El sistema hepatobiliar está compuesto por el hígado, la vesícula biliar y los LOS Neisseria conductos biliares (dentro del hígado y fuera del hígado). El hígado produce bilis, que es un líquido compuesto por colesterol, fosfolípidos, bilirrubina conjugada, sales biliares, electrolitos y agua. La bilis, que ayuda en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la digestión y ayuda a eliminar los LOS Neisseria productos de desecho, se almacena en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la vesícula biliar. El sistema hepatobiliar puede verse afectado por infecciones, quistes, masas sólidas, isquemia y obstrucción mecánica del flujo, lo que exige la presencia de pruebas de imagenología confiables para determinar la etiología. Los LOS Neisseria métodos que evalúan los LOS Neisseria cambios estructurales en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el hígado y las vías biliares incluyen ultrasonido, TC y RM (incluida la colangiopancreatografía por resonancia magnética). Además, la colescintigrafía, una imagenología funcional, ayuda a identificar la patología de la vesícula biliar mediante el seguimiento de la vía biliar.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Antes de la interpretación de cualquier imagen, el médico debe tomar ciertas medidas preparatorias. Se debe seguir el mismo enfoque sistemático en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum todo momento.
El reporte incluye:
| Tejido | Imágenes ponderadas en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum T1 | Imágenes ponderadas en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum T2 |
|---|---|---|
| Líquido (e.g., LCR) | Oscuro | Brillante |
| Grasa | Brillante | Brillante |
| Inflamación | Oscuro | Brillante |
La medicina nuclear se diferencia del resto de la radiología porque es imagenología funcional, más que estructural.
| Hallazgos de la imagenología | Significado |
|---|---|
| Conductos biliares visibles | Función hepática normal |
| Llenado de la vesícula biliar | Conducto cístico permeable |
| Radiotrazador visto en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el duodeno | Conducto biliar común permeable |
| No se observa radiotrazador en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la vesícula biliar | Vesícula biliar obstruida (colecistitis aguda) |
| No se observa radiotrazador en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el duodeno | Atresia Atresia Hypoplastic Left Heart Syndrome (HLHS) biliar |
| Radiotrazador fuera del sistema biliar | Fuga biliar |
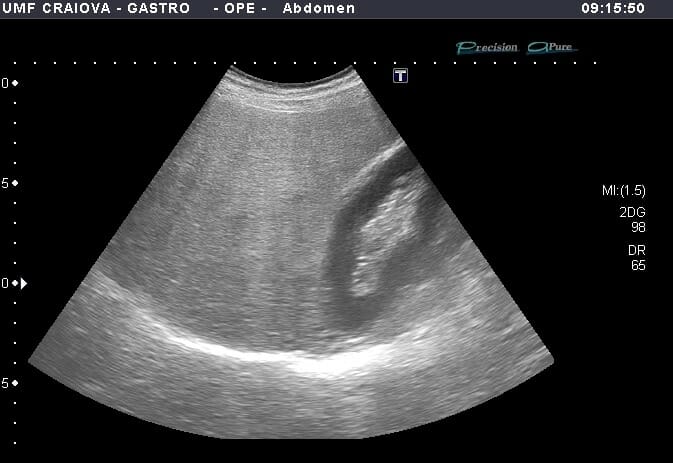
Ultrasonido en modo B que muestra hígado hiperecoico en comparación con el parénquima renal y atenuación posterior del parénquima hepático profundo en el contexto de esteatosis hepática
Imagen: “Figure 1” por Lăpădat, AM et al. Licencia: CC BY 3.0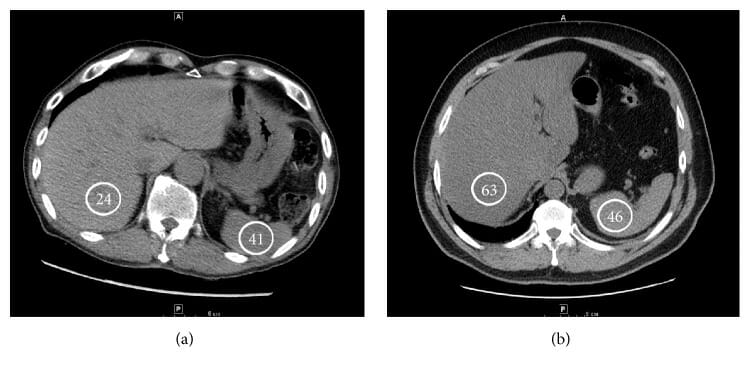
Imágenes de TC que muestran un ejemplo de un hígado esteatósico (a) y una atenuación hepática normal (B):
Las unidades de Hounsfield se indican en los círculos.
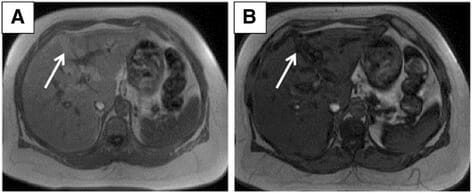
Esteatosis hepática subcapsular:
A: RM axial en fase con eco de gradiente ponderada en T1 que muestra áreas de hiperintensidad en la región subcapsular (flecha).
B: RM axial de fase opuesta con eco de gradiente ponderada en T1 que muestra pérdida de señal en las regiones subcapsulares correspondientes (flecha).

Colecistitis en el ultrasonido:
Vesícula biliar con pared engrosada
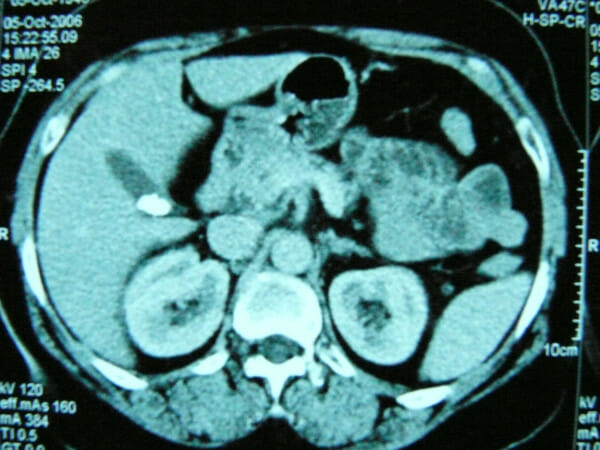
TC que muestra una vesícula biliar con cálculos biliares
Imagen: “F1” por Zagouri, F. et al. Licencia: CC BY 2.0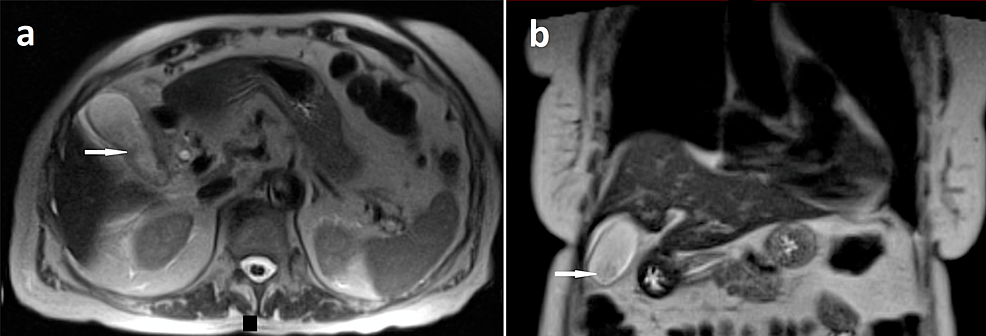
RM de abdomen que muestra colecistitis:
Secciones de RM abdominal axial (a) y coronal (b) con contraste y ponderada en T2 que muestra capas de barro en la vesícula biliar (flechas blancas) con engrosamiento de la pared de la vesícula biliar y trazas de líquido pericolequístico
