El mediastino es la parte central de la cavidad torácica que contiene muchas estructuras vitales, como el corazón, los LOS Neisseria grandes vasos, la tráquea, el esófago torácico, los LOS Neisseria ganglios linfáticos, varios nervios, las cadenas simpáticas y la columna torácica. La patología mediastínica (e.g., masas) se puede observar en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum las radiografías convencionales como parte de la evaluación de los LOS Neisseria síntomas relacionados con el tórax, o se puede detectar de manera incidental. Para dilucidar las características de la anomalía mediastínica, se justifican más estudios de imagenología. Las modalidades adicionales comunes son TC y RM.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
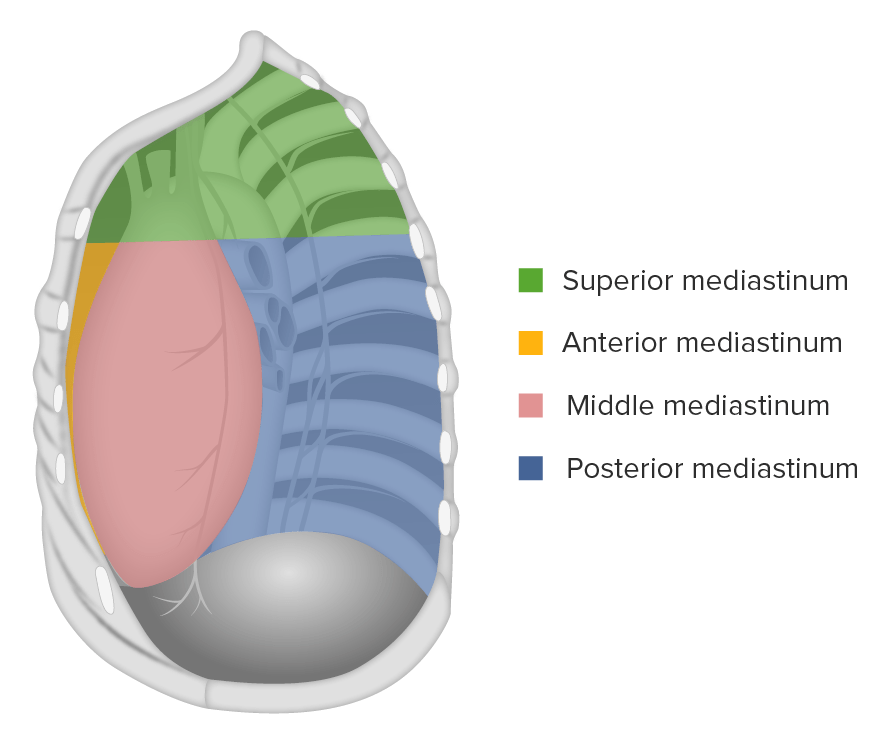
El mediastino:
subdividido en mediastino superior e inferior, que a su vez se divide en tercios anterior, medio y posterior.
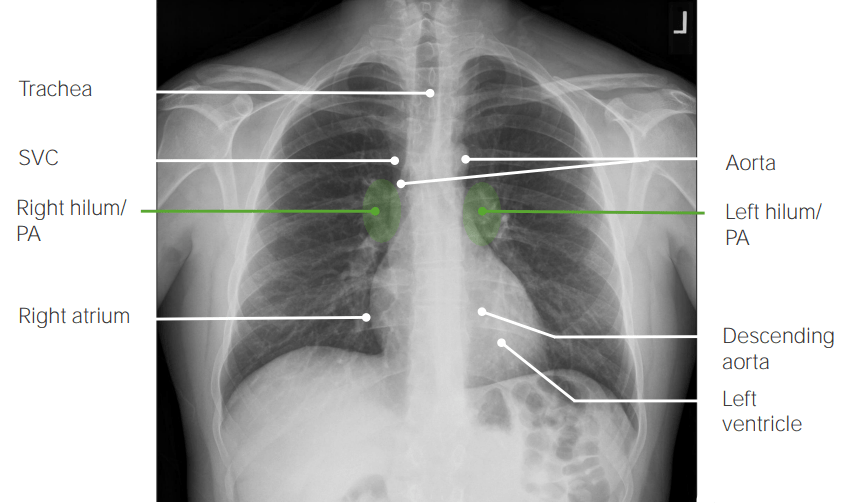
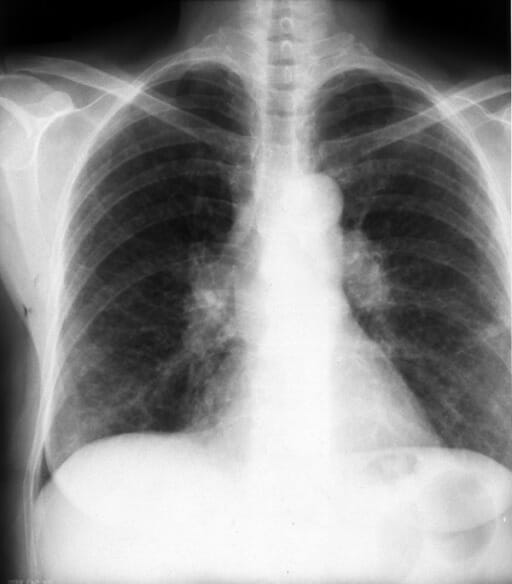
Vista posteroanterior (PA) en la radiografía de tórax que muestra hallazgos normales:
La tráquea es la línea media. La sombra de la vena cava superior está inmediatamente a la derecha del mediastino. Se ven los hilios derecho e izquierdo. Los bordes cardíacos, derecho (aurícula derecha) e izquierdo (ventrículo izquierdo), son claramente visibles. Son visibles porciones de la aorta ascendente y descendente.
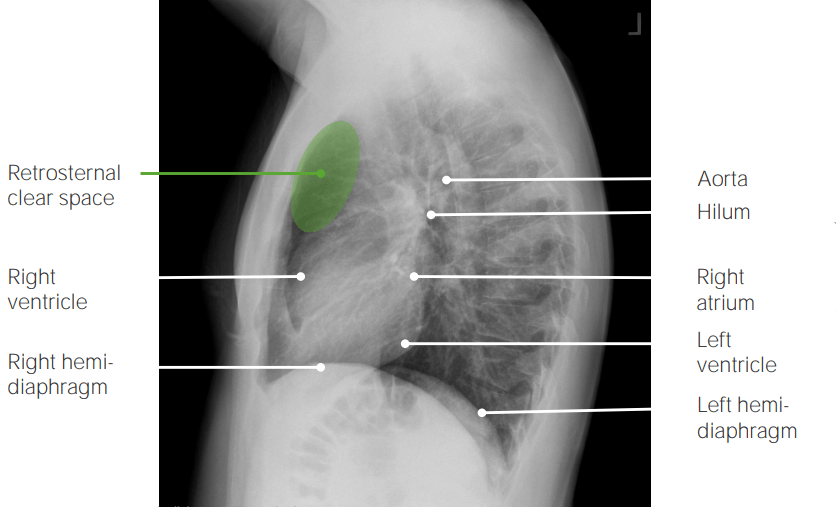
Vista lateral de la radiografía de tórax que muestra hallazgos normales:
El espacio retroesternal es claro. Los bordes del corazón, anterior (ventrículo derecho) y posterior (aurícula derecha), son claramente visibles.
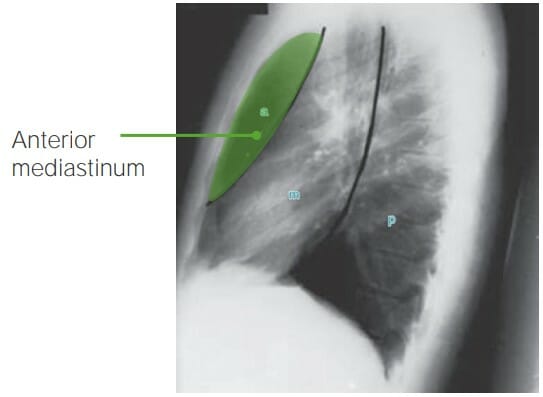
Vista lateral de la radiografía de tórax que ilustra el mediastino anterior (área entre el esternón y el borde anterior del corazón)
Imagen por Hetal Verma.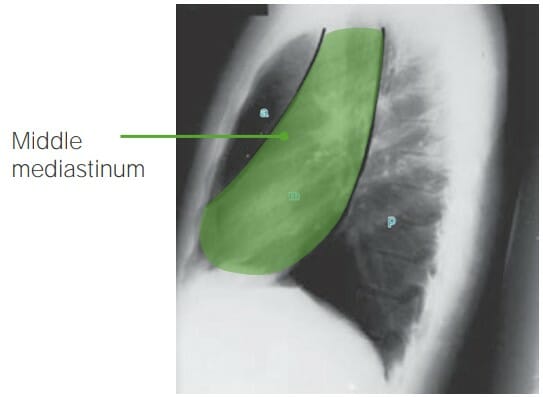
Vista lateral de la radiografía de tórax que ilustra el mediastino medio (área desde el pericardio anterior hasta la columna torácica)
Imagen por Hetal Verma.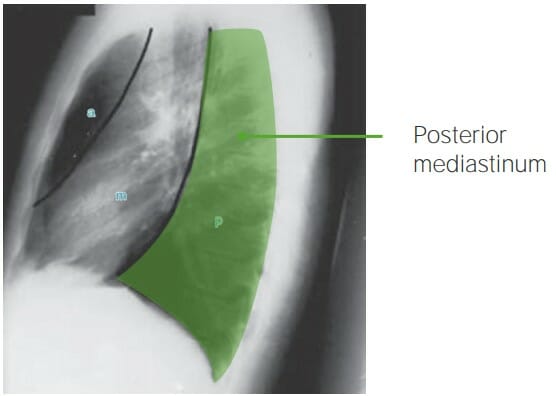
Vista lateral de la radiografía de tórax que ilustra el mediastino posterior (área desde la columna torácica anterior hasta los cuerpos vertebrales)
Imagen por Hetal Verma.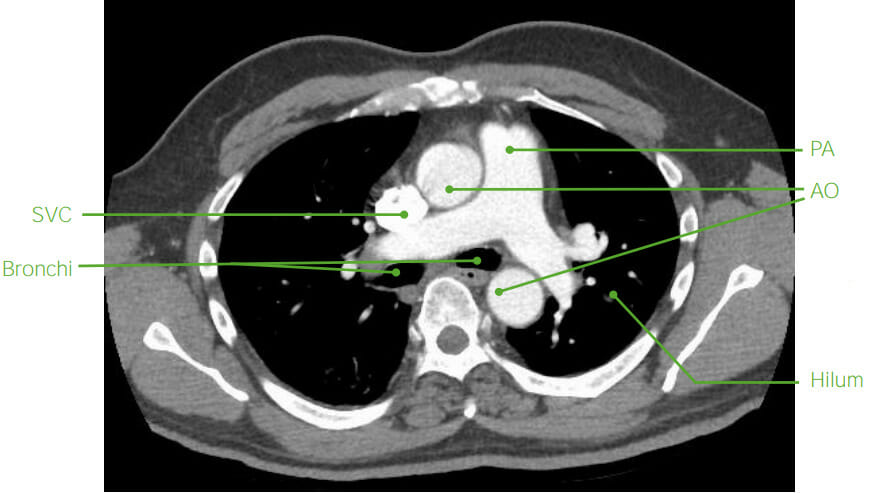
Anatomía mediastínica axial en TC (post-contraste):
los vasos sanguíneos (SVC: vena cava superior; PA: arteria pulmonar, AO: aorta) se llenan de contraste. Los bronquios están llenos de aire. Se observa que las estructuras óseas son brillantes en la TC.
RM
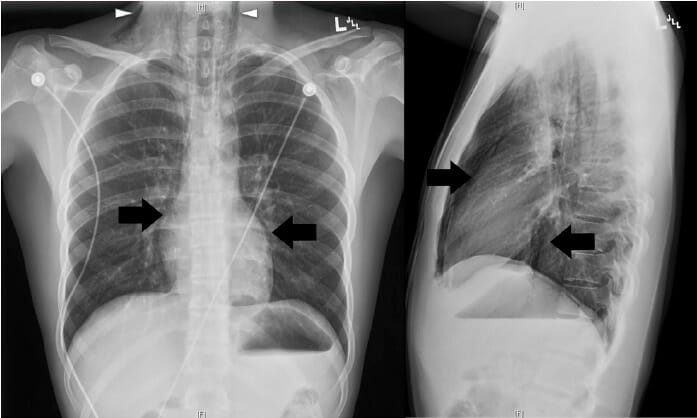
Radiografía de tórax, vistas posteroanterior (PA) y lateral:
El neumomediastino se confirmó en la radiografía de tórax, con base en la presencia de aire disecante a lo largo del mediastino (flechas) y en la región inferior del cuello bilateralmente (puntas de flecha).
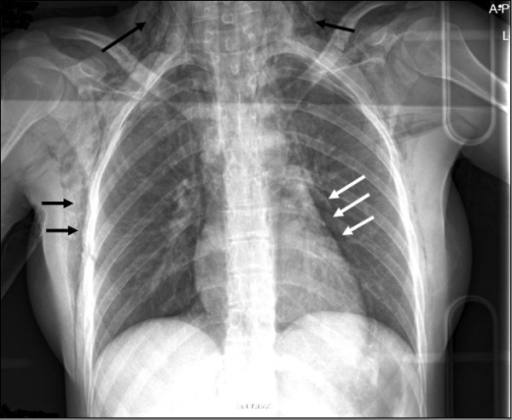
Radiografía de tórax que muestra enfisema subcutáneo (flechas negras) y neumomediastino (flechas blancas) en un individuo con ruptura esofágica
Imagen: “F1” por van Heijl, M., Saltzherr, TP, van Berge Henegouwen, MI, Goslings, JC Licencia: CC BY 2.0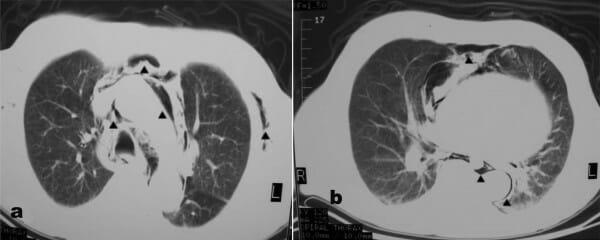
TC de tórax que demuestra enfisema subcutáneo y neumomediastino (flechas)
Imagen: “F2” por Alexiou, K., Sakellaridis, T., Sikalias, N., Karanikas, I., Economou, N., Antsaklis, G. Licencia: CC BY 2.0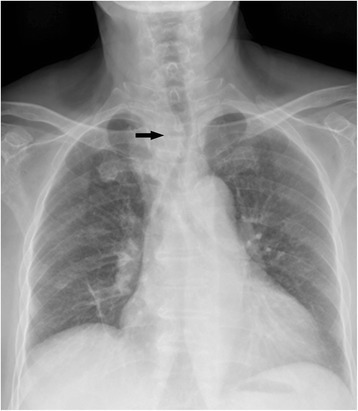
La radiografía de tórax que ilustra la tráquea desviada hacia la izquierda en un individuo al que se le diagnosticó cáncer de tiroides subesternal ectópico primario
Imagen: “Fig1” por Ma, RM, Lv, L., Zheng, SR, You, J., Huang, DP, Guo, GL Licencia: CC BY 4.0
Una TC que muestra una lesión de 5,9 cm × 4,3 cm que afecta el lóbulo izquierdo de la tiroides y el istmo que encierra la arteria carótida común izquierda y la arteria subclavia y se extiende hacia el espacio carotídeo izquierdo y el mediastino anterosuperior
Imagen: “fig2” por Ghosh, S., Rao, PB, Sarkar, S., Kotne, S., Turlapati, SP, Mishra, A. Licencia: CC BY 3.0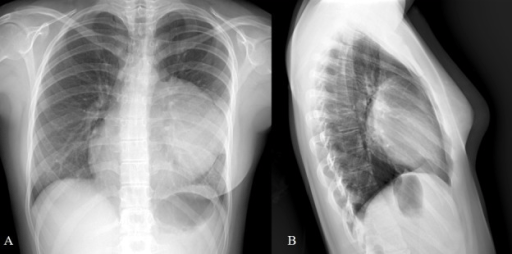
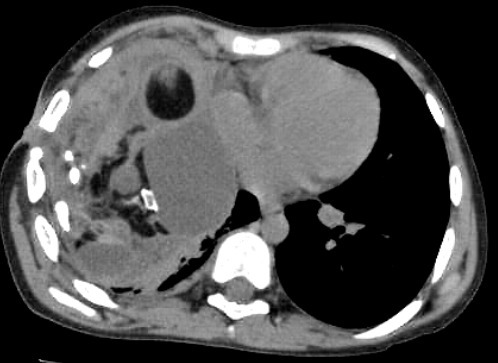
Una TC del tórax muestra lesiones calcificadas en un quiste en el mediastino, lo que sugiere hueso y dientes en la masa.
Imagen: “F2” por Reddy, KB, Murthy, GR, Ks, S. Licencia: CC BY 3.0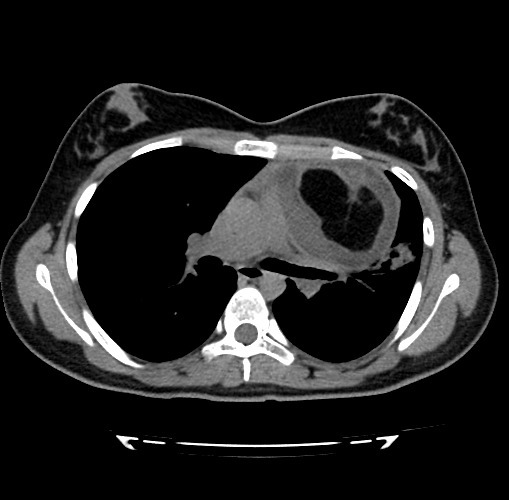
TC axial que muestra una masa quística multiseptada bien delimitada compatible con teratoma mediastínico
Imagen: “F2” por Vaccaro, A., Vierucci, F., Dini, F., Ruggieri, S., Crespin, L., Matteucci, L., Domenici, R. Licencia: CC BY 3.0Crespin, L., Matteucci, L., Domenici, R. License: CC BY 3.0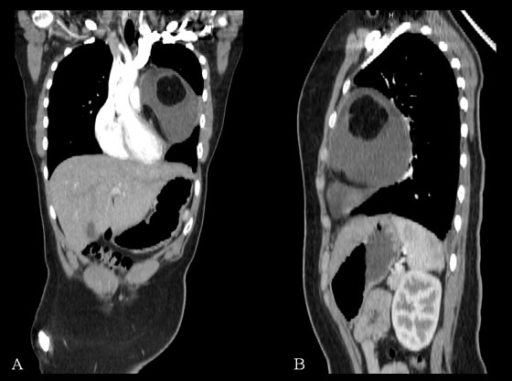
Vistas coronal (A) y sagital (B) de TC de teratoma quístico mediastínico. La masa parece comprimir las estructuras adyacentes sin invasión. Una calcificación es evidente en la reconstrucción coronal.
Imagen: “F3” por Vaccaro, A., Vierucci, F., Dini, F., Ruggieri, S., Crespin, L., Matteucci, L., Domenici, R. Licencia: CC BY 3.0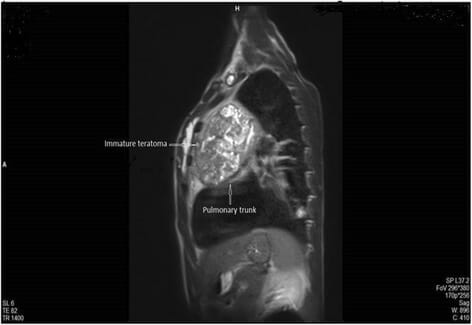
RM sagital ponderada en T2 que muestra una lesión quística multilocular que comprime el tronco pulmonar. La biopsia demostró que la masa era un teratoma inmaduro.
Imagen: “Fig. 4” por Koçinaj, D., Krasniqi, X. y Bakalli, A. Licencia: CC BY 4.0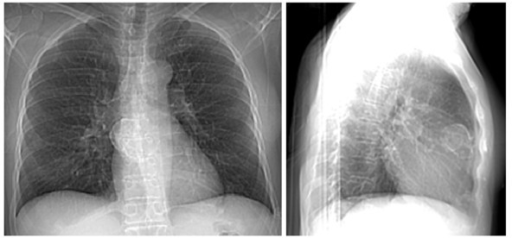
Imagen (radiografía de tórax):
La radiografía de tórax frontal muestra una lesión calcificada en el borde (panel izquierdo).
La radiografía de tórax lateral confirma que la masa calcificada del borde reside dentro del mediastino anterior (panel derecho).
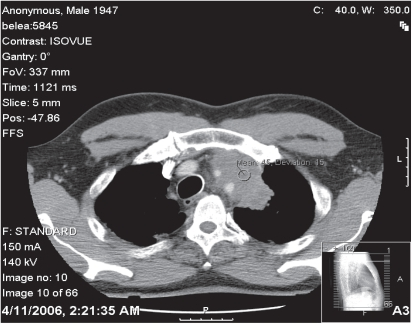
TC de tórax que muestra una masa, que representa un carcinoma tímico, con afectación del arco aórtico
Imagen: “f2-cmo-2-2008-477” por Kobrinsky, B., Khaykis, I., Hill, D., Petrovic, L., Yee, H., Chandra, A., Diehl, DL Licencia: CC POR 3.0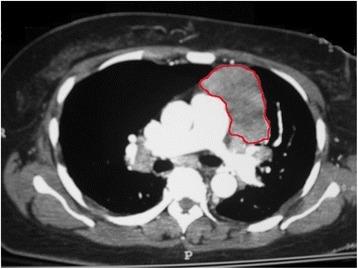
TC de tórax con contraste que muestra una gran masa mediastínica delineada en rojo y que posteriormente se descubrió que era un timoma
Imagen: “Fig2” por Downes, KM, Tarasewicz, D., Weisberg, LJ, Cunningham, ET Licencia: CC BY 4.0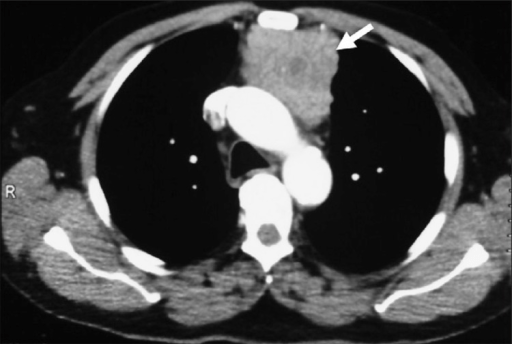
Una TC de tórax con contraste muestra una masa de tejido blando (flecha) en el mediastino anterior, que luego se confirmó que era un timoma.
Imagen: “f3” por Aydın, F., Sürer Budak, E., Dertsiz, L., Belgi, A., Arslan, G., Güngör, F. Licencia: CC BY 2.5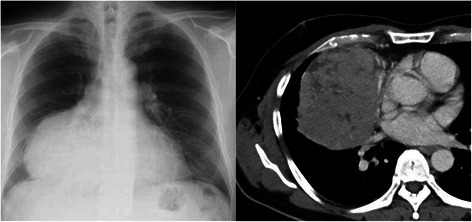
Una radiografía de tórax muestra una masa gigante en el campo pulmonar inferior derecho (izquierda). La TC de tórax muestra una masa de 13 x 10 cm de diámetro, en contacto con la vena pulmonar inferior derecha (derecha). Se confirmó que el tumor resecado era un timoma.
Imagen: “Fig1” por Saito, T., Makino, T., Hata, Y., Koezuka, S., Otsuka, H., Isobe, K., Tochigi, N., Shibuya, K., Homma, S. , Iyoda, A. Licencia: CC BY 4.0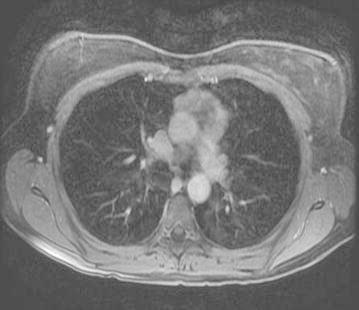
Imagen en T2 con contraste axial que muestra una masa en el mediastino anterior que representa un timoma
Imagen: “Fig4” por Bano, G., Sennik, D., Kenchaiah, M., Kyaw, Y., Snape, K., Tripathi, V., Wilson, P., Vlahos, I., Hunt, I. , Hodgson, S. Licencia: CC BY 4.0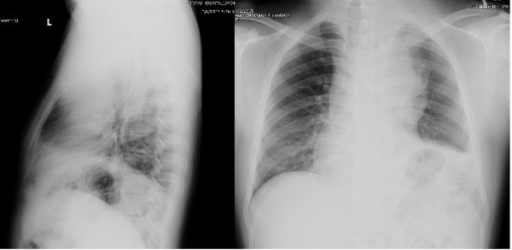
Las radiografías de tórax de un individuo con linfoma de células B grandes revelaron una gran masa en el mediastino anterior.
Observe el mediastino ensanchado (derecha) y el espacio retroesternal oscurecido en la vista lateral (izquierda)
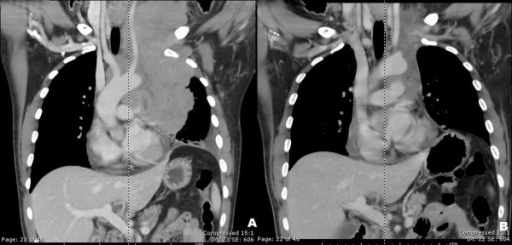
Una TC de cuello y tórax mostró una gran masa lobulada con realce heterogéneo con necrosis central en el mediastino anterior y medio con algunas partes que se extendían hacia el cuello anterior izquierdo (A).
Se observó una mejora significativa de la afectación linfomatosa en la región prevascular después de 8 ciclos de quimioterapia CHOP (B).
CHOP: ciclofosfamida (citoxan), hidroxirrubicina (adriamicina), oncovin (vincristina), prednisona
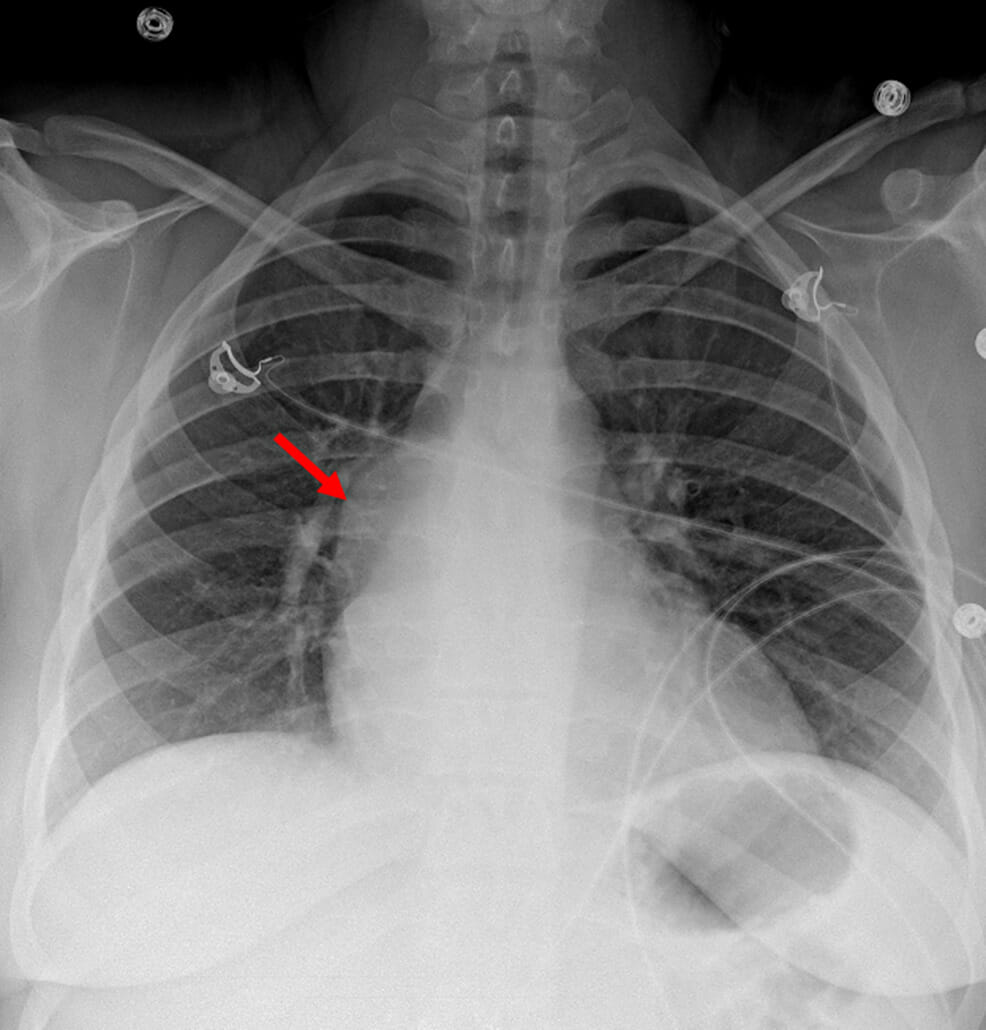
Radiografía de tórax que muestra un abultamiento en el contorno mediastínico derecho (flecha roja), que representa un quiste broncogénico mediastínico
Imagen: “Figure 1” por Ramireddy, K., Golamari, RR, Minupuri, A., et al. Licencia: CC BY 4.0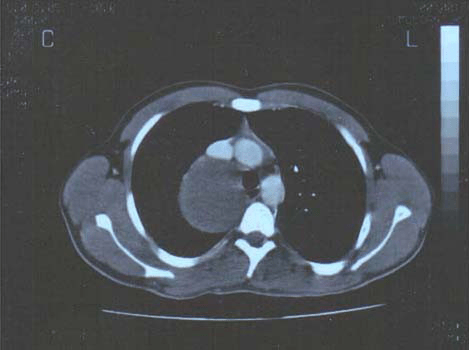
Una TC posterior a la inyección de medio de contraste revela una enorme lesión compresiva de baja densidad (quiste) en el mediastino posteromedial.
Imagen: “F1” por Kouerinis, IA, Zografos, GC, et al. Licencia: CC BY 2.0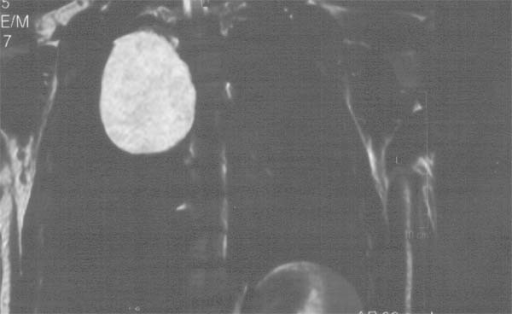
Radiografía de tórax posteroanterior (PA) que muestra linfadenopatía hiliar bilateral junto con densidades pulmonares intersticiales bilaterales más bajas (sarcoidosis)
Imagen: “F1” por Papaetis, GS, Pefanis, A., et al. Licencia: CC BY 2.0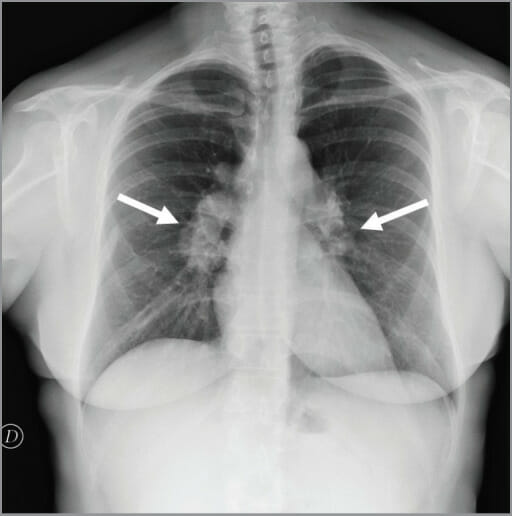
Linfadenopatía hiliar (flechas) vista en la radiografía de tórax
Imagen: “figure1” por Conte, G., Zugni, F., et al. Licencia: CC BY 3.0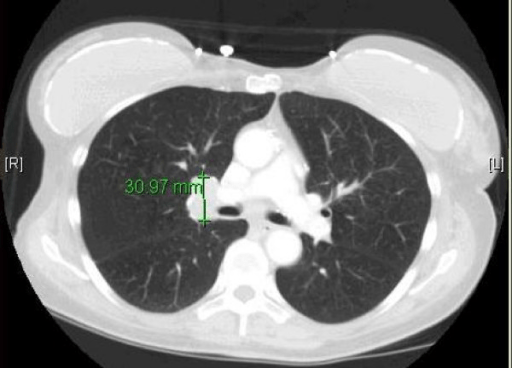
Una TC que demuestra linfadenopatía hiliar unilateral (derecha) en un individuo con cáncer de pulmón de células pequeñas
Imagen: “F1” por Hudhud, KH, Masood, A., Oh, Y., Hegazi, A. Licencia: CC BY 2.0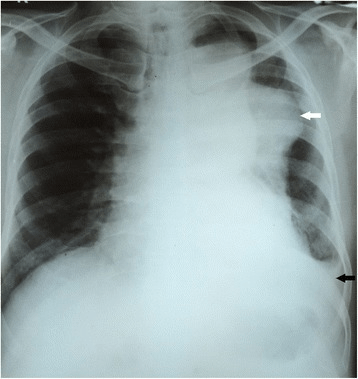
Radiografía de tórax que muestra una masa mediastínica del lado izquierdo (aneurisma de la aorta torácica):
Una lesión homogénea, de partes blandas, densa y bien definida en el pulmón izquierdo (flecha blanca) que se extiende desde el botón aórtico hasta el hemidiafragma izquierdo.
Su margen medial se fusiona con el mediastino y hay un derrame pleural leve a moderado del lado izquierdo (flecha negra).
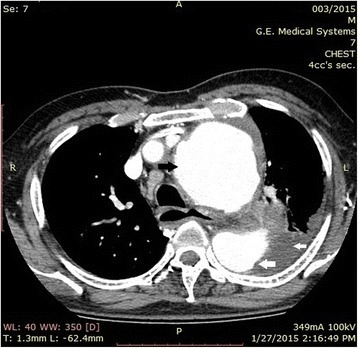
Una aortografía por TC que muestra una porción dilatada de la aorta compatible con un aneurisma aórtico ascendente (flecha negra) y descendente (flecha blanca grande). También se observa un derrame pleural del lado izquierdo (pequeña flecha blanca).
Imagen: “Fig2” por Pathirana, U., Kularatne, S., Handagala, S., Ranasinghe, G., Samarasinghe, R. Licencia: CC BY 4.0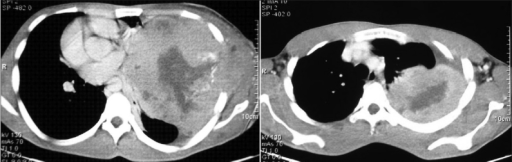
Una TC del tórax que muestra una masa heterogénea, grande y bien definida en el hemitórax izquierdo (schwannoma torácico):
La masa se extiende periféricamente hasta la pleura y la pared torácica y muestra infiltraciones en el tejido subcutáneo.
La masa también contiene áreas de baja atenuación, correspondientes a hemorragia y necrosis, y se extiende hasta la pleura y la pared torácica. Hay un desplazamiento del mediastino hacia el lado derecho.
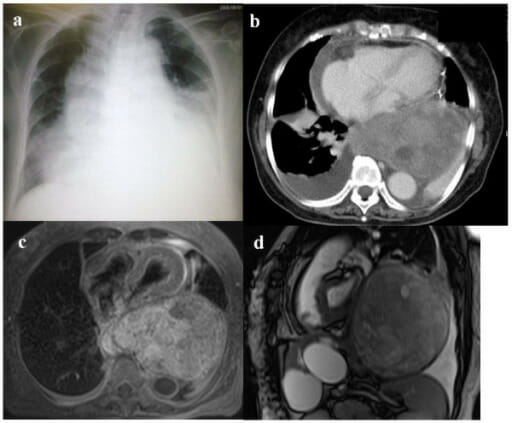
(a) La radiografía de tórax muestra derrame pleural bilateral, mediastino, ensanchamiento y agrandamiento cardíaco.
(b) Imagen de TC de tórax con contraste (ventana de pulmón) que muestra un tumor gigante en el mediastino posterior, derrame pericárdico y derrame pleural bilateral.
(c) El individuo se sometió a drenaje pericárdico, y una RM transversal ponderada en T1 tomada después muestra un tumor encapsulante gigante en el mediastino posterior que comprime el corazón.
(d) En una imagen de RM sagital con precesión libre en estado estacionario verdadero, se observa un tumor que ocupa la mayor parte de la cavidad torácica izquierda.