Las tiñas son un grupo de enfermedades causadas por hongos que infectan el tejido queratinizado (pelo, uñas y piel). Estas infecciones se denominan dermatomicosis y son causadas por los LOS Neisseria hongos dermatofitos. Existen aproximadamente 40 hongos dermatofitos que forman parte de 3 géneros, incluyendo Trichophyton Trichophyton A mitosporic fungal genus and an anamorphic form of arthroderma. Various species attack the skin, nails, and hair. Dermatophytes/Tinea Infections, Epidermophyton Epidermophyton A fungal genus which grows in the epidermis and is the cause of tinea. Dermatophytes/Tinea Infections y Microsporum Microsporum A mitosporic oxygenales fungal genus causing various diseases of the skin and hair. The species microsporum canis produces tinea capitis and tinea corporis, which usually are acquired from domestic cats and dogs. Teleomorphs includes arthroderma (nannizzia). Dermatophytes/Tinea Infections. Estas infecciones pueden afectar a cualquier parte del cuerpo, pero se producen con mayor frecuencia en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum regiones cálidas y húmedas como la ingle y los LOS Neisseria pies. El diagnóstico es clínico con hallazgos cutáneos característicos, pero puede confirmarse mediante la microscopía de los LOS Neisseria raspados de piel. El tratamiento depende del lugar y la magnitud de la infección, pero suele comenzarse con antifúngicos tópicos como los LOS Neisseria medicamentos -azoles y la terbinafina, y hasta puede progresar a presentaciones orales de estos medicamentos si el tratamiento tópico falla.
Last updated: Feb 14, 2022
Las infecciones por tiña se clasifican y denominan según la región del cuerpo afectada.
Los LOS Neisseria signos y síntomas son similares entre las infecciones por tiña, con algunas pequeñas diferencias según la región del cuerpo afectada. Las lesiones tienden a ser placas bien delimitadas, anulares y periféricas con un borde escamoso. También pueden estar asociadas a eritema y/o maceración.
| Nombre | Región del cuerpo | Etiología | Epidemiología y factores de riesgo | Características clínicas |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tinea pedis (“pie de atleta”) | Pies, espacios interdigitales de los LOS Neisseria dedos |
|
|
|
| Tinea corporis (“tiña corporal”) | Tronco y extremidades (excluyendo manos y pies) |
|
|
|
| Tinea cruris (“tiña inguinal”) | Ingle, pliegues inguinales |
|
|
|
| Tinea unguium Tinea unguium A fungal infection of the nail, usually caused by dermatophytes; yeasts; or nondermatophyte molds. Dermatophytes/Tinea Infections (onicomicosis) | Uñas de las manos o de los LOS Neisseria pies | T. rubrum |
|
|
| Tinea capitis Tinea capitis Ringworm of the scalp and associated hair mainly caused by species of Microsporum; Trichophyton; and Epidermophyton, which may occasionally involve the eyebrows and eyelashes. Dermatophytes/Tinea Infections | Folículos pilosos y cuero cabelludo |
|
|
|
| Granuloma de Majocchi (foliculitis fúngica) | Folículos pilosos en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el cuerpo | T. rubrum |
|
|
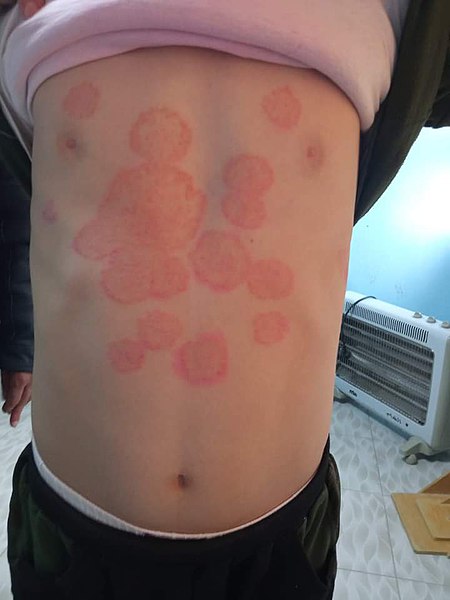
Tinea corporis, “tiña corporal” en un niño:
La infección se debe con mayor frecuencia al Trichophyton rubrum, que se presenta con placas circulares, eritematosas y pruriginosas, con escamas periféricas y un aclaramiento central.
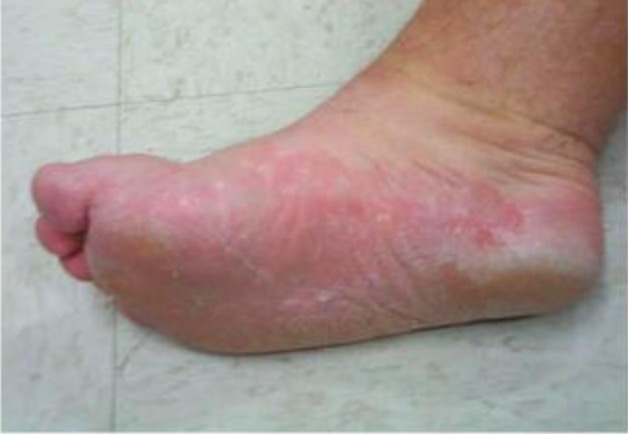
Tinea pedis:
La infección se debe con mayor frecuencia al Trichophyton rubrum. La forma hiperqueratósica se presenta con descamación en una distribución en forma de “mocasín”.
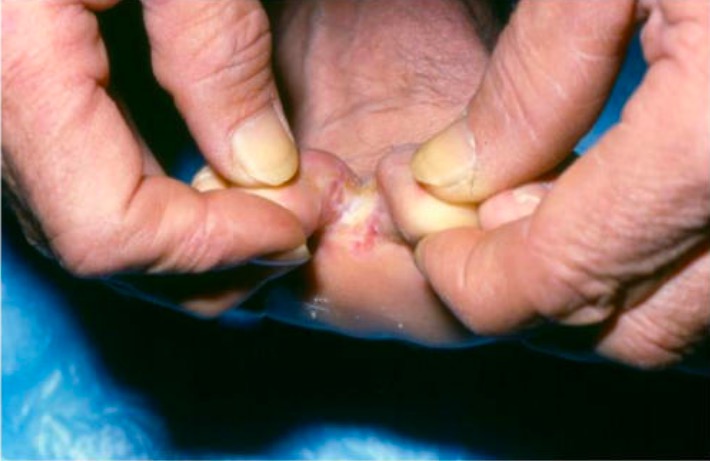
Tinea pedis:
La infección se debe con mayor frecuencia al Trichophyton rubrum. La forma interdigital se presenta con maceración pruriginosa y escamosa en las redes interdigitales de los dedos del pie.
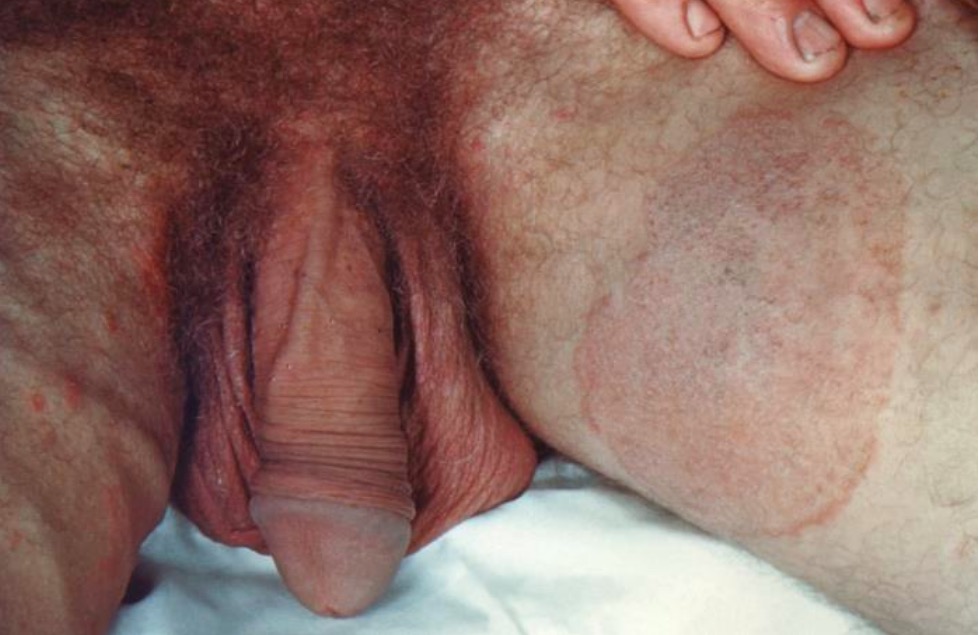
Tinea cruris, “tiña inguinal”:
Esta infección es causada con mayor frecuencia por Epidermophyton floccosum y se presenta con lesiones pruriginosas y eritematosas en forma de placa en la ingle que respeta la piel del escroto.
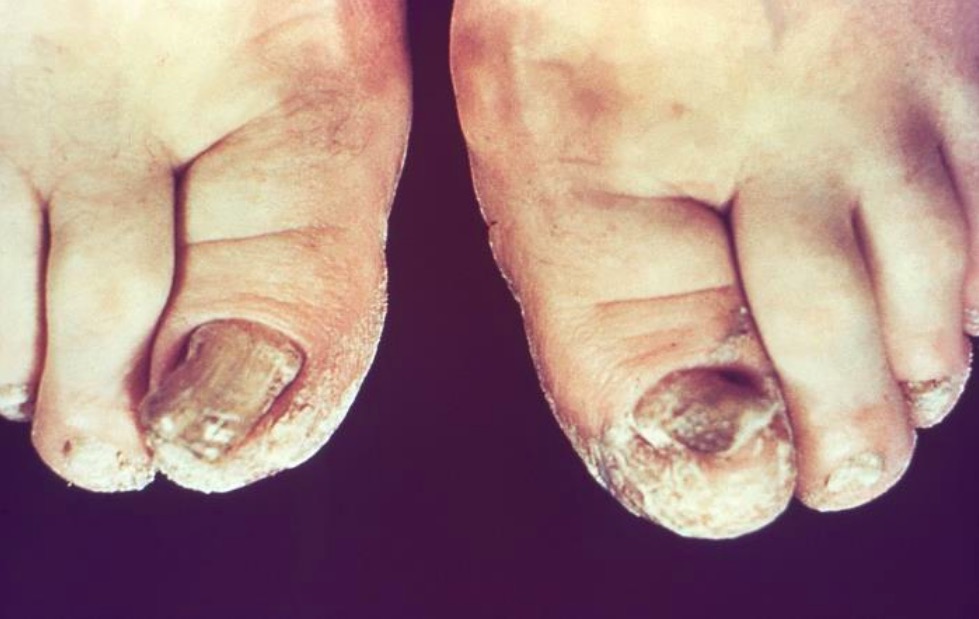
Tinea unguium (onicomicosis dermatófitica):
Esta infección suele ser causada por Trichophyton rubrum y se presenta con decoloración, engrosamiento y distrofia de las uñas de los pies, a menudo con restos subungueales.
