Los LOS Neisseria eicosanoides son moléculas de señalización celular producidas a partir del ácido araquidónico. Con la acción de la fosfolipasa A2, el ácido araquidónico se libera de la membrana plasmática. Las diferentes familias de eicosanoides, que son las prostaglandinas (PGs), los LOS Neisseria tromboxanos (TXA2), la prostaciclina ( PGI PGI An aldose-ketose isomerase that catalyzes the reversible interconversion of glucose 6-phosphate and fructose 6-phosphate. In prokaryotic and eukaryotic organisms it plays an essential role in glycolytic and gluconeogenic pathways. In mammalian systems the enzyme is found in the cytoplasm and as a secreted protein. This secreted form of glucose-6-phosphate isomerase has been referred to as autocrine motility factor or neuroleukin, and acts as a cytokine which binds to the autocrine motility factor receptor. Deficiency of the enzyme in humans is an autosomal recessive trait, which results in congenital nonspherocytic hemolytic anemia. Glycolysis2), las lipoxinas y los LOS Neisseria leucotrienos , surgen de una serie de reacciones catalizadas por diferentes enzimas. Los LOS Neisseria leucotrienos y las lipoxinas son productos de la vía de la lipoxigenasa. Los LOS Neisseria demás eicosanoides se producen a partir de la vía de la ciclooxigenasa (COX), en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la que intervienen 2 enzimas, COX-1 y COX-2. Los LOS Neisseria eicosanoides están implicados en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum diversos procesos fisiológicos y patológicos. Los LOS Neisseria tromboxanos provocan la agregación plaquetaria y son potentes vasoconstrictores. Los LOS Neisseria leucotrienos median las respuestas alérgicas, mientras que las lipoxinas tienen actividades antiinflamatorias. Las principales acciones de las prostaglandinas incluyen la vasodilatación, contracción del músculo liso e inflamación. La prostaciclina, miembro de la familia de las prostaglandinas, tiene un potente efecto vasodilatador. Tanto las acciones biológicas como las inhibiciones de los LOS Neisseria eicosanoides son mecanismos utilizados en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria medicamentos para diversas condiciones médicas y efectos clínicos deseados.
Last updated: Oct 23, 2022
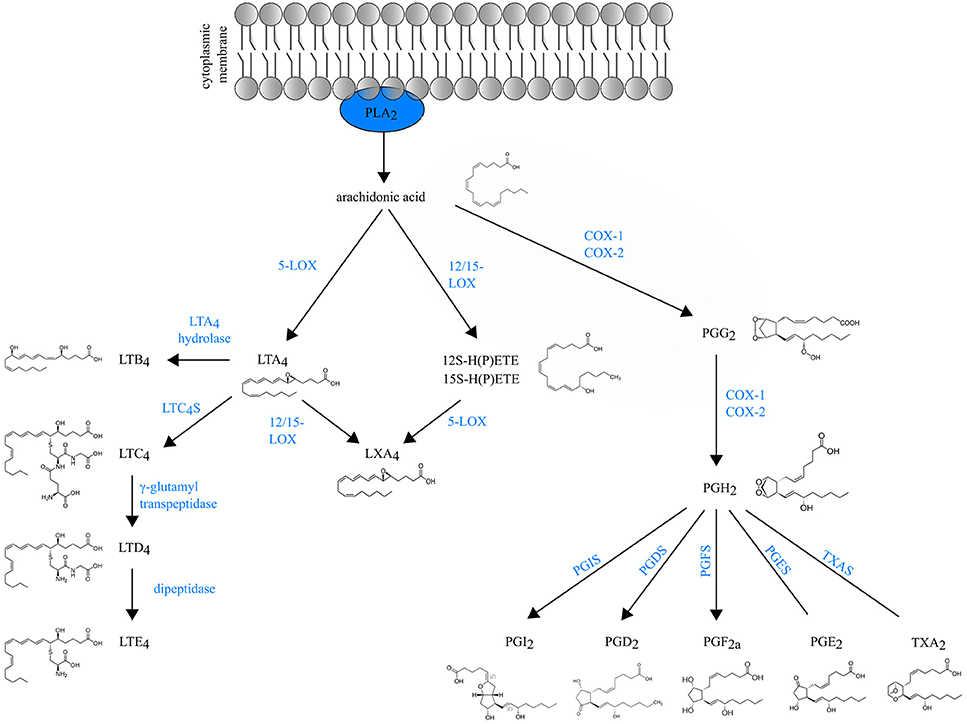
Resumen esquemático de la biosíntesis de eicosanoides:
El ácido araquidónico liberado de los fosfolípidos de la membrana por la fosfolipasa A2 citosólica puede ser convertido enzimáticamente en prostaglandinas (PGs) y tromboxano (TXA2) por las enzimas COX o en leucotrienos (LTs) y lipoxinas (LXA4) por las lipooxigenasas (LOXs).
5-LOX: 5-lipoxigenasa
12/15-LOX: 12/15-lipoxigenasa
LTC4S: LTC4 sintasa
PGIS: PGI o prostaciclina sintasa
PGDS: PG D2 sintasa
PGFS: PG F sintasa
PGES: PG E sintasa
TXAS: TXA2 sintasa
Efectos inflamatorios del TXA2 en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum algunas condiciones:
| Prostaglandinas | Efectos |
|---|---|
| PGD PGD Determination of the nature of a pathological condition or disease in the ovum; zygote; or blastocyst prior to implantation. Cytogenetic analysis is performed to determine the presence or absence of genetic disease. Reproductive Ethical Issues2 (producida predominantemente por mastocitos) |
|
| PGE1 |
|
| PGE2 |
|
| PGF2ɑ |
|
| PGI PGI An aldose-ketose isomerase that catalyzes the reversible interconversion of glucose 6-phosphate and fructose 6-phosphate. In prokaryotic and eukaryotic organisms it plays an essential role in glycolytic and gluconeogenic pathways. In mammalian systems the enzyme is found in the cytoplasm and as a secreted protein. This secreted form of glucose-6-phosphate isomerase has been referred to as autocrine motility factor or neuroleukin, and acts as a cytokine which binds to the autocrine motility factor receptor. Deficiency of the enzyme in humans is an autosomal recessive trait, which results in congenital nonspherocytic hemolytic anemia. Glycolysis2 (producida por células endoteliales de la pared vascular) |
Con múltiples efectos biológicos, varias prostaglandinas tienen usos clínicos:
Los LOS Neisseria leucotrienos median en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum las respuestas alérgicas e inflamatorias y su liberación es estimulada por antígenos.
| Eicosanoides | Efectos |
|---|---|
| LTC4, LTD4, LTE4 |
|
| LTB4 (y HETE (hidroxieicosatetraenoico)) |
|
| LXsA4 y B4 |
|
Los LOS Neisseria leucotrienos son liberados por las células y sus efectos inflamatorios se observan en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el asma ASMA Autoimmune Hepatitis y las alergias.
La inhibición de las vías lo cual reduce la producción de eicosanoides, también tiene usos clínicos.