La órbita es la cavidad del cráneo en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la que se encuentran el ojo y sus apéndices. La órbita se compone de 7 huesos y tiene forma piramidal, con su vértice apuntando posteromedialmente. El contenido de la órbita comprende el ojo; la fascia Fascia Layers of connective tissue of variable thickness. The superficial fascia is found immediately below the skin; the deep fascia invests muscles, nerves, and other organs. Cellulitis orbitaria y retrobulbar; los LOS Neisseria músculos extraoculares; los LOS Neisseria nervios craneales II, III, IV, V y VI; los LOS Neisseria vasos sanguíneos; grasa; la glándula lagrimal con su saco y el conducto nasolagrimal; los LOS Neisseria párpados; los LOS Neisseria ligamentos palpebrales y suspensorios; el ganglio ciliar y los LOS Neisseria nervios ciliares cortos.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
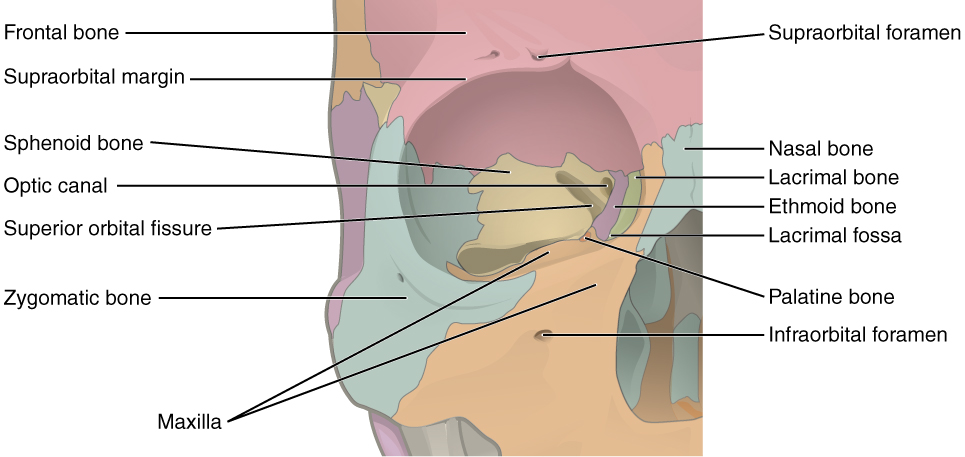
La órbita derecha y los 7 huesos que componen sus paredes: frontal (rojo), maxilar (naranja), lagrimal (verde), etmoides (morado), esfenoides (amarillo), palatino (naranja oscuro) y cigomático (azul)
Imagen: “Illustration from Anatomy & Physiology” por OpenStax College. Licencia: CC-BY-3.0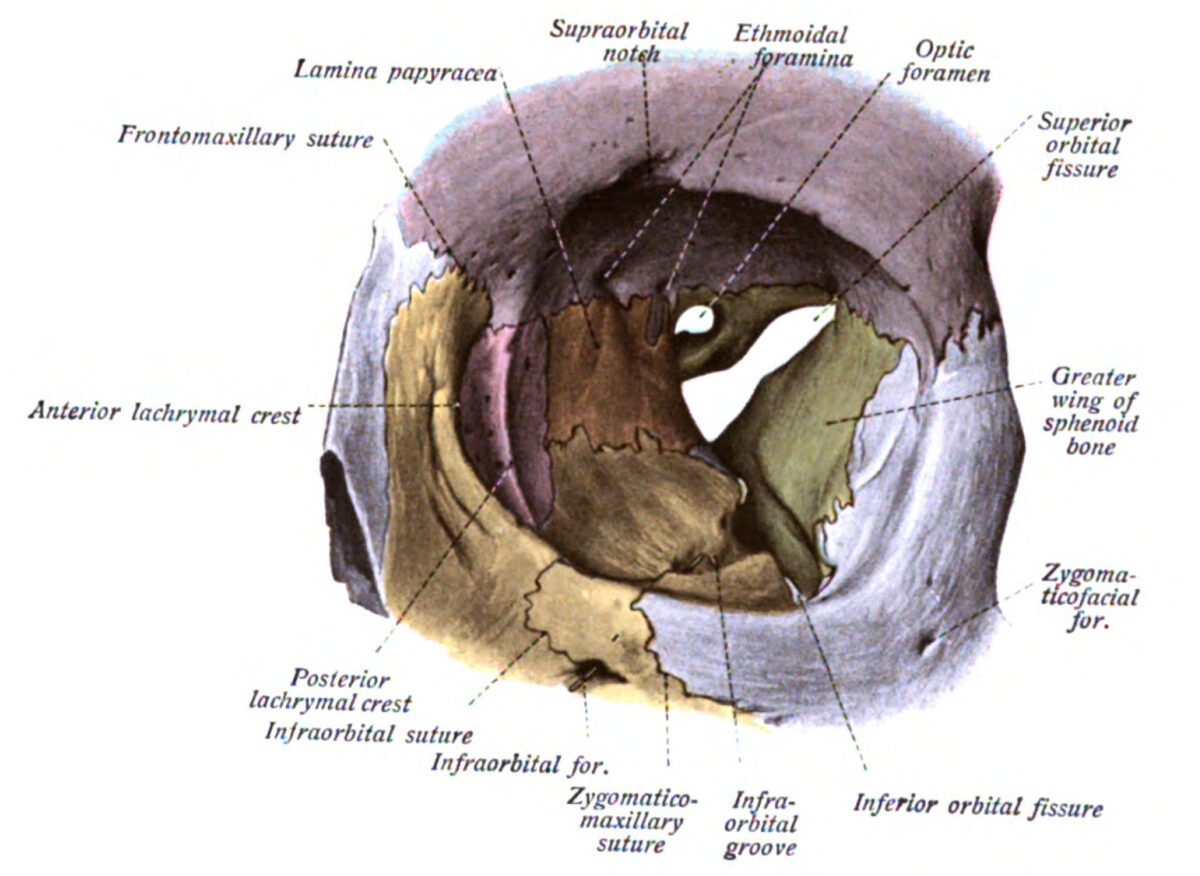
La órbita izquierda, con sus múltiples aberturas: agujero óptico, forámenes etmoidales, fisuras orbitarias superior e inferior, surco infraorbitario y escotadura supraorbitaria.
Imagen: “An illustration from the 1909 American edition of Sobotta’s anatomy” por Dr. Johannes Sobotta. Licencia: Dominio Público| Localización | Contenido | |
|---|---|---|
| Agujero o canal óptico | Vértice, bordeado por el cuerpo y el ala menor del esfenoides |
|
| Agujeros etmoidales |
|
Venas, arterias y nervios etmoidales anteriores y posteriores |
| Fisura orbitaria superior | Entre las alas ALAS An enzyme of the transferase class that catalyzes condensation of the succinyl group from succinyl coenzyme a with glycine to form delta-aminolevulinate. It is a pyridoxal phosphate protein and the reaction occurs in mitochondria as the first step of the heme biosynthetic pathway. The enzyme is a key regulatory enzyme in heme biosynthesis. In liver feedback is inhibited by heme. Heme Metabolism mayor y menor del hueso esfenoides | Dentro del anillo tendinoso común:
|
| Fisura orbitaria inferior |
|
|
| Foramen infraorbitario | Mitad del suelo orbitario (maxilar) | Salida de la vena, la arteria y el nervio infraorbitarios |
| Escotadura o foramen supraorbitario | Margen superior de la órbita (hueso frontal Frontal The bone that forms the frontal aspect of the skull. Its flat part forms the forehead, articulating inferiorly with the nasal bone and the cheek bone on each side of the face. Skull: Anatomy) | Salida de la vena, arteria y nervio supraorbitarios |
Para ayudar a memorizar los LOS Neisseria huesos que componen la órbita, recuerda la mnemotecnia en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum inglés: Many Friendly Zebras Enjoy Lazy Summer Picnics ( en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum inglés) (muchas cebras amistosas disfrutan de los LOS Neisseria pícnics de verano)
| Músculo | Origen | Inserción | Irrigación | Inervación | Función |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Recto medial | Anillo de Zinn (anillo tendinoso común) | Superficie anterior y medial del ojo | Rama muscular inferior de la arteria oftálmica | Rama inferior del nervio oculomotor (nervio craneal III) | Aducción |
| Recto lateral | Superficie anterior y lateral del ojo | Arteria lagrimal | Nervio abducens (nervio craneal VI) | Abducción | |
| Recto inferior | Superficie anterior e inferior del ojo | Rama muscular inferior de la arteria oftálmica y la rama infraorbitaria de la arteria maxilar | Rama inferior del nervio oculomotor (nervio craneal III) | Depresión, extorsión y aducción. En EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum abducción: solo deprime | |
| Recto superior | Superficie anterior y superior del ojo | Rama muscular superior de la arteria oftálmica | Rama superior del nervio oculomotor (nervio craneal III) | Elevación, intorsión y aducción. En EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum abducción: solo eleva | |
| Oblicuo superior | Ala menor del esfenoides, medial al AL Amyloidosis canal óptico | Superficie posterior, superior y lateral del ojo | Rama muscular superior de la arteria oftálmica | Nervio troclear (nervio craneal IV) | Intorsión, depresión y abducción |
| Oblicuo inferior | Lateral al AL Amyloidosis surco lagrimal (maxilar) | Superficie posterior, inferior y lateral del ojo | Rama inferior de la arteria oftálmica y arteria infraorbitaria | Rama inferior del nervio oculomotor (nervio craneal III) | Extorsión, elevación y abducción |
| Elevador del párpado superior | Ala menor del esfenoides, por encima del canal óptico | Placa tarsal del párpado superior | Rama supraorbitaria de la arteria oftálmica | Rama superior del nervio oculomotor (nervio craneal III). Las fibras simpáticas inervan las fibras musculares lisas de la superficie inferior de este músculo. |
Retracción y elevación del párpado |
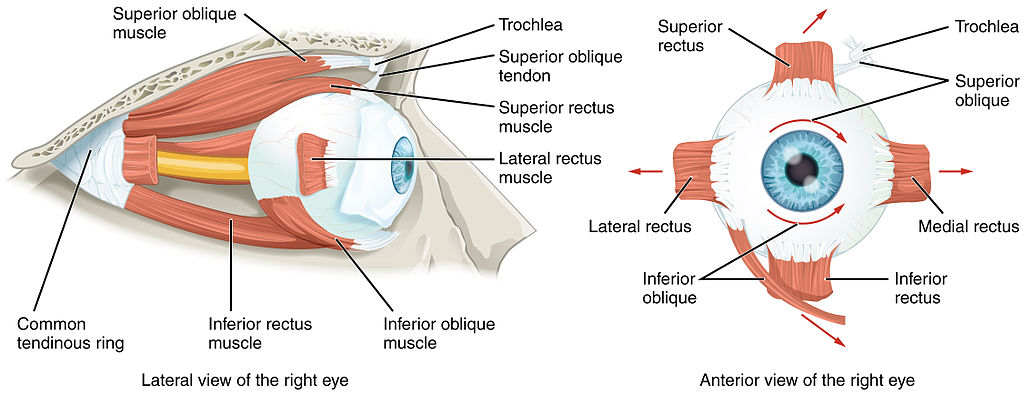
Origen e inserción de los músculos extraoculares. Obsérvese que los cuatro músculos rectos se originan en un anillo tendinoso común (los oblicuos no) y la ubicación de la tróclea para el oblicuo superior.
Imagen: “Extraocular Muscles” por OpenStax College. Licencia: CC BY 3.0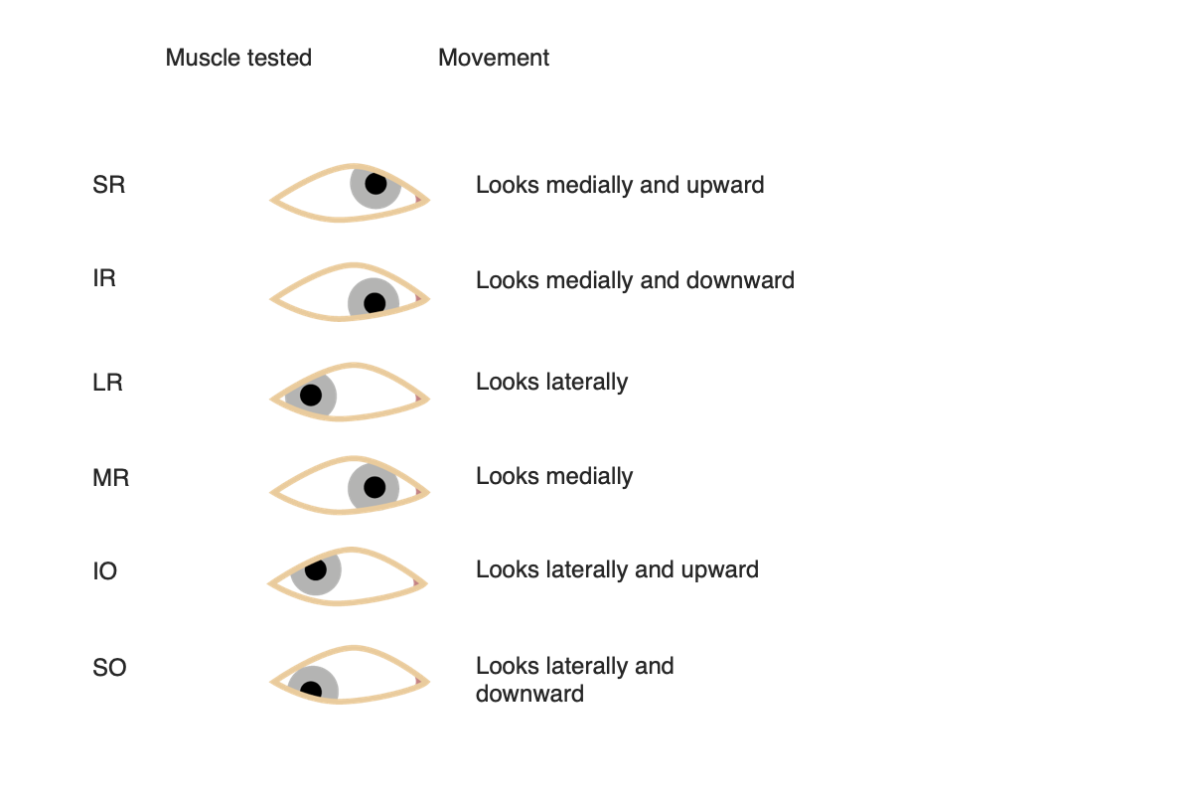
Movimientos oculares para cada músculo extraocular
Imagen por Lecturio.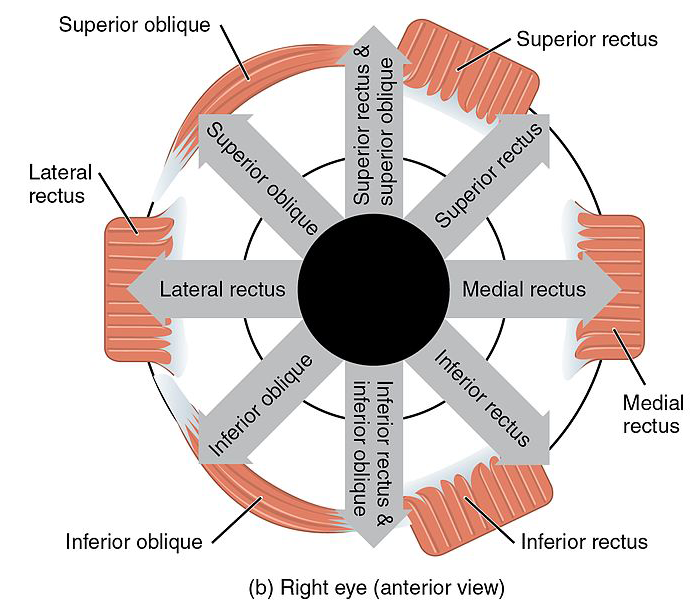
Movimientos oculares para cada músculo extraocular. Observe los movimientos sinérgicos de los músculos rectos y oblicuos superiores, así como de los rectos y oblicuos inferiores.
Imagen: “Version 8.25” por OpenStax. Licencia: CC BY 4.0, editada por Lecturio.Para ayudar a memorizar la inervación de los LOS Neisseria músculos extraoculares, recuerda: LR6, SO4, 3
Para ayudar a memorizar las acciones de los LOS Neisseria músculos, recuerda: RAD
Recti are Ad AD The term advance directive (AD) refers to treatment preferences and/or the designation of a surrogate decision-maker in the event that a person becomes unable to make medical decisions on their own behalf. Advance directives represent the ethical principle of autonomy and may take the form of a living will, health care proxy, durable power of attorney for health care, and/or a physician’s order for life-sustaining treatment. Advance Directivesductors, except the lateral rectus Lateral rectus Orbit and Extraocular Muscles: Anatomy ( los LOS Neisseria rectos son aductores, excepto el recto lateral)
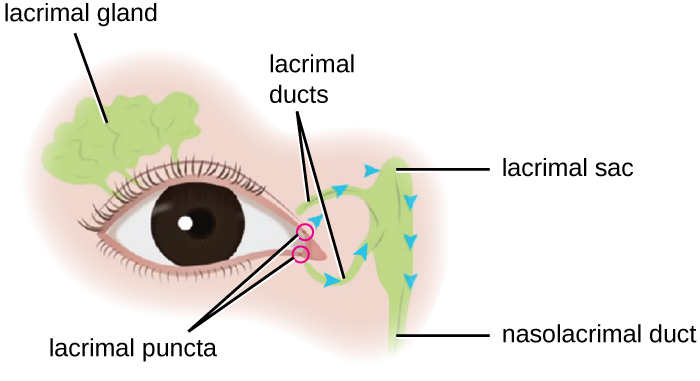
Diagrama esquemático de la ubicación de la glándula y el aparato lagrimal
Imagen: “Microbiology” por CNX OpenStax. Licencia: CC BY 4.0| Parálisis nerviosa | Causas | Síntomas que comprometen al AL Amyloidosis ojo afectado |
|---|---|---|
| Oculomotor (nervio craneal III) |
|
|
| Troclear (nervio craneal IV) |
|
El ojo está desviado hacia arriba y hacia adentro |
| Abducens (nervio craneal VI) |
|
Ojo dirigido medialmente |