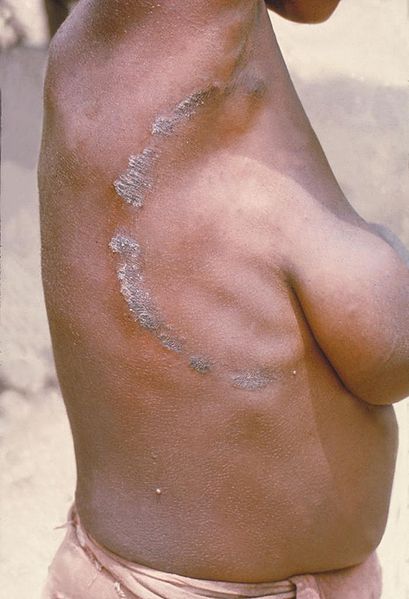
Tinea corporis, “tiña corporal” en un adulto:
La infección se debe con mayor frecuencia al Trichophyton rubrum y se presenta con placas circulares, eritematosas y pruriginosas, con escamas periféricas y un aclaramiento central.
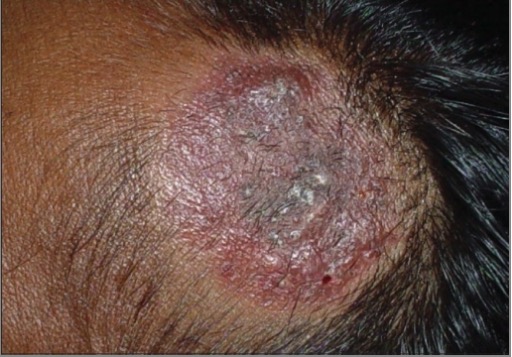
Querión de Celso
Imagen: “Trichomycoses” por Department of Dermatology, Madras Medical College (Retd.), Chennai – 600 003, India. Licencia: CC BY 2.0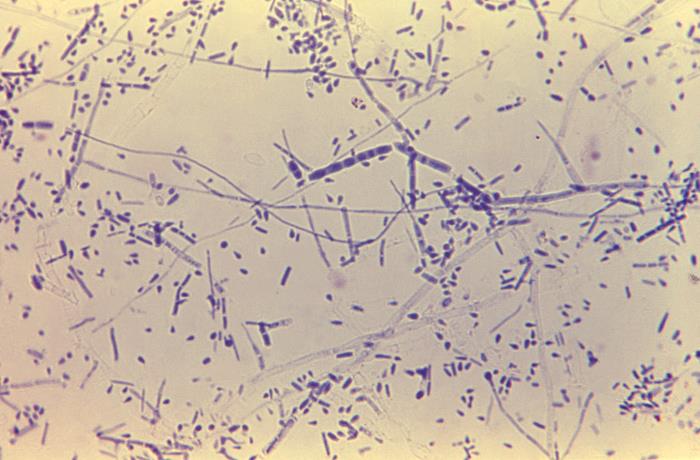
Trichophyton rubrum: Esta ampliación de 475× de T. rubrum muestra macroconidias alargadas y agrupadas centralmente con septaciones. También hay muchos microconidios en forma de lágrima.
Imagen: “Trichophyton rubrum” por CDC/Dr. Lucille K. Georg. Licencia: Dominio Público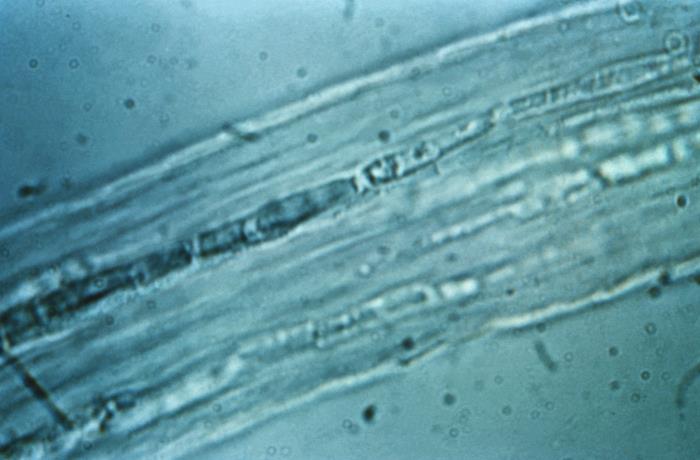
Infección por Endothrix: Microsporum visible dentro del eje del folículo piloso
Todas las variantes de la tiña se tratan con antifúngicos.