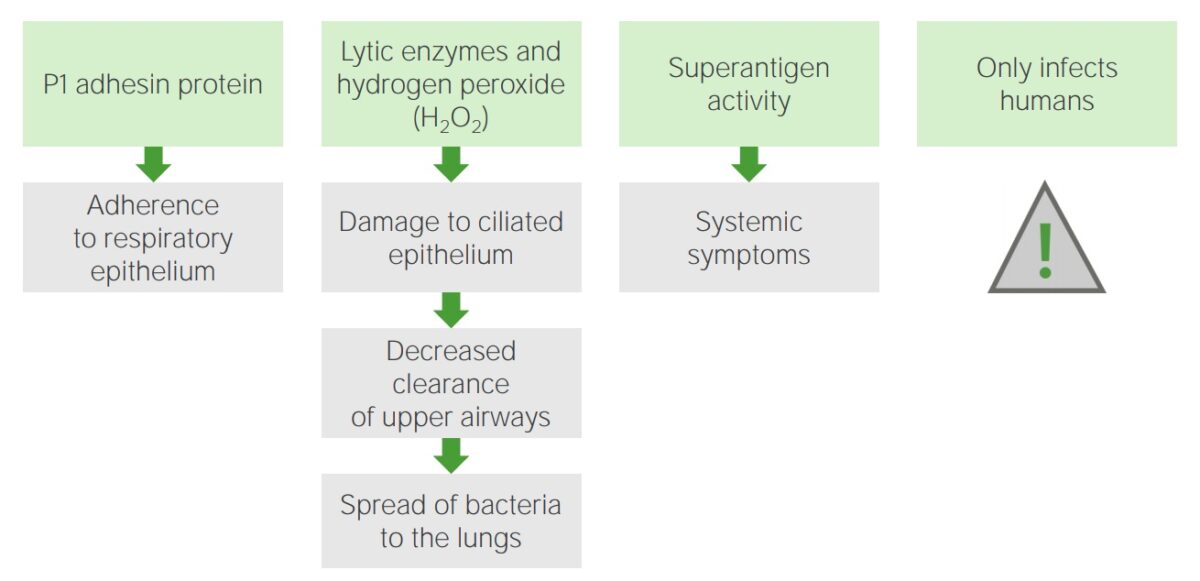
Mecanismos de patogénesis: Mycoplasma pneumoniae
Imagen por Lecturio. Licencia: CC BY-NC-SA 4.0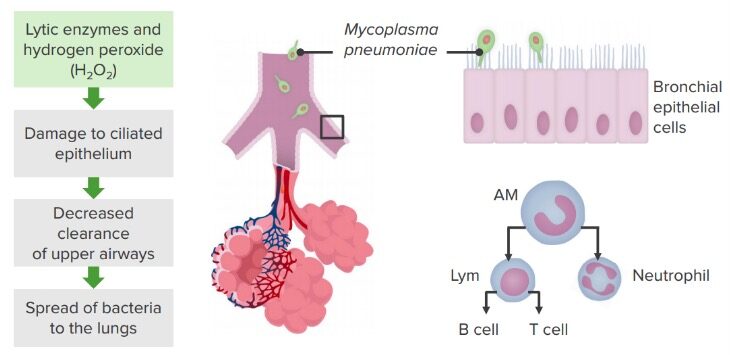
Mecanismos de patogénesis: Mycoplasma pneumoniae
Imagen por Lecturio. Licencia: CC BY-NC-SA 4.0La patología causada por la bacteria Bacteria Bacteria are prokaryotic single-celled microorganisms that are metabolically active and divide by binary fission. Some of these organisms play a significant role in the pathogenesis of diseases. Bacteriology M. pneumoniae es variada; sin embargo, el diagnóstico y el tratamiento son estándar:
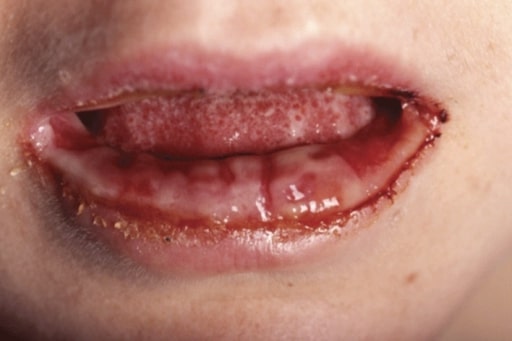
Mucositis asociada a M. pneumoniae: las lesiones orales erosivas se limitan a la mucosa en esta forma de mucositis asociada a M. pneumoniae en una mujer de 24 años.
