El crup, también conocido como laringotraqueobronquitis, es una enfermedad causada en la mayoría de los casos por una infección viral que provoca una grave inflamación de las vías respiratorias superiores. Suele presentarse en niños < 5 años de edad. Los pacientes desarrollan una tos ronca como "ladrido de foca" y un estridor inspiratorio. Los LOS Neisseria virus Virus Viruses are infectious, obligate intracellular parasites composed of a nucleic acid core surrounded by a protein capsid. Viruses can be either naked (non-enveloped) or enveloped. The classification of viruses is complex and based on many factors, including type and structure of the nucleoid and capsid, the presence of an envelope, the replication cycle, and the host range. Virology de la parainfluenza humana son los LOS Neisseria responsables de la mayoría de los LOS Neisseria casos, seguidos del virus Virus Viruses are infectious, obligate intracellular parasites composed of a nucleic acid core surrounded by a protein capsid. Viruses can be either naked (non-enveloped) or enveloped. The classification of viruses is complex and based on many factors, including type and structure of the nucleoid and capsid, the presence of an envelope, the replication cycle, and the host range. Virology sincitial respiratorio, los LOS Neisseria adenovirus Adenovirus Adenovirus (member of the family Adenoviridae) is a nonenveloped, double-stranded DNA virus. Adenovirus is transmitted in a variety of ways, and it can have various presentations based on the site of entry. Presentation can include febrile pharyngitis, conjunctivitis, acute respiratory disease, atypical pneumonia, and gastroenteritis. Adenovirus, los LOS Neisseria rinovirus y los LOS Neisseria enterovirus Enterovirus A genus of the family picornaviridae whose members preferentially inhabit the intestinal tract of a variety of hosts. The genus contains many species. Newly described members of human enteroviruses are assigned continuous numbers with the species designated 'human enterovirus'. Coxsackievirus. El crup se suele diagnosticar clínicamente o con la ayuda de la radiografía (signo del campanario). El tratamiento consiste en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum esteroides y epinefrina.
Last updated: May 21, 2025
Transmisión
Factores de riesgo
El crup suele ser causado por un virus Virus Viruses are infectious, obligate intracellular parasites composed of a nucleic acid core surrounded by a protein capsid. Viruses can be either naked (non-enveloped) or enveloped. The classification of viruses is complex and based on many factors, including type and structure of the nucleoid and capsid, the presence of an envelope, the replication cycle, and the host range. Virology (75% de los LOS Neisseria casos) y, con menor frecuencia, por bacterias.
Microfotografía electrónica de transmisión del virus de la parainfluenza
Imagen: “Transmission electron micrograph” por Public Health Image Library. Licencia: CDC/Dominio público| Hallazgo | Número de puntos asignados para este hallazgo | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | |
| Retracción de la pared torácica | Ausente | Leve | Moderado | Severo | ||
| Estridor | Ausente | Con la agitación | En EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum reposo | |||
| Cianosis | Ausente | Con la agitación | En EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum reposo | |||
| Nivel de conciencia | Normal | Desorientado | ||||
| Entrada de aire | Normal | Disminuida | Marcadamente disminuida | |||
Consejo: Aunque una radiografía de tórax mostrará un estrechamiento de la columna de aire en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la tráquea (signo del campanario), la radiografía de tórax rara vez se realiza en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la práctica y siempre es la respuesta incorrecta cuando se pregunta por el siguiente paso más apropiado en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el diagnóstico.
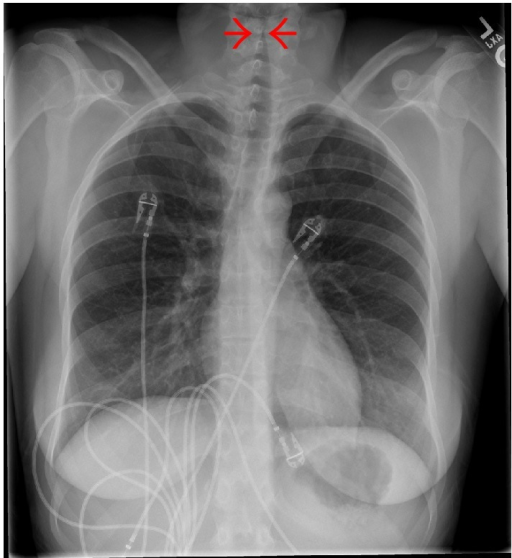
Radiografía de tórax que muestra la estenosis subglótica, conocida como signo del campanario, que se observa comúnmente en la radiografía anteroposterior en pacientes con crup.
Imagen: “Steeple sign” por Jayshil J. Patel, Emily Kitchin y Kurt Pfeifer. Licencia: CC BY 4.0Los LOS Neisseria siguientes son diagnósticos diferenciales del crup: