Los LOS Neisseria antiarrítmicos de clase 3 son medicamentos que bloquean los LOS Neisseria canales de K del tejido cardíaco. Estos incluyen amiodarona, dronedarona, sotalol Sotalol An adrenergic beta-antagonist that is used in the treatment of life-threatening arrhythmias. Class 3 Antiarrhythmic Drugs (Potassium Channel Blockers), ibutilida, dofetilida y bretilio. El principal mecanismo de acción incluye el bloqueo de los LOS Neisseria canales de K cardíacos para prolongar la repolarización. Sin embargo, algunos medicamentos de esta clase también ejercen efectos sobre los LOS Neisseria canales de Na, los LOS Neisseria canales de calcio y los LOS Neisseria receptores adrenérgicos. Las indicaciones varían entre los LOS Neisseria medicamentos, pero incluyen tanto las arritmias auriculares como las ventriculares. Dado que estos medicamentos prolongan el intervalo QT, las torsades de pointes Torsades de pointes A malignant form of polymorphic ventricular tachycardia that is characterized by heart rate between 200 and 250 beats per minute, and QRS complexes with changing amplitude and twisting of the points. The term also describes the syndrome of tachycardia with prolonged ventricular repolarization, long qt intervals exceeding 500 milliseconds or bradycardia. Torsades de pointes may be self-limited or may progress to ventricular fibrillation. Ventricular Tachycardia son una complicación potencial del tratamiento.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
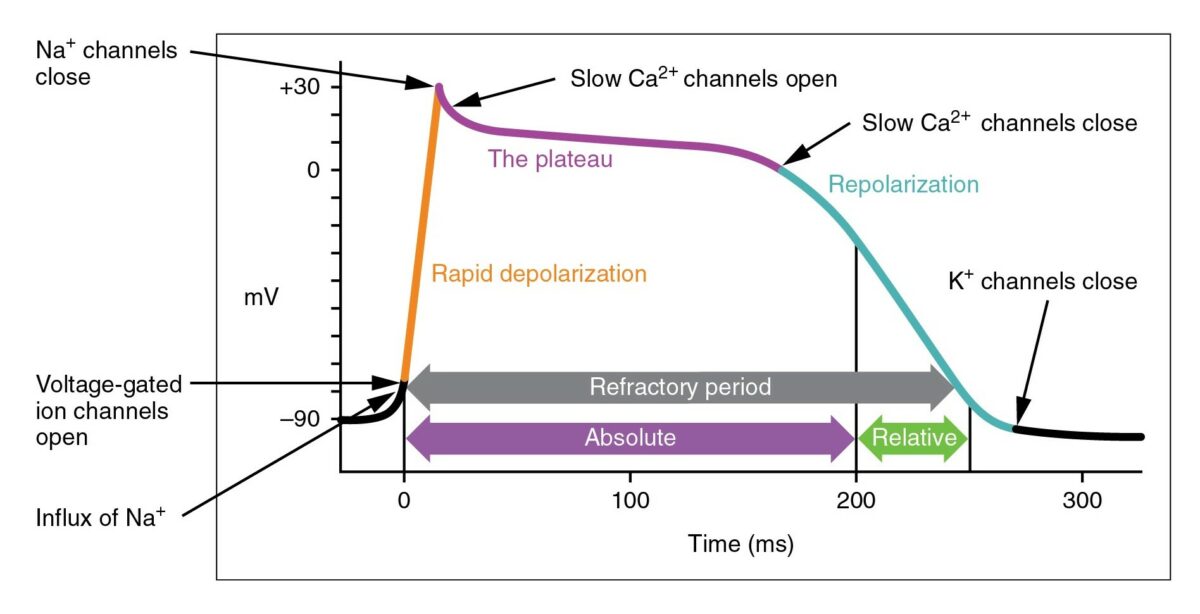
El potencial de acción cardíaco
Imagen: “Action Potential Heart Contraction, Illustration from Anatomy & Physiology” por OpenStax College. License: CC BY 3.0, editada por Lecturio.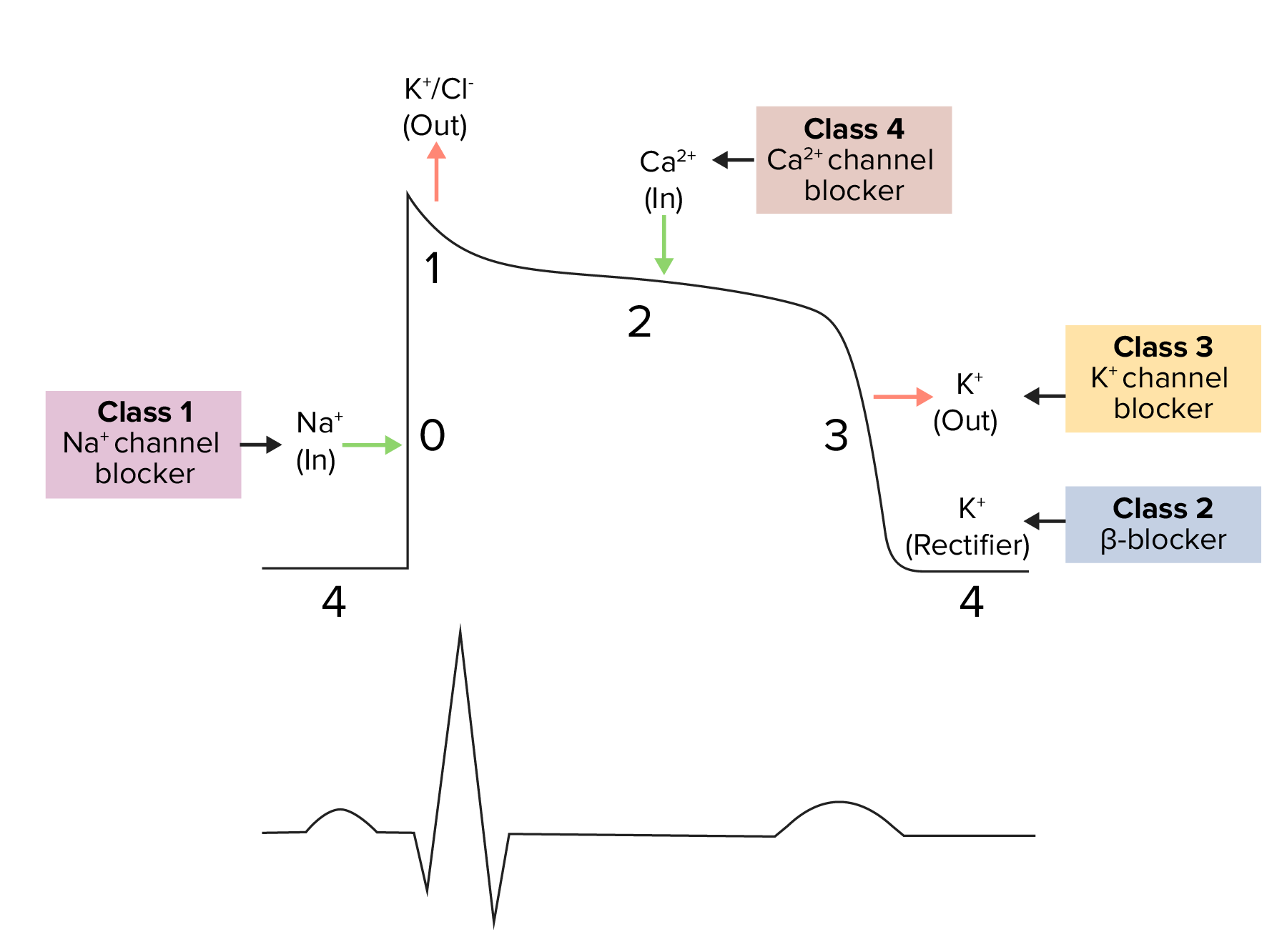
Diagrama que muestra un potencial de acción cardíaco y las fases de acción de diferentes clases de medicamentos antiarrítmicos:
El ciclo comienza con la fase 4, el potencial de reposo. La fase 0 es cuando se produce una despolarización rápida debido a la entrada de iones de sodio en la célula. A continuación se produce la repolarización, con salida de potasio a través de los canales de potasio rápidos en la fase 1, entrada de calcio en la fase 2 y salida de potasio a través de los canales de potasio retardados en la fase 3. Los bloqueadores de los canales de potasio suelen afectar a la fase 3.
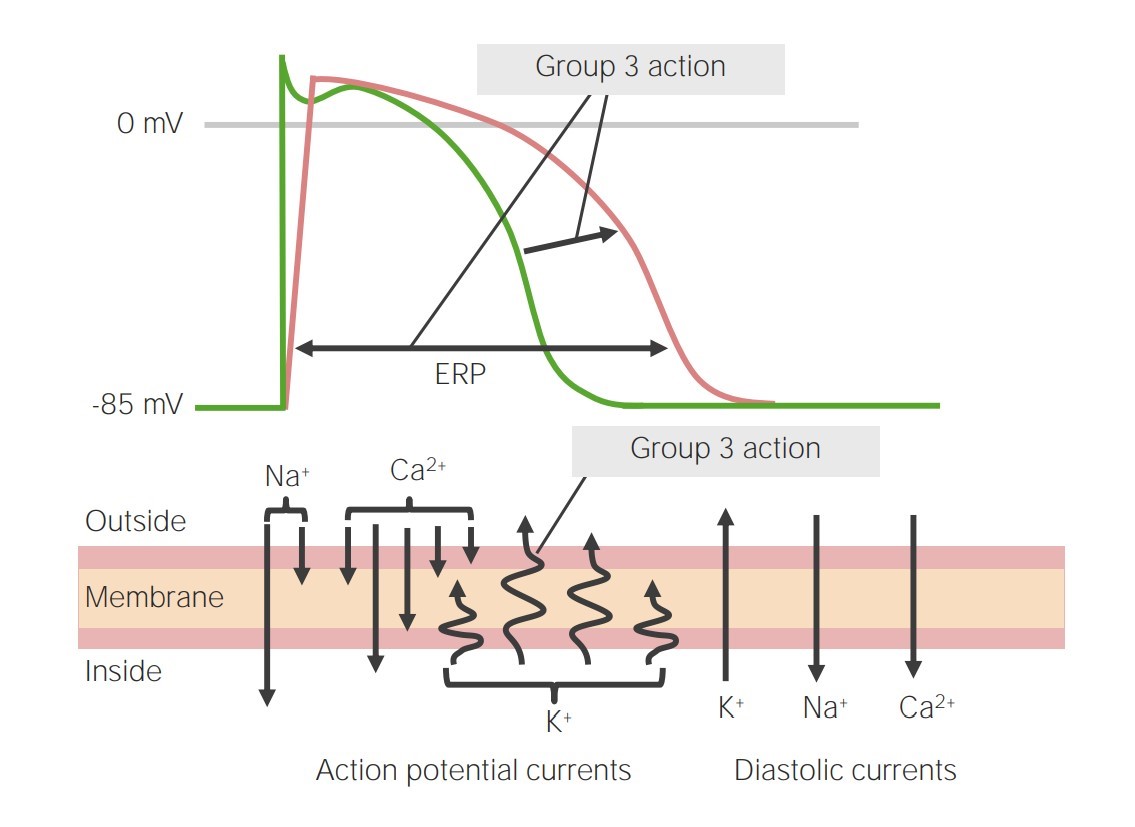
Imagen que representa la acción de los antiarrítmicos de clase 3 sobre la fase 3 del potencial de acción:
Al bloquear los canales de potasio, la fase 3 se prolonga, lo que conduce a un aumento del período refractario efectivo (ERP, por sus siglas en inglés).
Los LOS Neisseria antiarrítmicos de clase 3 incluyen una variedad de medicamentos que varían en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum cuanto a la selectividad del canal de K y otros efectos antiarrítmicos:
Los LOS Neisseria efectos secundarios de la amiodarona se observan principalmente en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la terapia oral a largo plazo (más que en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la terapia intravenosa a corto plazo).
Efectos cardiovasculares:
Toxicidad pulmonar:
Disfunción tiroidea:
Hepatotoxicidad:
Toxicidad neurológica:
Efectos oculares:
Reacciones cutáneas:
La ibutilida se utiliza para convertir farmacológicamente la fibrilación auricular o el flutter auricular en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum ritmo sinusal.
El aumento de la prolongación del QT puede ocurrir con:
La dofetilida se utiliza para la cardioversión y el mantenimiento del ritmo sinusal en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la fibrilación y el flutter auricular.
El bretilio se utiliza para las arritmias ventriculares:
La siguiente tabla compara las clases de antiarrítmicos 1-4. La clase 5 no se incluye debido a los LOS Neisseria variados mecanismos de acción y efectos.
| Clase | Mecanismo de acción | Efectos | Indicaciones de arritmia | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1A |
|
|
|
| 1B | Ventricular | |||
| 1C | Mayormente auricular | |||
| 2 |
|
|
Auricular y ventricular | |
| 3 |
|
Auricular y ventricular | ||
| 4 |
|
|
Auricular | |