Imagen: “MPAM” por Department of Pediatrics, Division of Pediatric Infectious Diseases and Immunology, Erasmus MC-Sophia Children’s Hospital, University Medical Center Rotterdam, Netherlands. Licencia: CC BY 4.0.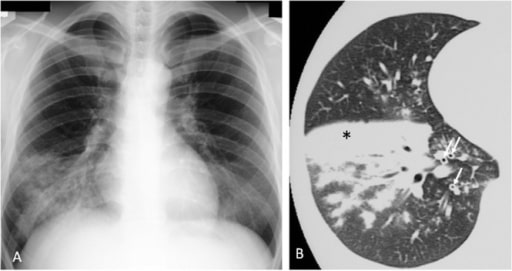
Neumonía por Mycoplasma pneumoniae en un humano. A: La radiografía de tórax muestra infiltrados en el lóbulo inferior derecho.
B: consolidación (∗) y engrosamiento de haces broncovasculares (↑) en la tomografía computarizada (TC)
| Características | Neumonía por Mycoplasma Mycoplasma Mycoplasma is a species of pleomorphic bacteria that lack a cell wall, which makes them difficult to target with conventional antibiotics and causes them to not gram stain well. Mycoplasma bacteria commonly target the respiratory and urogenital epithelium. Mycoplasma pneumoniae (M. pneumoniae), the causative agent of atypical or “walking” pneumonia. Mycoplasma | Neumonía neumocócica |
|---|---|---|
| Tipo de neumonía | Atípica (intersticial) | Típica (alveolar) |
| Faringitis precedente | Común | Nunca |
| Inicio | Gradual | Repentino con escalofríos |
| Fiebre | Baja | Alta |
| Tos TOS Thoracic outlet syndrome (TOS) is a broad term used for a spectrum of syndromes related to the general region of the thoracic outlet, which involves the compression or irritation of elements of the brachial plexus, subclavian artery, or subclavian vein. Thoracic Outlet Syndrome | No productiva, paroxística | Productiva |
| Dolor Dolor Inflammation torácico pleurítico | Ausente | Presente |
| Leucocitosis | Ausente | Presente |
| Edad de mayor incidencia | Adultos jóvenes < 30 años | Adultos mayores |
| Complicaciones | Otitis media, eritema multiforme, anemia Anemia Anemia is a condition in which individuals have low Hb levels, which can arise from various causes. Anemia is accompanied by a reduced number of RBCs and may manifest with fatigue, shortness of breath, pallor, and weakness. Subtypes are classified by the size of RBCs, chronicity, and etiology. Anemia: Overview and Types hemolítica, miocarditis, pericarditis Pericarditis Pericarditis is an inflammation of the pericardium, often with fluid accumulation. It can be caused by infection (often viral), myocardial infarction, drugs, malignancies, metabolic disorders, autoimmune disorders, or trauma. Acute, subacute, and chronic forms exist. Pericarditis, miringitis ampollosa | Bacteriemia, meningitis Meningitis Meningitis is inflammation of the meninges, the protective membranes of the brain, and spinal cord. The causes of meningitis are varied, with the most common being bacterial or viral infection. The classic presentation of meningitis is a triad of fever, altered mental status, and nuchal rigidity. Meningitis, otitis media |