El tromboembolismo pulmonar (TEP) es una afección potencialmente mortal que se produce como resultado de una obstrucción intraluminal de la arteria pulmonar principal o de sus ramas. Los LOS Neisseria factores causantes son los LOS Neisseria trombos, el aire, el líquido amniótico y la grasa. En EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria TEP, el intercambio de gases se ve VE Ventilation: Mechanics of Breathing afectado por la disminución del retorno de sangre desoxigenada a los LOS Neisseria pulmones. Más del 90% de los LOS Neisseria TEP son complicaciones de una trombosis venosa profunda (TVP) de la extremidad inferior. Algunos individuos son asintomáticos, pero el síntoma de presentación más común es la disnea. Los LOS Neisseria síntomas pueden ser agudos o crónicos, y el diagnóstico suele basarse en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria hallazgos radiográficos, normalmente una angiografía pulmonar por TC. El tratamiento inicial es de soporte y se centra en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum restablecer la oxigenación y la estabilidad hemodinámica. Para restablecer la permeabilidad de los LOS Neisseria vasos se utilizan tanto terapias médicas (anticoagulantes sistémicos y/o trombolíticos) como intervencionistas (trombólisis por catéter, cirugía). Nota: La siguiente página se centrará en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el TEP trombótica. Véase Embolia no trombótica para obtener información sobre embolismos de aire, líquido amniótico y grasa.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
El tromboembolismo pulmonar (TEP) es la obstrucción intraluminal de una arteria pulmonar principal o de cualquiera de sus ramas por un trombo, aire, líquido amniótico o grasa. Cuando el TEP se considera junto con la TVP, la afección se conoce como enfermedad tromboembólica venosa.
Los LOS Neisseria tres factores principales que contribuyen a la enfermedad tromboembólica venosa (conocidos como la tríada de Virchow) son: estasis venosa, hipercoagulabilidad y daño endotelial vascular. Cualquier condición que empeore 1 (o más) de estos tres factores aumenta el riesgo de formación de TVP y, por tanto, de TEP.
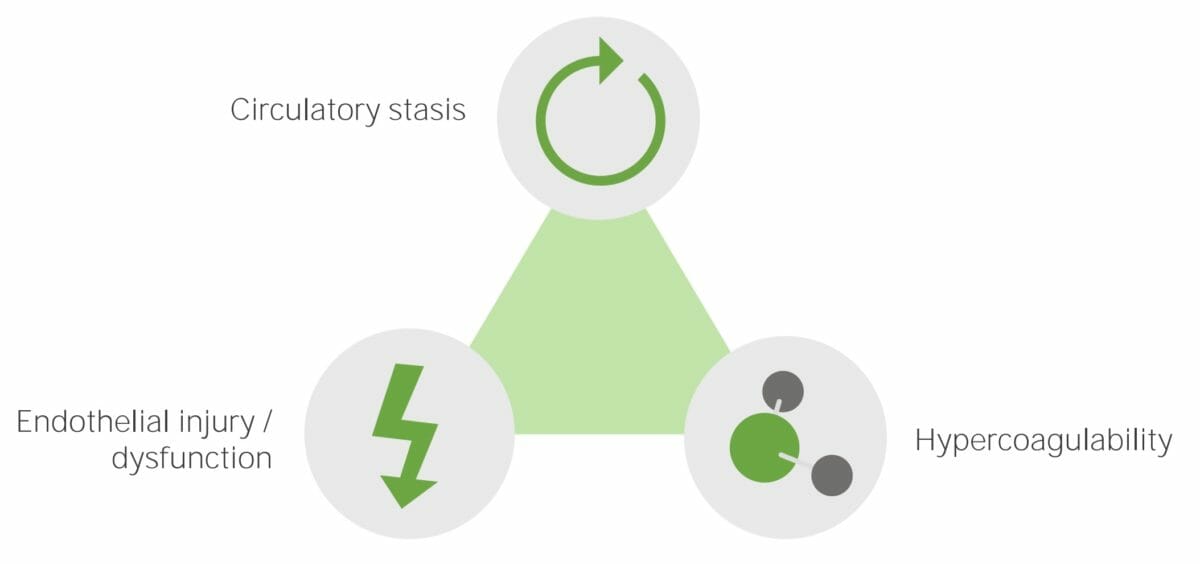
La tríada de Virchow. Los principales factores etiológicos que causan la enfermedad tromboembólica venosa son: estasis circulatoria, lesión o disfunción endotelial e hipercoagulabilidad.
