Un examen neurológico es una evaluación sistemática de las respuestas cognitivas, sensoriales y motoras para identificar patologías del sistema nervioso. Un examen neurológico permite la localización de lesiones neurológicas para estrechar el diagnóstico diferencial y centrarse en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum exámenes de laboratorio e imagenológicos posteriores. El examen debe incluir evaluaciones del estado mental, el habla, los LOS Neisseria pares craneales, el sistema motor Motor Neurons which send impulses peripherally to activate muscles or secretory cells. Nervous System: Histology, los LOS Neisseria reflejos tendinosos profundos, la sensación, el equilibrio y la coordinación del sujeto.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
El examen del estado mental es una evaluación de la capacidad mental actual de un sujeto basada en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria siguientes factores:
Se requiere una comprensión básica de la neuroanatomía subyacente de la cabeza y el cuello antes de discutir los LOS Neisseria componentes del examen de los LOS Neisseria pares craneales.
| Par PAR The PAR is the attributable risk for an entire population. It represents the fraction of cases that would not occur in a population if the exposure was eliminated. Measures of Risk craneal | Examen |
|---|---|
| I: nervio olfatorio | Probar el olfato del sujeto utilizando sustancias no irritantes. |
| II: nervio óptico |
|
| III: nervio motor Motor Neurons which send impulses peripherally to activate muscles or secretory cells. Nervous System: Histology ocular común; IV: nervio troclear; VI: nervio abducens |
|
| V: nervio trigémino |
|
| VII: nervio facial |
|
| VIII: nervio vestibulococlear | |
| IX: nervio glosofaríngeo; X: nervio vago |
|
| XI: nervio accesorio |
|
| XII: nervio hipogloso |
|
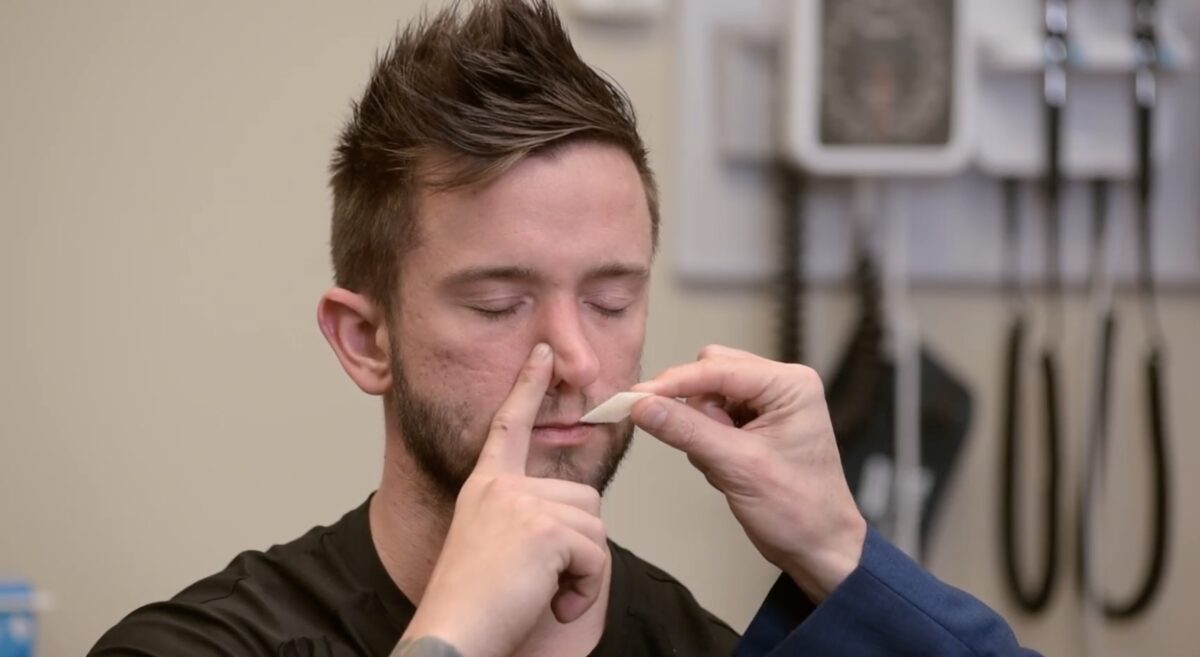

Prueba del olfato, par craneal I:
Aquí, se usa una gasa con alcohol.
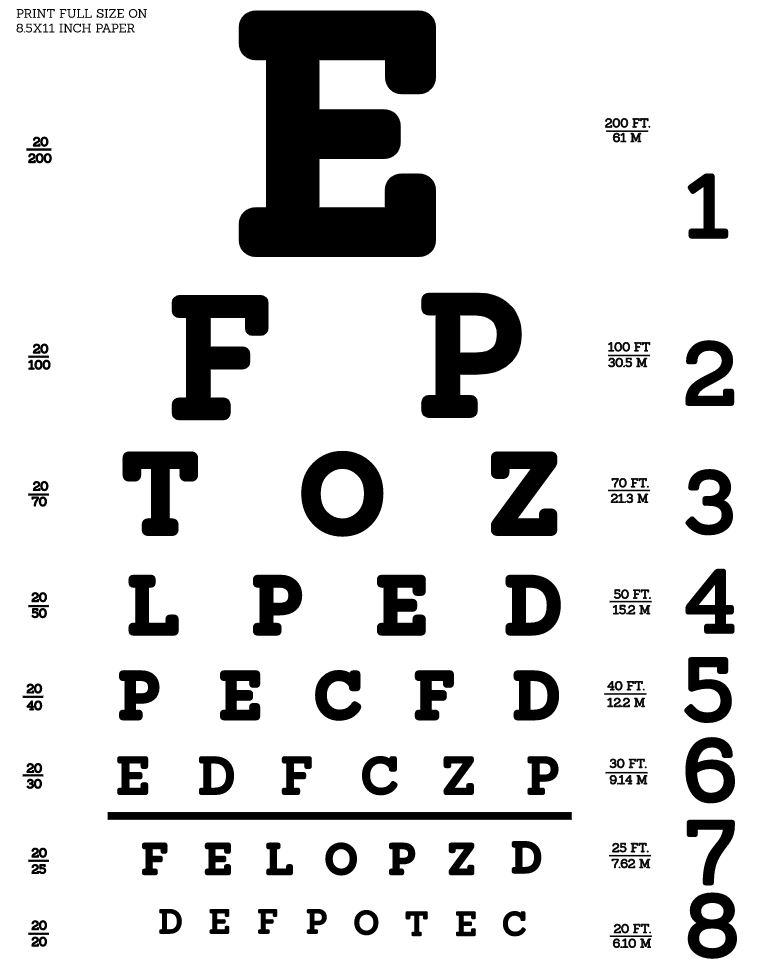
Tabla optométrica de Snellen para evaluar la agudeza visual
Imagen: “Snellen chart by Openclipart” por Openclipart. Licencia: CC0 1.0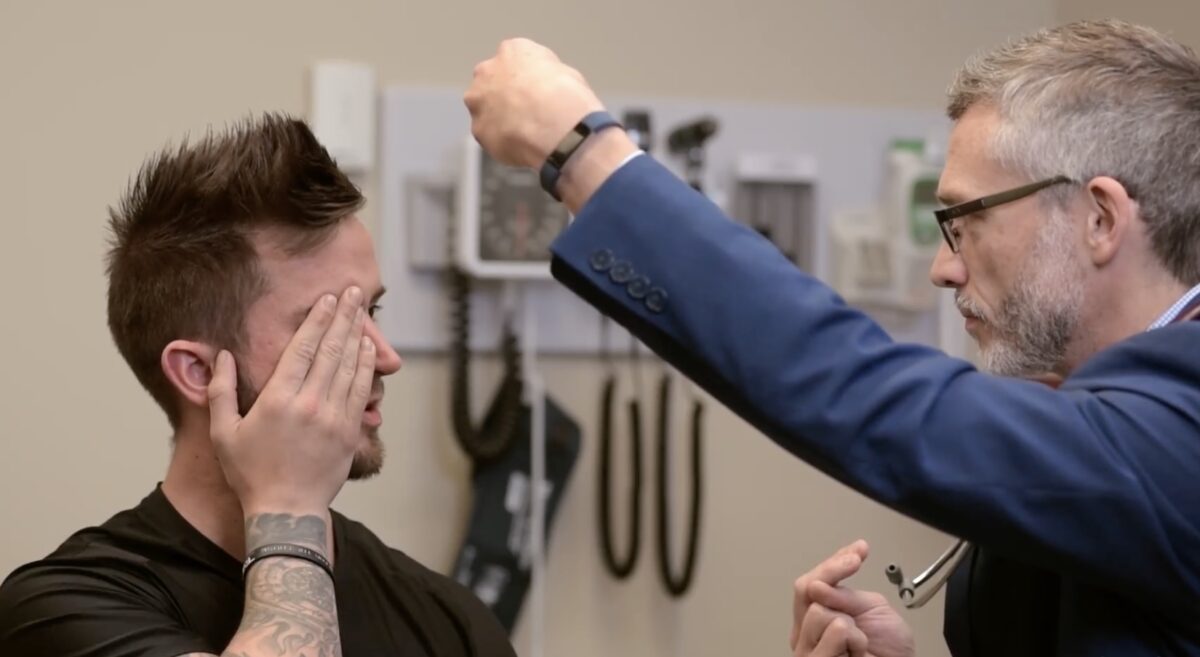
Prueba de campos visuales, par craneal II:
Se pide al sujeto que se cubra 1 ojo y se concentre en la nariz del examinador. Luego, el examinador mueve los dedos en los campos visuales superior o inferior.
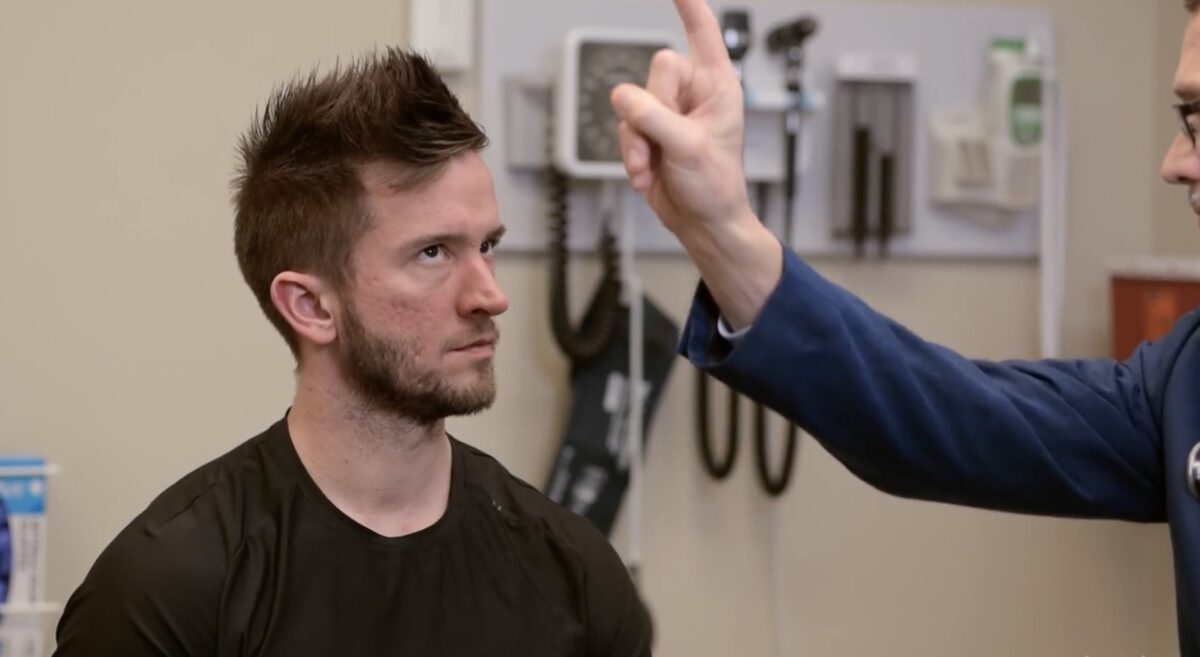
Prueba de movimientos extraoculares, pares craneales III, IV y VI:
Se le pide al sujeto que mantenga la cabeza quieta y siga el dedo del examinador solo con los ojos.
