La encefalopatía hepática es una afección reversible en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la que los LOS Neisseria niveles elevados de amoníaco provocan un deterioro de la función cerebral en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum pacientes con enfermedad hepática avanzada. La encefalopatía hepática puede precipitarse por condiciones que afectan la absorción normal, el metabolismo o la depuración de amoníaco, como deshidratación, insuficiencia renal, infecciones y hemorragia digestiva. Los LOS Neisseria pacientes presentan una progresión de los LOS Neisseria síntomas, desde confusión mínima y asterixis Asterixis Hepatic Encephalopathy hasta estupor y coma Coma Coma is defined as a deep state of unarousable unresponsiveness, characterized by a score of 3 points on the GCS. A comatose state can be caused by a multitude of conditions, making the precise epidemiology and prognosis of coma difficult to determine. Coma. El diagnóstico es clínico y requiere la exclusión de diagnósticos alternativos. El tratamiento implica abordar el factor causal y disminuir la absorción sistémica de amoníaco con lactulosa o rifaximina.
Last updated: Jan 17, 2024
La encefalopatía hepática se observa en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum pacientes con enfermedad hepática grave o insuficiencia hepática y puede exacerbarse por:
Los factores precipitantes de la encefalopatía hepática pueden recordarse mediante la nemotécnica “HEPATICS” ( En EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum inglés):
| H | Hemorrhage in the GI tract (Hemorragia digestiva) |
|---|---|
| E | Excess dietary protein (Exceso de proteínas en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la dieta) |
| P | Potassium Potassium An element in the alkali group of metals with an atomic symbol k, atomic number 19, and atomic weight 39. 10. It is the chief cation in the intracellular fluid of muscle and other cells. Potassium ion is a strong electrolyte that plays a significant role in the regulation of fluid volume and maintenance of the water-electrolyte balance. Hyperkalemia ( hypokalemia Hypokalemia Hypokalemia is defined as plasma potassium (K+) concentration < 3.5 mEq/L. Homeostatic mechanisms maintain plasma concentration between 3.5-5.2 mEq/L despite marked variation in dietary intake. Hypokalemia can be due to renal losses, GI losses, transcellular shifts, or poor dietary intake. Hypokalemia) (Potasio (hipopotasemia)) |