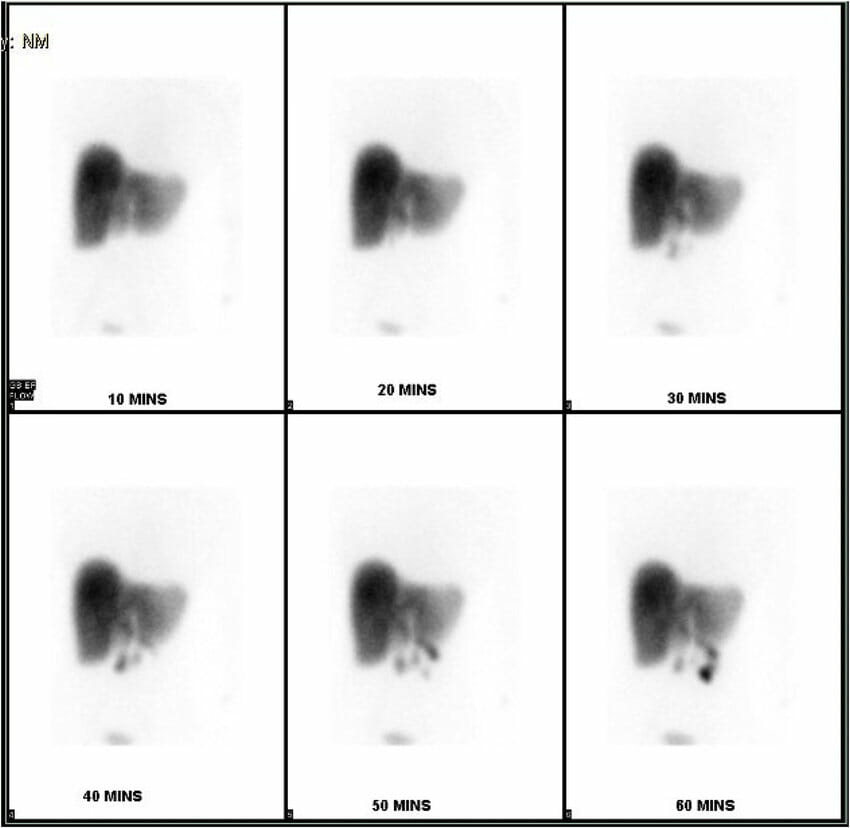
Gammagrafía con ácido iminodiacético hepatobiliar que muestra la no acumulación del isótopo dentro de la vesícula biliar en un caso de colecistitis acalculosa
Imagen: “HIDA scan showing non-accumulation of the isotope within the gallbladder” por Rezkallah, K. et al. Licencia: CC BY 4.0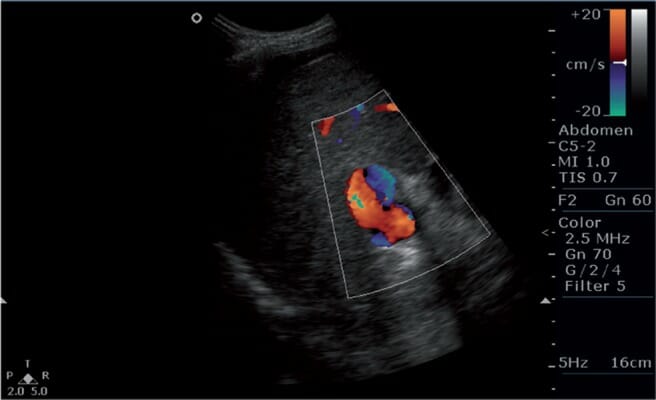
Imagen de Doppler color que muestra flujo bidireccional (o inversión del flujo) en la vena porta, hallazgo sugestivo de hipertensión portal
Imagen: “s5fig2” por Mittal, P. et al. Licencia: CC BY 2.5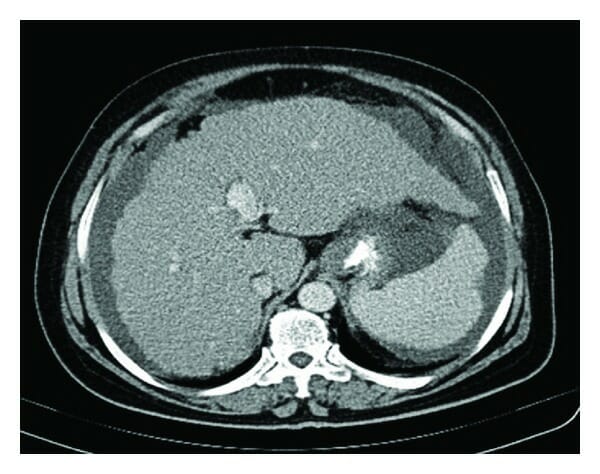
TC abdominal que muestra un hígado cirrótico, esplenomegalia y ascitis
Imagen: “Figure 1” por Nasrollah, M. et al. Licencia: CC BY 3.0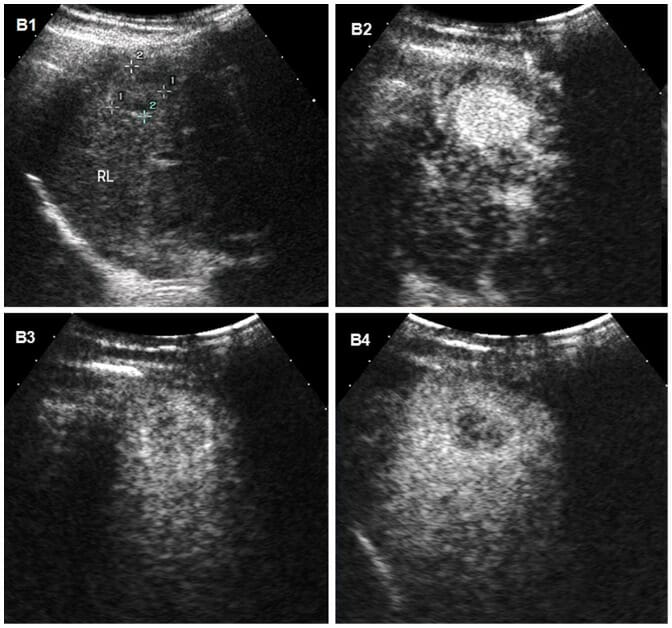
Carcinoma hepatocelular en un ultrasonido:
Imágenes de ultrasonido de carcinoma hepatocelular en el hígado de un hombre de 31 años con cirrosis.
