La foliculitis infecciosa es una afección cutánea común caracterizada por la inflamación de los LOS Neisseria folículos pilosos causada por un agente infeccioso (bacteriano, fúngico, viral o parasitario). Staphylococcus aureus Staphylococcus aureus Potentially pathogenic bacteria found in nasal membranes, skin, hair follicles, and perineum of warm-blooded animals. They may cause a wide range of infections and intoxications. Brain Abscess es el agente causal más común. El diagnóstico es clínico y las presentaciones incluyen prurito, pústulas foliculares y pápulas eritematosas. El tratamiento es generalmente de soporte, pero en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum casos graves puede ser necesaria la terapia con antibióticos tópicos u orales.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
La foliculitis infecciosa ocurre debido a la inflamación de la porción superficial o profunda del folículo piloso, causada por un agente infeccioso (véase la tabla a continuación).
| Etiología | Factores de riesgo | Patógenos |
|---|---|---|
| Bacteriana |
|
Bacterias gram-positivas: Staphylococcus aureus Staphylococcus aureus Potentially pathogenic bacteria found in nasal membranes, skin, hair follicles, and perineum of warm-blooded animals. They may cause a wide range of infections and intoxications. Brain Abscess (muy común), tanto sensible a la meticilina como resistente a la meticilina ( MRSA MRSA A strain of Staphylococcus aureus that is non-susceptible to the action of methicillin. The mechanism of resistance usually involves modification of normal or the presence of acquired penicillin binding proteins. Staphylococcus, por sus siglas en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum inglés) (la foliculitis contribuye al AL Amyloidosis aumento de la prevalencia de infecciones por MRSA MRSA A strain of Staphylococcus aureus that is non-susceptible to the action of methicillin. The mechanism of resistance usually involves modification of normal or the presence of acquired penicillin binding proteins. Staphylococcus adquiridas en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la comunidad). |
Bacterias gram-negativas (más comunes en el área inguinal):
|
||
| Fúngica |
|
|
| Viral |
|
|
| Parasitaria | Foliculitis por Demodex | Demodex folliculorum Demodex Folliculorum Infectious Folliculitis, un ácaro parásito |
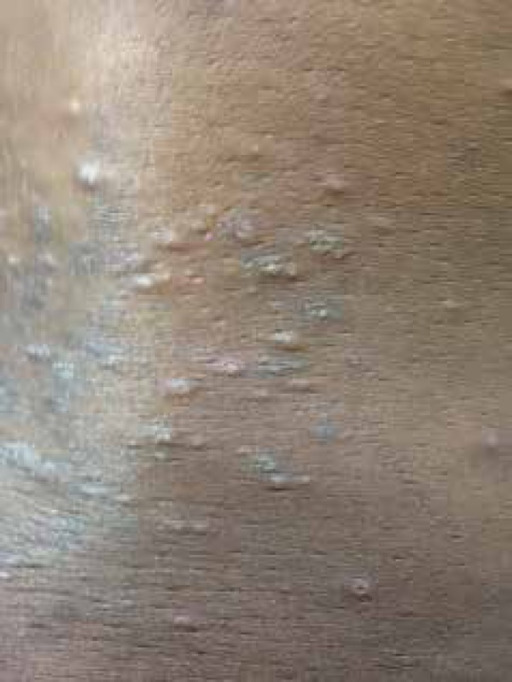
Foliculitis pruriginosa del embarazo, con lesiones en la zona lumbar
Imagen: “Lesions on the lower back” por U.S. National Library of Medicine. Licencia: CC BY 4.0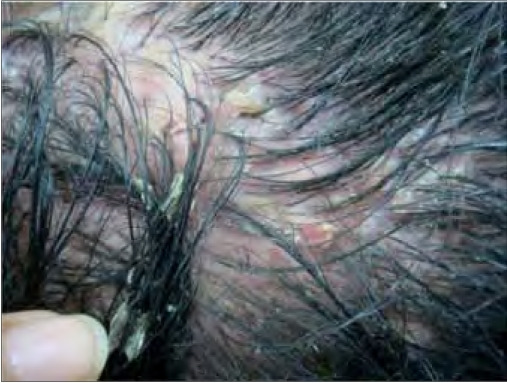
Foliculitis decalvante, induración del cuero cabelludo que puede presentarse como pústulas, erosiones, costras, úlceras y escamas.
Imagen: “Patient 11 on presentation” por Department of Dermatology, The First Affiliated Hospital, Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou, Guangdong, People’s Republic of China. Licencia: CC BY 2.0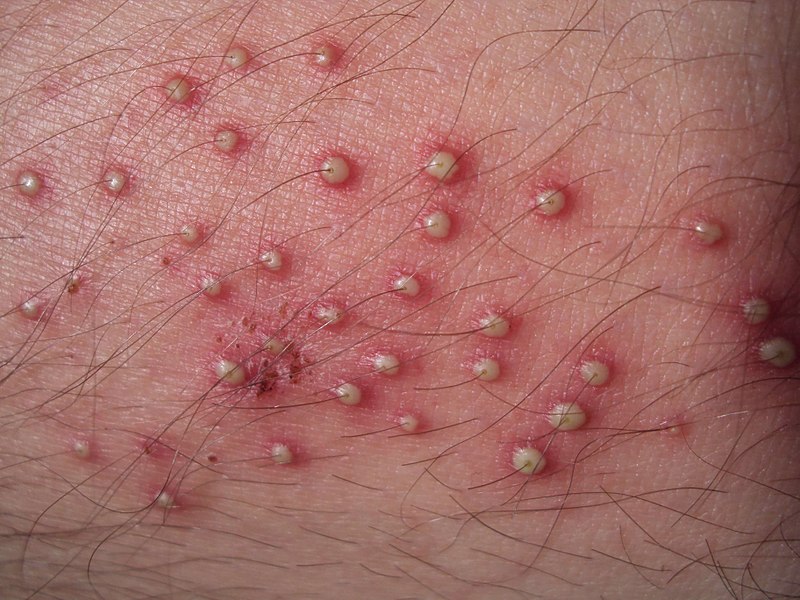
Foliculitis bacteriana en la parte inferior de la pierna que se presenta como pústulas foliculares
Imagen: “Folliculitis on lower leg” por Da pacem Domine. Licencia: Dominio Público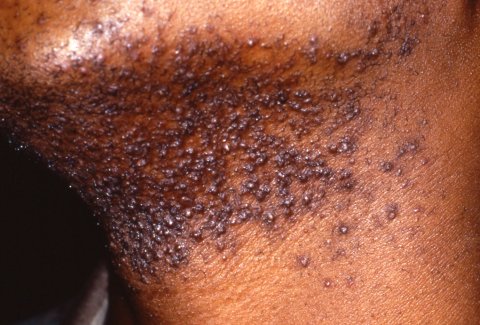
Seudofoliculitis de la barba que se presenta como pápulas hiperpigmentadas firmes en el cuello y la mandíbula. Esto es causado por la inflamación provocada por el vello que penetra en la piel interfolicular después del afeitado (“vellos encarnados”) y puede ocurrir en cualquier lugar donde se afeite o depile el pelo.
Imagen: “Picture of Pseudofolliculitis Barbae” por Army Medical Department. Licencia: Dominio Público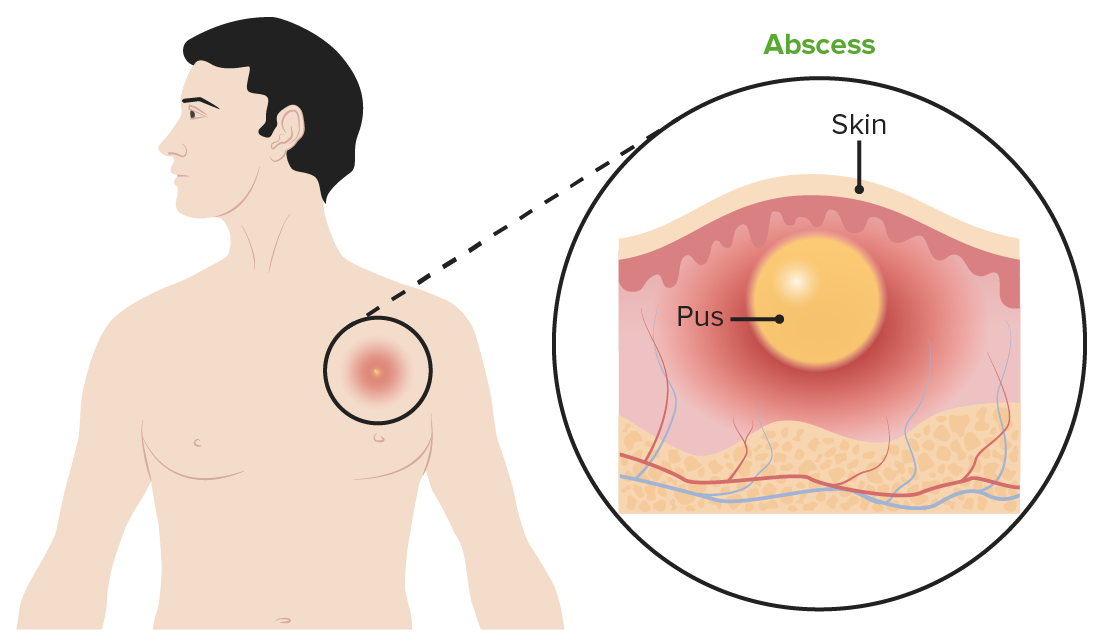
Absceso subcutáneo
Imagen por Lecturio.El tratamiento consiste principalmente en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum medidas de soporte:
La terapia con antibióticos es guiada por el organismo causante sospechado o conocido:
Las siguientes afecciones pueden confundirse con foliculitis infecciosa.