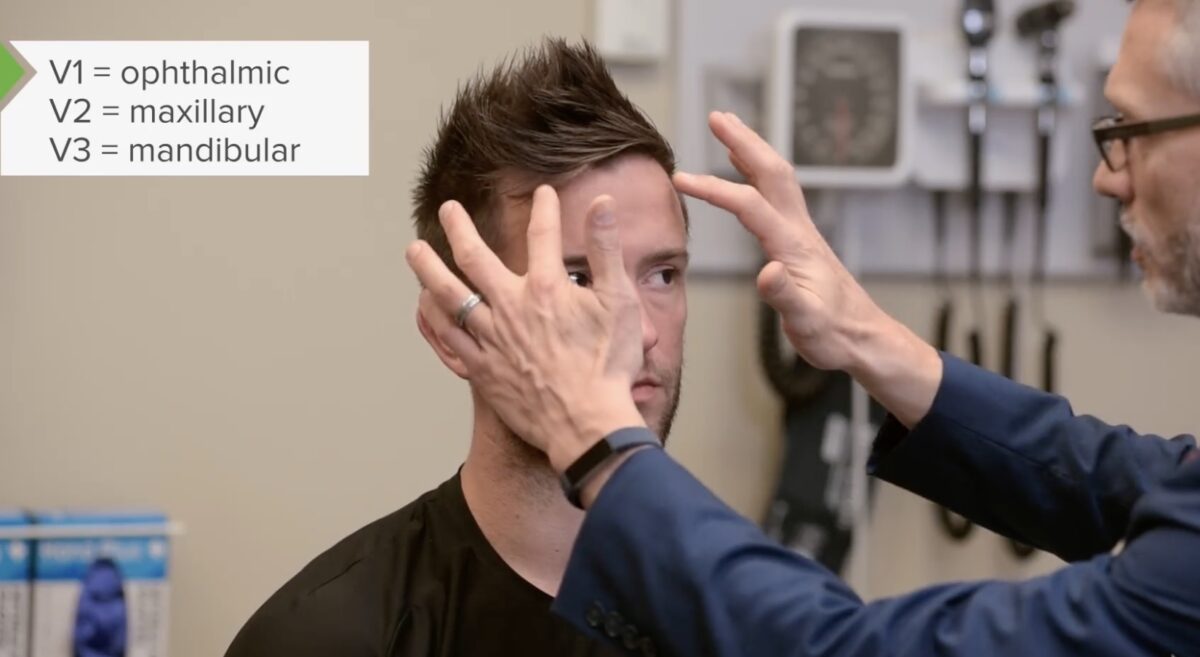
Prueba de la sensación facial, par craneal V:
Es importante evaluar la sensación al tacto ligero para cada rama del par craneal V, incluida la frente (V1), la región maxilar (V2) y la región mandibular (V3).
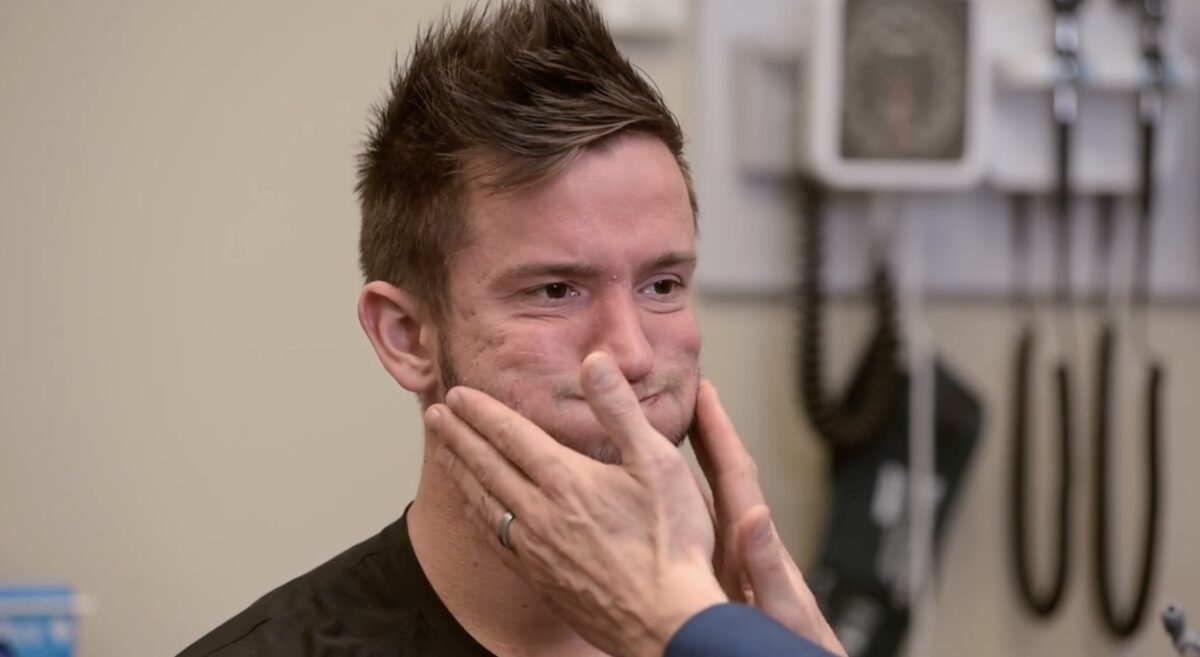

Prueba de la musculatura facial, par craneal VII:
Se le pide al sujeto que infle las mejillas para demostrar fuerza en los músculos faciales. Otras tareas pueden incluir levantar las cejas, cerrar los ojos con fuerza y sonreír.
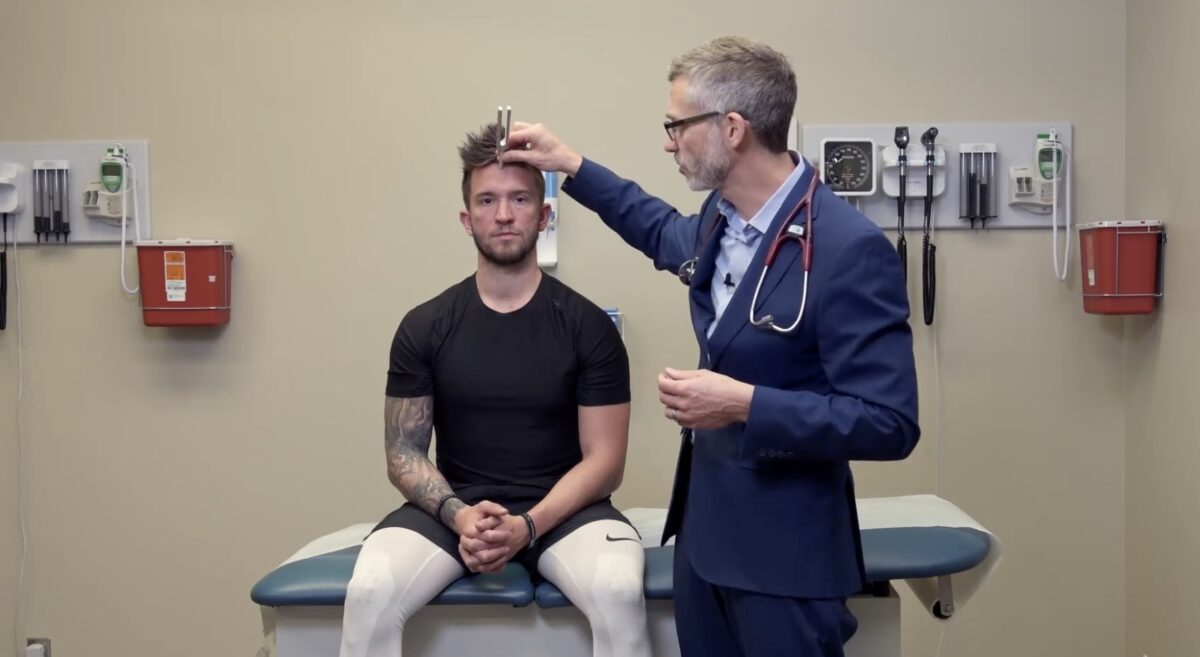
Prueba de la función coclear, par craneal VIII:
Para la prueba de Weber, se coloca un diapasón vibrante en la frente del sujeto (línea media). Una prueba positiva para la hipoacusia conductiva daría como resultado que el sujeto notara un sonido más fuerte en el lado afectado. Para la pérdida auditiva neurosensorial, el sonido sería más fuerte en el lado no afectado.

Pruebas de Weber y Rinne
Imagen por Lecturio.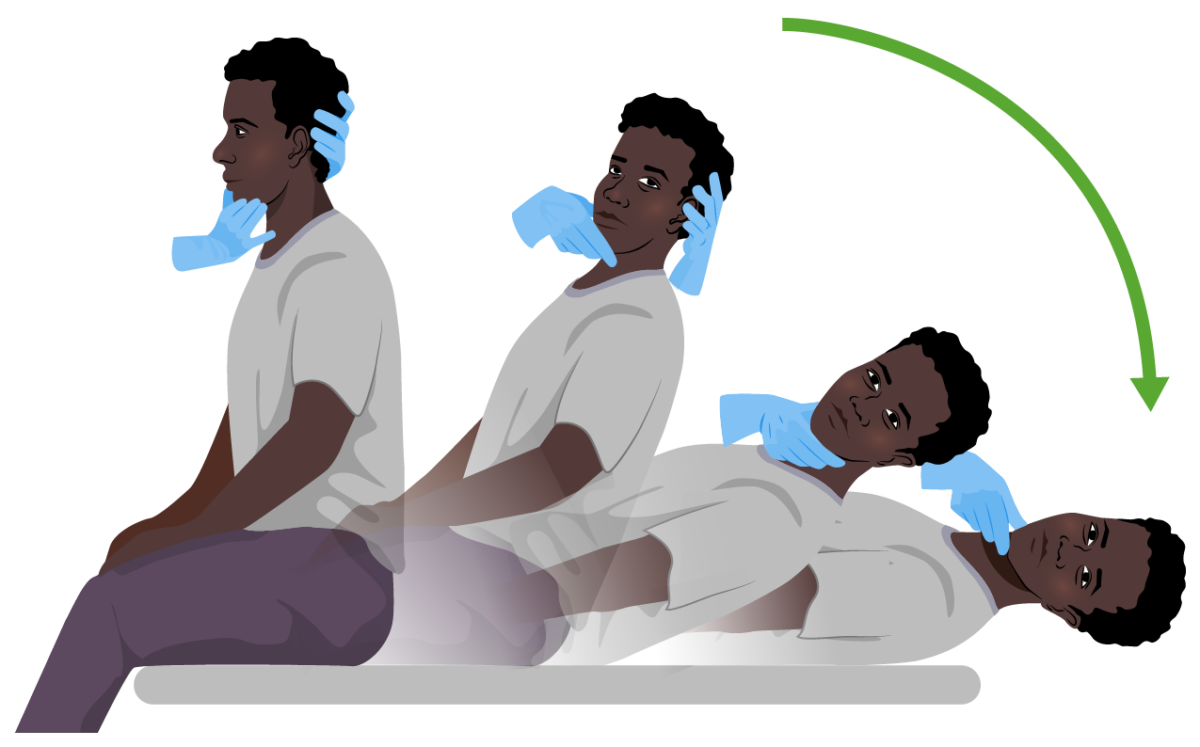
Maniobra de Dix-Hallpike:
Tanto diagnóstico como curativo en el vértigo postural paroxístico benigno. El sujeto se sienta en una mesa de examen y rápidamente adopta una posición supina mientras el examinador apoya su cabeza (hacia la derecha o hacia la izquierda) en un ángulo de 20º por debajo del borde de la cama. La posición se mantiene durante 30 segundos. En personas con vértigo postural paroxístico benigno, los síntomas de vértigo con o sin nistagmo se hacen evidentes.

Prueba de elevación del paladar blando y úvula, pares craneales IX y X:
Es importante evaluar la simetría del paladar blando. La úvula debe estar en la línea media.
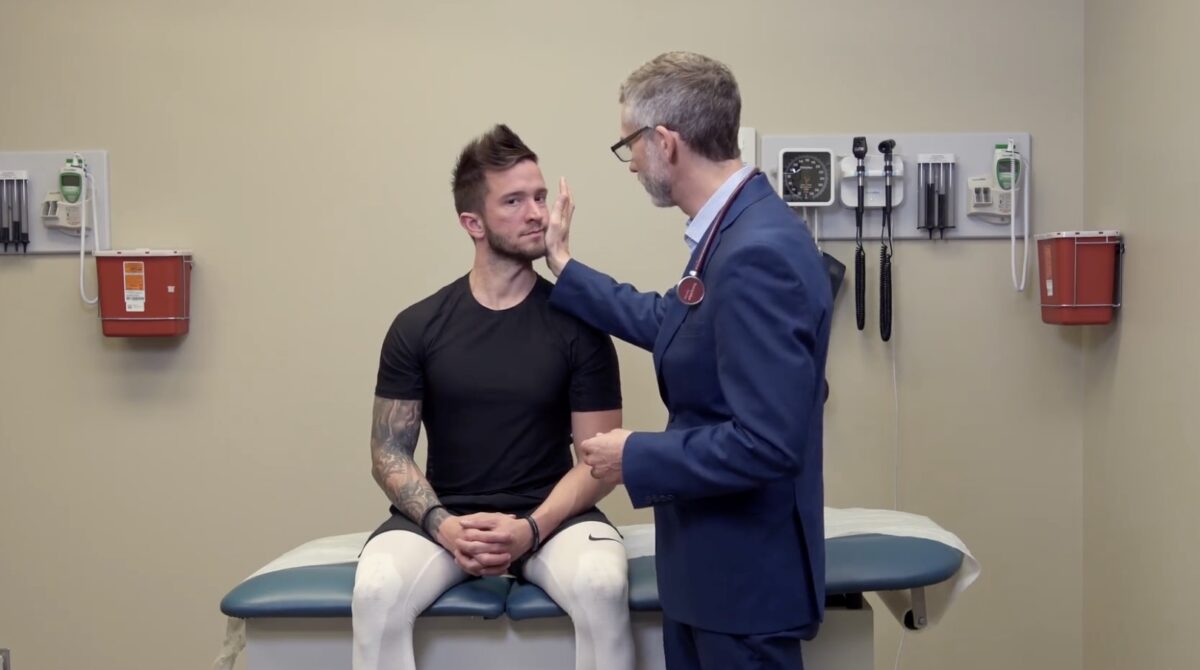
Prueba de la función del músculo esternocleidomastoideo, par craneal XI:
Para esta prueba, haga que el sujeto gire la cabeza contra una resistencia.
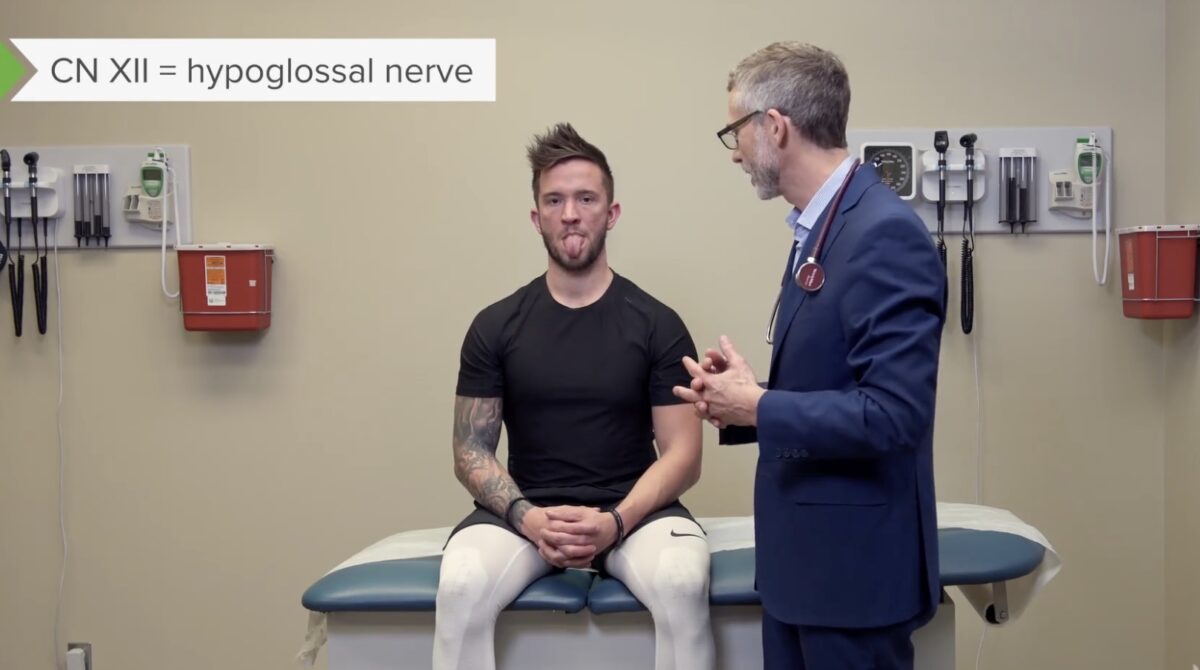
Prueba de los movimientos de la lengua, par craneal XII:
Para esta prueba, haga que el sujeto saque la lengua y la mueva de un lado a otro. En la parálisis del par craneal XII, la lengua se desviará hacia el lado afectado.
El examen del sistema motor Motor Neurons which send impulses peripherally to activate muscles or secretory cells. Nervous System: Histology incluye lo siguiente:
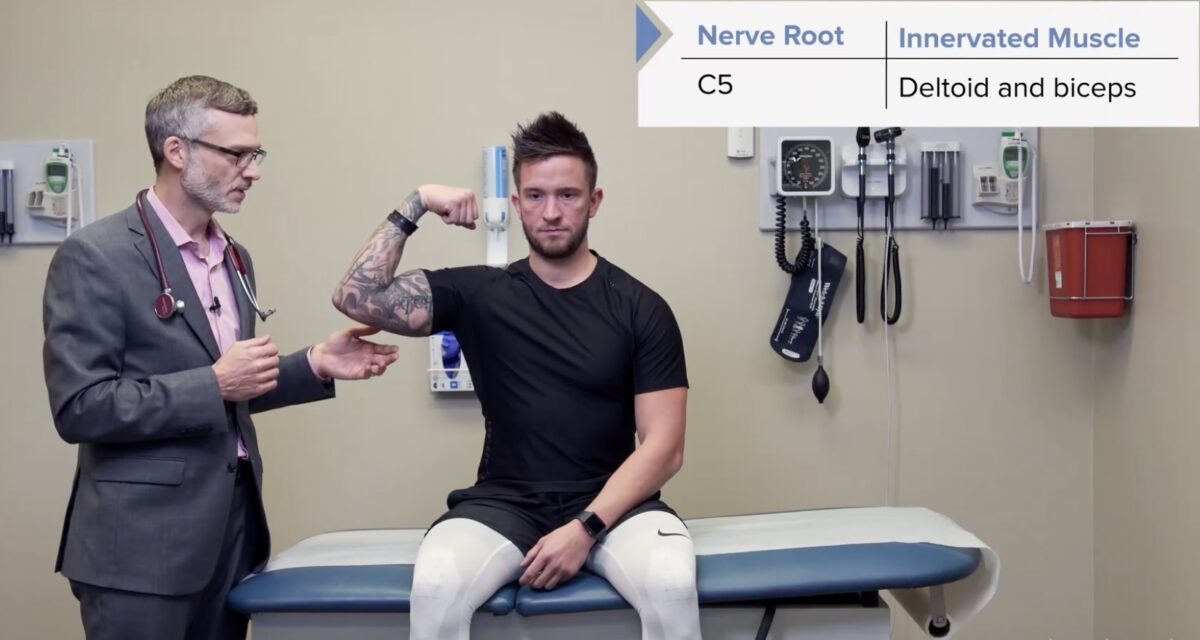
Prueba de fuerza del miotoma C5: deltoides y bíceps
Imagen por Lecturio.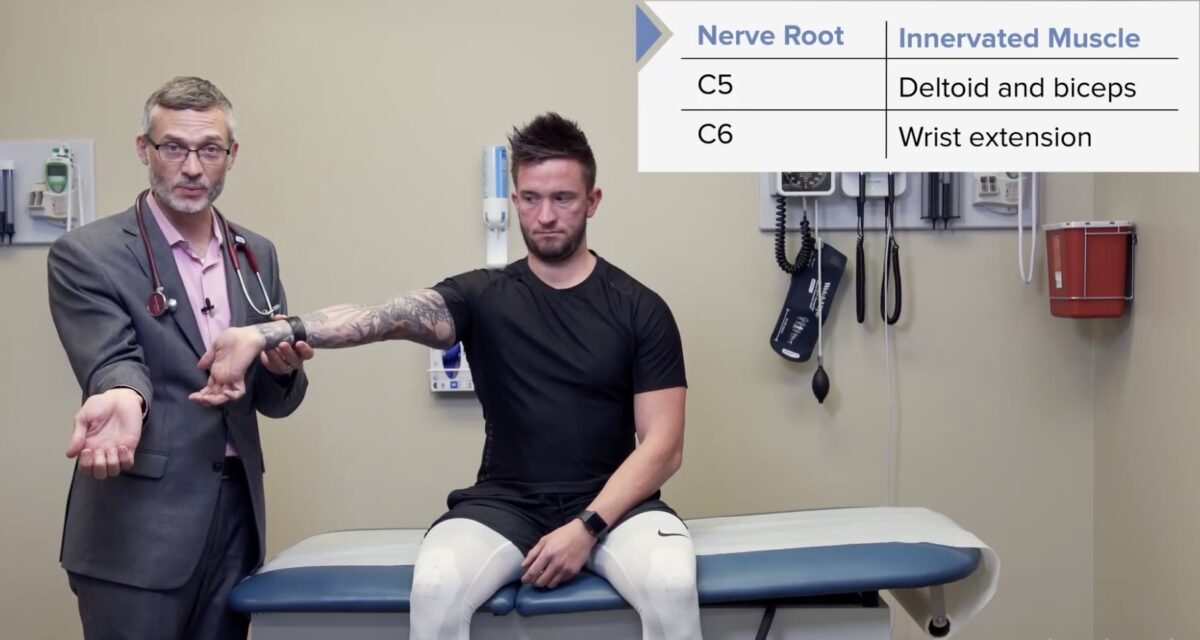
Prueba de fuerza del miotoma C6: tríceps y extensores de muñeca
Imagen por Lecturio.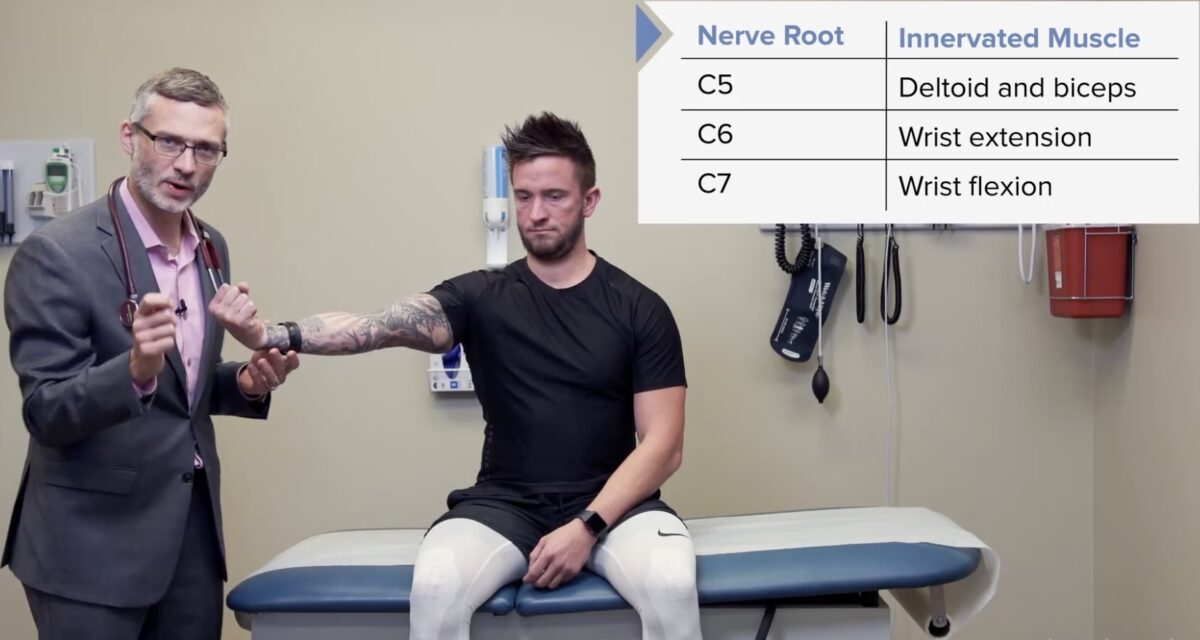
Prueba de fuerza del miotoma C7: flexores de muñeca
Imagen por Lecturio.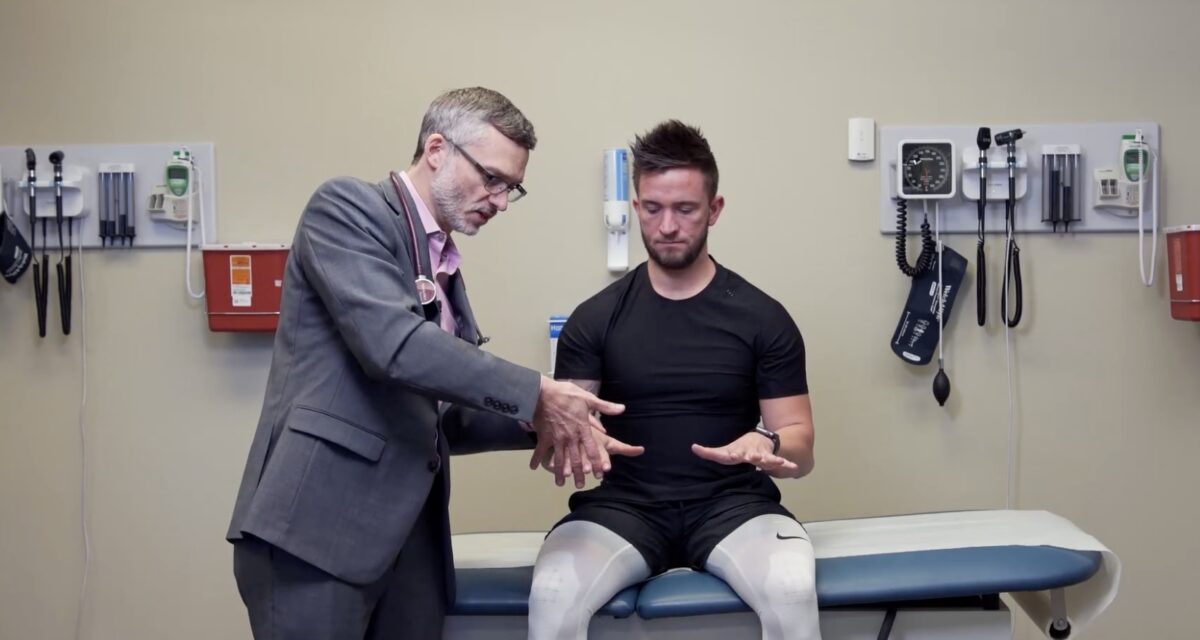
Prueba de fuerza de los miotomas C8 y T1: músculos interóseos:
Para esta prueba, el sujeto aprieta los dedos del examinador.
