Los LOS Neisseria medicamentos antimicobacterianos representan un grupo diverso de compuestos que tienen actividad contra las infecciones micobacterianas, incluidas la tuberculosis Tuberculosis Tuberculosis (TB) is an infectious disease caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex bacteria. The bacteria usually attack the lungs but can also damage other parts of the body. Approximately 30% of people around the world are infected with this pathogen, with the majority harboring a latent infection. Tuberculosis spreads through the air when a person with active pulmonary infection coughs or sneezes. Tuberculosis, lepra y enfermedades ocasionadas por el complejo Mycobacterium avium Mycobacterium avium A bacterium causing tuberculosis in domestic fowl and other birds. In pigs, it may cause localized and sometimes disseminated disease. The organism occurs occasionally in sheep and cattle. It should be distinguished from the m. avium complex, which infects primarily humans. Mycobacterium. Los LOS Neisseria agentes de 1ra línea para la tuberculosis Tuberculosis Tuberculosis (TB) is an infectious disease caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex bacteria. The bacteria usually attack the lungs but can also damage other parts of the body. Approximately 30% of people around the world are infected with this pathogen, with the majority harboring a latent infection. Tuberculosis spreads through the air when a person with active pulmonary infection coughs or sneezes. Tuberculosis son rifampicina, isoniazida, pirazinamida y etambutol. Los LOS Neisseria medicamentos varían en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum sus mecanismos de acción: la rifampicina inhibe la síntesis de ácido ribonucleico (ARN), la isoniazida inhibe la síntesis de ácido micólico, la pirazinamida altera la energía de la membrana tras su conversión a ácido pirazinoico y el etambutol previene la síntesis de la pared celular. No se recomienda la monoterapia debido al AL Amyloidosis mayor riesgo de resistencia a los LOS Neisseria medicamentos. El tratamiento con múltiples medicamentos lleva varios meses y requiere control de esputo. En EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum cuanto a la lepra, una infección por Mycobacterium leprae Mycobacterium leprae A species of gram-positive, aerobic bacteria that causes leprosy in man. Its organisms are generally arranged in clumps, rounded masses, or in groups of bacilli side by side. Mycobacterium, también se usa rifampicina con dapsona. La forma lepromatosa requiere un 3er agente (clofazimina). Las infecciones pulmonares por el complejo Mycobacterium avium Mycobacterium avium A bacterium causing tuberculosis in domestic fowl and other birds. In pigs, it may cause localized and sometimes disseminated disease. The organism occurs occasionally in sheep and cattle. It should be distinguished from the m. avium complex, which infects primarily humans. Mycobacterium se tratan con macrólidos (azitromicina), rifampicina y etambutol.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Los LOS Neisseria medicamentos antimicobacterianos representan un grupo diverso de compuestos utilizados contra infecciones micobacterianas (e.g., tuberculosis Tuberculosis Tuberculosis (TB) is an infectious disease caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex bacteria. The bacteria usually attack the lungs but can also damage other parts of the body. Approximately 30% of people around the world are infected with this pathogen, with the majority harboring a latent infection. Tuberculosis spreads through the air when a person with active pulmonary infection coughs or sneezes. Tuberculosis, lepra, complejo Mycobacterium avium Mycobacterium avium A bacterium causing tuberculosis in domestic fowl and other birds. In pigs, it may cause localized and sometimes disseminated disease. The organism occurs occasionally in sheep and cattle. It should be distinguished from the m. avium complex, which infects primarily humans. Mycobacterium).
| Bacteria Bacteria Bacteria are prokaryotic single-celled microorganisms that are metabolically active and divide by binary fission. Some of these organisms play a significant role in the pathogenesis of diseases. Bacteriology | Régimen de tratamiento* | Profilaxis |
|---|---|---|
| Mycobacterium tuberculosis Mycobacterium tuberculosis Tuberculosis (TB) is an infectious disease caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex bacteria. The bacteria usually attack the lungs but can also damage other parts of the body. Approximately 30% of people around the world are infected with this pathogen, with the majority harboring a latent infection. Tuberculosis spreads through the air when a person with active pulmonary infection coughs or sneezes. Tuberculosis |
|
Isoniazida |
| M. leprae |
|
Ninguna |
Las especies predominantes del complejo M. avium incluyen:
|
|
Azitromicina o rifabutina |
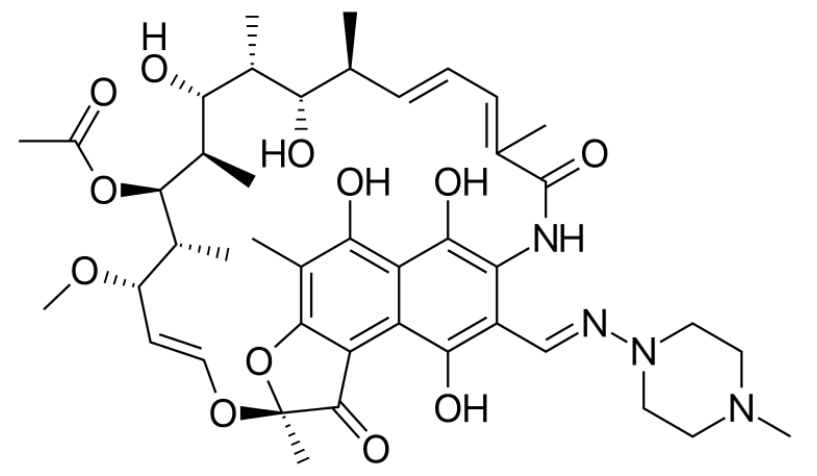
Fórmula esquelética de rifampicina
Imagen: “Skeletal formula of rifampin” por Vaccinationist. Licencia: Dominio Público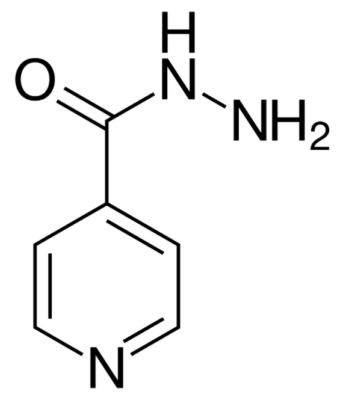
Fórmula esquelética de isoniazida (hidrazida de ácido isonicotínico)
Imagen: “Skeletal formula of isoniazid” por Fvasconcellos. Licencia: Dominio Público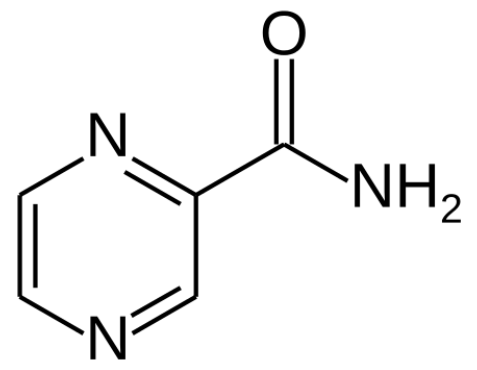
Estructura de pirazinamida
Imagen: “Structure of pyrazinamide” por Fvasconcellos. Licencia: Dominio Público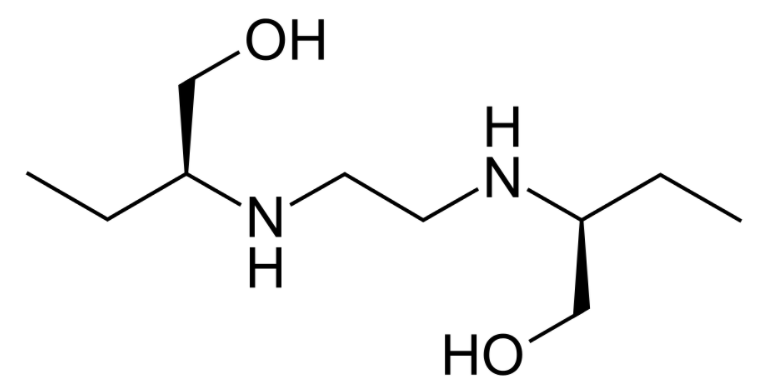
Estructura del etambutol
Imagen: “Structure of ethambutol” por Fvasconcellos. Licencia: Dominio PúblicoHidróxido de aluminio ↓ absorción del medicamento
Se utilizan otros agentes según las condiciones subyacentes y la presencia de Mycobacterium Mycobacterium Mycobacterium is a genus of the family Mycobacteriaceae in the phylum Actinobacteria. Mycobacteria comprise more than 150 species of facultative intracellular bacilli that are mostly obligate aerobes. Mycobacteria are responsible for multiple human infections including serious diseases, such as tuberculosis (M. tuberculosis), leprosy (M. leprae), and M. avium complex infections. Mycobacterium resistente a múltiples medicamentos.
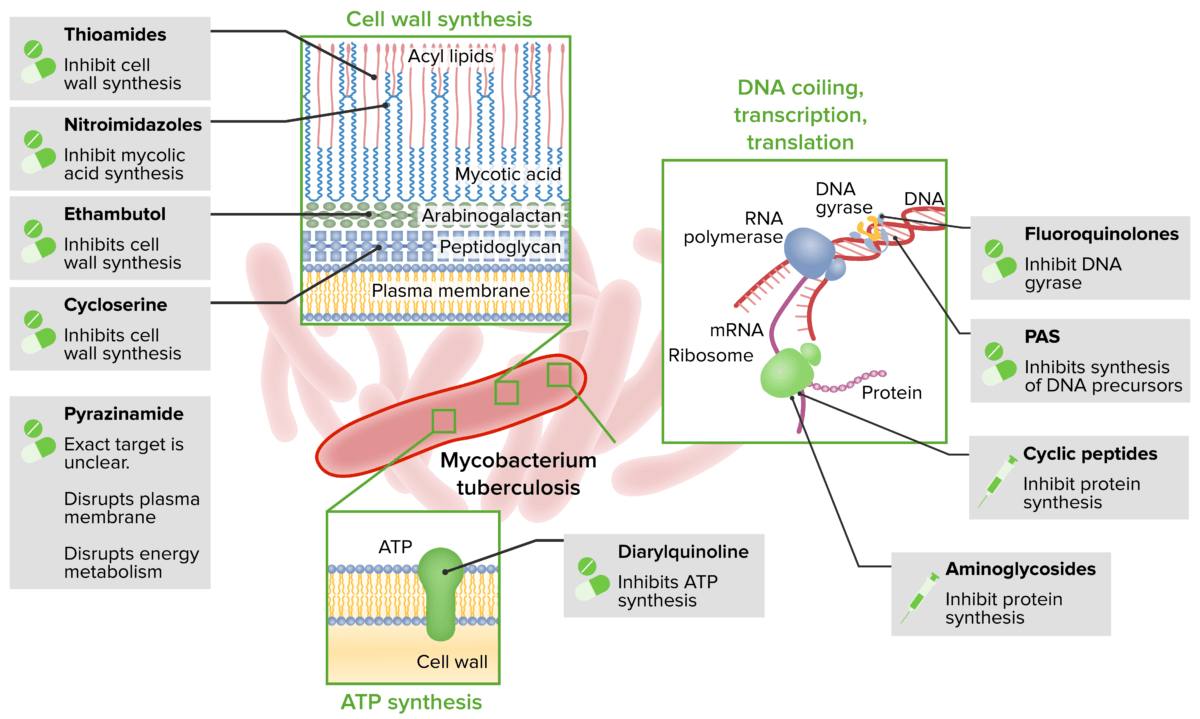
Agentes y mecanismos antituberculosos
PAS: ácido paraaminosalicílico