| A | Alkalosis Alkalosis A pathological condition that removes acid or adds base to the body fluids. Respiratory Alkalosis or azotemia Azotemia A biochemical abnormality referring to an elevation of blood urea nitrogen and creatinine. Azotemia can be produced by kidney diseases or other extrarenal disorders. When azotemia becomes associated with a constellation of clinical signs, it is termed uremia. Acute Kidney Injury (Alcalosis o azotemia Azotemia A biochemical abnormality referring to an elevation of blood urea nitrogen and creatinine. Azotemia can be produced by kidney diseases or other extrarenal disorders. When azotemia becomes associated with a constellation of clinical signs, it is termed uremia. Acute Kidney Injury) |
| T | TIPS procedure (TIPS, por sus siglas en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum inglés, procedimiento de derivación portosistémica intrahepática transyugular) |
| I | Infection (Infección) |
| C | Constipation Constipation Constipation is common and may be due to a variety of causes. Constipation is generally defined as bowel movement frequency < 3 times per week. Patients who are constipated often strain to pass hard stools. The condition is classified as primary (also known as idiopathic or functional constipation) or secondary, and as acute or chronic. Constipation (Constipación) |
| S | Sedatives (Sedantes) |
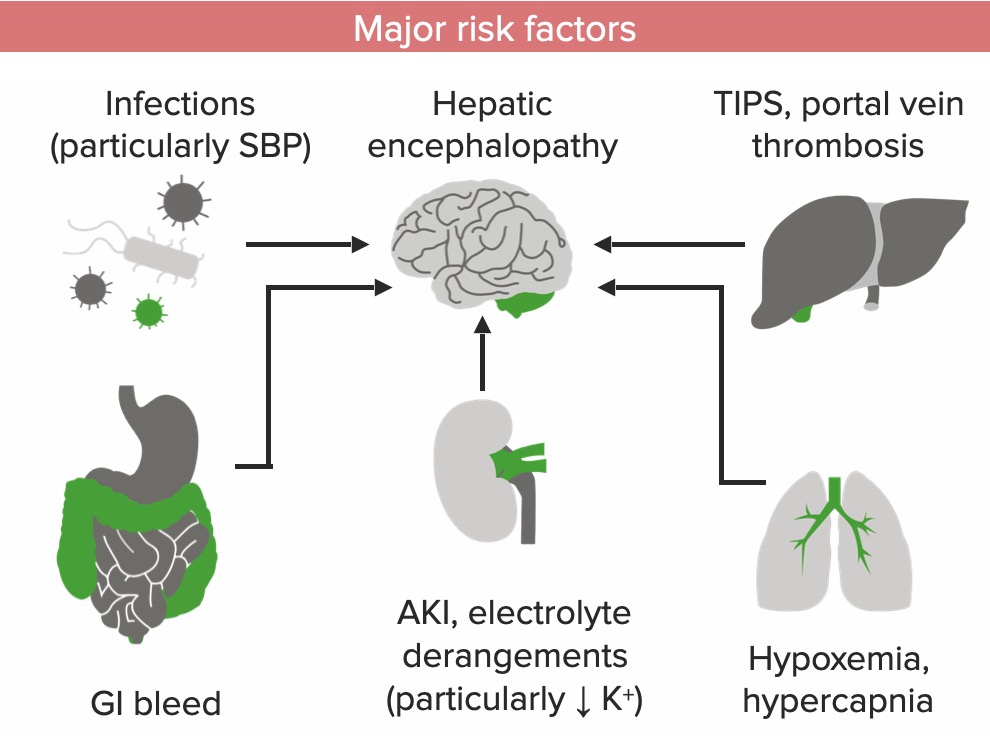
Principales factores de riesgo de encefalopatía hepática en un paciente con insuficiencia hepática
AKI: lesión renal aguda
SBP: peritonitis bacteriana espontánea
Fisiología normal:
La enfermedad hepática permite la interrupción de la regulación normal del amoníaco a través de:
El deterioro de la función cerebral resulta de una acumulación de amoníaco, donde:
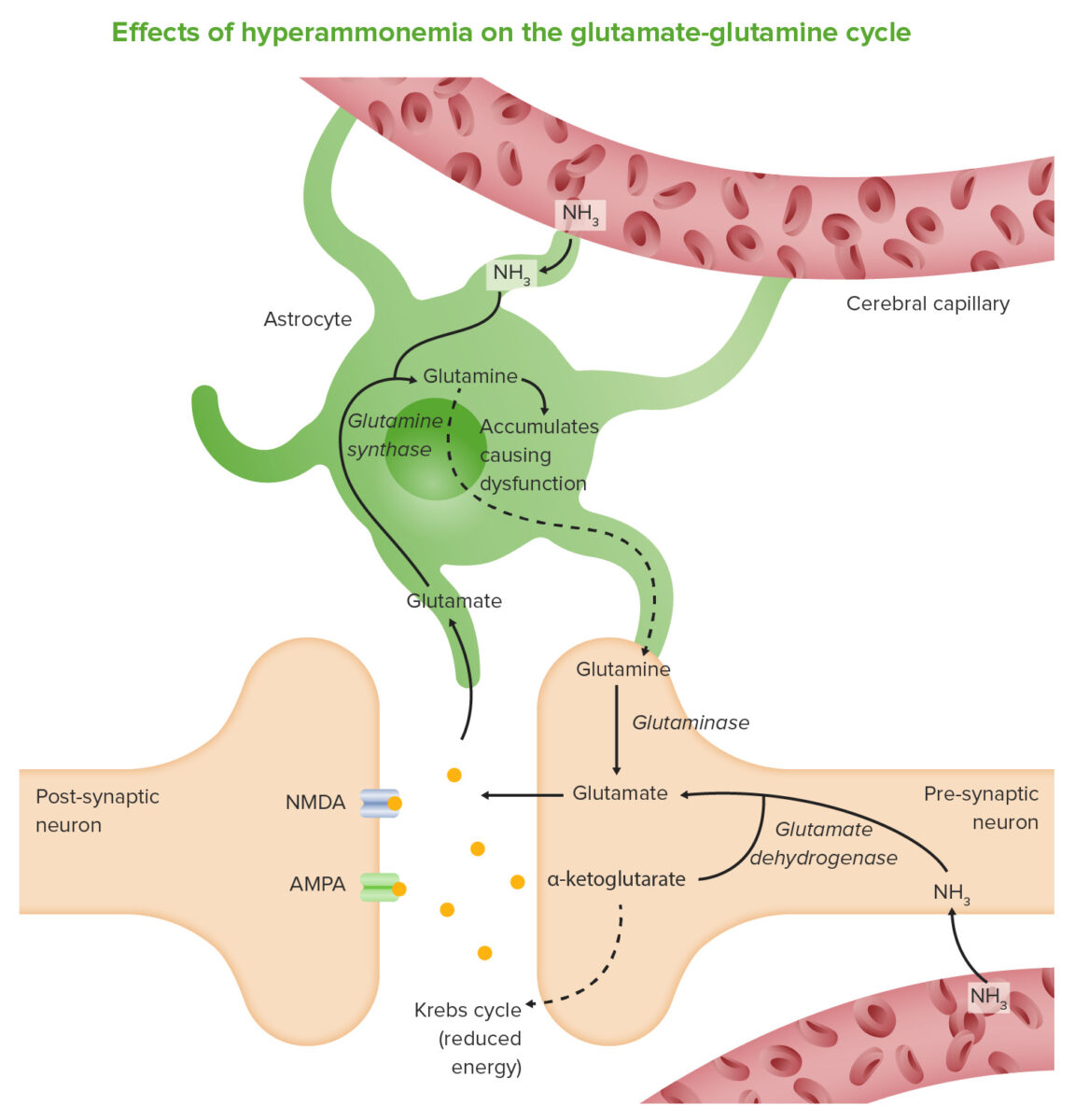
El amoníaco (NH3) atraviesa la barrera hematoencefálica y es absorbido y metabolizado por los astrocitos. Estas células usan amoníaco cuando sintetizan glutamina a partir de glutamato. El aumento de los niveles de glutamina conduce a un aumento de la presión osmótica en los astrocitos, que se hinchan y provocan edema cerebral. El amoníaco también aumenta la actividad del sistema inhibitorio GABA y reduce la producción de energía.
Imagen por Lecturio.Los LOS Neisseria criterios de West Haven se utilizan para establecer la severidad clínica.
| Estadio | Conciencia | Intelecto y comportamiento | Hallazgos neurológicos |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | Normal | Normal | Normal |
| Mínimo | Normal | Psicométrico (velocidad psicomotora/función ejecutora) o pruebas neurofisiológicas son anormales. | Psicométrico (velocidad psicomotora/función ejecutora) o pruebas neurofisiológicas son anormales. |
| 1 | Leve falta de conciencia | Intelecto lento, apatía, inquietud, sueño desordenado | Asterixis Asterixis Hepatic Encephalopathy leve, cálculo alterado |
| 2 | Letárgico | Desorientación moderada, somnolencia, comportamiento inapropiado | Asterixis Asterixis Hepatic Encephalopathy, dificultad para hablar |
| 3 | Somnoliento pero excitable | Desorientación, habla incoherente | Asterixis Asterixis Hepatic Encephalopathy, hiperreflexia, clonus Clonus Ehrlichiosis and Anaplasmosis, rigidez muscular |
| 4 | Coma Coma Coma is defined as a deep state of unarousable unresponsiveness, characterized by a score of 3 points on the GCS. A comatose state can be caused by a multitude of conditions, making the precise epidemiology and prognosis of coma difficult to determine. Coma | Coma Coma Coma is defined as a deep state of unarousable unresponsiveness, characterized by a score of 3 points on the GCS. A comatose state can be caused by a multitude of conditions, making the precise epidemiology and prognosis of coma difficult to determine. Coma | Posturas de descerebración o decorticación, la asterixis Asterixis Hepatic Encephalopathy suele estar ausente |
La encefalopatía hepática es un diagnóstico clínico y deben excluirse otras condiciones.
Consejo: La peritonitis Peritonitis Inflammation of the peritoneum lining the abdominal cavity as the result of infectious, autoimmune, or chemical processes. Primary peritonitis is due to infection of the peritoneal cavity via hematogenous or lymphatic spread and without intra-abdominal source. Secondary peritonitis arises from the abdominal cavity itself through rupture or abscess of intra-abdominal organs. Penetrating Abdominal Injury bacteriana espontánea debe descartarse en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum todos los LOS Neisseria pacientes que presentan encefalopatía hepática y ascitis.
Se enfoca en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum identificar y tratar los LOS Neisseria factores precipitantes y reducir la concentración sérica de amoníaco.