Prueba de fuerza del miotoma L2: flexores de cadera
Imagen por Lecturio.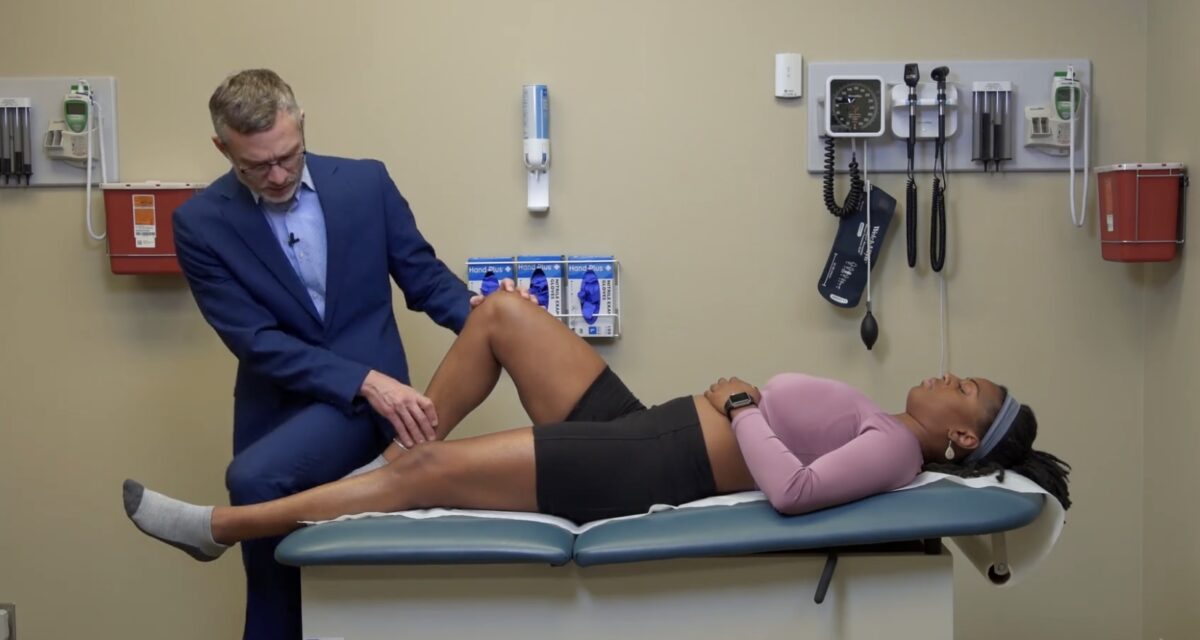
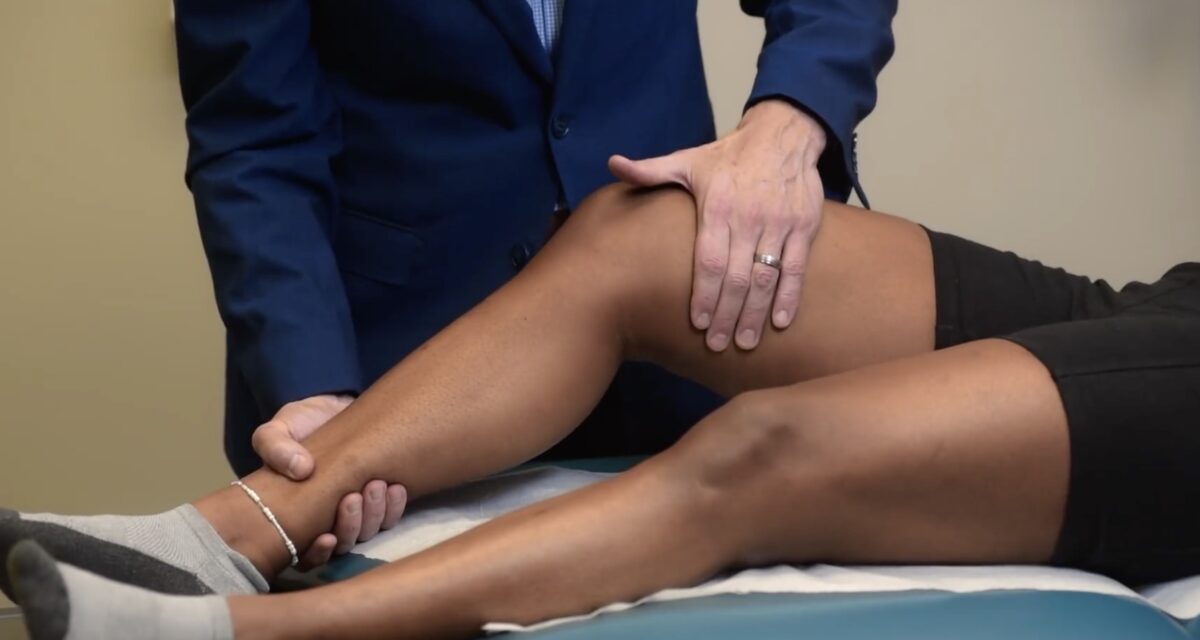
Prueba de fuerza del miotoma L3: extensores de rodilla
Imagen por Lecturio.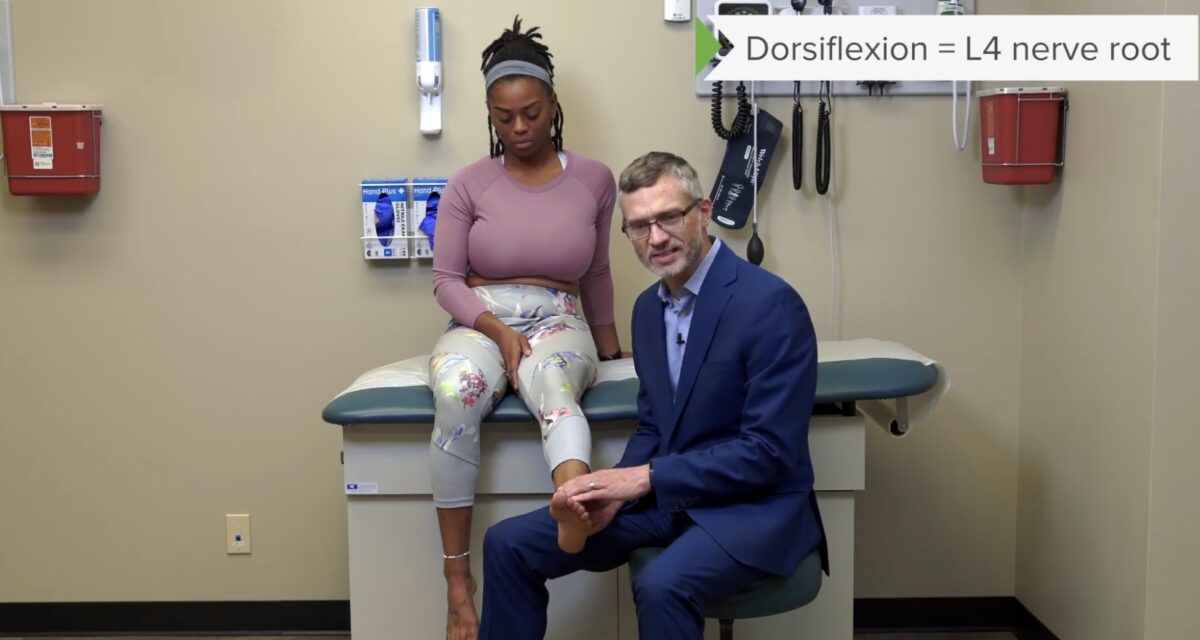
Prueba de fuerza del miotoma L4: flexores dorsales del tobillo
Imagen por Lecturio.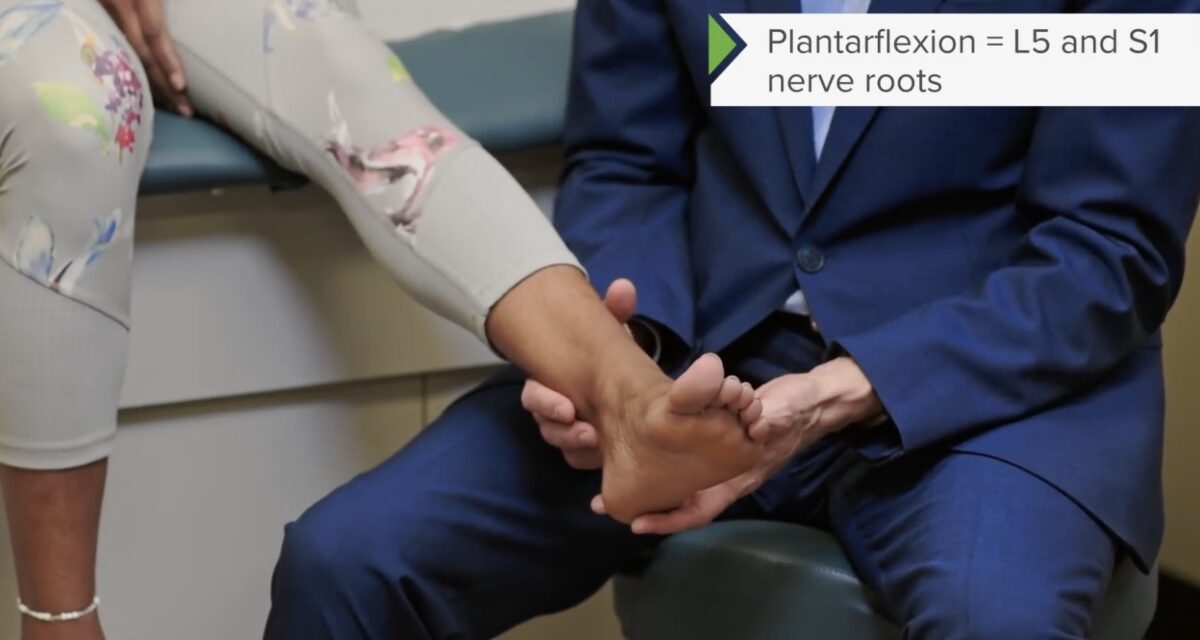
Prueba de fuerza de los miotomas L5 y S1: flexores plantares del tobillo
Imagen por Lecturio.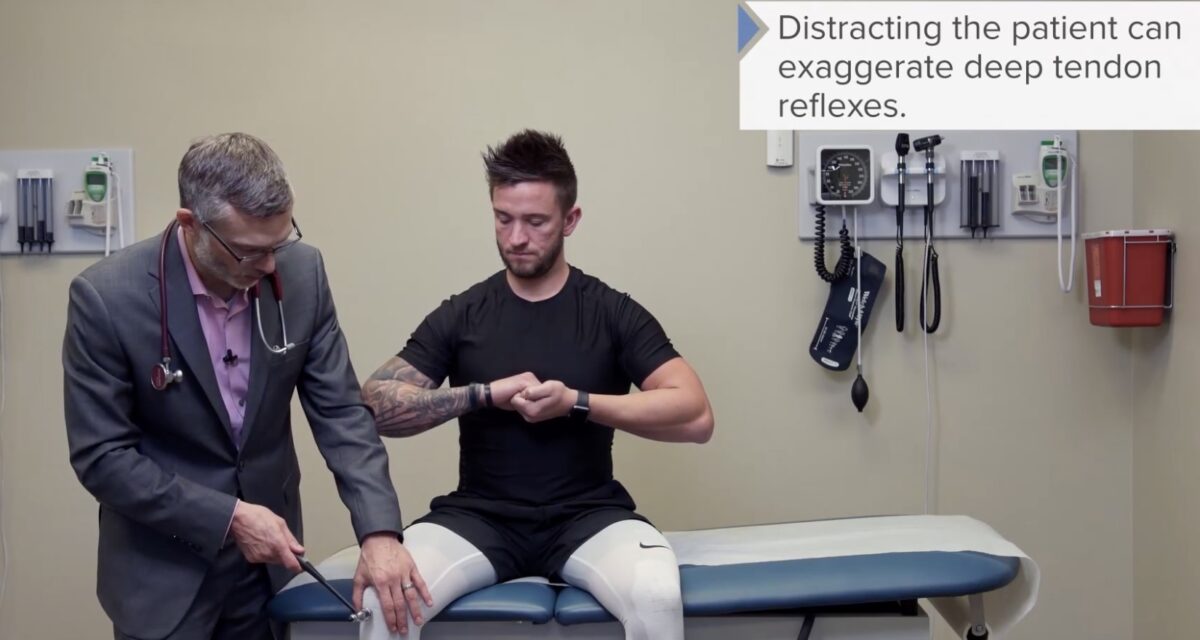
Distraer al sujeto usando la maniobra de Jendrassik puede conducir a una prueba de reflejos más confiable.