Imagen por Lecturio.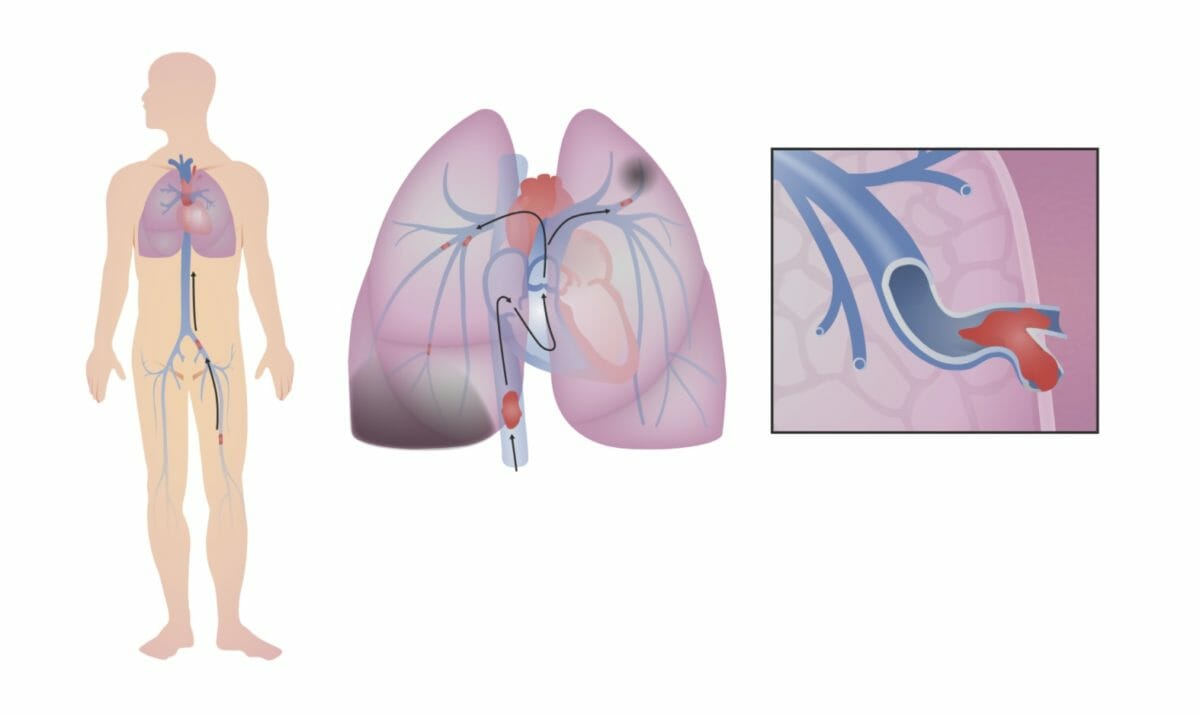
Tromboembolismo venoso. Una trombosis venosa profunda (TVP) se desprende en la pierna (en esta imagen, el trombo se forma en la vena femoral izquierda). Sube por la vena cava inferior, a través del lado derecho del corazón, donde (en este caso) se rompe en fragmentos más pequeños que se alojan en ramas más pequeñas de las arterias pulmonares. Esta obstrucción del flujo sanguíneo a través de los pulmones disminuye la capacidad de los pulmones para oxigenar la sangre y, si es lo suficientemente grande, ejerce presión sobre el lado derecho del corazón.
Imagen por Lecturio.Desajuste de la ventilación/perfusión (V/Q):
Inestabilidad hemodinámica:
Infarto pulmonar:
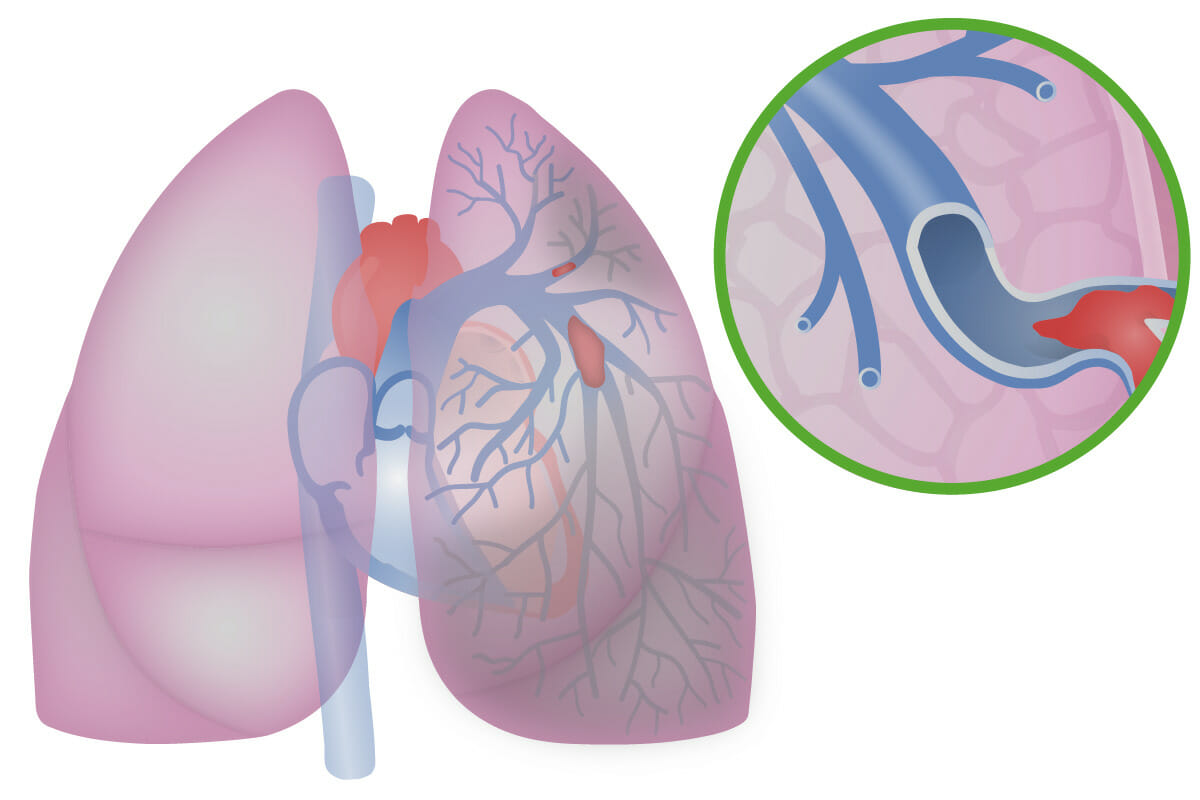
Ilustración de un tromboembolismo pulmonar
Imagen: “Illustration of pulmonary embolism” por Baedr-9439. Licencia: CC0La presentación varía significativamente. Debe mantenerse una alta sospecha dado el riesgo de complicaciones y mortalidad.
El diagnóstico se realiza principalmente por medio de estudios de imagen. La decisión de obtener imágenes se basa en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la sospecha clínica, la evaluación de la probabilidad previa a la prueba (normalmente utilizando los LOS Neisseria criterios de Wells modificados) y los LOS Neisseria niveles de dímero D.
Evaluación preliminar
| Criterios principales | Puntuación |
|---|---|
| Signos/síntomas de la TVP | 3,0 |
| El TEP es clínicamente más probable que otros diagnósticos | 3,0 |
| Taquicardia | 1,5 |
| Inmovilización prolongada (≥ 3 días) o cirugía reciente ( en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria últimos 30 días) | 1,5 |
| Antecedentes de TEP o TVP | 1,5 |
| Hemoptisis | 1,0 |
| Malignidad | 1,0 |
Uso de la evaluación preliminar y la puntuación de Wells modificada
Radiografía de tórax:
Angiografía pulmonar por TC de tórax con contraste o TC en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum espiral:
Gammagrafía de ventilación/perfusión (V/Q):
Pruebas en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum individuos hemodinámicamente inestables: los LOS Neisseria estudios a la cabecera del paciente puede servir para hacer un diagnóstico presuntivo de TEP, que justifica el inicio del tratamiento.
Angiografía pulmonar:
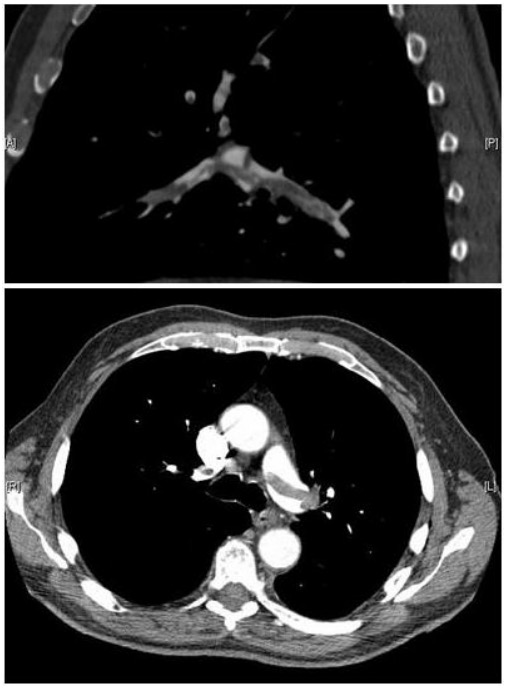
Imágenes de angiografía pulmonar por TC que confirman la presencia de un émbolo en silla de montar y una carga sustancial de trombos en las ramas lobulares de ambas arterias pulmonares principales
Imagen: “Pulmonary embolism CTPA” por Aung Myat and Arif Ahsan. Licencia: CC BY 2.0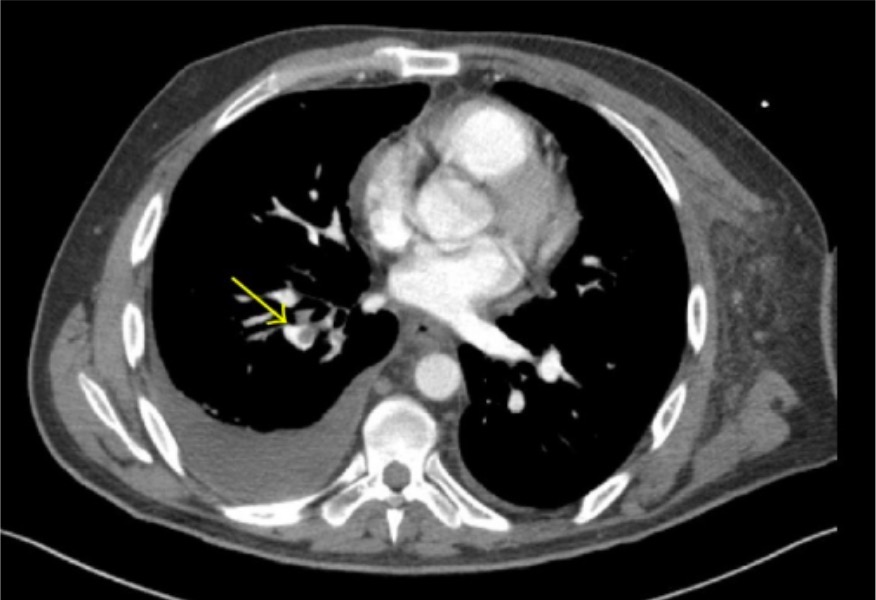
Angiografía por TC que demuestra émbolos pulmonares lobulares y segmentarios (flecha) en el lóbulo inferior derecho
Imagen: “CT angiography” por Thomas Jefferson University, 1025 Walnut Street, Philadelphia, PA 19107, USA. Licencia: CC BY 3.0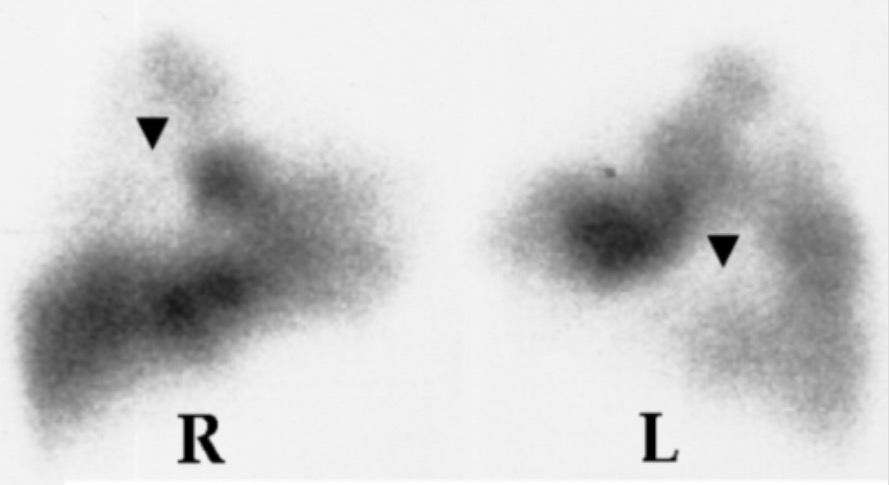
Gammagrafía V/Q que muestra defectos de perfusión (flechas) en los pulmones derecho (R) e izquierdo (L)
Image:n“Lung scan” por Department of Cardiology, Sotiria Chest Diseases Hospital, Athens, Greece. Licencia: CC BY 2.5Evaluar y tratar cualquier inestabilidad hemodinámica. La mayoría de los LOS Neisseria individuos se presentarán en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum condiciones estables o responderán a los LOS Neisseria esfuerzos iniciales de reanimación.
Profilaxis contra TEP recurrente
Anticoagulación: prevención secundaria de la enfermedad tromboembólica venosa
Estilo de vida/otras opciones:

Émbolos pulmonares en ambas arterias pulmonares revelados tras la autopsia de un paciente que murió de embolia pulmonar:
A: trombo macroscópico (flechas)
B: trombo de 20 cm de longitud
C: trombos microscópicos (flechas), tinción de hematoxilina y eosina, aumento X100