La diabetes Diabetes Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a metabolic disease characterized by hyperglycemia and dysfunction of the regulation of glucose metabolism by insulin. Type 1 DM is diagnosed mostly in children and young adults as the result of autoimmune destruction of β cells in the pancreas and the resulting lack of insulin. Type 2 DM has a significant association with obesity and is characterized by insulin resistance. Diabetes Mellitus mellitus ( DM DM Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a metabolic disease characterized by hyperglycemia and dysfunction of the regulation of glucose metabolism by insulin. Type 1 DM is diagnosed mostly in children and young adults as the result of autoimmune destruction of β cells in the pancreas and the resulting lack of insulin. Type 2 DM has a significant association with obesity and is characterized by insulin resistance. Diabetes Mellitus) es un trastorno metabólico crónico caracterizado por hiperglucemia persistente debido a una secreción de insulina deficiente ( DM DM Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a metabolic disease characterized by hyperglycemia and dysfunction of the regulation of glucose metabolism by insulin. Type 1 DM is diagnosed mostly in children and young adults as the result of autoimmune destruction of β cells in the pancreas and the resulting lack of insulin. Type 2 DM has a significant association with obesity and is characterized by insulin resistance. Diabetes Mellitus tipo 1), resistencia a la insulina ( DM DM Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a metabolic disease characterized by hyperglycemia and dysfunction of the regulation of glucose metabolism by insulin. Type 1 DM is diagnosed mostly in children and young adults as the result of autoimmune destruction of β cells in the pancreas and the resulting lack of insulin. Type 2 DM has a significant association with obesity and is characterized by insulin resistance. Diabetes Mellitus tipo 2) o diabetes Diabetes Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a metabolic disease characterized by hyperglycemia and dysfunction of the regulation of glucose metabolism by insulin. Type 1 DM is diagnosed mostly in children and young adults as the result of autoimmune destruction of β cells in the pancreas and the resulting lack of insulin. Type 2 DM has a significant association with obesity and is characterized by insulin resistance. Diabetes Mellitus autoinmune de inicio en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la edad adulta ( diabetes Diabetes Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a metabolic disease characterized by hyperglycemia and dysfunction of the regulation of glucose metabolism by insulin. Type 1 DM is diagnosed mostly in children and young adults as the result of autoimmune destruction of β cells in the pancreas and the resulting lack of insulin. Type 2 DM has a significant association with obesity and is characterized by insulin resistance. Diabetes Mellitus autoinmune latente del adulto, LADA). El objetivo del control de la diabetes Diabetes Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a metabolic disease characterized by hyperglycemia and dysfunction of the regulation of glucose metabolism by insulin. Type 1 DM is diagnosed mostly in children and young adults as the result of autoimmune destruction of β cells in the pancreas and the resulting lack of insulin. Type 2 DM has a significant association with obesity and is characterized by insulin resistance. Diabetes Mellitus es prevenir complicaciones crónicas graves y potencialmente incapacitantes debido al AL Amyloidosis daño en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum varios órganos. El control adecuado a largo plazo de la glucosa en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum sangre es crucial en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la prevención de complicaciones. Las complicaciones macrovasculares incluyen enfermedad cardiovascular, accidente cerebrovascular, enfermedad vascular periférica y ERC en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum varias etapas, incluida la enfermedad renal en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum etapa terminal que requiere diálisis. Las complicaciones macrovasculares incluyen la cardiopatía, la enfermedad cerebrovascular y la enfermedad vascular periférica. La enfermedad microvascular puede causar retinopatía, neuropatía, nefropatía o angina microvascular.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
La diabetes Diabetes Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a metabolic disease characterized by hyperglycemia and dysfunction of the regulation of glucose metabolism by insulin. Type 1 DM is diagnosed mostly in children and young adults as the result of autoimmune destruction of β cells in the pancreas and the resulting lack of insulin. Type 2 DM has a significant association with obesity and is characterized by insulin resistance. Diabetes Mellitus mellitus ( DM DM Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a metabolic disease characterized by hyperglycemia and dysfunction of the regulation of glucose metabolism by insulin. Type 1 DM is diagnosed mostly in children and young adults as the result of autoimmune destruction of β cells in the pancreas and the resulting lack of insulin. Type 2 DM has a significant association with obesity and is characterized by insulin resistance. Diabetes Mellitus) es una enfermedad común que puede conducir a múltiples complicaciones graves. El control glucémico a largo plazo es imperativo para prevenir estas complicaciones.