Imagen por Lecturio.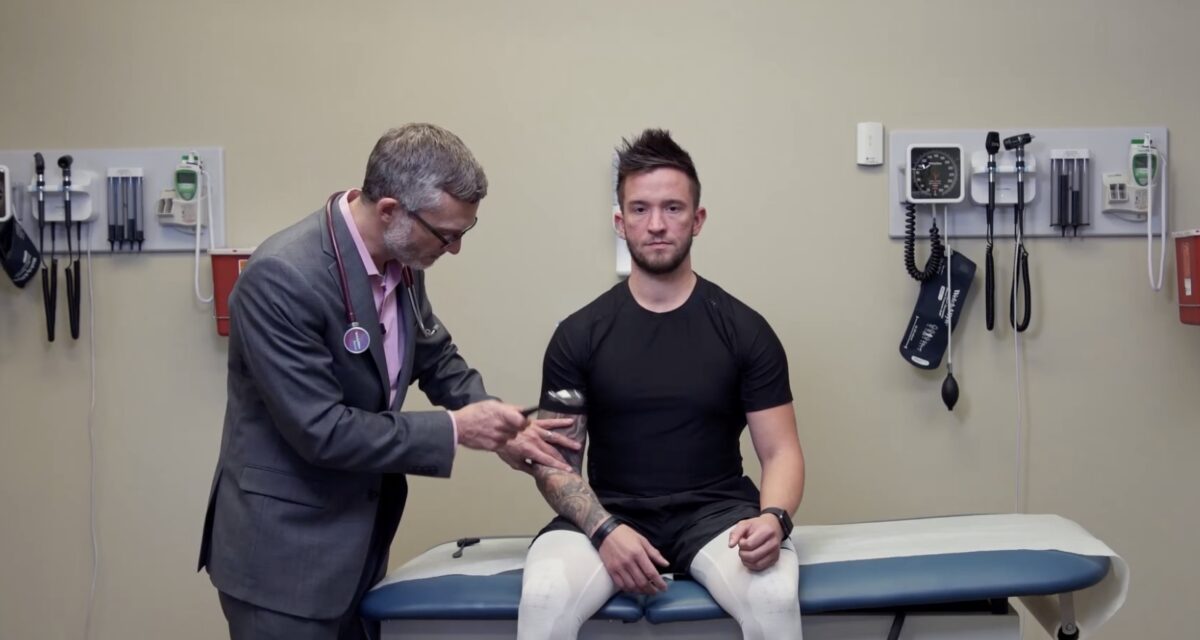
Prueba de reflejos de la raíz nerviosa C5, reflejo del tendón del bíceps
Imagen por Lecturio.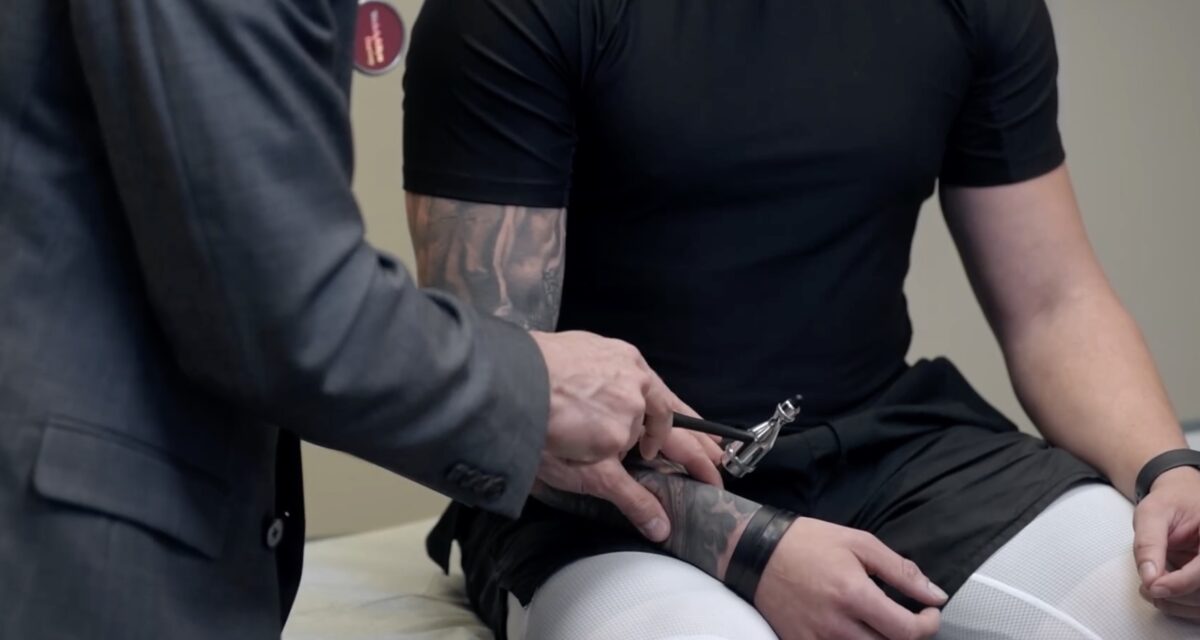
Prueba de reflejos de la raíz nerviosa C6, reflejo del tendón braquiorradial
Imagen por Lecturio.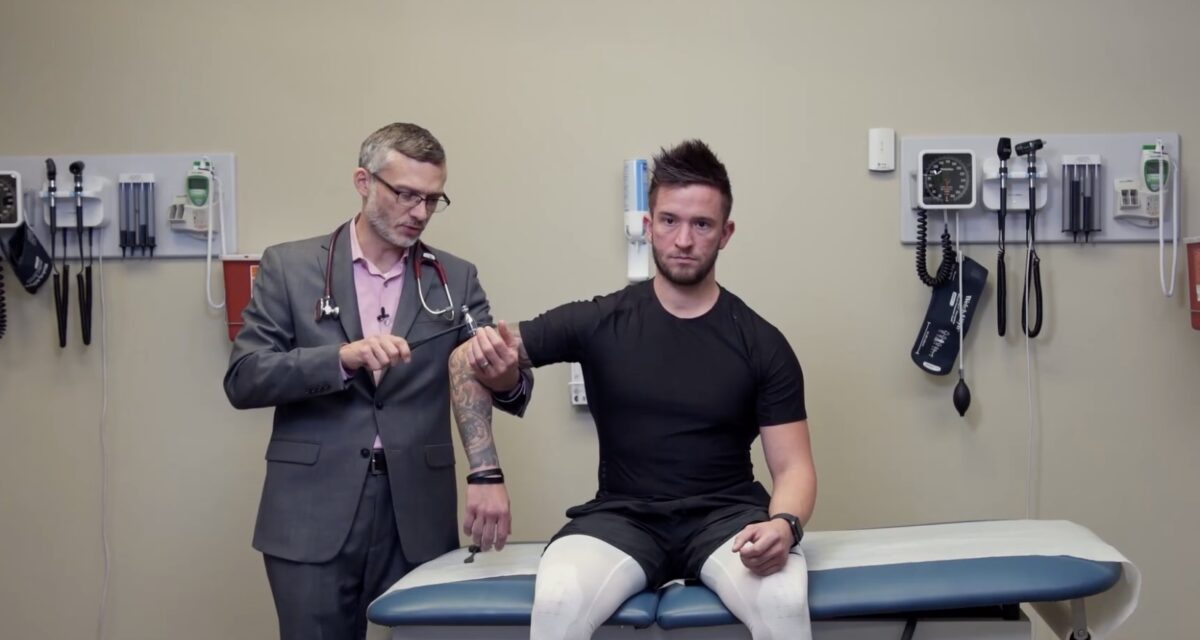
Prueba de reflejos de la raíz nerviosa C7, reflejo del tendón del tríceps
Imagen por Lecturio.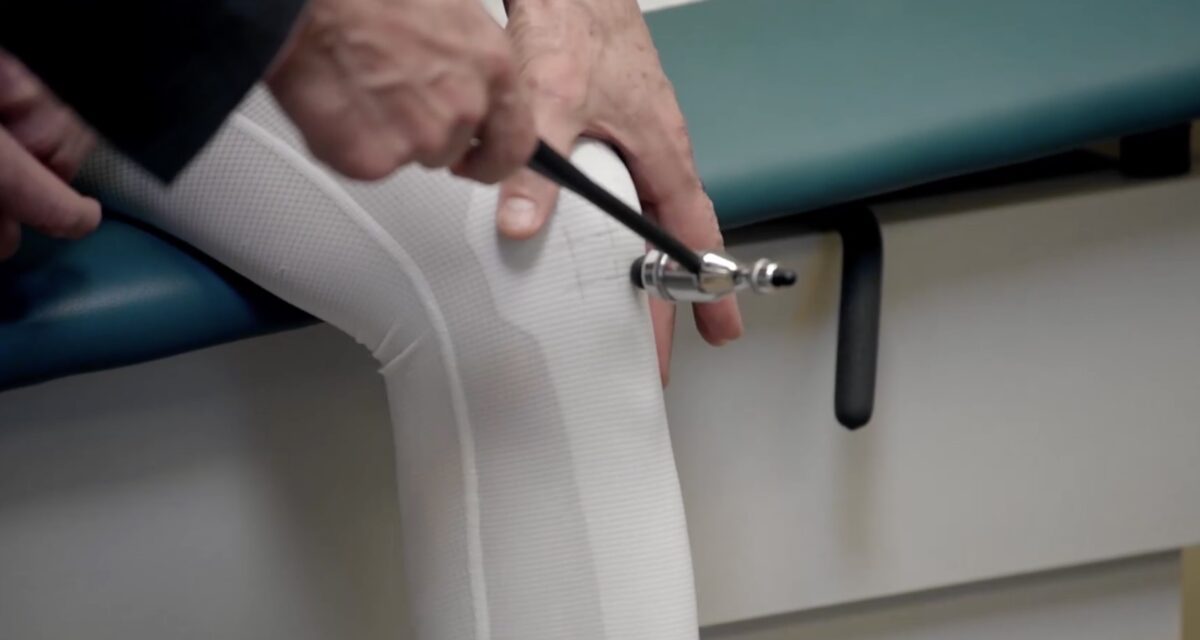
Prueba de reflejos de las raíces nerviosas L3 y L4, reflejo del tendón rotuliano
Imagen por Lecturio.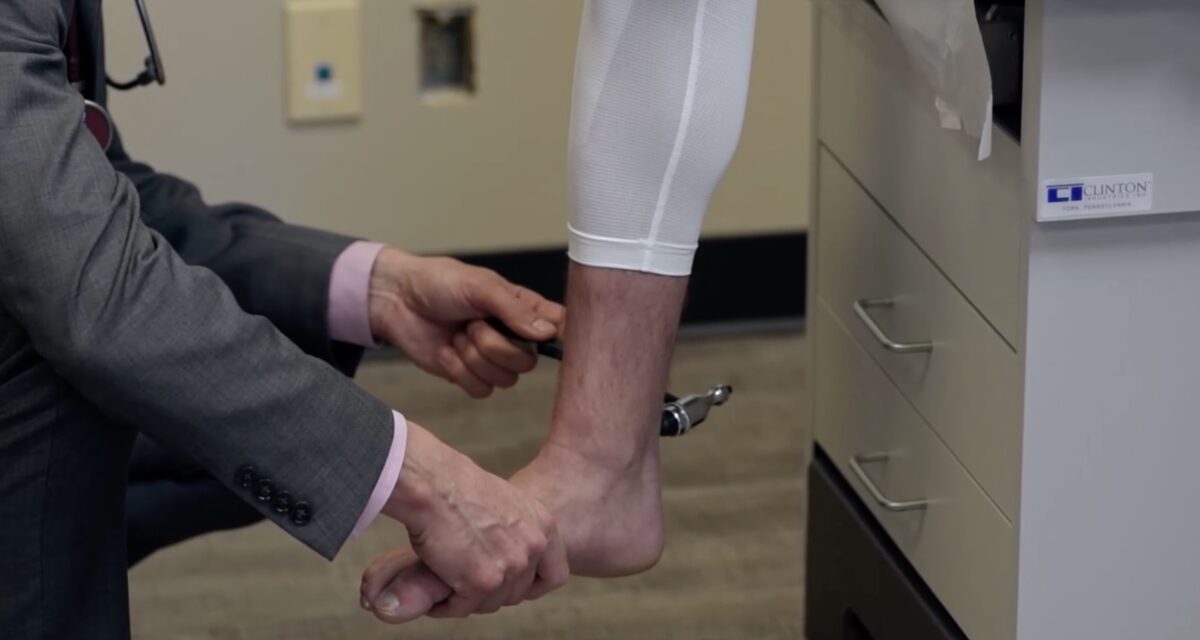
Prueba de reflejos de las raíces nerviosas L5 y S1, reflejo del tendón de Aquiles
Imagen por Lecturio.La evidencia de lesiones de la motoneurona superior frente a la inferior puede hacerse evidente durante el examen motor Motor Neurons which send impulses peripherally to activate muscles or secretory cells. Nervous System: Histology del sujeto debido a anomalías en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum:
| Motoneurona superior | Motoneurona inferior | |
|---|---|---|
| Sitio de la lesión | Cerebro, médula espinal | Asta anterior, raíz nerviosa, nervio periférico |
| Fuerza muscular | Debilidad | Debilidad |
| Tono muscular | Hipertónico | Flácido |
| Fasciculaciones | Ausentes | Presentes |
| Reflejos tendinosos profundos | Hiperreflexia | Hiporreflexia |
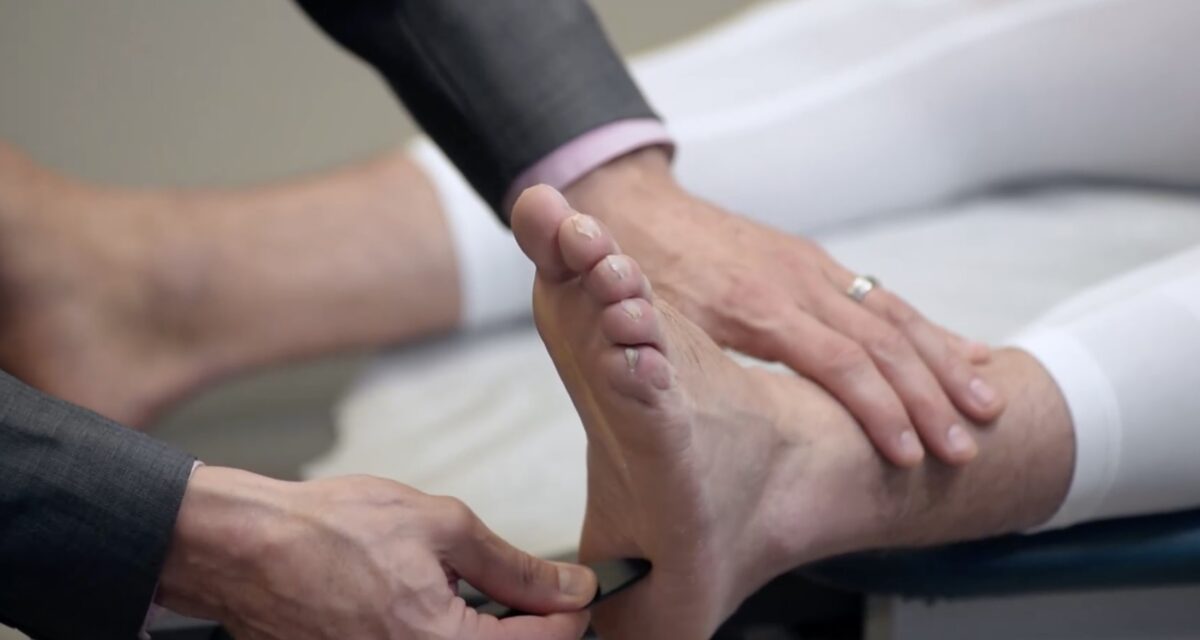
Prueba del reflejo de Babinski (extensor/plantar):
La planta del pie se acaricia en forma de “palo de hockey”. En una respuesta normal (negativa), los dedos del pie exhibirán flexión plantar.
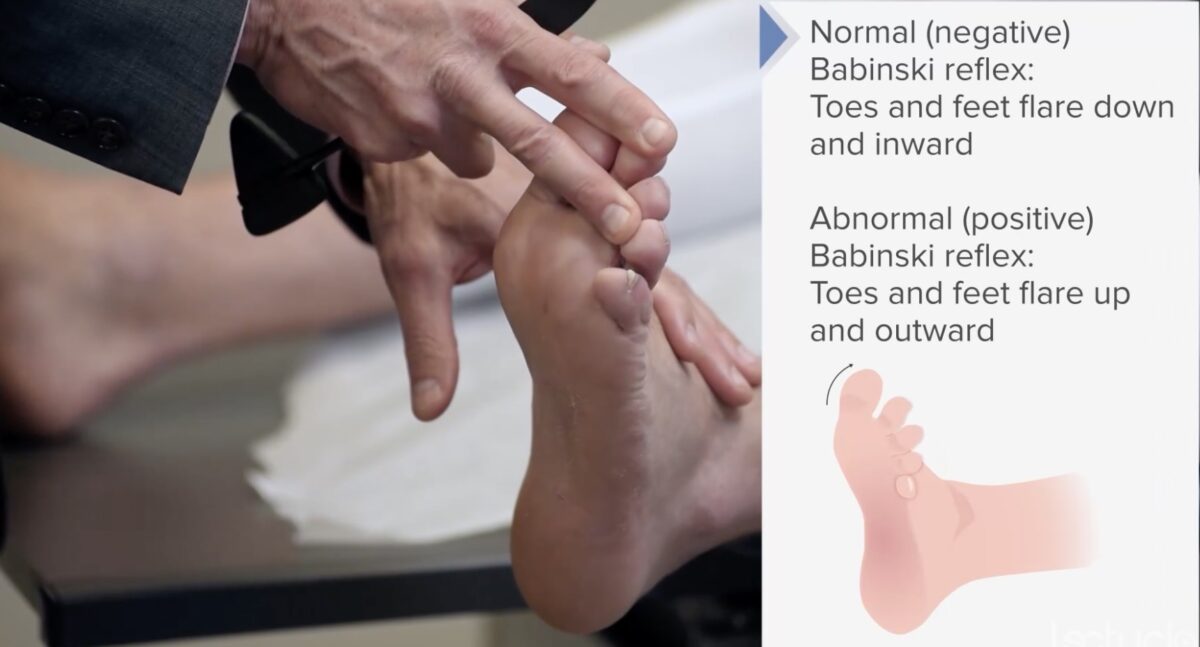
Un reflejo de Babinski anormal (positivo) es un signo de una lesión de motoneurona superior.
En una respuesta anormal (positiva), el hallux se flexiona dorsalmente mientras los otros dedos se abren en abanico.
| Sensación | Vía | Evaluación | Hallazgos anormales |
|---|---|---|---|
| Toque ligero | Tracto espinotalámico | Toque el cuerpo del sujeto en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum diferentes lugares de forma bilateral. |
|
| Vibración | Columnas dorsales | Proyecciones óseas probadas con un diapasón | La disminución de la sensación de vibración indica daño de los LOS Neisseria nervios periféricos. |
| Propiocepción | Columnas dorsales | Identifique el cambio posicional del hallux mientras lo mueve hacia arriba y abajo. | La propiocepción anormal indica daño de los LOS Neisseria nervios periféricos. |
| Dolor Dolor Inflammation y temperatura | Tracto espinotalámico |
|
La percepción anormal del dolor Dolor Inflammation y la temperatura indica daño de los LOS Neisseria nervios periféricos. |
| Estereognosis | Corteza cerebral | Pídale al AL Amyloidosis sujeto que identifique un objeto familiar con los LOS Neisseria ojos cerrados. | Incapacidad para identificar un objeto familiar |
| Grafestesia | Corteza cerebral | Trace un símbolo familiar en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la palma del sujeto mientras sus ojos estén cerrados. | Incapacidad para identificar el símbolo |
| Extinción táctil | Corteza cerebral | Aplique un estímulo táctil en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum cada lado del cuerpo y luego bilateralmente y compare la percepción. | Asimetría de percepción o incapacidad para percibir estímulos en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum 1 lado del cuerpo |
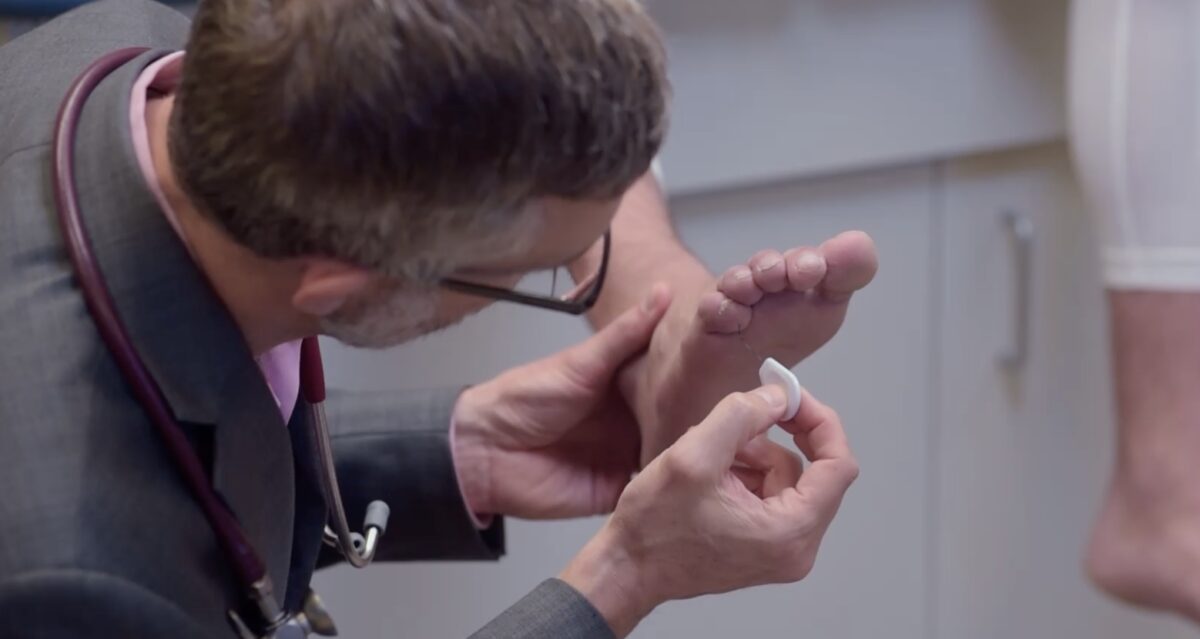
Las pruebas de tacto ligero a menudo se realizan utilizando el monofilamento de Semmes-Weinstein, una herramienta útil en el tamizaje de polineuropatía diabética. Aquí, se ve al examinador probando con un toque ligero en los pies.
Imagen por Lecturio.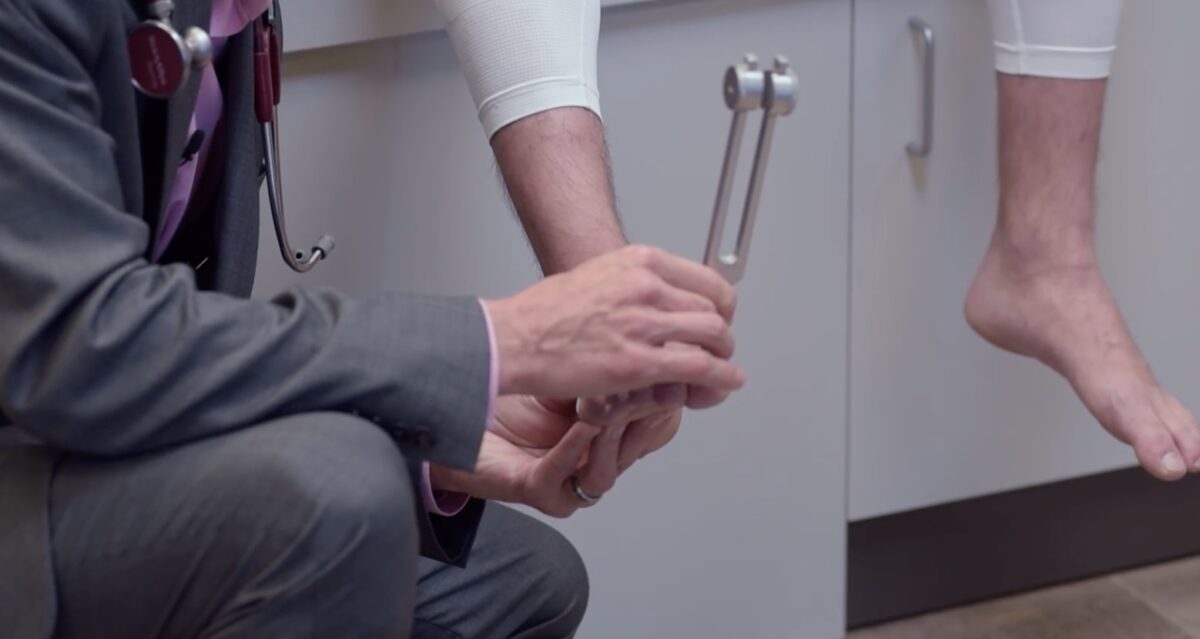
El sentido vibratorio se evalúa a menudo con un diapasón de 120 Hz. Aquí, el examinador está probando la sensación vibratoria de la extremidad inferior distal.
Imagen por Lecturio.
El sentido de la posición (propiocepción) se prueba pidiendo al sujeto que detecte movimiento de los dedos con los ojos cerrados. Aquí, el examinador está probando la propiocepción del miembro superior distal.
Imagen por Lecturio.
La prueba de estereognosis (identificación táctil de objetos con los ojos cerrados) se realiza a menudo pidiendo al sujeto que identifique un objeto aleatorio pero familiar con los ojos cerrados. Aquí, el examinador está probando la estereognosis con una llave.
Imagen por Lecturio.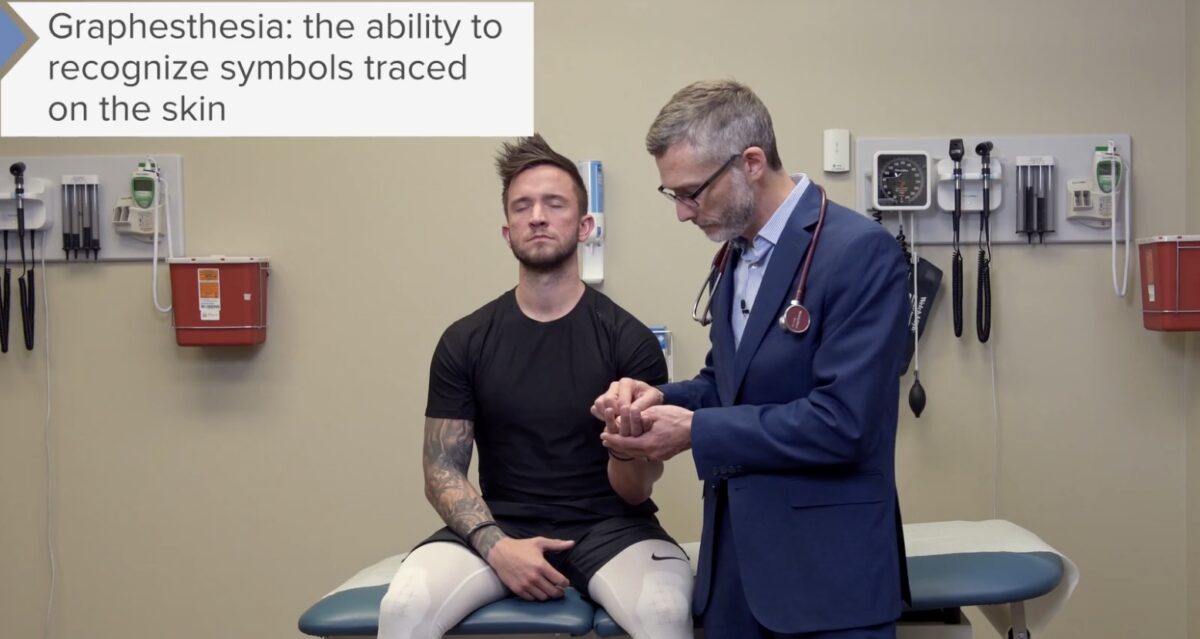
La prueba de grafestesia (capacidad de reconocer símbolos trazados en la piel) a menudo se realiza pidiendo al sujeto que identifique una figura aleatoria pero familiar dibujada en su piel mientras sus ojos están cerrados. Aquí, el examinador está probando la grafestesia dibujando una letra imaginaria en la palma del sujeto.
Imagen por Lecturio.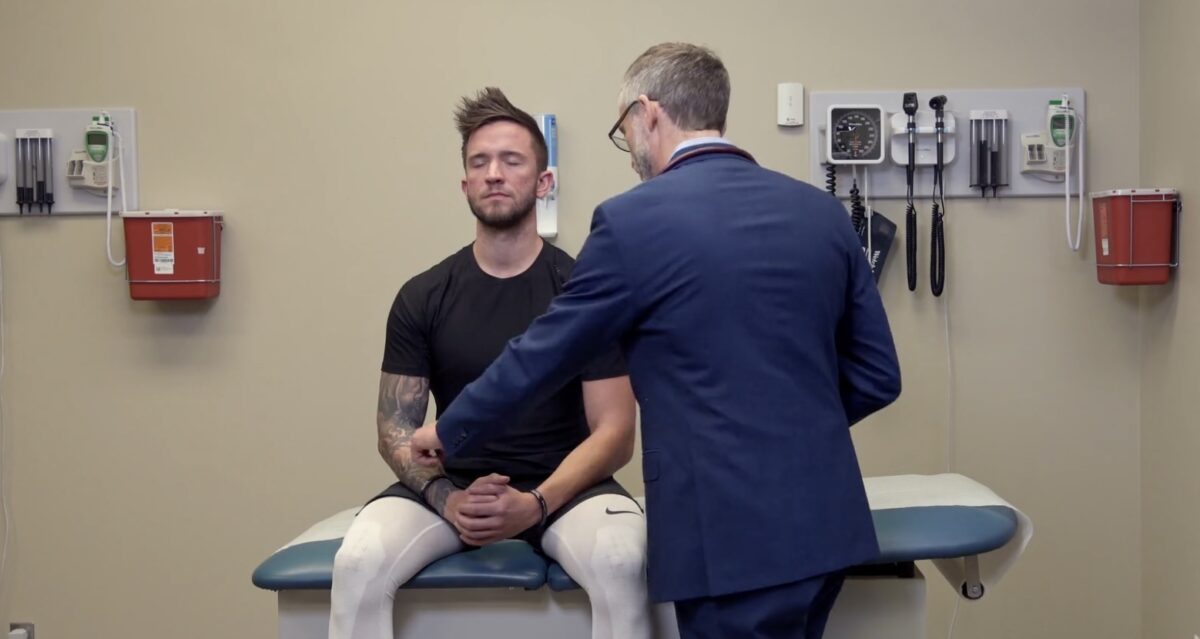
La prueba de extinción táctil (incapacidad para percibir los estímulos) a menudo se realiza pidiendo al sujeto que identifique un estímulo en 1 lado, luego en el otro y luego en ambos simultáneamente con los ojos cerrados. Aquí, el examinador está probando la extinción aplicando un ligero movimiento de caricia a las extremidades superiores.
Imagen por Lecturio.Se debe realizar un examen del cerebelo en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum cualquier sujeto que presente signos o síntomas de patología cerebelosa, incluidos:
Hay muchas causas de disfunción cerebelosa, que incluyen:
El examen del cerebelo incluye lo siguiente:
Coordinación:
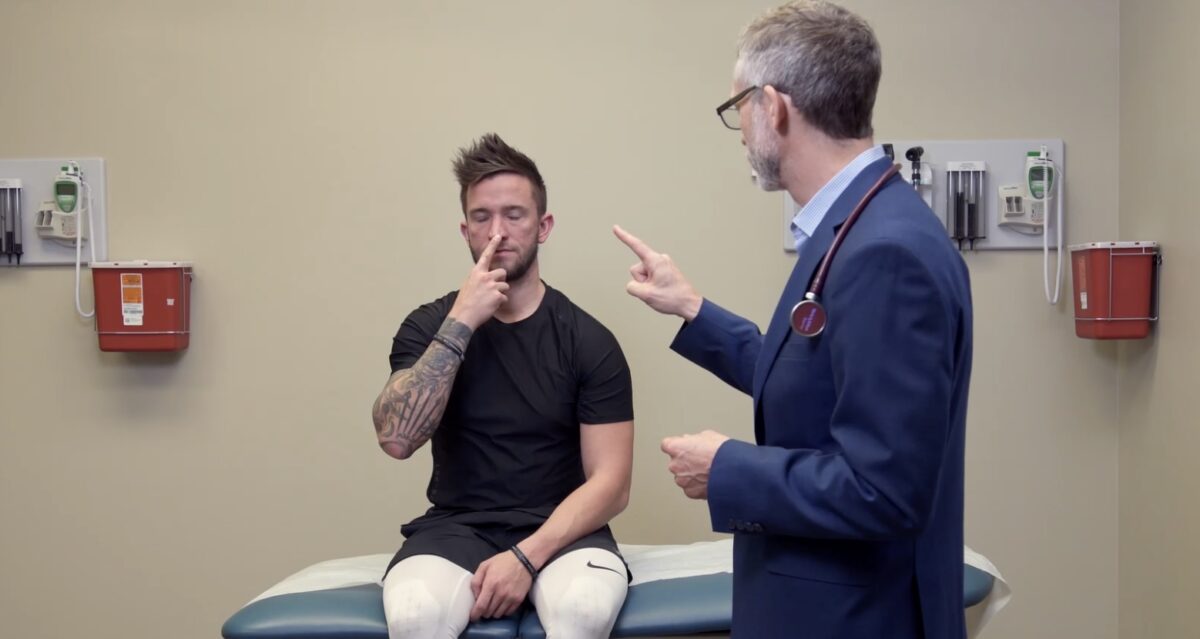

La ataxia de las extremidades se evalúa haciendo que el sujeto realice la prueba de dedo-nariz.
