Las glándulas salivales son glándulas exocrinas localizadas dentro y alrededor de la cavidad oral. Estas glándulas son responsables de secretar saliva Saliva The clear, viscous fluid secreted by the salivary glands and mucous glands of the mouth. It contains mucins, water, organic salts, and ptyalin. Salivary Glands: Anatomy en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la boca, lo que ayuda a la digestión. La saliva Saliva The clear, viscous fluid secreted by the salivary glands and mucous glands of the mouth. It contains mucins, water, organic salts, and ptyalin. Salivary Glands: Anatomy ayuda a mantener lubricada la mucosa oral y brinda protección antimicrobiana. Hay 3 glándulas salivales pares mayores: las glándulas sublinguales, submandibulares y parótidas. También hay cientos de glándulas salivales menores que se encuentran en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum parches alrededor de la cavidad oral.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Los LOS Neisseria 3 pares de glándulas salivales mayores son las glándulas parótidas, submandibulares y sublinguales.
Producción de saliva Saliva The clear, viscous fluid secreted by the salivary glands and mucous glands of the mouth. It contains mucins, water, organic salts, and ptyalin. Salivary Glands: Anatomy, que es importante en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum:
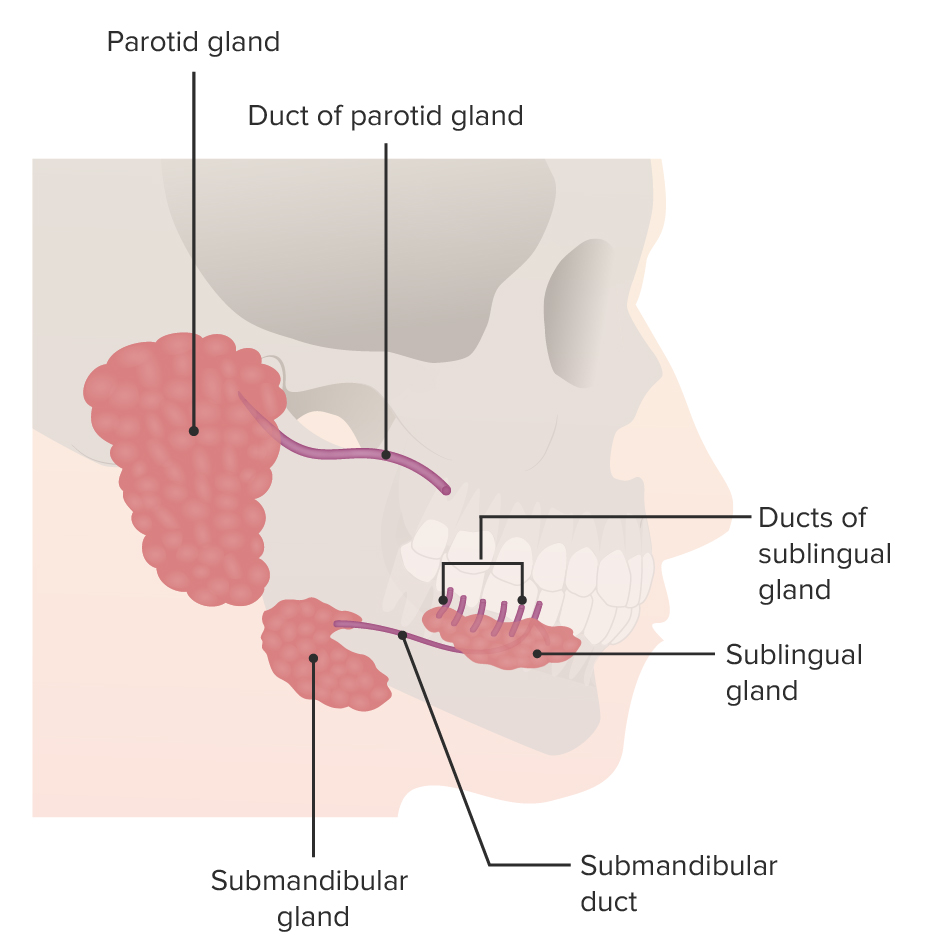
Descripción general de las glándulas salivales y los puntos de referencia anatómicos circundantes
Imagen por Lecturio.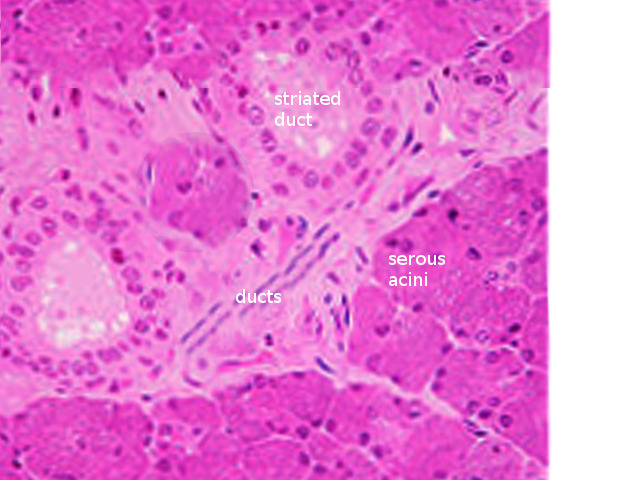
Histología de las glándulas salivales
Imagen: “Salivary gland histology” por S. Bhimji MD. Licencia: CC BY 4.0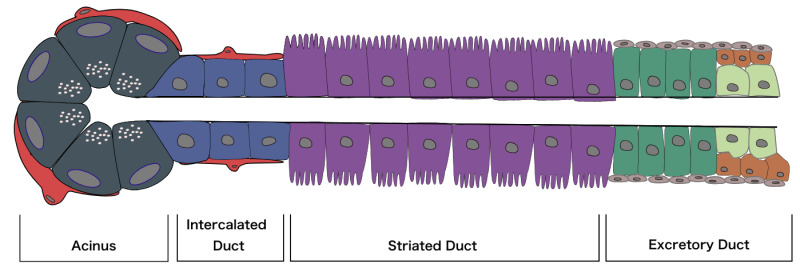
Diagrama de un acino, así como los 3 tipos principales de conductos a través de los cuales se secreta la saliva
Imagen: “Diagram of an acinus, as well as the three main types of duct through which the salivary fluid is secreted” por Mousa Ghannam. Licencia: CC BY 4.0| Parótida | Submandibular | Sublingual | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Localización | Anterior a la oreja | Inferior y posterior a la mandíbula | Inferior a la lengua |
| Desarrollo | Ectodermo | Endodermo | Endodermo |
| Tamaño | Más grande (15–30 g) | Más pequeña (10–20 g) | La más pequeña (3–4 g) |
| Forma | Piramidal | En EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum forma de J | En EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum forma de almendra |
| Conducto y lugar de apertura | Conducto de Stensen: abre enfrente del 2do molar maxilar |
Conducto de Wharton: abre en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la papila sublingual (lateral a cada lado del frenillo de la lengua) |
Serie de conductos: piso de la cavidad oral en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el pliegue sublingual |
| Inervación | Nervio petroso menor | Cuerda del tímpano | Cuerda del tímpano |
| Tipo de secreción | Serosa | Serosa y mucinosa | Mucinosa (principalmente) y serosa |
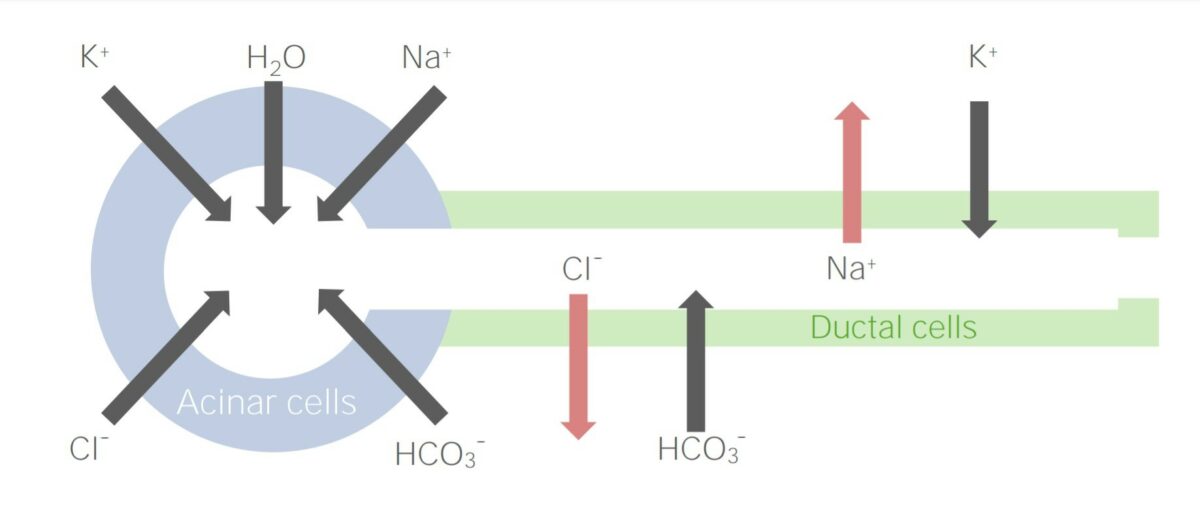
Movimiento de iones durante la producción de saliva y su transporte a través del conducto salival
Imagen por Lecturio.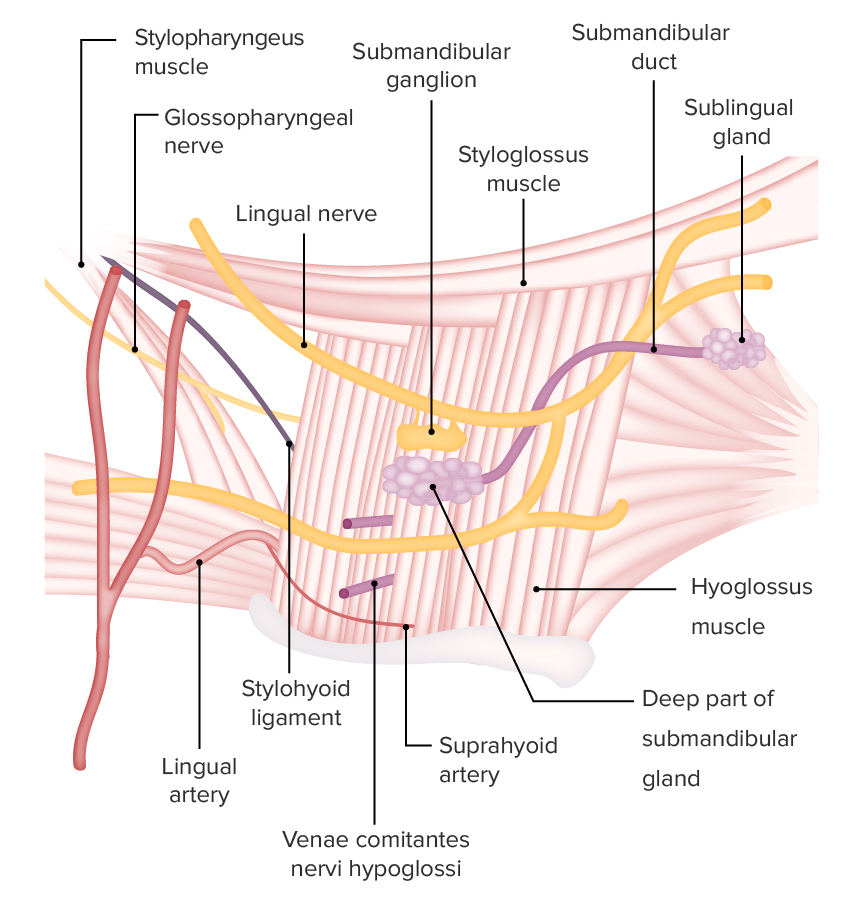
Glándula submandibular y estructuras de irrigación e inervación asociadas
Imagen por Lecturio.Localizada en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la fosa retromandibular, la glándula parótida:
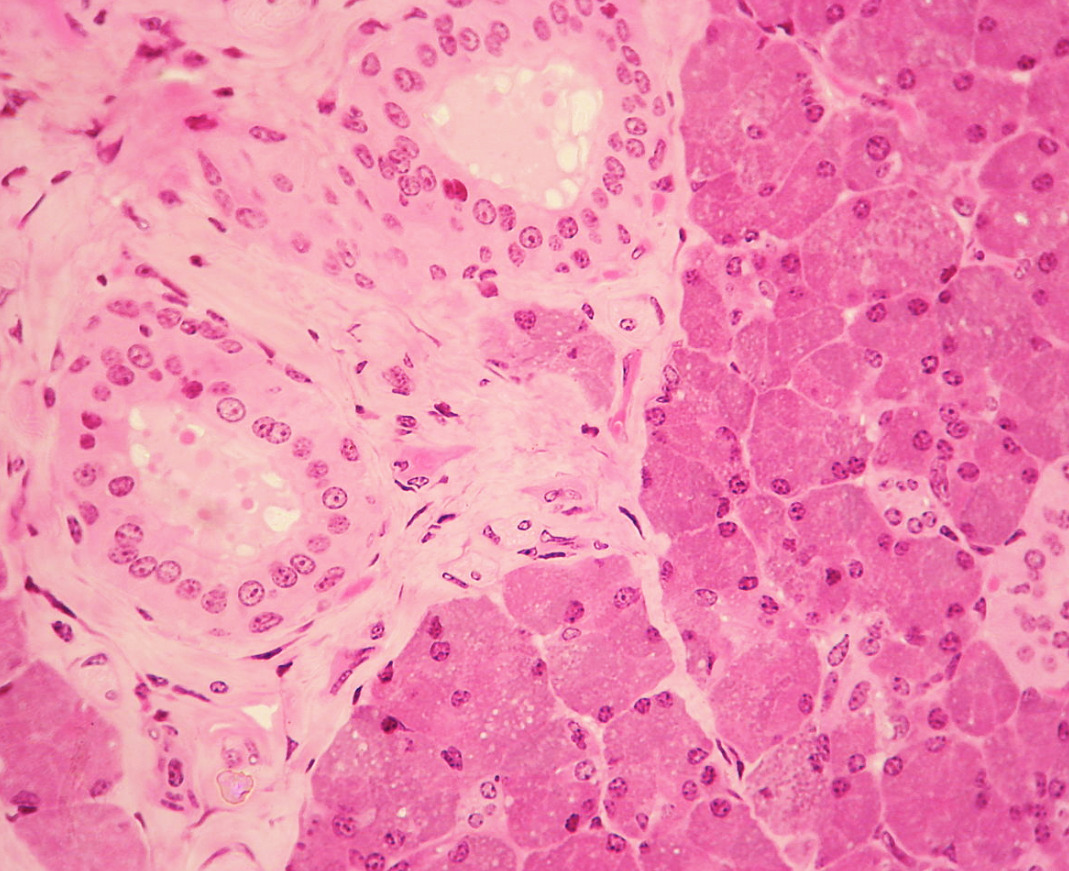
Histología de la glándula parótida (acinos serosos)
Imagen: “Histology of the parotid gland” por Wbensmith. Licencia: CC BY 3.0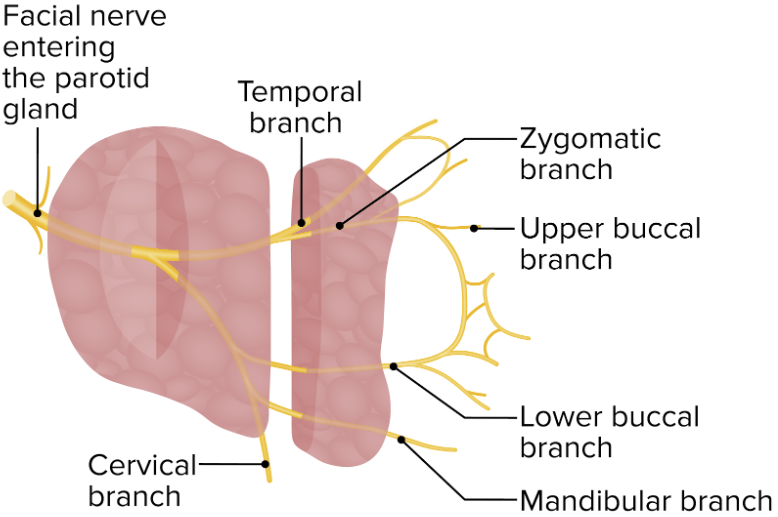
El nervio facial y sus ramas atraviesan la glándula parótida.
Imagen por Lecturio.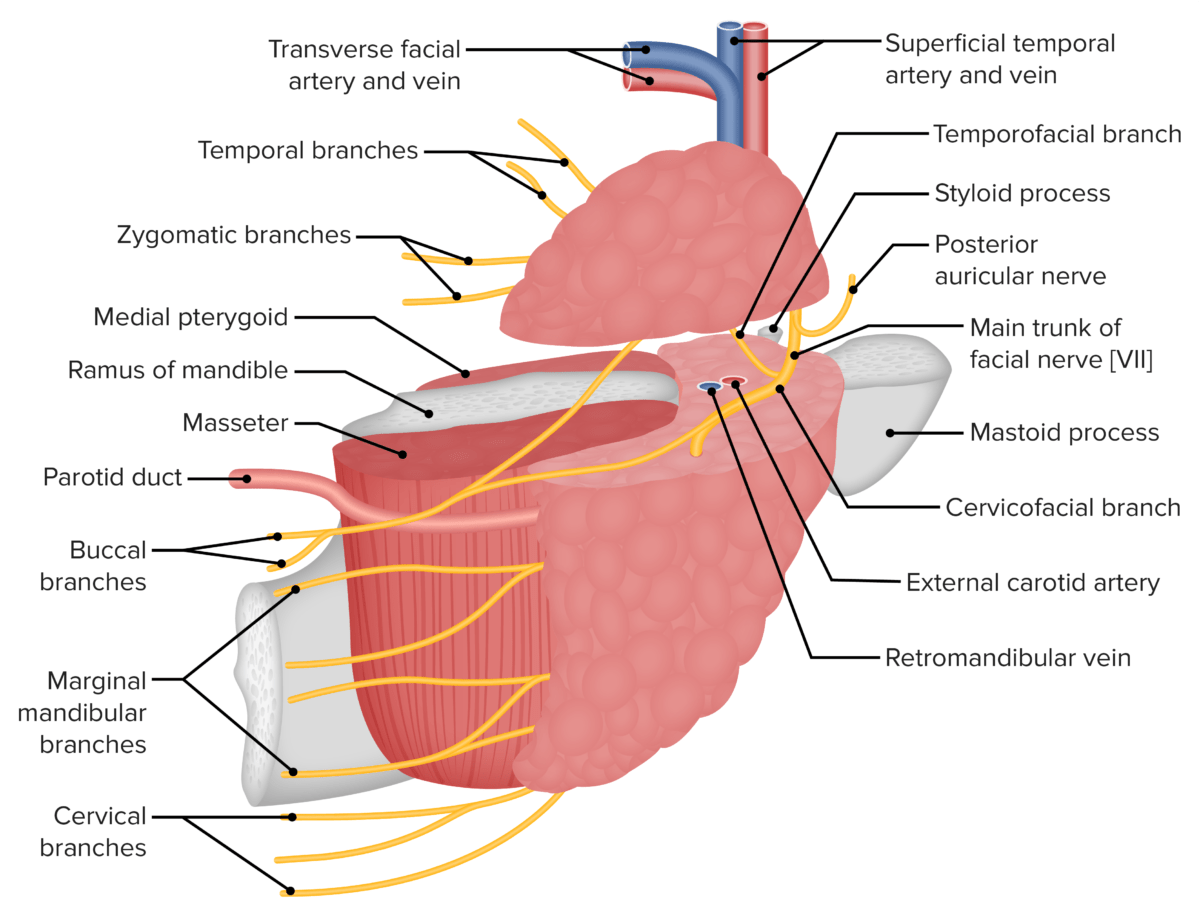
El suministro vascular de la glándula parótida en relación con el nervio facial y sus ramas
Imagen por Lecturio.