B1: El ultrasonido convencional muestra la masa como un nódulo hipoecogénico mal delimitado.
B2–B4: Se obtuvieron imágenes en secuencia de tiempo de ultrasonido con contraste después de la inyección de un agente de contraste de microburbujas.
B2: la hipervascularización típica (realce) del carcinoma hepatocelular se observa durante la fase arterial, 95 segundos después de la inyección del agente de contraste.
B3, B4: la masa se vuelve hipoecoica en las fases portal y tardía, y la imagen de la fase tardía en B4 muestra un ligero lavado del medio de contraste a los 179 segundos, lo que ayuda a diferenciar el carcinoma hepatocelular del colangiocarcinoma o del tumor metastásico, que tienen tiempos de lavado más rápidos.
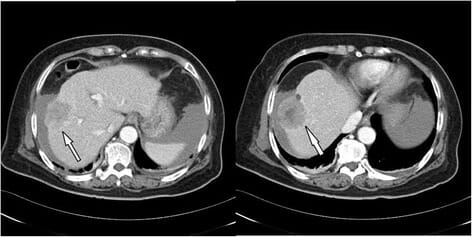
Carcinoma hepatocelular en TC:
TC abdominal trifásica que muestra un gran tumor (4,8 cm de diámetro) en el lóbulo derecho, compatible con carcinoma hepatocelular (flecha)
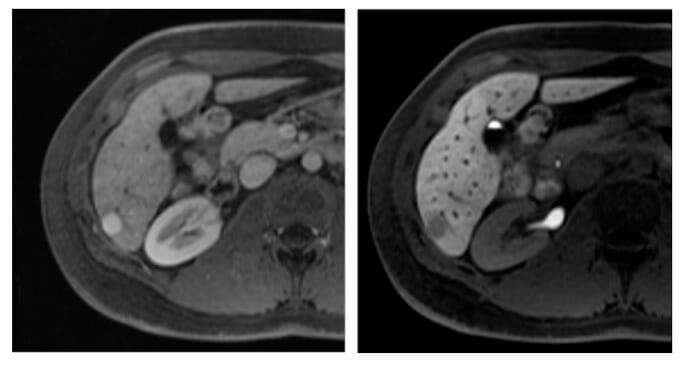
Carcinoma hepatocelular en la RM:
Imágenes axiales de RM del hígado obtenidas después de la administración intravenosa de un agente de contraste específico para hepatocitos en fases arterial (izquierda) y hepatobiliar (derecha), obtenidas 20 minutos después de la aplicación de contraste intravenoso.
Se observa una lesión hipervascular (imagen izquierda, flecha apuntando a la lesión). En la imagen de la fase hepatobiliar de la imagen de la derecha, la lesión (en la flecha) es hipointensa en relación con el hígado circundante debido a la reducción de la captación del agente de contraste (atribuida a la pérdida de hepatocitos funcionales en la lesión de carcinoma hepatocelular mal diferenciado).
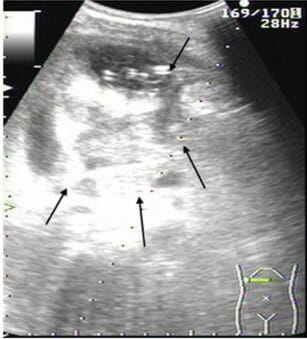
Ultrasonido abdominal de absceso hepático en lóbulo derecho del hígado:
Grandes (82 mm × 78 mm) y múltiples áreas de baja señal (flechas)
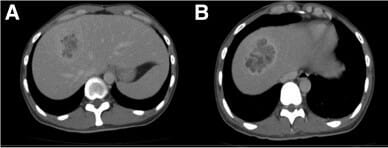
Imágenes de TC de un absceso hepático:
A: Lesión heterogénea quística en el segmento 8 del lóbulo hepático derecho, con un componente parcialmente licuado.
B: Imágenes axiales que muestran una lesión de borde realzado con hipoatenuación central, que apunta a un absceso
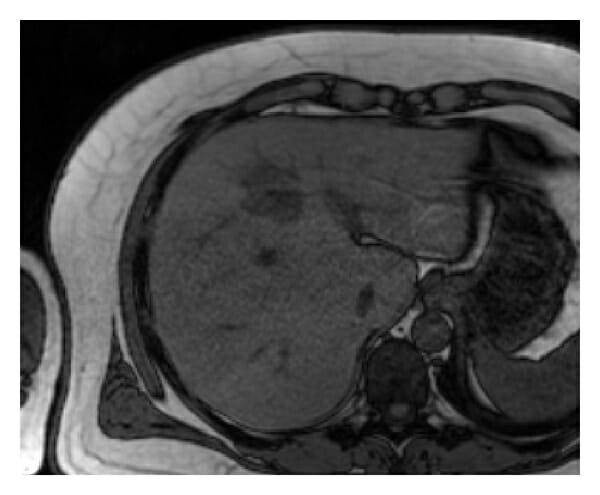
RM del hígado que muestra un absceso:
La masa nodular es hipointensa en la RM axial fuera de fase ponderada en T1.
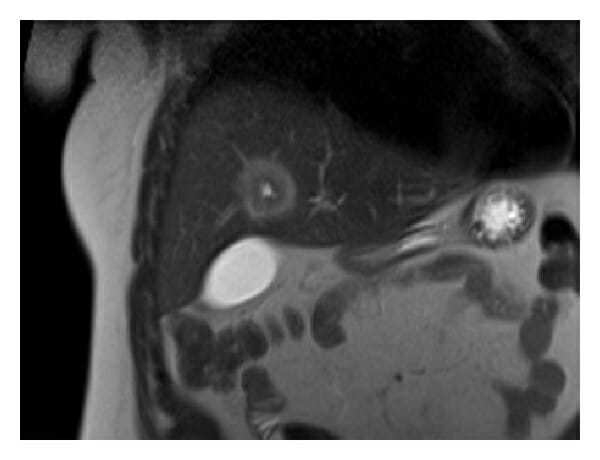
RM del hígado que muestra un absceso:
La lesión muestra una apariencia de diana en la RM coronal ponderada en T2, con el borde que tiene una intensidad de señal más alta que el componente central.
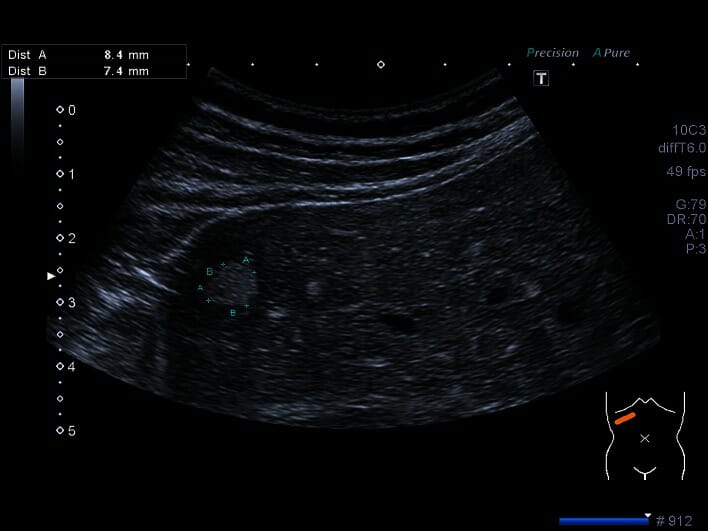
Imagen de ultrasonido que muestra una lesión hiperecogénica difusa que representa un hemangioma
Imagen: “Fig3” por Kaltenbach, T.E. et al. Licencia: CC BY 4.0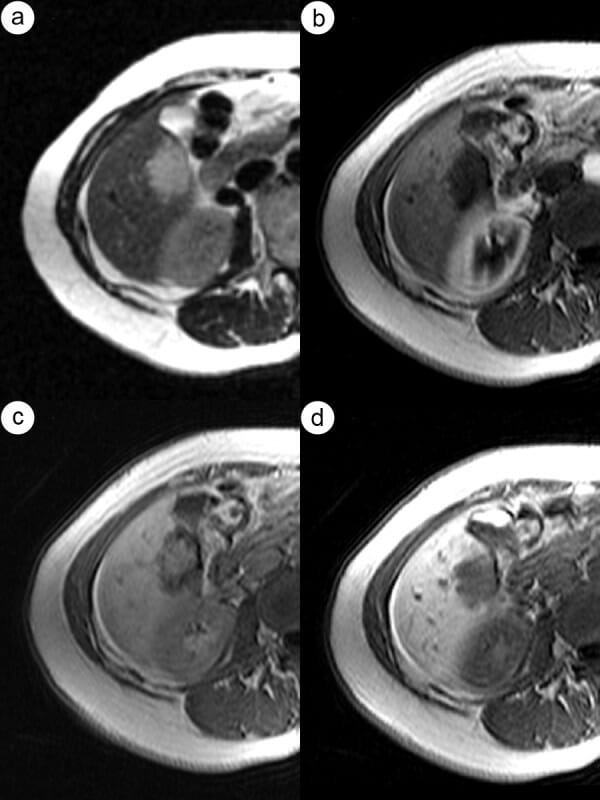
Imágenes de TC y RM de hemangioma hepático:
a: Imagen de TC de fase arterial hepática que visualiza un tipo de realce globular.
b: E patrón globular de realce también es visible en la imagen de fase arterial hepática en la MR.
c y d: Se puede observar un patrón de realce de relleno progresivo en la vena porta (c) y fases de equilibrio (d) de la RM.
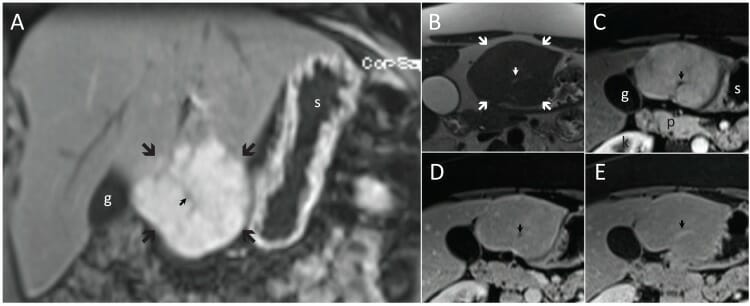
Hiperplasia nodular focal típica (flechas grandes) en planos coronal (A) y transversal (B-E). La hiperplasia nodular focal es ligeramente hiperintensa para el hígado en T2 (B) y realza significativamente en T1 en la fase arterial (A y C) seguido de isointensidad en las fases tardías (D y E).
Obsérvese la cicatriz central (flecha pequeña), que es hiperintensa en T2 (B) e hipointensa en T1 en las fases arterial (A y C) y portal venosa (D), e hiperintensa después de 5 minutos (E).
g: vesícula biliar (por sus sigla en inglés)
k: riñón derecho (por sus sigla en inglés)
p: páncreas
s: estómago (por sus sigla en inglés)
Imagen: “F4” por Albiin, N. Licencia: CC BY 2.5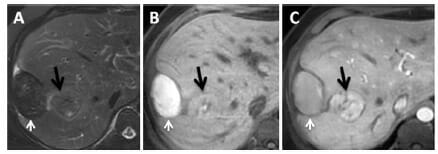
RM en un paciente con adenoma con hemorragia:
A: Una secuencia T2 con saturación grasa muestra un nódulo subcapsular hepático con señal hipointensa.
B: Una secuencia T1 precontraste revela una lesión con una señal hiperintensa, lo que indica productos de degradación de la hemoglobina
C: una secuencia T1 postcontraste en fase arterial enfatiza la lesión intrahepática, donde la flecha negra apunta a la lesión y la flecha blanca al hematoma.