La insulina es una hormona peptídica producida por las células beta del páncreas. La insulina juega un papel importante en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum funciones metabólicas como la captación de glucosa, glucólisis, glucogénesis, lipogénesis y síntesis de proteínas. La insulina exógena puede ser necesaria para las personas con diabetes Diabetes Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a metabolic disease characterized by hyperglycemia and dysfunction of the regulation of glucose metabolism by insulin. Type 1 DM is diagnosed mostly in children and young adults as the result of autoimmune destruction of β cells in the pancreas and the resulting lack of insulin. Type 2 DM has a significant association with obesity and is characterized by insulin resistance. Diabetes Mellitus mellitus, en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum las que existe una deficiencia de insulina endógena o una mayor resistencia a la insulina. Hay varias formas de insulina y difieren en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum su inicio de acción, efecto máximo y duración. Las insulinas se pueden clasificar en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum acción rápida, acción corta, acción intermedia o acción prolongada. Se puede utilizar una combinación de estas clases para mantener el control de la glucosa durante el día. Los LOS Neisseria efectos adversos comunes incluyen hipoglucemia, aumento de peso después del inicio de un régimen de insulina y cambios en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el lugar de la inyección.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Los LOS Neisseria tipos de insulina se pueden clasificar según su farmacocinética:
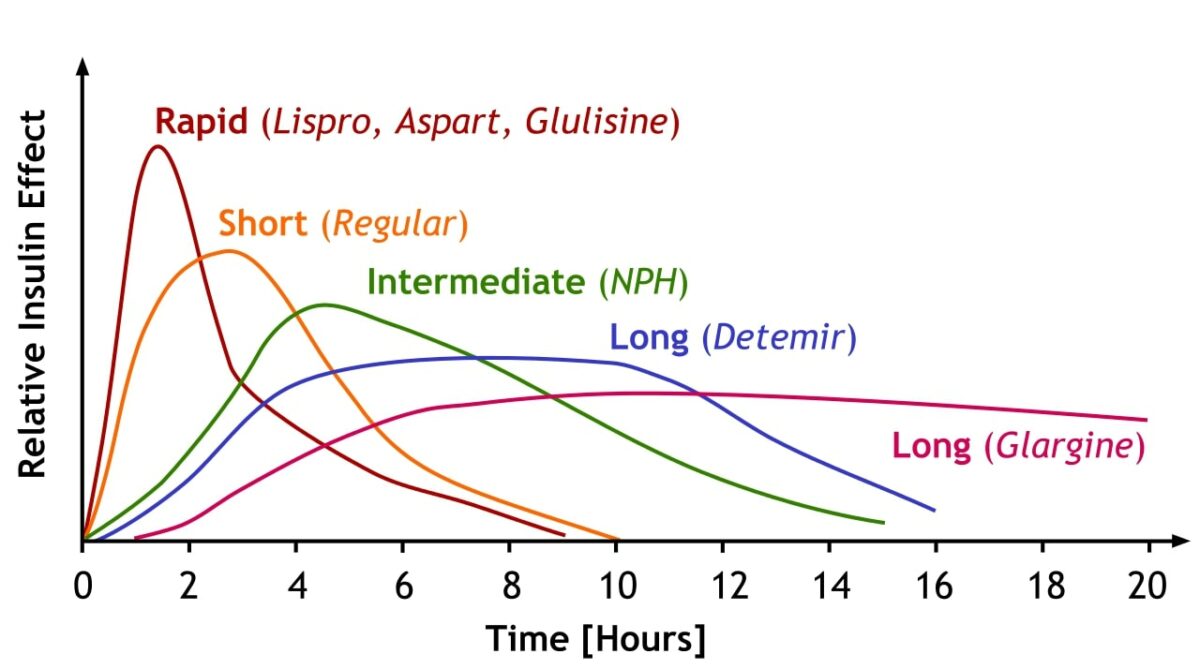
Una comparación del inicio, el efecto máximo y la duración de los diferentes subtipos de insulina.
Imagen: “Insulin is categorized by how fast it works in the body, how soon it peaks and then how long it lasts. Notice how rapid acting insulins have a rapid rise and fall while longer acting insulin builds more slowly to a stable baseline before declining.” por A. Peters, M. Komorniczak. Licencia: CC BY 3.0Insulina subcutánea:
Insulina intravenosa:
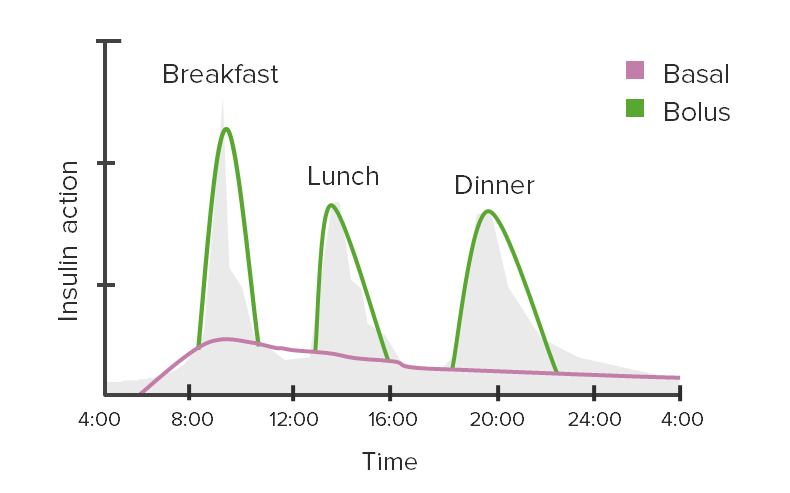
Excursiones glucémicas y acción de la insulina:
Este gráfico muestra el uso de insulina basal y en bolo (a la hora de comer) para cubrir las variaciones en los niveles de glucosa en sangre a lo largo del día.
Además de la diabetes Diabetes Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a metabolic disease characterized by hyperglycemia and dysfunction of the regulation of glucose metabolism by insulin. Type 1 DM is diagnosed mostly in children and young adults as the result of autoimmune destruction of β cells in the pancreas and the resulting lack of insulin. Type 2 DM has a significant association with obesity and is characterized by insulin resistance. Diabetes Mellitus, la insulina intravenosa se puede utilizar en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum otras varias condiciones (a menudo junto con la dextrosa para mantener la euglucemia).
Es posible que sea necesario realizar ajustes de dosis y un control estricto para las personas con:
| Efecto insulina | Tipo de insulina | Clasificación | Inicio de acción | Pico de acción | Duración de la acción |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Acción rápida | Insulina lispro Lispro Insulin that has been modified so that the b-chain contains a lysine at position 28 instead of a proline and a proline at position 29 instead of a lysine. It is used to manage blood glucose levels in patients with type 2 diabetes. Insulin | Análoga | 15–30 minutos | 1–3 horas | 4–6 horas |
| Aspart Aspart Insulin that has been modified to contain an aspartic acid instead of a proline at position 38 of the b-chain. Insulin | |||||
| Glulisina | |||||
| Acción corta | Regular Regular Insulin | Humana | 30 minutos | 1,5–3,5 horas | 8 horas |
| Acción intermedia | NPH NPH Normal pressure hydrocephalus (NPH) is a neurodegenerative disorder characterized by the triad of gait abnormalities, dementia, and urinary urgency or incontinence. Normal pressure hydrocephalus can be either idiopathic or secondary to intraventricular or subarachnoid hemorrhage. Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus | Humana | 1–2 horas | 4–6 horas | > 12 horas |
| Acción prolongada | Detemir Detemir A recombinant long-acting insulin and hypoglycemic agent in which a myristic acid is conjugated to a lysine at position b29. It is used to manage blood glucose levels in patients with diabetes mellitus. Insulin | Análoga | 1–2 horas | 3–9 horas | 14–24 horas |
| Insulina glargina | 3–4 horas | Sin pico | Aproximadamente 24 horas | ||
| Degludec Degludec Insulin | Aproximadamente 1 hora | Sin pico | > 40 horas |