La médula espinal es la principal vía de conducción que conecta el cerebro con el cuerpo; forma parte del sistema nervioso central (SNC). La médula espinal se divide en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum regiones cervical, torácica, lumbar y sacra, aunque como la médula espinal es más corta que la columna vertebral, estas regiones no se alinean con sus correspondientes niveles vertebrales. En EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum un corte transversal, la médula espinal se divide en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum una zona de materia gris en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum forma de H (formada por cuerpos celulares neuronales en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum sinapsis) y una zona circundante de materia blanca (formada por tractos ascendentes y descendentes de axones mielinizados). Al AL Amyloidosis igual que el cerebro, la médula espinal está rodeada por 3 capas de tejido conectivo, conocidas colectivamente como meninges Meninges The brain and the spinal cord are enveloped by 3 overlapping layers of connective tissue called the meninges. The layers are, from the most external layer to the most internal layer, the dura mater, arachnoid mater, and pia mater. Between these layers are 3 potential spaces called the epidural, subdural, and subarachnoid spaces. Meninges: Anatomy; estas capas son la duramadre, la aracnoides y la piamadre. La médula espinal está irrigada por 1 arteria espinal anterior y 2 posteriores.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
La neurulación es el proceso por el cual el tubo neural en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el embrión trilaminar se desarrolla a partir del ectodermo. Este proceso se produce a medida que las células destinadas a convertirse en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la médula espinal avanzan por las siguientes estructuras:
El tubo neural se diferencia en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum 3 capas.
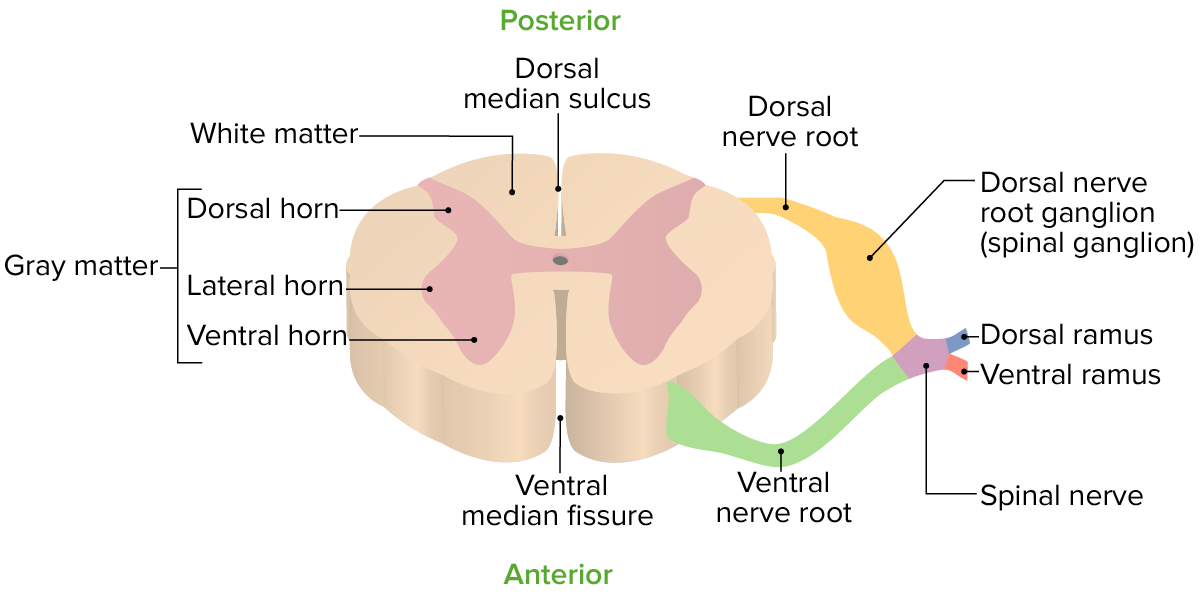
Vista transversal de un segmento espinal
Imagen por Lecturio.Cuando se observa en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum un corte transversal, la médula espinal se divide en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum materia gris y materia blanca.
Materia gris:
Materia blanca:
Las meninges Meninges The brain and the spinal cord are enveloped by 3 overlapping layers of connective tissue called the meninges. The layers are, from the most external layer to the most internal layer, the dura mater, arachnoid mater, and pia mater. Between these layers are 3 potential spaces called the epidural, subdural, and subarachnoid spaces. Meninges: Anatomy son las membranas fibrosas que recubren la médula espinal (y el cerebro). Las 3 capas y los LOS Neisseria 2 espacios definidos entre/alrededor de las capas son (de externa a interna):
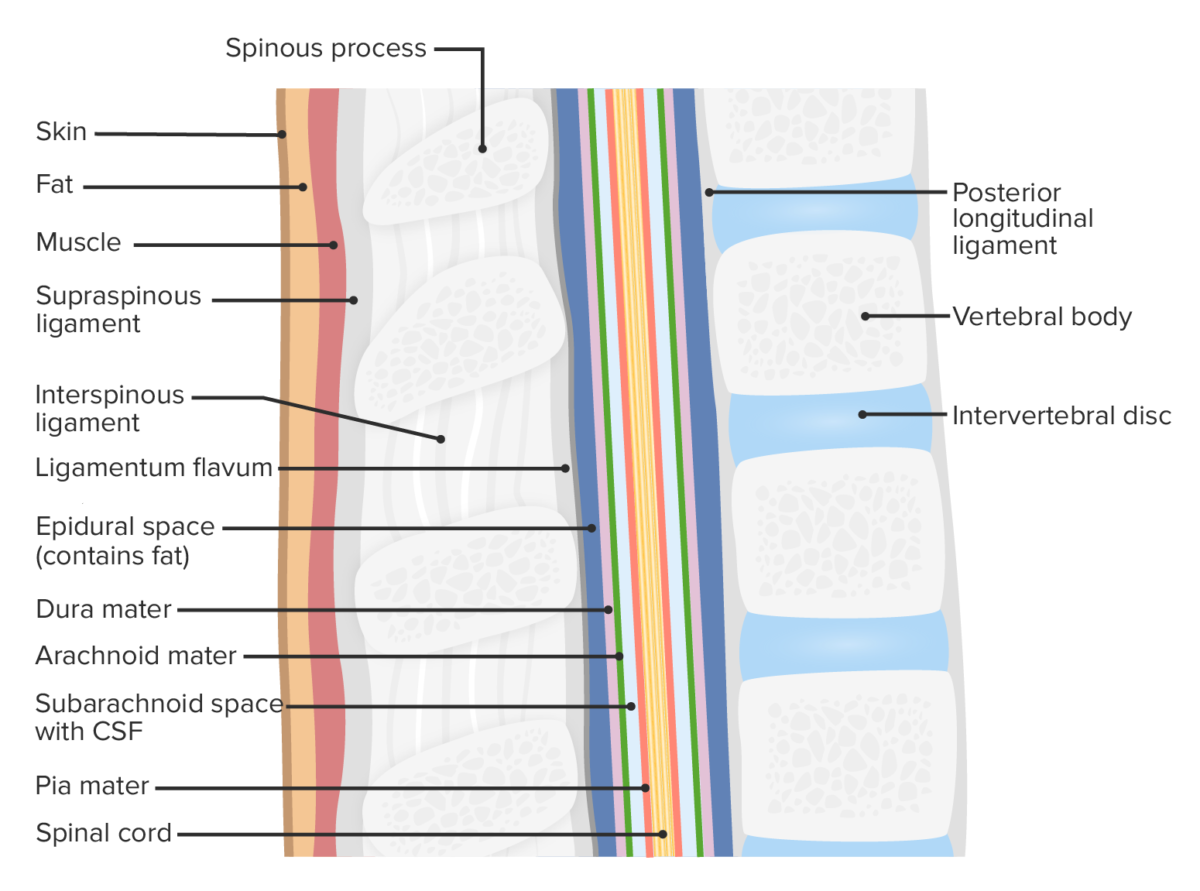
Capas de la espalda y la médula espinal
Imagen por Lecturio.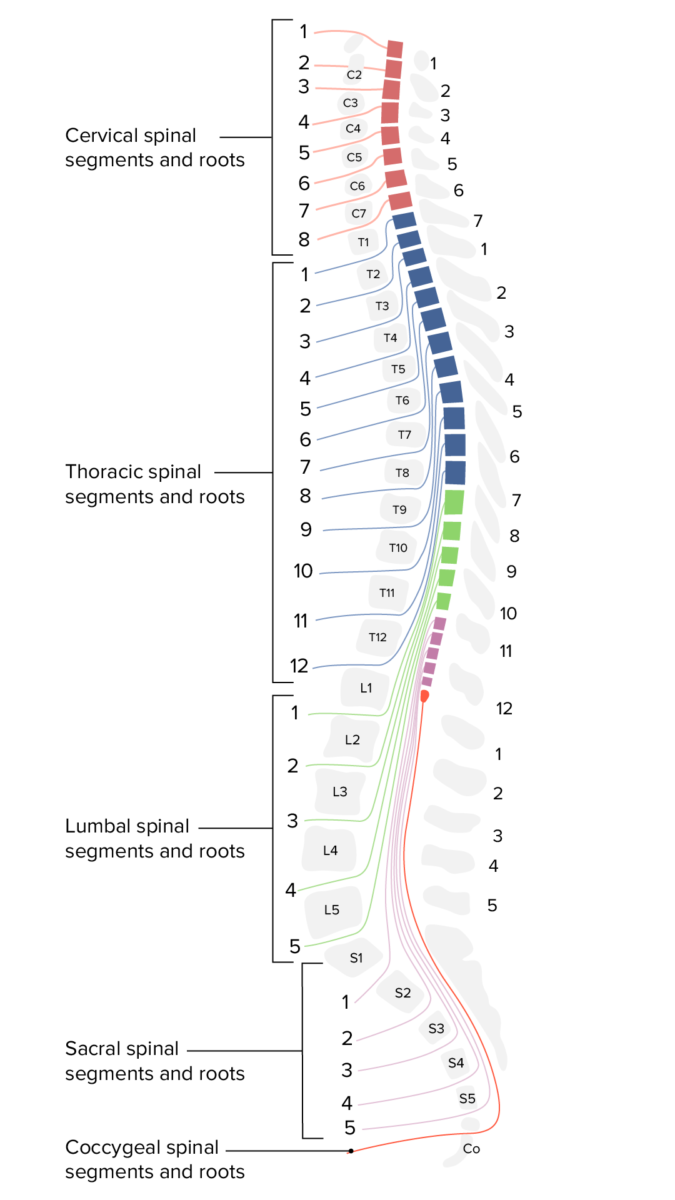
Vista transversal de los 31 segmentos espinales y su relación con la columna vertebral ósea
Imagen por Lecturio.En EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum general, las principales funciones de la médula espinal son:
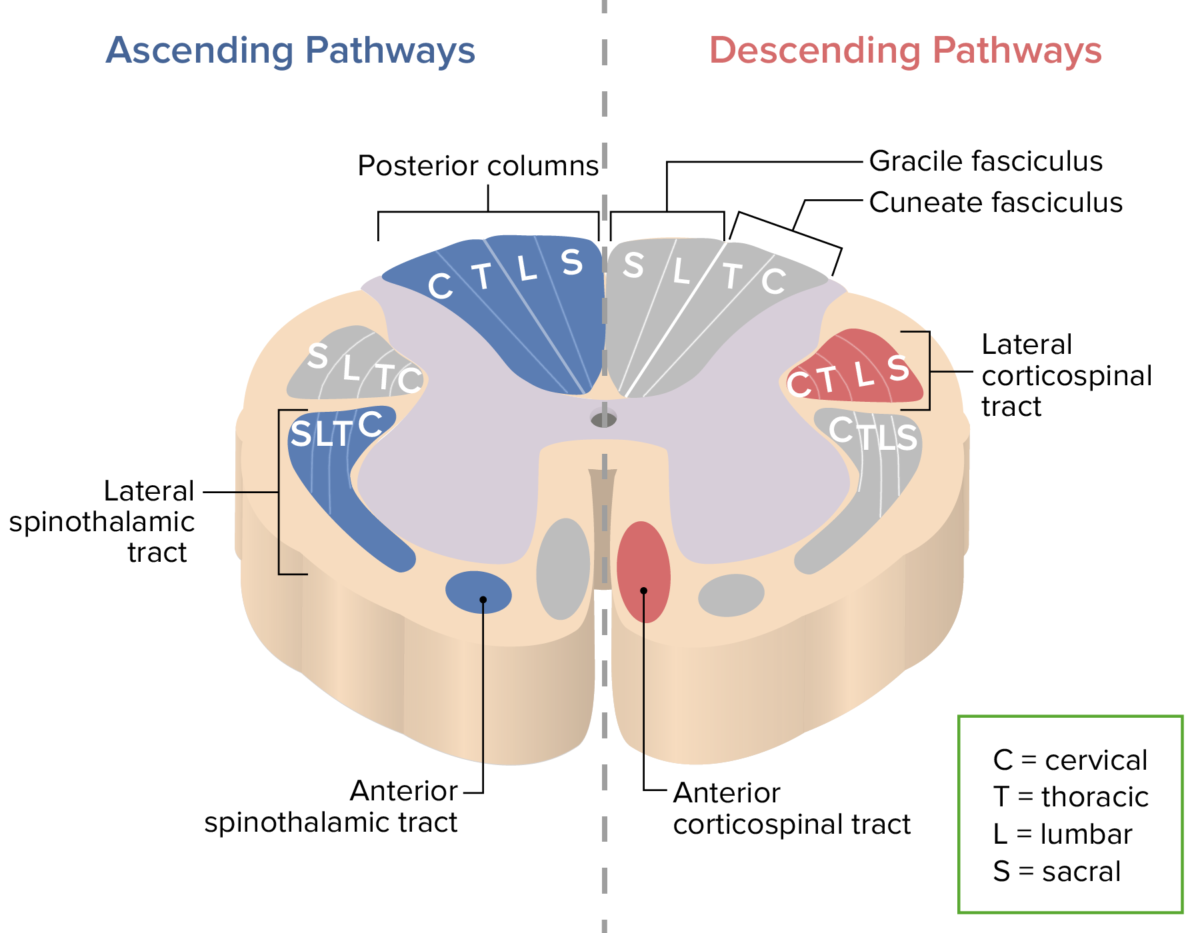
Principales tractos ascendentes (azul) y descendentes (rojo) de la médula espinal:
Las letras C, T, L y S denotan dónde se encuentran las fibras asociadas a cada región.
Columnas dorsales:
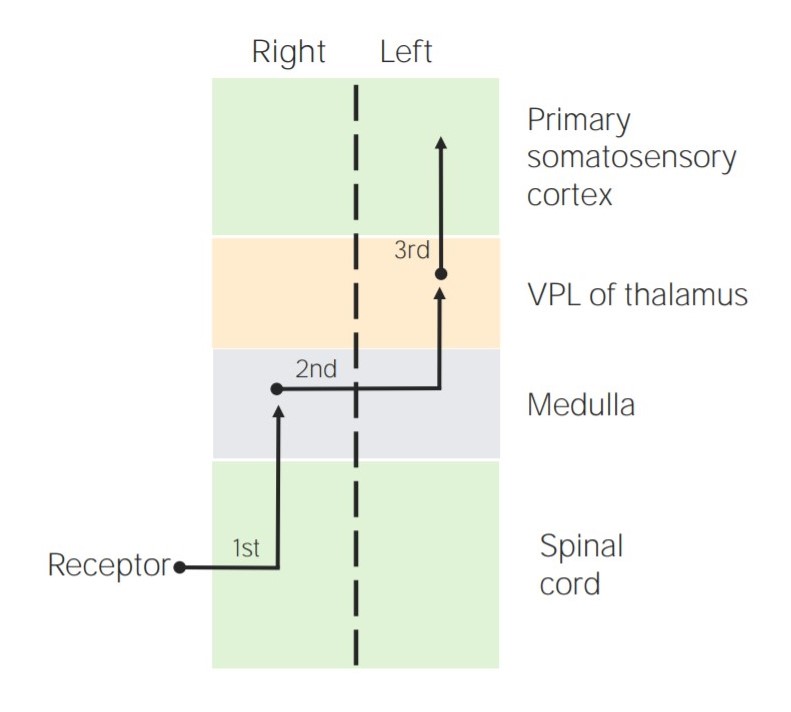
Diagrama que representa la localización de las neuronas sensoriales de 1er, 2do y 3er orden en las columnas dorsales
VPL = núcleo posterolateral ventral del tálamo
Tractos espinotalámicos:
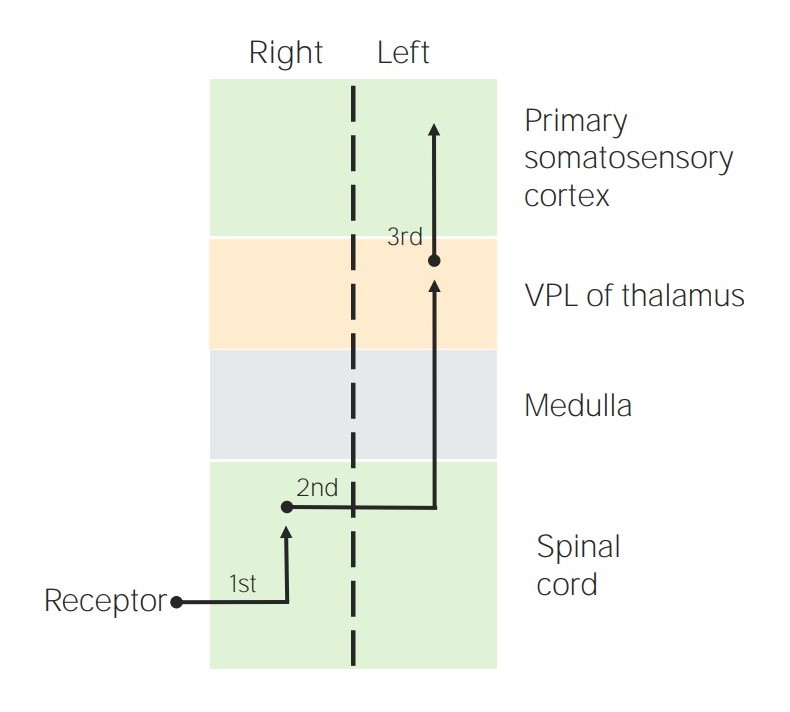
Diagrama que representa la ubicación de las neuronas sensoriales de 1er, 2do y 3er orden en los tractos espinotalámicos
Imagen por Lecturio.Tractos espinocerebelosos:
Tractos corticoespinales:
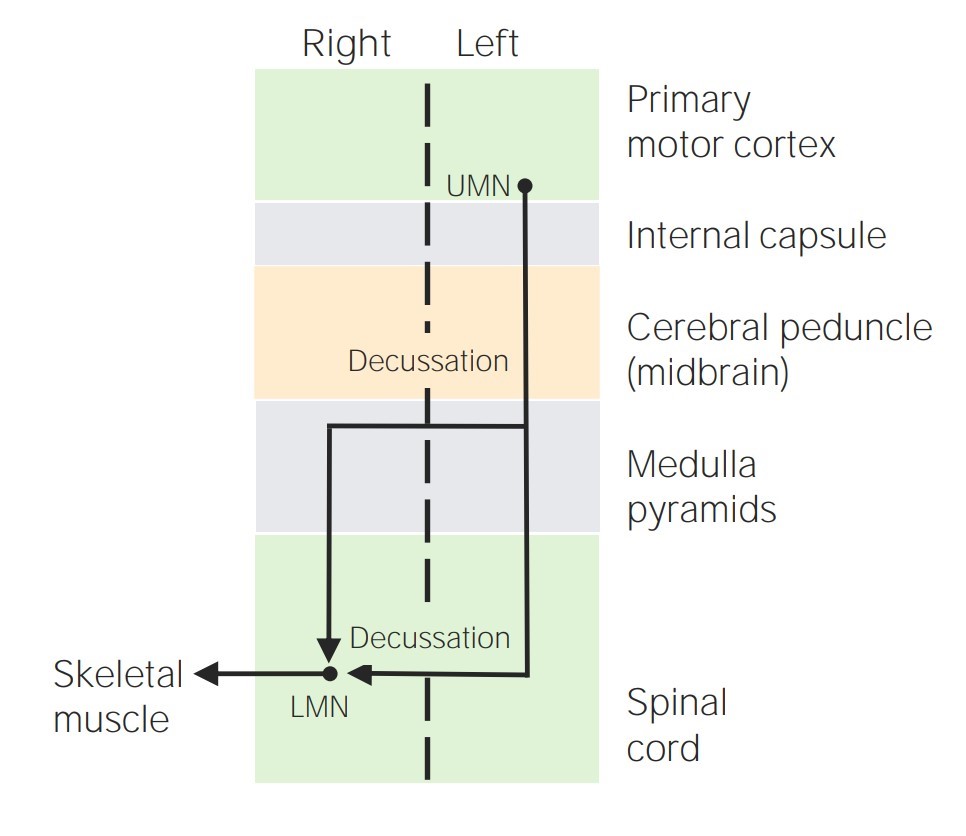
Diagrama que muestra el recorrido del tracto corticoespinal
UMN = neurona motora superior
LMN = neurona motora inferior
Tractos extrapiramidales:
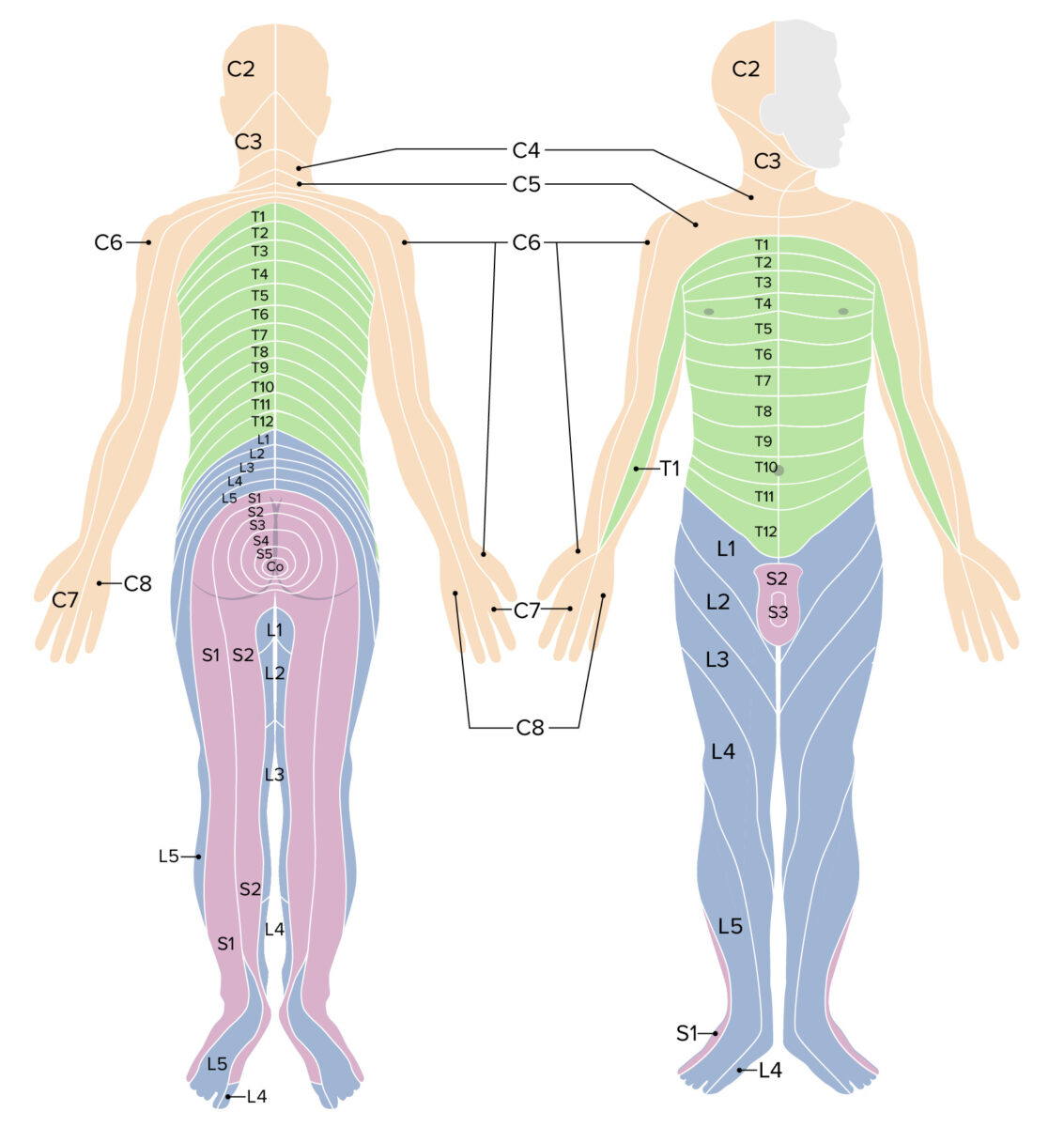
Dermatomas
Imagen por Lecturio.La médula espinal está irrigada por 3 arterias longitudinales, 1 arteria espinal anterior y 2 posteriores
La médula espinal se drena a través de las venas espinales: