El hueso es el principal lugar de almacenamiento de calcio en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el cuerpo; por tanto, el metabolismo óseo desempeña un papel fundamental en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el mantenimiento de los LOS Neisseria niveles normales de calcio. El metabolismo óseo (y, por tanto, los LOS Neisseria niveles de calcio) está regulado principalmente por 3 hormonas: la calcitonina, la hormona paratiroidea (PTH, por sus siglas en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum inglés) y la vitamina D. La calcitonina estimula la deposición ósea, disminuyendo el calcio sérico, mientras que la PTH actúa para estimular la resorción ósea, aumentando el calcio sérico. Los LOS Neisseria niveles de vitamina D están regulados por la PTH. La vitamina D aumenta la absorción de calcio desde el intestino y estimula la deposición ósea. Las anomalías en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el metabolismo óseo pueden dar lugar a cuadros clínicos como osteoporosis Osteoporosis Osteoporosis refers to a decrease in bone mass and density leading to an increased number of fractures. There are 2 forms of osteoporosis: primary, which is commonly postmenopausal or senile; and secondary, which is a manifestation of immobilization, underlying medical disorders, or long-term use of certain medications. Osteoporosis, osteomalacia Osteomalacia Disorder caused by an interruption of the mineralization of organic bone matrix leading to bone softening, bone pain, and weakness. It is the adult form of rickets resulting from disruption of vitamin d; phosphorus; or calcium homeostasis. Osteomalacia and Rickets, enfermedad ósea de Paget y la hipo o hipercalcemia.
Last updated: May 8, 2022
Los LOS Neisseria 3 principales reguladores del metabolismo óseo son:
El calcio tiene muchas funciones importantes en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el organismo y sus niveles deben estar muy regulados para mantenerse en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum torno a los LOS Neisseria 10 mg/dL. El calcio es el mineral más abundante en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el organismo.
La hormona paratiroidea es el regulador más importante de la homeostasis Homeostasis The processes whereby the internal environment of an organism tends to remain balanced and stable. Cell Injury and Death del calcio.
La función principal de la PTH es ↑ los LOS Neisseria niveles séricos de Ca CA Condylomata acuminata are a clinical manifestation of genital HPV infection. Condylomata acuminata are described as raised, pearly, flesh-colored, papular, cauliflower-like lesions seen in the anogenital region that may cause itching, pain, or bleeding. Condylomata Acuminata (Genital Warts)2+. Los LOS Neisseria principales efectos de la PTH son en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria huesos, riñones y tracto gastrointestinal.
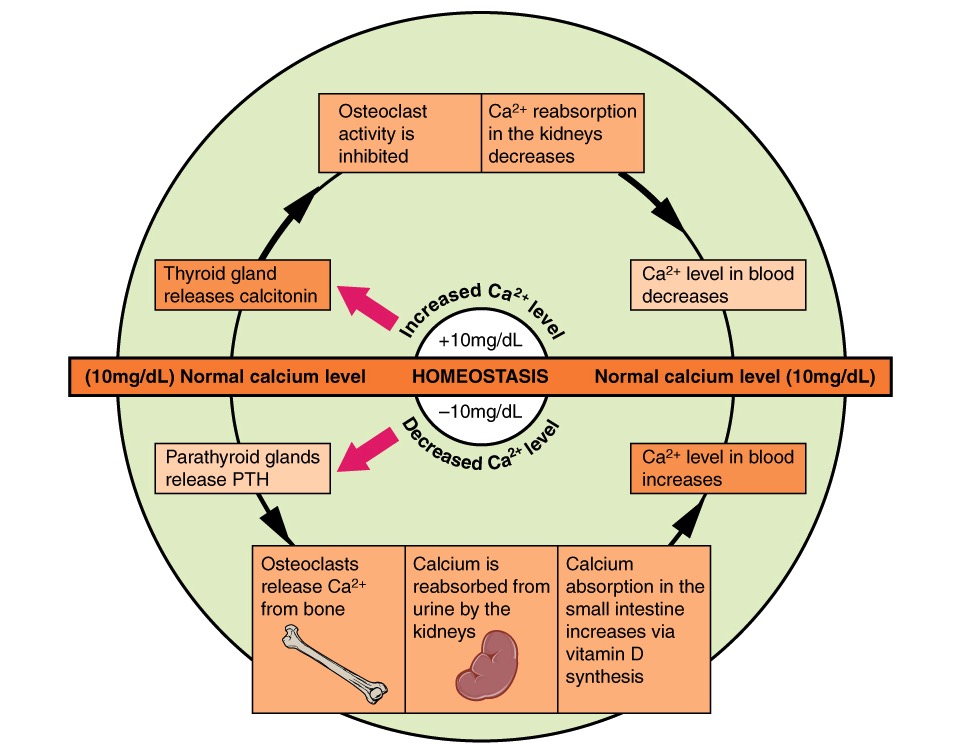
Vías en la homeostasis del calcio que demuestran cómo la hormona paratiroidea (PTH) y la calcitonina actúan para mantener los niveles normales de calcio:
Aunque es una vitamina, la vitamina D actúa más como una hormona que como una verdadera vitamina. La vitamina D3 se sintetiza en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la piel de todos los LOS Neisseria vertebrados cuando se exponen a la luz solar.
Los LOS Neisseria efectos más importantes de la vitamina D están relacionados con la regulación del calcio y el fosfato.
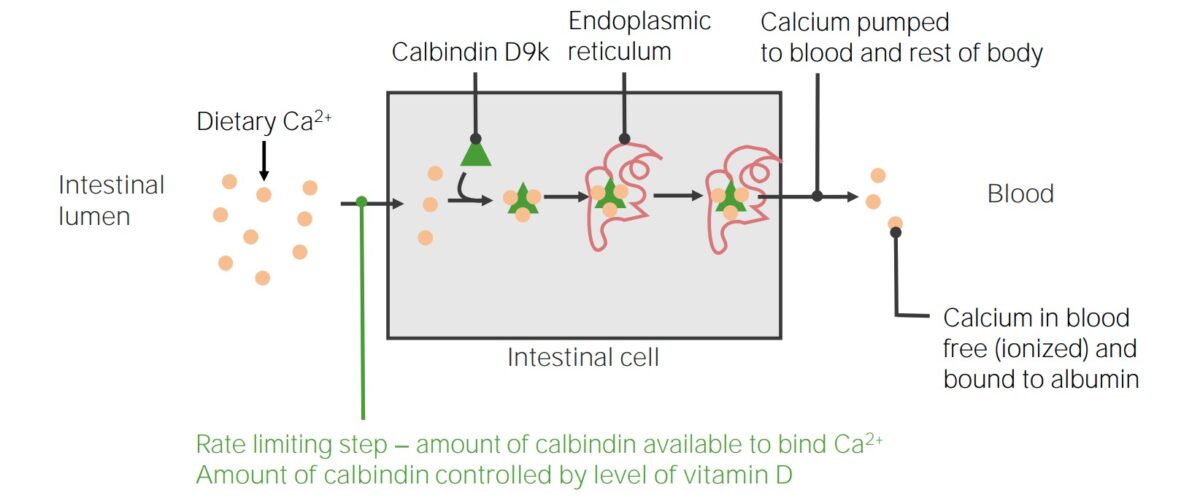
La absorción del calcio de la dieta, que requiere la calbindina D9k: La vitamina D aumenta la producción de la proteína intracelular de fijación del calcio, calbindina D9k. La cantidad de calbindina en los enterocitos es el paso que limita la velocidad de absorción del calcio. Debido a la toxicidad del calcio libre intracelular, todo el calcio absorbido en los intestinos debe ser ligado inmediatamente por las calbindinas, que luego transportan el calcio al retículo endoplásmico (RE), donde se almacena hasta que se libera directamente en la sangre.
La vitamina D se sintetiza a partir del colesterol al AL Amyloidosis ser estimulada por la exposición a la luz ultravioleta (UV). La vitamina D debe someterse a 2 reacciones de hidroxilación para ser activa.
Vitamina D3: 1,25-dihidroxi-vitamina D3:
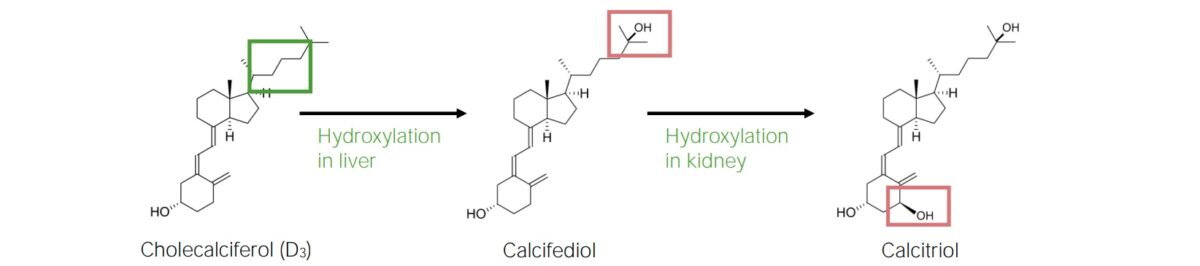
Vía biosintética del calcitriol
Imagen por Lecturio.Otros factores que ayudan a regular Regular Insulin el metabolismo óseo son
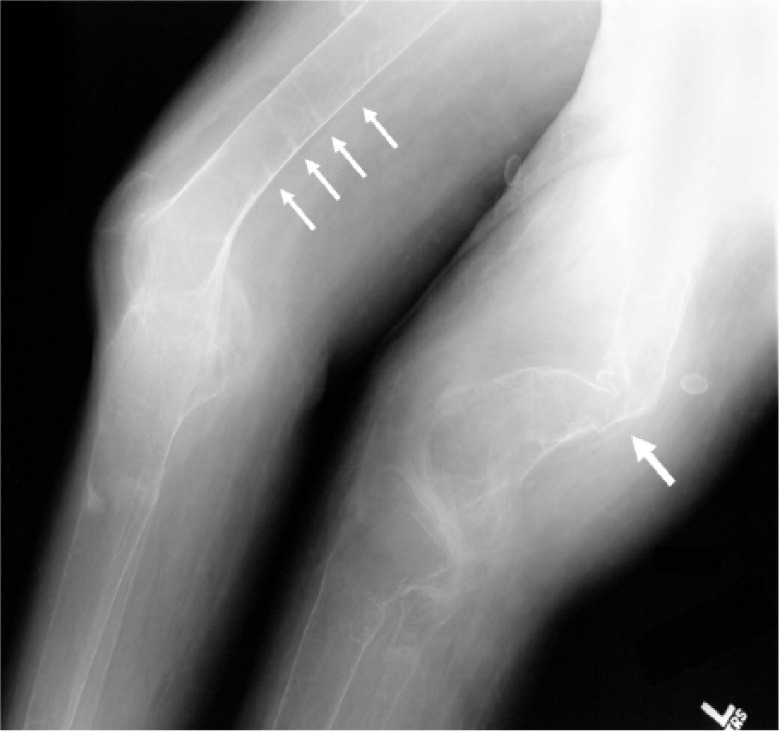
Osteomalacia. Una radiografía de los fémures distales muestra evidencias de huesos muy malformados secundarios a una osteomalacia severa (flecha grande), así como varias pseudofracturas (flechas pequeñas).
Imagen: “Severe osteomalacia” por Gamache L, Burge MR. Licencia: CC BY 3.0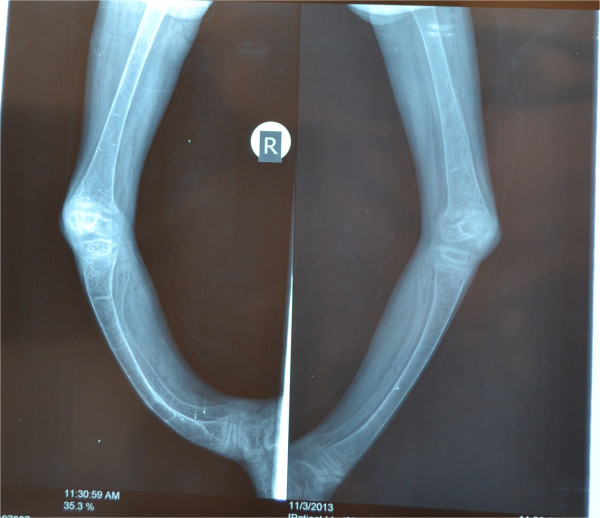
Raquitismo. La radiografía de ambos miembros inferiores muestra un arqueo severo de las piernas y densas líneas transversales en la tibia que sugieren raquitismo.
Imagen: “Severe rickets in a young girl caused by celiac disease: the tragedy of delayed diagnosis: a case report” por Al-Sharafi BA, Al-Imad SA, Shamshair AM, Al-Faqeeh DH. Licencia: CC BY 4.0