La mielofibrosis primaria (MFP) es una neoplasia mieloproliferativa caracterizada por mieloproliferación crónica con depósito fibroblástico no clonal, lo que resulta en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum fibrosis Fibrosis Any pathological condition where fibrous connective tissue invades any organ, usually as a consequence of inflammation or other injury. Bronchiolitis Obliterans de la médula ósea. La anomalía proviene de mutaciones genéticas de las células madre hematopoyéticas (que suelen implicar las mutaciones impulsoras JAK2, CALR o MPL). Los LOS Neisseria síntomas primarios son anemia Anemia Anemia is a condition in which individuals have low Hb levels, which can arise from various causes. Anemia is accompanied by a reduced number of RBCs and may manifest with fatigue, shortness of breath, pallor, and weakness. Subtypes are classified by the size of RBCs, chronicity, and etiology. Anemia: Overview and Types y hematopoyesis extramedular, que incluyen fatiga severa, pérdida de peso y hepatoesplenomegalia. Los LOS Neisseria hallazgos de laboratorio incluyen anemia Anemia Anemia is a condition in which individuals have low Hb levels, which can arise from various causes. Anemia is accompanied by a reduced number of RBCs and may manifest with fatigue, shortness of breath, pallor, and weakness. Subtypes are classified by the size of RBCs, chronicity, and etiology. Anemia: Overview and Types (y otras citopenias), y la biopsia de médula ósea revela fibrosis Fibrosis Any pathological condition where fibrous connective tissue invades any organ, usually as a consequence of inflammation or other injury. Bronchiolitis Obliterans extensa. El tratamiento consiste en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum trasplante alogénico de células madre hematopoyéticas e intervenciones dirigidas a los LOS Neisseria síntomas.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
La mielofibrosis primaria (MFP) es una neoplasia mieloproliferativa crónica caracterizada por la proliferación de células mieloides, con proliferación de fibroblastos no clonales e hiperactividad, lo que resulta en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum una fibrosis Fibrosis Any pathological condition where fibrous connective tissue invades any organ, usually as a consequence of inflammation or other injury. Bronchiolitis Obliterans medular obliterante. Otros nombres incluyen mielofibrosis idiopática crónica y metaplasia Metaplasia A condition in which there is a change of one adult cell type to another similar adult cell type. Cellular Adaptation mieloide agnogénica.
La hematopoyesis comienza con la célula madre hematopoyética, quien es incitada a dividirse y diferenciarse por estímulos químicos apropiados (factores de crecimiento hematopoyético)
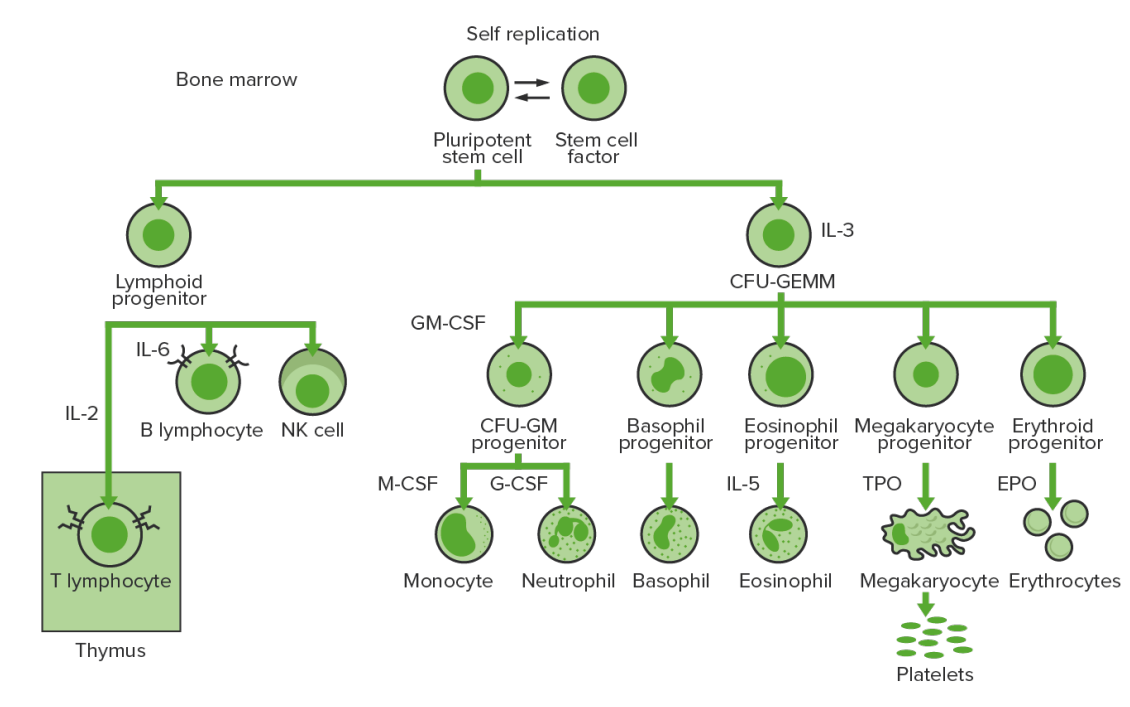
Hematopoyesis de la médula ósea: proliferación y diferenciación de los elementos formes de la sangre.
CFU-GEMM: unidad formadora de colonias de granulocitos, eritrocitos, monocitos y megacariocitos
CFU-GM: unidad formadora de colonias de granulocitos y macrófagos
GM-CSF: factor estimulante de colonias de granulocitos y macrófagos
M-CSF: factor estimulante de colonias de macrófagos
G-CSF: factor estimulante de colonias de granulocitos
NK: asesina natural
TPO: trombopoyetina
Las mutaciones en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria genes Genes A category of nucleic acid sequences that function as units of heredity and which code for the basic instructions for the development, reproduction, and maintenance of organisms. DNA Types and Structure asociados con la hematopoyesis se observan en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum una proporción significativa de casos de MFP.
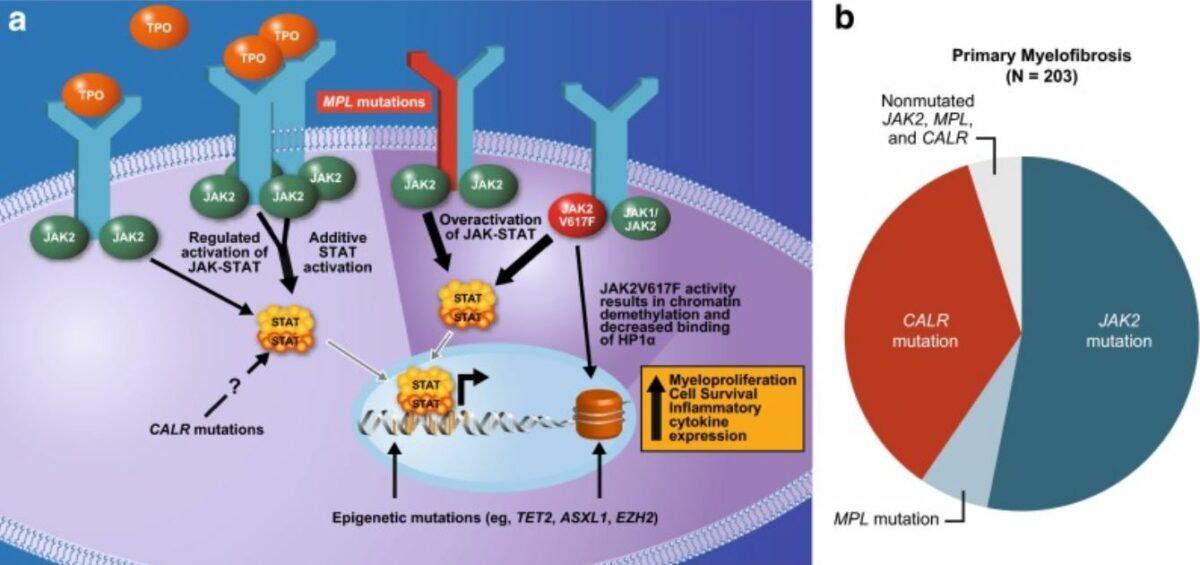
Mutaciones subyacentes a la fisiopatología de la mielofibrosis:
Comúnmente afecta la vía JAK-STAT
JAK2 (gen JAK2 implicado): tirosina quinasa no receptora que facilita que las señales extracelulares lleguen al núcleo y activen los genes.
MPL o receptor de trombopoyetina (gen MPL implicado): activación del receptor de trombopoyetina
La calreticulina (gen CALR implicado) es un regulador de STAT, y la mutación provoca la activación del receptor de trombopoyetina.
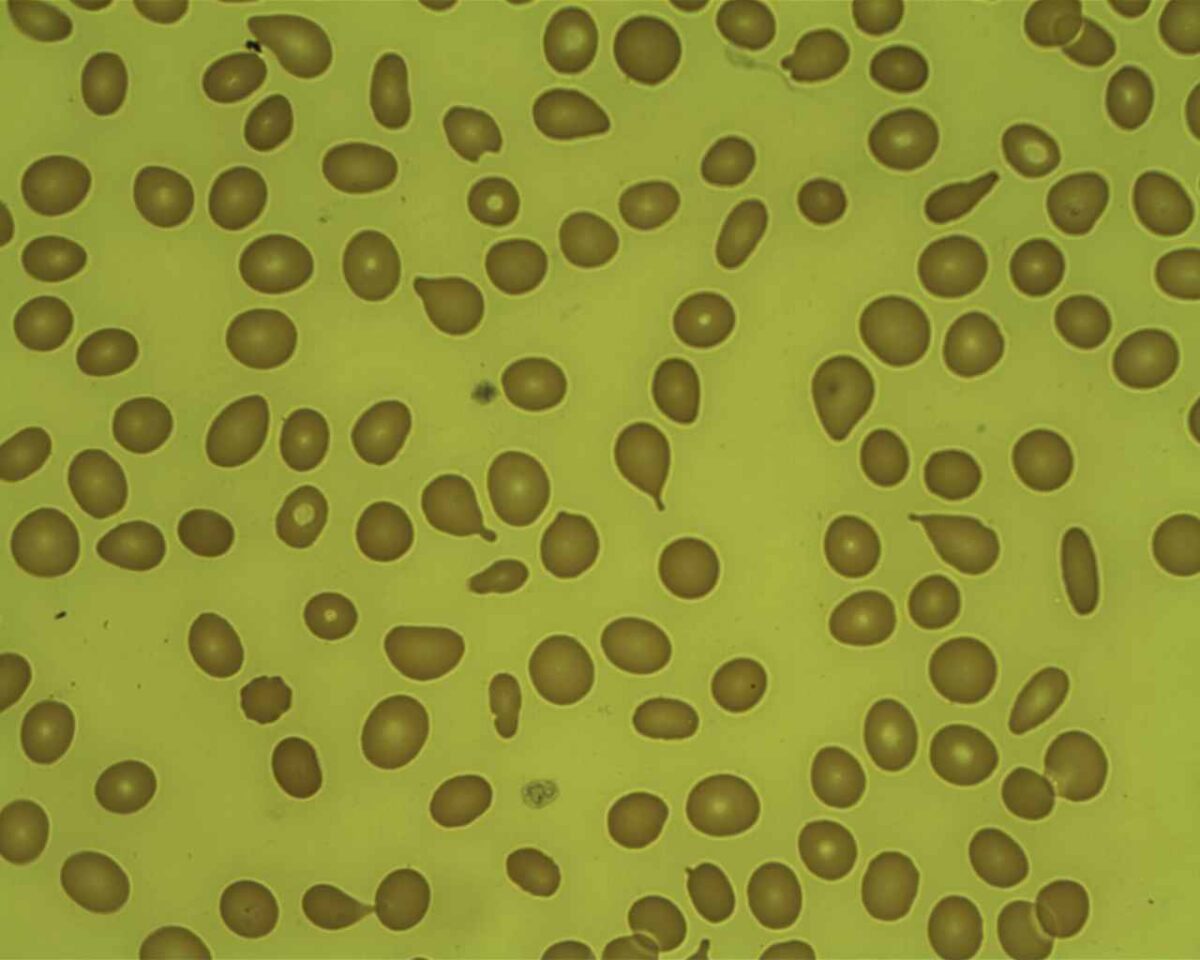
Mielofibrosis: células en forma de lágrima en frotis de sangre periférica
Imagen: “Poiquilocitos en forma de lágrima” por Prof. Osaro Erhabor. Licencia: CC0 1.0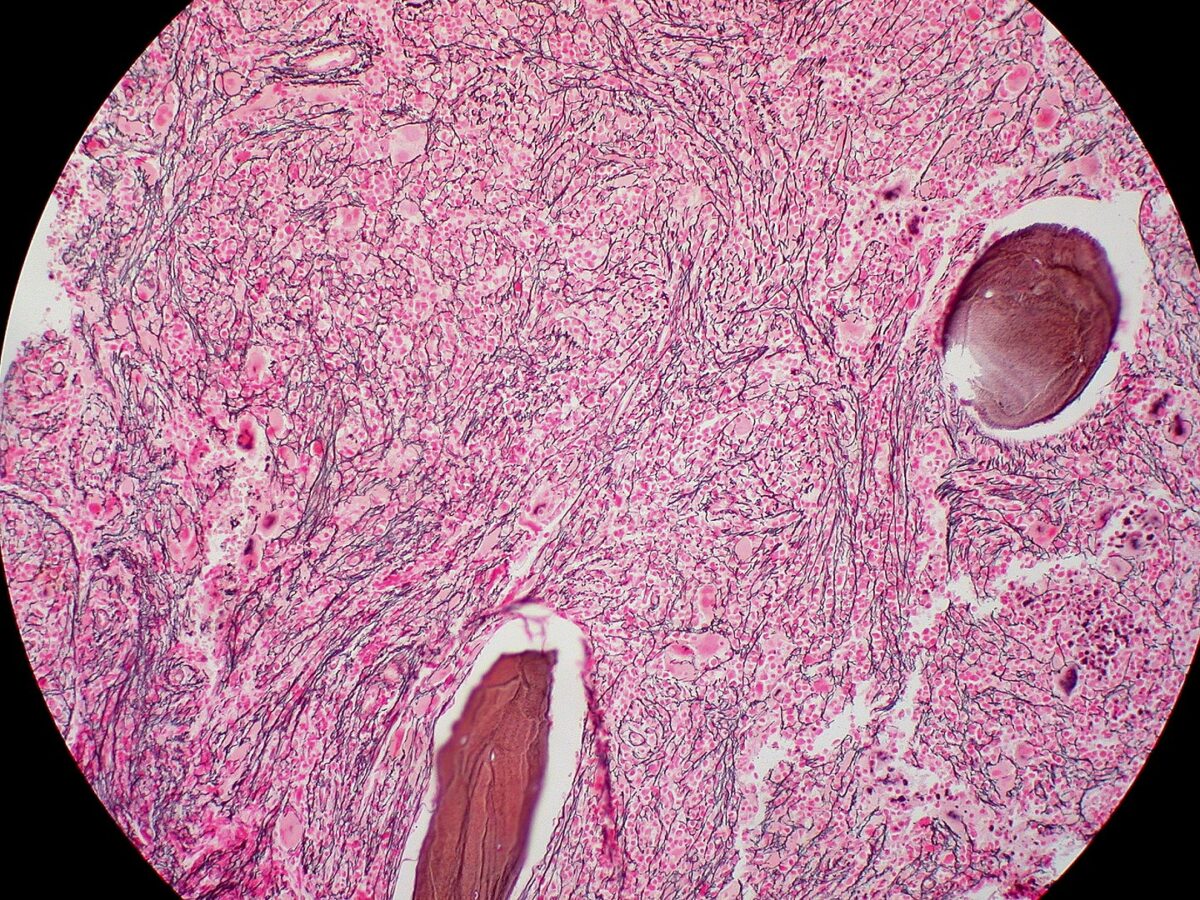
Biopsia de médula ósea de mielofibrosis: fibrosis extensa (tinción de reticulina)
Imagen: “Mielofibrosis, tinción de reticulina (6032644716)” por Ed Uthman. Licencia: CC BY 2.0Para recordar MFP en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum resumen: La médula ósea está llorando (células de lágrima) porque está fibrosada y es un grifo seco.
Mielofibrosis primaria prefibrótica/temprana (pre-PMF)
Mielofibrosis primaria manifiesta (fibrótica)
Las neoplasias mieloproliferativas se pueden comparar con la siguiente clasificación de la OMS:
| Enfermedad | Mutaciones | Puntos clave |
|---|---|---|
| LMC | BCR-ABL1 (cromosoma Filadelfia) | Proliferación de granulocitos maduros y en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum proceso de maduración |
| Trombocitemia esencial | JAK2, CALR o MPL | Producción clonal excesiva de plaquetas |
| Policitemia vera | JAK2 | Masa de eritrocitos elevada |
| Mielofibrosis primaria | JAK2, CALR o MPL | Fibrosis Fibrosis Any pathological condition where fibrous connective tissue invades any organ, usually as a consequence of inflammation or other injury. Bronchiolitis Obliterans obliterante de la médula ósea |
Otros tipos:
La evaluación del riesgo es importante para tomar decisiones de tratamiento.