Las complicaciones crónicas de la diabetes Diabetes Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a metabolic disease characterized by hyperglycemia and dysfunction of the regulation of glucose metabolism by insulin. Type 1 DM is diagnosed mostly in children and young adults as the result of autoimmune destruction of β cells in the pancreas and the resulting lack of insulin. Type 2 DM has a significant association with obesity and is characterized by insulin resistance. Diabetes Mellitus tienen procesos fisiopatológicos únicos y dependen del sistema orgánico involucrado.
Existen varias formas de enfermedad renal en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la diabetes Diabetes Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a metabolic disease characterized by hyperglycemia and dysfunction of the regulation of glucose metabolism by insulin. Type 1 DM is diagnosed mostly in children and young adults as the result of autoimmune destruction of β cells in the pancreas and the resulting lack of insulin. Type 2 DM has a significant association with obesity and is characterized by insulin resistance. Diabetes Mellitus, incluidas las lesiones glomerulares no clásicas y la enfermedad tubulointersticial.
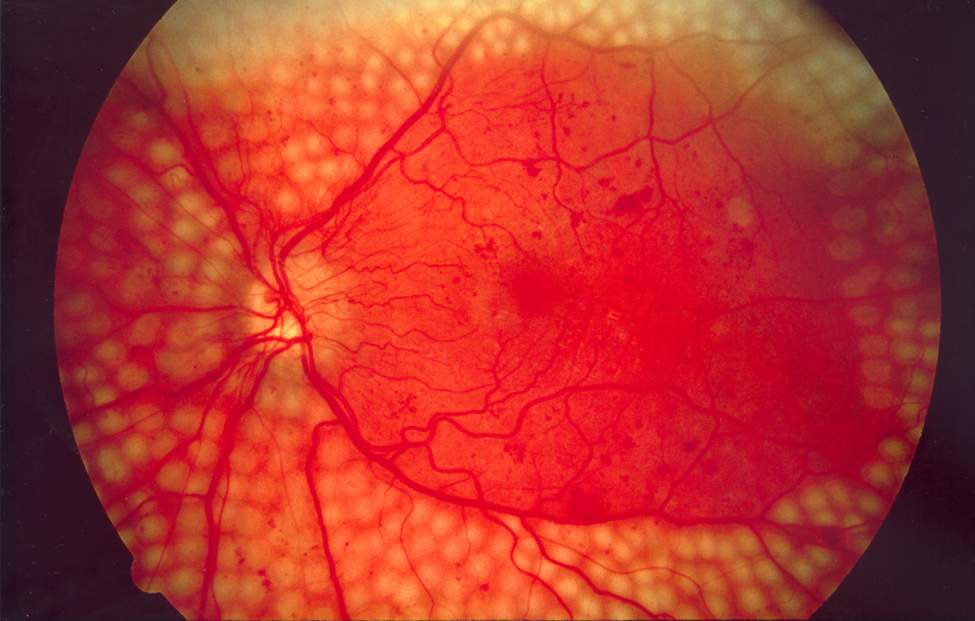
Imagen del fondo de ojo que muestra la cirugía con láser disperso para la retinopatía diabética
Imagen: “Fundus photo showing scatter laser surgery for diabetic retinopathy” por National Eye Institute, National Institutes of Health. Licencia: Dominio Público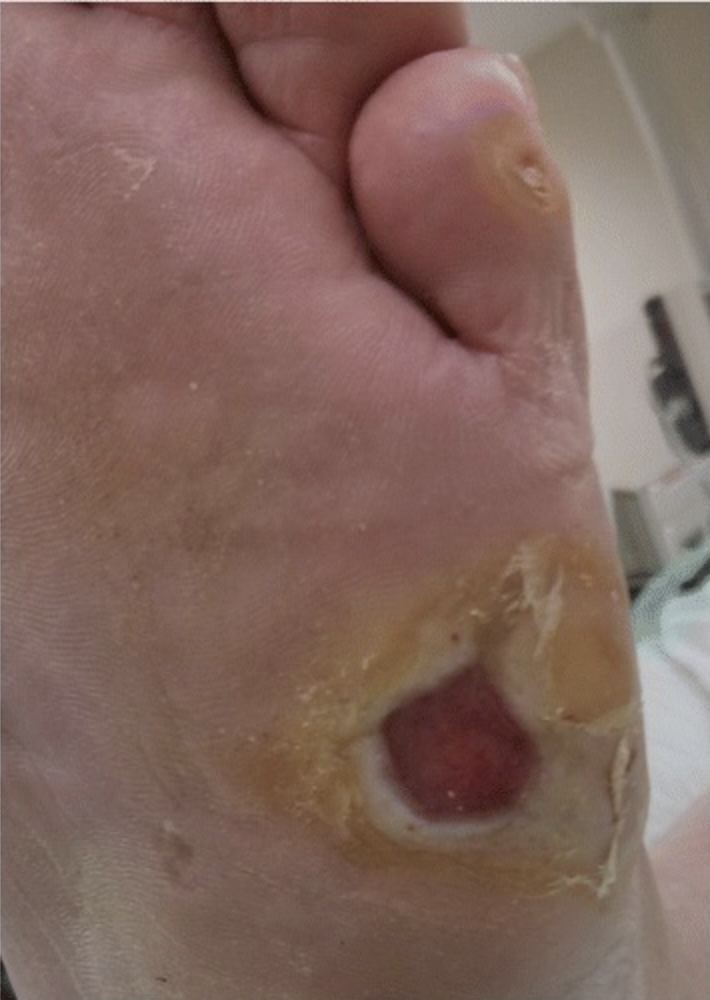
Lesión en el pie en un individuo con neuropatía periférica:
La neuropatía periférica hace que las personas afectadas no sientan pequeñas lesiones en las extremidades, que a menudo quedan desatendidas. Combinadas con la reducción del flujo sanguíneo a las extremidades, estas lesiones pueden provocar úlceras crónicas en los pies que incluso pueden requerir un desbridamiento quirúrgico en personas con diabetes.
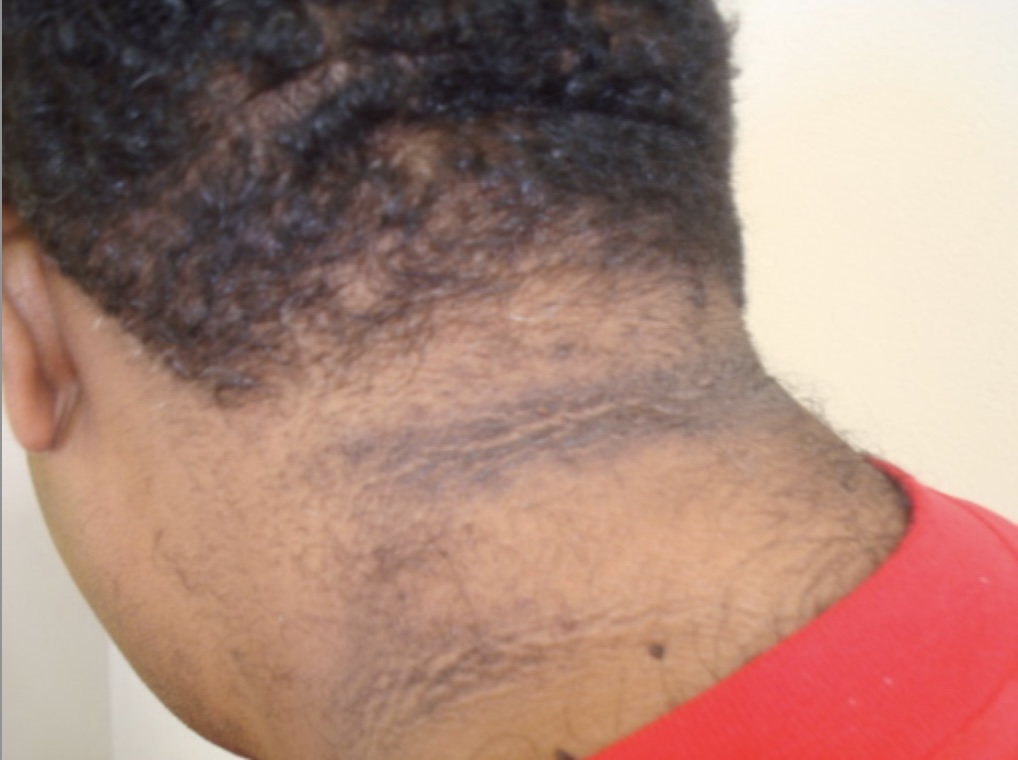
Acantosis nigricans: un hallazgo común en personas con resistencia a la insulina (como en la diabetes). La acantosis nigricans se describe como áreas aterciopeladas, engrosadas y oscurecidas de la piel, que a menudo se ven en la nuca.
Imagen: “Acanthosis nigricans Grade 1” por Department of Clinical Medical Sciences, The University of West Indies, St Augustine, Trinidad & Tobago, WI. Licencia: CC BY 2.0Arteriopatía coronaria:
Enfermedad arterial periférica:
Estenosis carotídea: ultrasonido para evaluar la extensión de la enfermedad oclusiva
La nefropatía diabética generalmente se diagnostica durante una prueba anual de detección de microalbuminuria en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum orina.
Diagnosticada durante los LOS Neisseria exámenes oculares de tamizaje anual con un especialista en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum ojos (oftalmólogo u optometrista)
Con todas las complicaciones diabéticas, la prevención es clave y el control glucémico es la máxima prioridad.