Las especies de Burkholderia Burkholderia Burkholderia species are gram-negative bacilli with 2 clinically relevant pathogens: B. pseudomallei (causing melioidosis) and B. cepacia complex (causing opportunistic infections). Melioidosis is commonly seen in Asia and Australia. Infection is transmitted by contact with contaminated soil or water (via skin wounds). Burkholderia son bacilos gramnegativos con 2 patógenos clínicamente relevantes: B. pseudomallei (causante de melioidosis Melioidosis A disease of humans and animals that resembles glanders. It is caused by burkholderia pseudomallei and may range from a dormant infection to a condition that causes multiple abscesses, pneumonia, and bacteremia. Burkholderia) y el complejo B. cepacia (causante de infecciones oportunistas). La melioidosis Melioidosis A disease of humans and animals that resembles glanders. It is caused by burkholderia pseudomallei and may range from a dormant infection to a condition that causes multiple abscesses, pneumonia, and bacteremia. Burkholderia se observa comúnmente en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum Asia ASIA Spinal Cord Injuries y Australia. La infección se transmite por contacto con suelo o agua contaminada (a través de heridas en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la piel). La enfermedad afecta múltiples sistemas y puede presentarse con neumonía, encefalomielitis y abscesos cutáneos. El diagnóstico se realiza mediante cultivo de la muestra (según el órgano afectado). El tratamiento requiere una terapia antibiótica intensiva inicial seguida de una terapia de erradicación prolongada. El complejo Burkholderia Burkholderia Burkholderia species are gram-negative bacilli with 2 clinically relevant pathogens: B. pseudomallei (causing melioidosis) and B. cepacia complex (causing opportunistic infections). Melioidosis is commonly seen in Asia and Australia. Infection is transmitted by contact with contaminated soil or water (via skin wounds). Burkholderia cepacia generalmente afecta a personas inmunocomprometidas, como aquellas con fibrosis Fibrosis Any pathological condition where fibrous connective tissue invades any organ, usually as a consequence of inflammation or other injury. Bronchiolitis Obliterans quística. Puede transmitirse de persona a persona o a través de dispositivos contaminados. Si bien el complejo Burkholderia Burkholderia Burkholderia species are gram-negative bacilli with 2 clinically relevant pathogens: B. pseudomallei (causing melioidosis) and B. cepacia complex (causing opportunistic infections). Melioidosis is commonly seen in Asia and Australia. Infection is transmitted by contact with contaminated soil or water (via skin wounds). Burkholderia cepacia es una infección rara, es importante diagnosticarla, ya que el complejo Burkholderia Burkholderia Burkholderia species are gram-negative bacilli with 2 clinically relevant pathogens: B. pseudomallei (causing melioidosis) and B. cepacia complex (causing opportunistic infections). Melioidosis is commonly seen in Asia and Australia. Infection is transmitted by contact with contaminated soil or water (via skin wounds). Burkholderia cepacia es resistente a múltiples medicamentos y la infección es una contraindicación relativa para el trasplante de pulmón.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
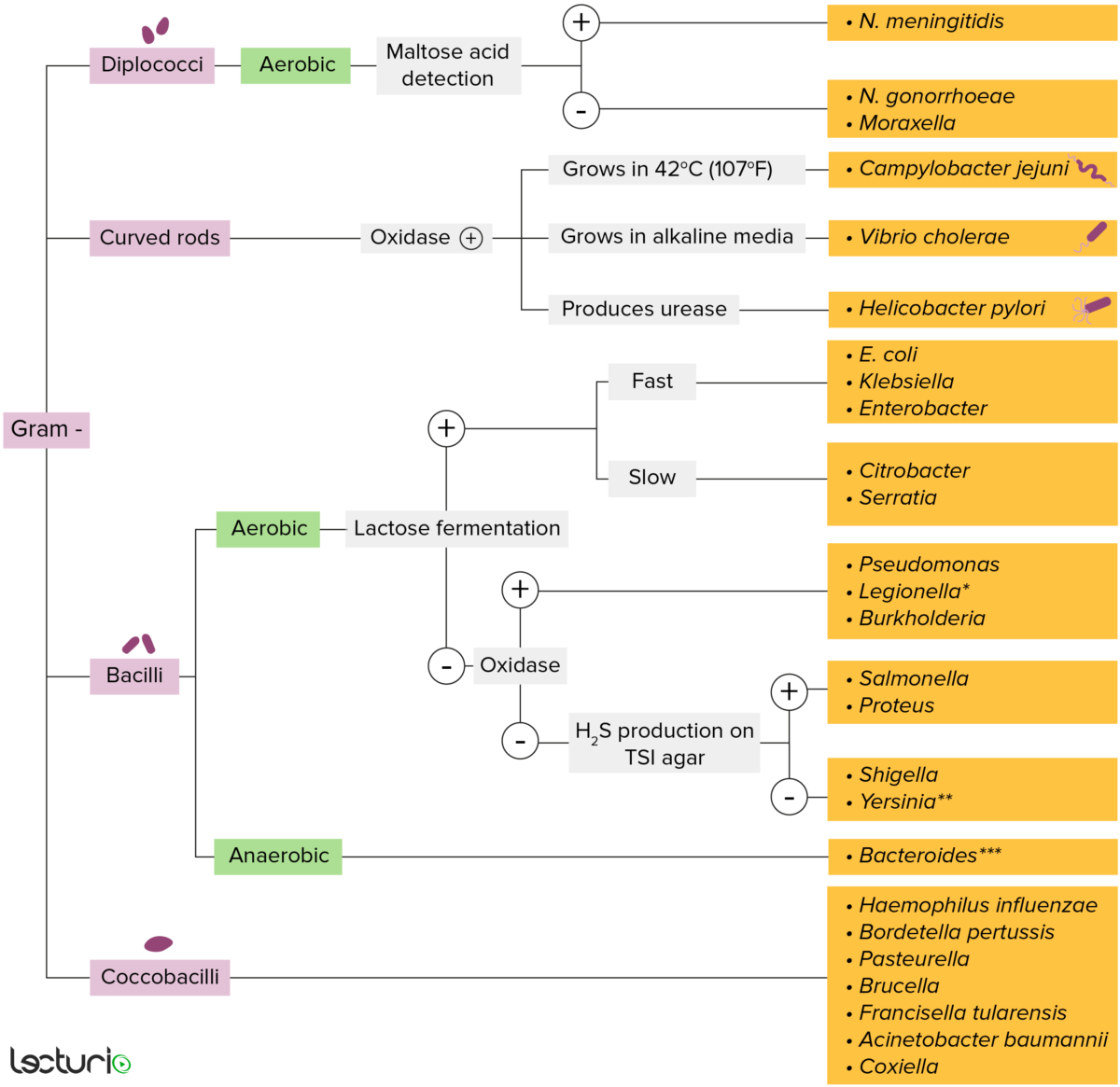
Bacterias gramnegativas:
La mayoría de las bacterias se pueden clasificar de acuerdo a un procedimiento de laboratorio llamado tinción de Gram.
Las bacterias con paredes celulares que tienen una capa delgada de peptidoglicano no retienen la tinción de cristal violeta utilizada en la tinción de Gram. Sin embargo, estas bacterias retienen la contratinción de safranina y, por lo tanto, adoptan un color rojo-rosado en la tinción, lo que las hace gramnegativas. Estas bacterias pueden clasificarse además según su morfología (diplococos, bastones curvos, bacilos y cocobacilos) y su capacidad para crecer en presencia de oxígeno (aeróbicos versus anaeróbicos). Las bacterias se pueden identificar de manera más profunda cultivándolas en medios específicos (agar hierro triple azúcar) donde se pueden identificar sus enzimas (ureasa, oxidasa) y se puede probar su capacidad para fermentar lactosa.
* Se tiñe mal en la tinción de Gram
** Bastón pleomórfico/cocobacilo
*** Requiere medios de transporte especiales
Burkholderia Burkholderia Burkholderia species are gram-negative bacilli with 2 clinically relevant pathogens: B. pseudomallei (causing melioidosis) and B. cepacia complex (causing opportunistic infections). Melioidosis is commonly seen in Asia and Australia. Infection is transmitted by contact with contaminated soil or water (via skin wounds). Burkholderia:
Especies clínicamente relevantes:
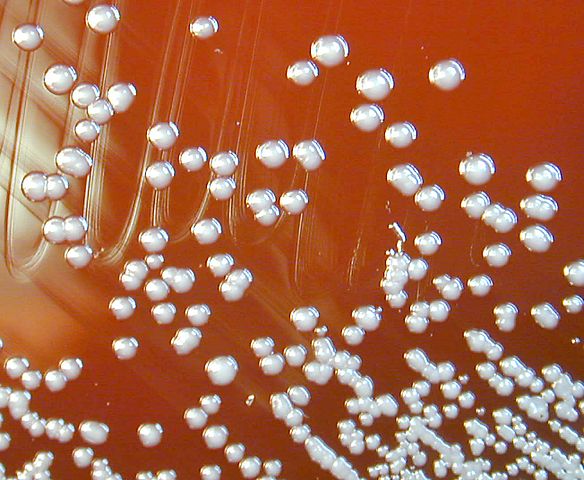

Colonias de Burkholderia pseudomallei en una placa de agar sangre
Imagen: “Burkholderia pseudomallei 01” por CDC. Licencia: Dominio PúblicoTransmisión:
Los LOS Neisseria factores de riesgo del huésped incluyen:
Los LOS Neisseria síntomas pueden presentarse en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum varios sistemas:
Pruebas diagnósticas:
Exámenes adicionales:
Resistente a:
Los LOS Neisseria regímenes iniciales dependen de la gravedad de la enfermedad y de los LOS Neisseria sistemas afectados:
Tratamiento de erradicación:
Prevención:
Complejo Burkholderia Burkholderia Burkholderia species are gram-negative bacilli with 2 clinically relevant pathogens: B. pseudomallei (causing melioidosis) and B. cepacia complex (causing opportunistic infections). Melioidosis is commonly seen in Asia and Australia. Infection is transmitted by contact with contaminated soil or water (via skin wounds). Burkholderia cepacia:
Epidemiología:
Transmisión:
Dispositivos médicos que pueden contaminarse y producir infección:
Factores de riesgo del huésped:
La mayoría de las personas infectadas no presentan síntomas. Aquellos con síntomas pueden tener:
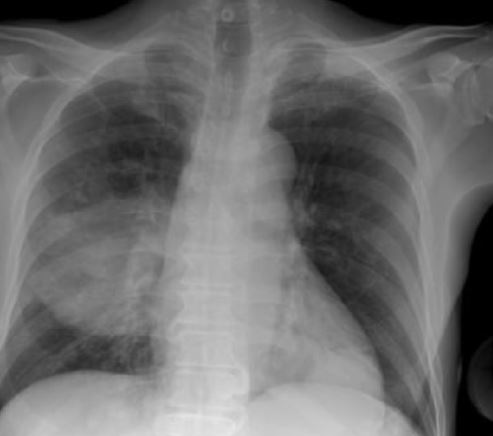
Infección por complejo B. cepacia:
Radiografía de tórax de un paciente que muestra neumonía del lado derecho. En el aspirado traqueal y en los hemocultivos creció B. cepacia.