Los LOS Neisseria medicamentos para la gota incluyen medicamentos antiinflamatorios y reductores de uratos. La colchicina es un medicamento antiinflamatorio que se puede utilizar para los LOS Neisseria episodios agudos de gota. Las clases de medicamentos reductores de uratos incluyen los LOS Neisseria inhibidores de la xantina oxidasa, los LOS Neisseria agentes uricosúricos y las uricasas. Estos medicamentos son beneficiosos para la prevención de las exacerbaciones de la gota y funcionan a través de una variedad de mecanismos. Los LOS Neisseria inhibidores de la xantina oxidasa son el tratamiento de reducción de uratos más utilizado; estos funcionan inhibiendo la enzima necesaria para la conversión de purinas en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum ácido úrico. Los LOS Neisseria agentes uricosúricos reducen la reabsorción de ácido úrico por el túbulo proximal, lo que aumenta la excreción renal. Por último, las uricasas son enzimas recombinantes que metabolizan el ácido úrico a alantoína. Además de la gota, los LOS Neisseria tratamientos reductores de uratos también tienen otras indicaciones, como la prevención del síndrome de lisis tumoral y la nefrolitiasis por ácido úrico.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
La colchicina es un alcaloide extraído de Colchicum autumnale (azafrán de otoño).
Absorción:
Distribución:
Metabolismo:
Excreción:
Gota:
Otras indicaciones incluyen:
Se debe tener precaución en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum personas con:
Los LOS Neisseria siguientes podrían provocar un aumento en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria niveles de colchicina:
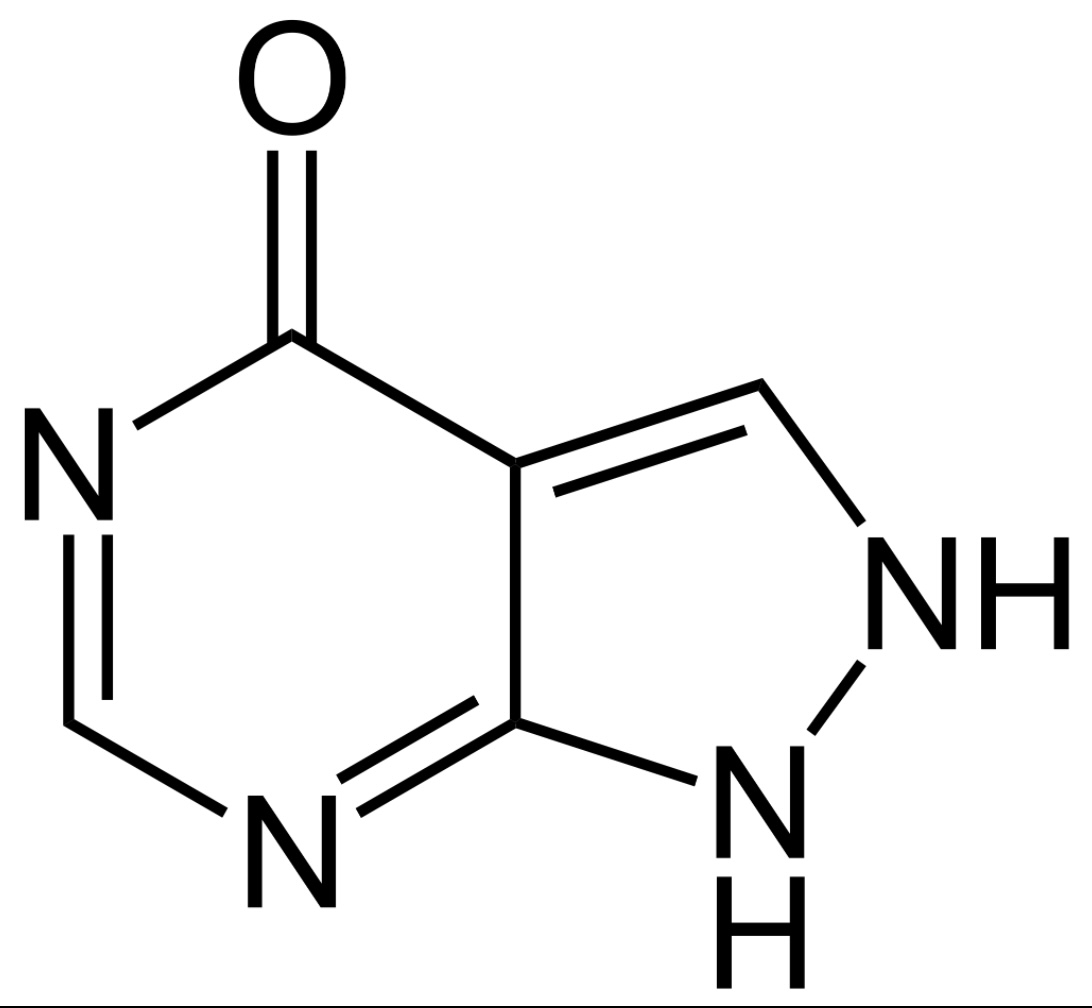
Estructura química del alopurinol
Imagen: “Allopurinol” por Jü. Licencia: Dominio Público
Estructura química de la hipoxantina:
Obsérvese la similitud con el alopurinol, un inhibidor de la xantina oxidasa.
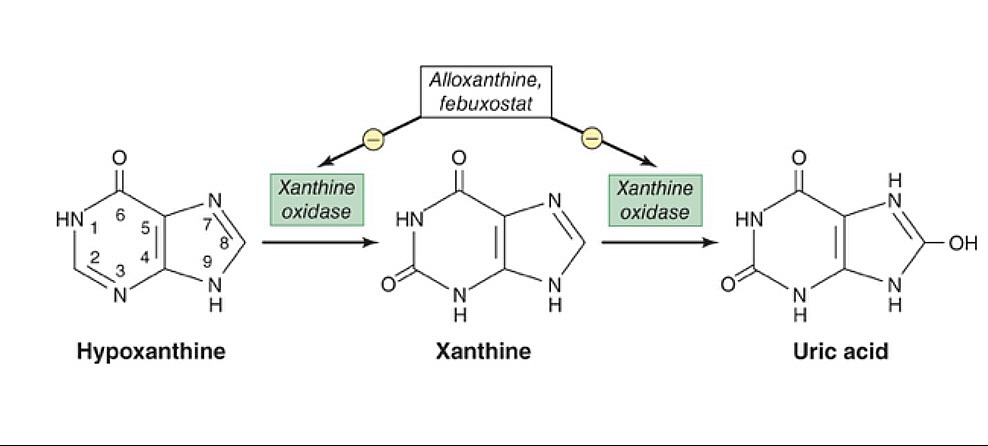
Los inhibidores de la xantina oxidasa (alopurinol y febuxostat), previenen la conversión de la hipoxantina y la xantina en ácido úrico.
Imagen por Lecturio.| Medicamento | Absorción | Distribución | Metabolismo | Excreción |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alopurinol | Buena absorción por vía oral | Unión a proteínas insignificante |
|
Orina y heces |
| Febuxostat Febuxostat A thiazole derivative and inhibitor of xanthine oxidase that is used for the treatment of hyperuricemia in patients with chronic gout. Gout Drugs | Altamente unido a proteínas |
|
Alopurinol:
Febuxostat Febuxostat A thiazole derivative and inhibitor of xanthine oxidase that is used for the treatment of hyperuricemia in patients with chronic gout. Gout Drugs:
Alopurinol:
Febuxostat Febuxostat A thiazole derivative and inhibitor of xanthine oxidase that is used for the treatment of hyperuricemia in patients with chronic gout. Gout Drugs:
Los LOS Neisseria inhibidores de la xantina oxidasa pueden aumentar la concentración de 6-mercaptopurina y azatioprina (que son metabolizadas por la xantina oxidasa).
La mayor parte del ácido úrico filtrado se reabsorbe en el túbulo proximal.
Imagen por Lecturio.
Los agentes uricosúricos, como el probenecid, inhiben competitivamente los transportadores responsables de la reabsorción del ácido úrico.
Esto conduce a un aumento de la excreción urinaria y a una disminución de los niveles plasmáticos de ácido úrico.
| Medicamentos | Absorción | Distribución | Metabolismo | Excreción |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Probenecid Probenecid The prototypical uricosuric agent. It inhibits the renal excretion of organic anions and reduces tubular reabsorption of urate. Probenecid has also been used to treat patients with renal impairment, and, because it reduces the renal tubular excretion of other drugs, has been used as an adjunct to antibacterial therapy. Gout Drugs | Rápida, buena absorción | Alta unión a proteínas | Hepático | Orina |
| Lesinurad Lesinurad Gout Drugs | Hepático, citocromo P450 | Orina y heces |
Los LOS Neisseria agentes uricosúricos se utilizan con poca frecuencia para el tratamiento de la hiperuricemia y la gota crónica.
Probenecid Probenecid The prototypical uricosuric agent. It inhibits the renal excretion of organic anions and reduces tubular reabsorption of urate. Probenecid has also been used to treat patients with renal impairment, and, because it reduces the renal tubular excretion of other drugs, has been used as an adjunct to antibacterial therapy. Gout Drugs:
Lesinurad Lesinurad Gout Drugs:
Las siguientes interacciones medicamentosas están asociadas con el probenecid Probenecid The prototypical uricosuric agent. It inhibits the renal excretion of organic anions and reduces tubular reabsorption of urate. Probenecid has also been used to treat patients with renal impairment, and, because it reduces the renal tubular excretion of other drugs, has been used as an adjunct to antibacterial therapy. Gout Drugs:
Estos medicamentos se clasifican como urato oxidasas recombinantes (uricasas).
Las uricasas metabolizan el ácido úrico a alantoína, que es:
Pegloticasa:
Rasburicasa:
Las uricasas no deben usarse en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum personas con deficiencia de glucosa-6-fosfato deshidrogenasa ( G6PD G6PD Pentose Phosphate Pathway) (puede precipitar una hemólisis grave).