Imagen por Lecturio.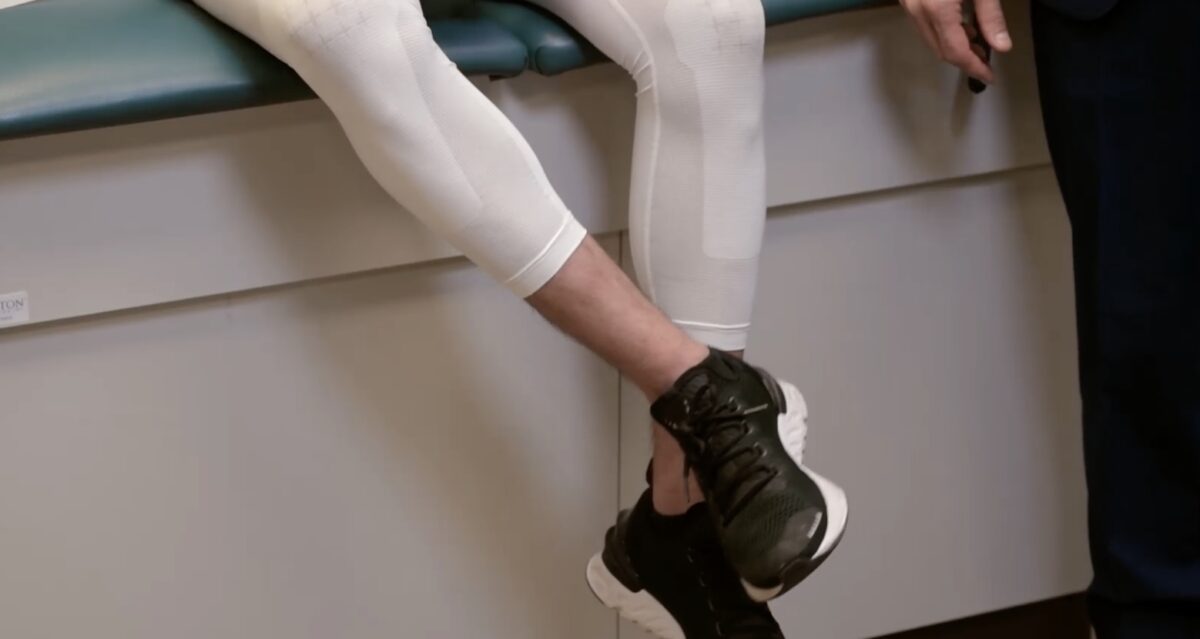
La ataxia de las extremidades se evalúa haciendo que el sujeto realice la prueba del talón-espinilla.
Imagen por Lecturio.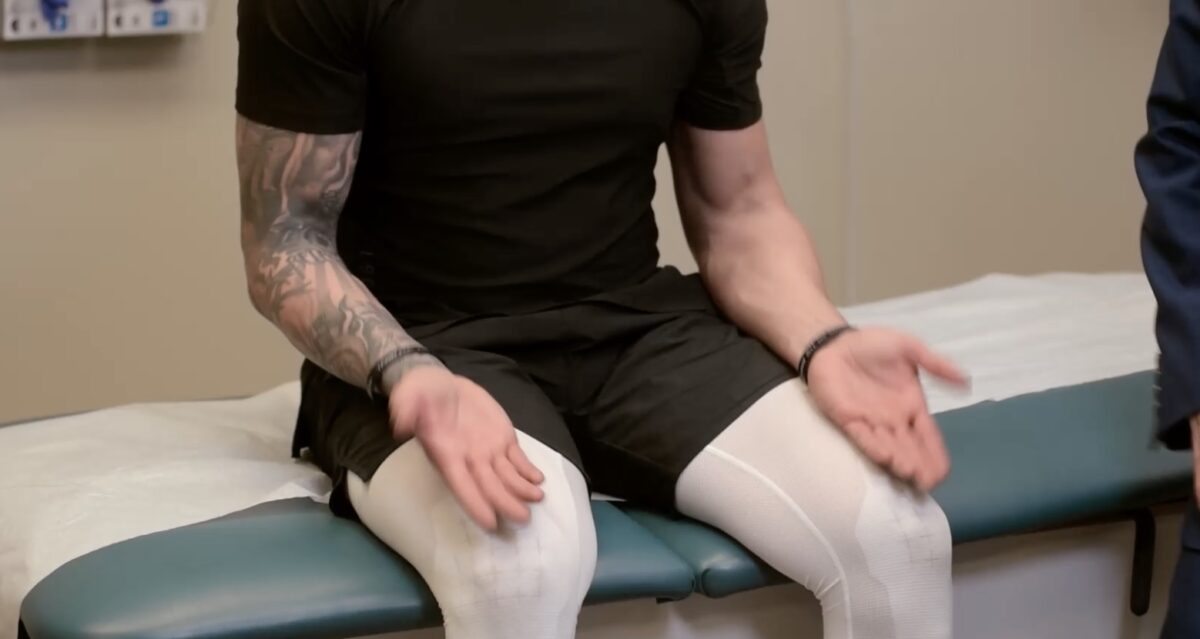
La disdiadococinesia se evalúa haciendo que el sujeto realice movimientos alternos rápidos.
Imagen por Lecturio.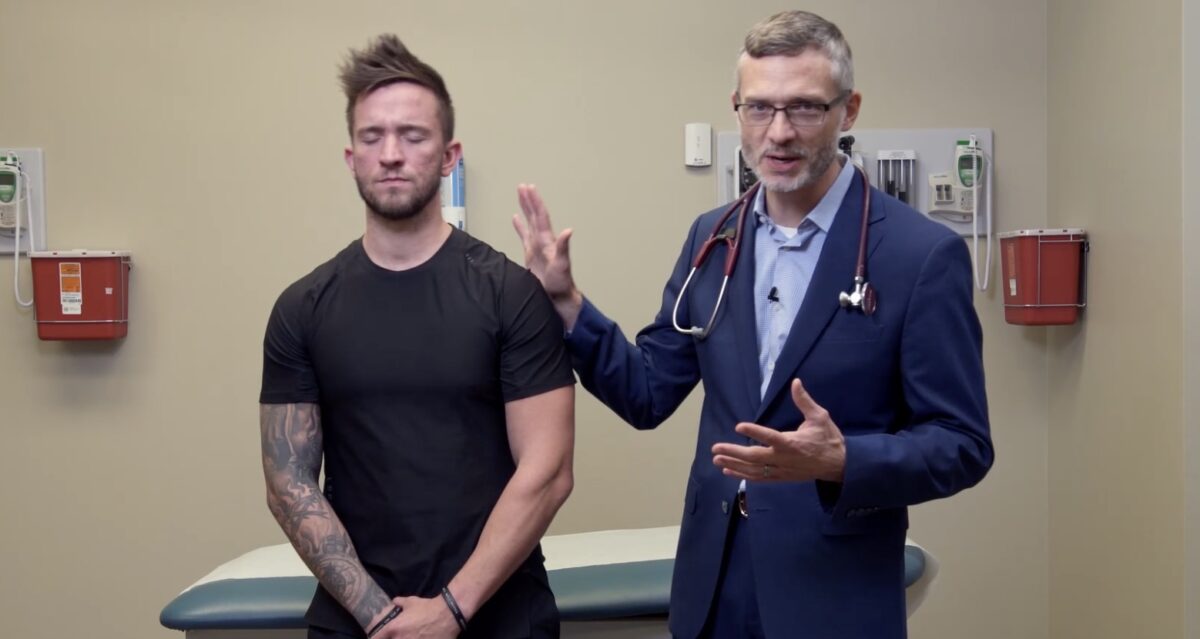
La prueba de Romberg ayuda a distinguir la ataxia debida a trastornos sensoriales periféricos de las causas cerebelosas de ataxia.
Un sujeto con ataxia sensorial se balanceará durante la prueba, mientras que un sujeto con un trastorno cerebeloso puede no balancearse hasta que se perturbe su equilibrio. Aquí, el examinador ha introducido un suave “empujón” al sujeto que presenta una prueba de Romberg negativa.
Evaluación de la marcha:
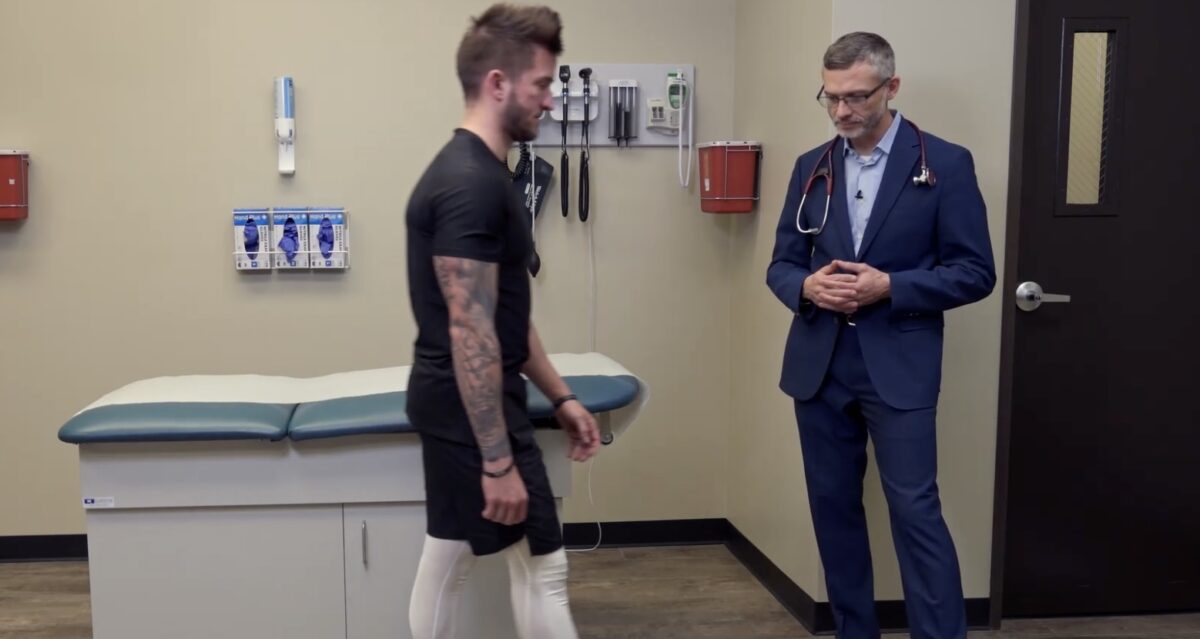
La prueba de ataxia de la marcha a menudo se realiza simplemente haciendo que el sujeto deambule por la habitación.
Imagen por Lecturio.Muchos síndromes cerebelosos pueden manifestarse con anomalías en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la marcha.
| Marcha | Descripción | Signos asociados | Causas |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cerebelar |
|
|
|
| Sensorial |
|
|
|
| Vestibular |
|
|
|
| Parkinsoniana |
|
|
|
| Estepaje | Pie caído al AL Amyloidosis caminar | Pérdida sensorial distal y debilidad | Neuropatía motora |
| Marcha/signo de Trendelenburg | La pelvis Pelvis The pelvis consists of the bony pelvic girdle, the muscular and ligamentous pelvic floor, and the pelvic cavity, which contains viscera, vessels, and multiple nerves and muscles. The pelvic girdle, composed of 2 “hip” bones and the sacrum, is a ring-like bony structure of the axial skeleton that links the vertebral column with the lower extremities. Pelvis: Anatomy desciende hacia el lado no afectado. | Debilidad en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria músculos gluteus medius Gluteus medius Gluteal Region: Anatomy y gluteus minimus Gluteus minimus Gluteal Region: Anatomy | Daño al AL Amyloidosis nervio glúteo superior |
| Espástica | Movimientos lentos, rígidos y laboriosos | Tijereteo de piernas |
|
Las siguientes afecciones se pueden encontrar durante el examen neurológico: