La mpox (antes conocida como viruela símica) es una enfermedad zoonótica viral causada por el virus Virus Viruses are infectious, obligate intracellular parasites composed of a nucleic acid core surrounded by a protein capsid. Viruses can be either naked (non-enveloped) or enveloped. The classification of viruses is complex and based on many factors, including type and structure of the nucleoid and capsid, the presence of an envelope, the replication cycle, and the host range. Virology mpox de la familia Poxviridae Poxviridae A family of double-stranded DNA viruses infecting mammals (including humans), birds and insects. There are two subfamilies: chordopoxvirinae, poxviruses of vertebrates, and entomopoxvirinae, poxviruses of insects. Orthopoxvirus. La transmisión puede ser de animal a humano (por mordedura de animal o por contacto directo con fluidos corporales) o de humano a humano (por contacto estrecho con lesiones cutáneas, secreciones respiratorias u objetos contaminados). La presentación clínica es similar a la del virus Virus Viruses are infectious, obligate intracellular parasites composed of a nucleic acid core surrounded by a protein capsid. Viruses can be either naked (non-enveloped) or enveloped. The classification of viruses is complex and based on many factors, including type and structure of the nucleoid and capsid, the presence of an envelope, the replication cycle, and the host range. Virology de la viruela, que incluye síntomas prodrómicos como fiebre, cefalea, mialgia y linfadenopatía. La erupción comienza unos 5 días después del inicio de los LOS Neisseria síntomas; suele presentarse en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum forma de máculas y más tarde evoluciona a pápulas, vesículas y pústulas. Estas lesiones se secan (costras) y se caen. El método de diagnóstico preferido es la reacción en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum cadena de la polimerasa en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum muestras clínicas (lesiones cutáneas). La enfermedad suele ser autolimitada y dura entre 2-4 semanas. Por lo general, se brinda tratamiento de soporte. Los LOS Neisseria agentes antivirales, como el tecovirimat Tecovirimat Orthopoxvirus, pueden administrarse a pacientes con enfermedad severa o en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum riesgo de padecerla.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
La mpox (antes conocida como viruela símica) es una enfermedad zoonótica viral causada por el virus Virus Viruses are infectious, obligate intracellular parasites composed of a nucleic acid core surrounded by a protein capsid. Viruses can be either naked (non-enveloped) or enveloped. The classification of viruses is complex and based on many factors, including type and structure of the nucleoid and capsid, the presence of an envelope, the replication cycle, and the host range. Virology mpox. La mpox tiene un perfil clínico similar al AL Amyloidosis de la viruela, pero es menos mortal.

Imagen de microscopía electrónica de transmisión de un virión mpox:
Esta imagen de tinción negativa muestra una única partícula en forma de ladrillo cubierta de filamentos espiralados.
Los LOS Neisseria síntomas que aparecen durante este periodo pueden incluir:
El curso de la enfermedad es seguido por el desarrollo de una erupción con las siguientes características:
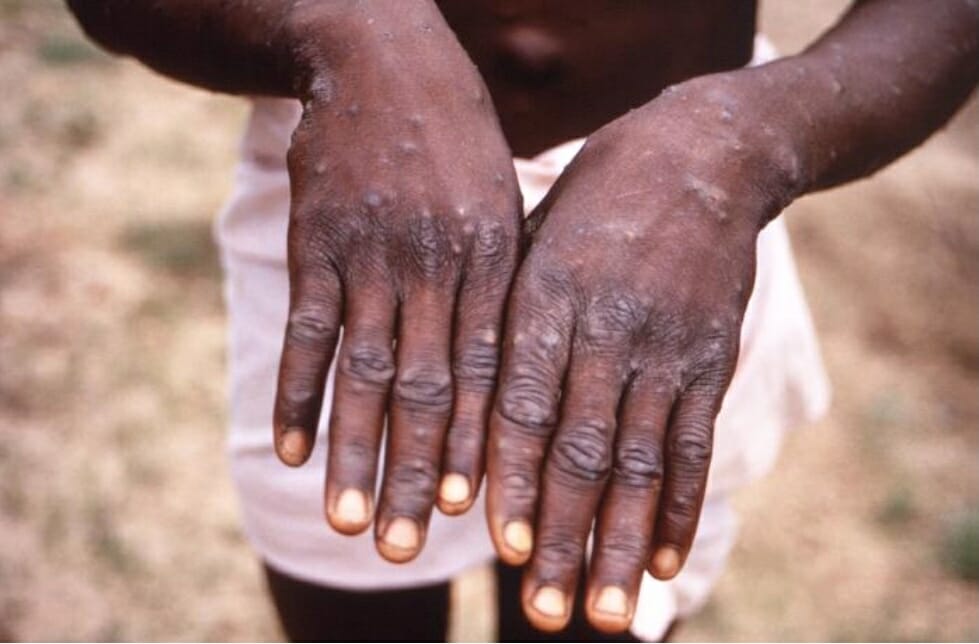
Lesiones en las superficies dorsales de las manos de un individuo con mpox.
Imagen: “12763” por CDC/Brian W.J. Mahy, BSc, MA, PhD, ScD, DSc. Licencia: CC0 1.0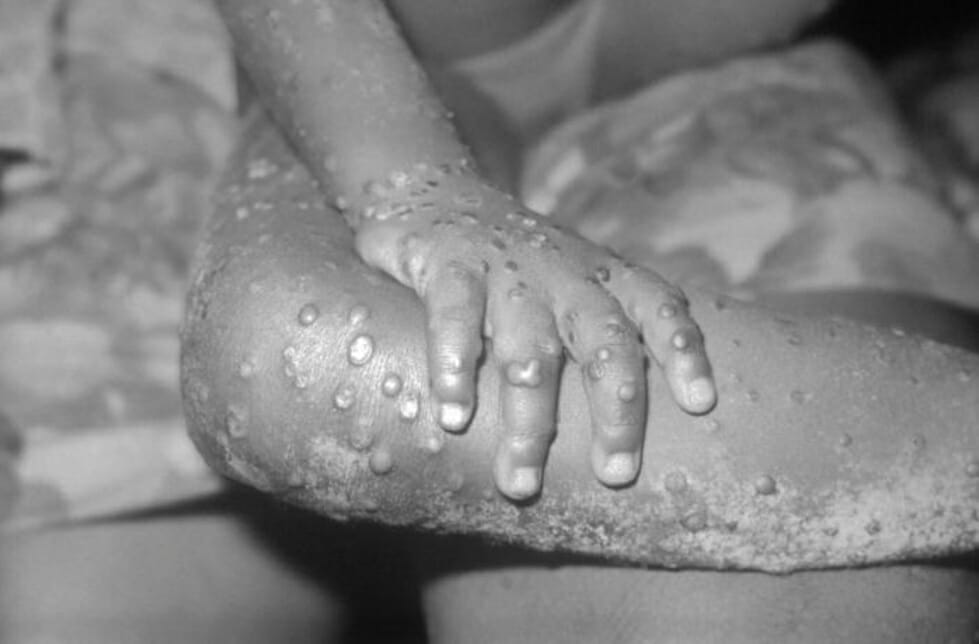
Numerosas lesiones maculopapulares de mpox en un joven
Imagen: “2329” por CDC. Licencia: CC0 1.0Otros hallazgos en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el brote de 2022 incluyen:
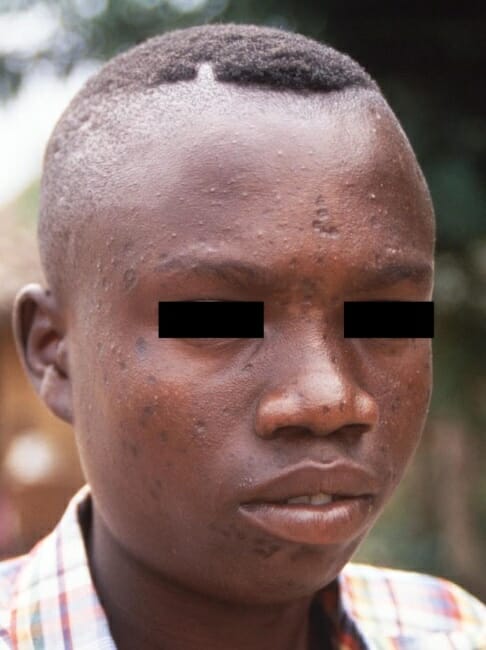
La cara de un joven que se recuperó de un caso de mpox y llevaba cicatrices permanentes de marcas de viruela.
Imagen: “12777” por CDC/Brian W.J. Mahy, BSc, MA, PhD, ScD, DSc. Licencia: CC0 1.0Los LOS Neisseria clínicos deben sospechar mpox en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria casos con factores clínicos y epidemiológicos:
Principios de tratamiento:
Considerar tratamiento antiviral Antiviral Antivirals for Hepatitis B para:
Tratamientos disponibles:
Prevención:
Aislamiento:
Después de la recuperación:
Toda persona en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum contacto o que haya atendido a pacientes con mpox debe vigilarse para detectar síntomas:
Las vacunas desarrolladas contra la viruela también pueden utilizarse contra la mpox.
Referencias