Los LOS Neisseria antidiabéticos insulinotrópicos son utilizados para tratar la diabetes Diabetes Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a metabolic disease characterized by hyperglycemia and dysfunction of the regulation of glucose metabolism by insulin. Type 1 DM is diagnosed mostly in children and young adults as the result of autoimmune destruction of β cells in the pancreas and the resulting lack of insulin. Type 2 DM has a significant association with obesity and is characterized by insulin resistance. Diabetes Mellitus mellitus tipo 2 porque aumentan la secreción de insulina, lo que resulta en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum una disminución de los LOS Neisseria niveles de glucosa. Este grupo de medicamentos incluyen a las sulfonilureas, las meglitinidas, los LOS Neisseria agonistas del receptor Receptor Receptors are proteins located either on the surface of or within a cell that can bind to signaling molecules known as ligands (e.g., hormones) and cause some type of response within the cell. Receptors del péptido similar al AL Amyloidosis glucagón-1 y los LOS Neisseria inhibidores de la dipeptidil peptidasa-4. Estos agentes generalmente se utilizan en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum combinación con otras terapias para el control de la diabetes Diabetes Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a metabolic disease characterized by hyperglycemia and dysfunction of the regulation of glucose metabolism by insulin. Type 1 DM is diagnosed mostly in children and young adults as the result of autoimmune destruction of β cells in the pancreas and the resulting lack of insulin. Type 2 DM has a significant association with obesity and is characterized by insulin resistance. Diabetes Mellitus. Las sulfonilureas y las meglitinidas se asocian con el aumento de peso, mientras que los LOS Neisseria agonistas del péptido similar al AL Amyloidosis glucagón-1 pueden brindar el beneficio adicional de la pérdida de peso. Otros efectos secundarios varían entre las clases de medicamentos. Ninguno de los LOS Neisseria medicamentos deben utilizarse en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el tratamiento de la diabetes Diabetes Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a metabolic disease characterized by hyperglycemia and dysfunction of the regulation of glucose metabolism by insulin. Type 1 DM is diagnosed mostly in children and young adults as the result of autoimmune destruction of β cells in the pancreas and the resulting lack of insulin. Type 2 DM has a significant association with obesity and is characterized by insulin resistance. Diabetes Mellitus mellitus tipo 1 o la cetoacidosis diabética.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Los LOS Neisseria medicamentos hipoglucemiantes (o antihiperglucémicos) se pueden clasificar según sea el mecanismo de acción:
Medicamentos insulinotrópicos (↑ secreción de insulina):
Medicamentos no insulinotrópicos (no afectan la liberación de insulina):
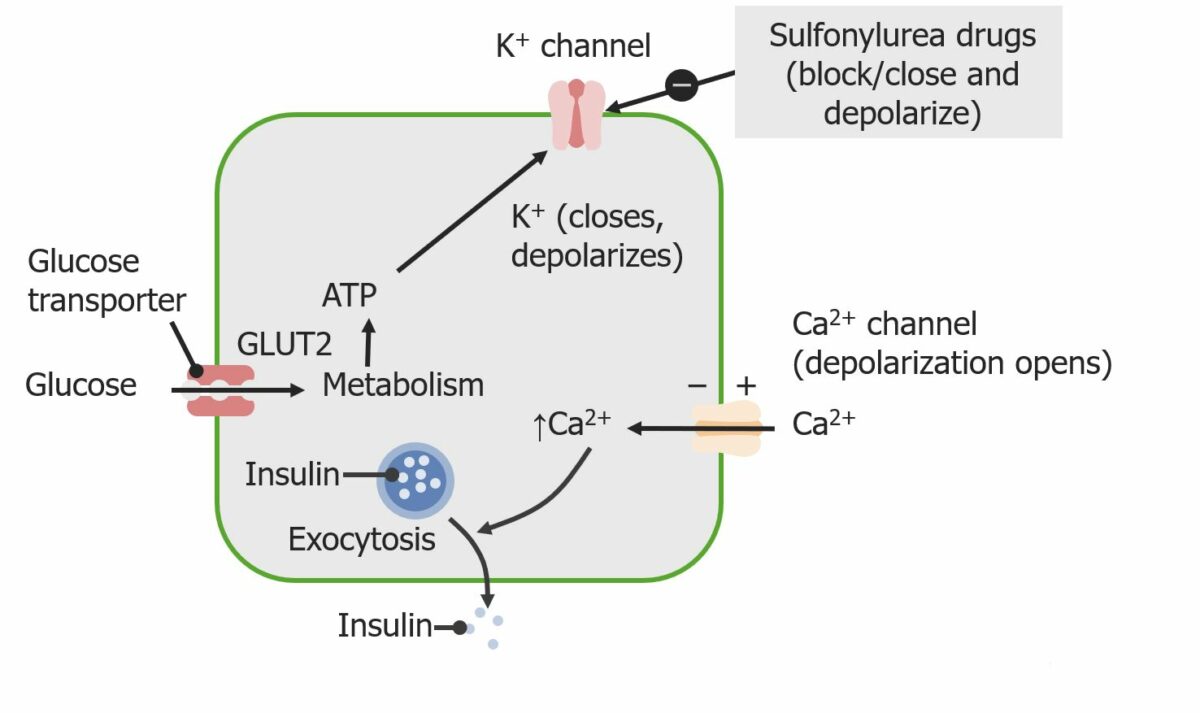
Las sulfonilureas estimulan la secreción de insulina al actuar sobre los canales de potasio de las células beta pancreáticas.
Imagen por Lecturio.A continuación se describe la farmacocinética de las sulfonilureas de 2da generación:
Las sulfonilureas se utilizan en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el tratamiento de la diabetes Diabetes Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a metabolic disease characterized by hyperglycemia and dysfunction of the regulation of glucose metabolism by insulin. Type 1 DM is diagnosed mostly in children and young adults as the result of autoimmune destruction of β cells in the pancreas and the resulting lack of insulin. Type 2 DM has a significant association with obesity and is characterized by insulin resistance. Diabetes Mellitus mellitus tipo 2:
Las meglitinidas se utilizan para tratar la diabetes Diabetes Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a metabolic disease characterized by hyperglycemia and dysfunction of the regulation of glucose metabolism by insulin. Type 1 DM is diagnosed mostly in children and young adults as the result of autoimmune destruction of β cells in the pancreas and the resulting lack of insulin. Type 2 DM has a significant association with obesity and is characterized by insulin resistance. Diabetes Mellitus mellitus tipo 2:
Se puede observar un aumento del efecto hipoglucemiante con:
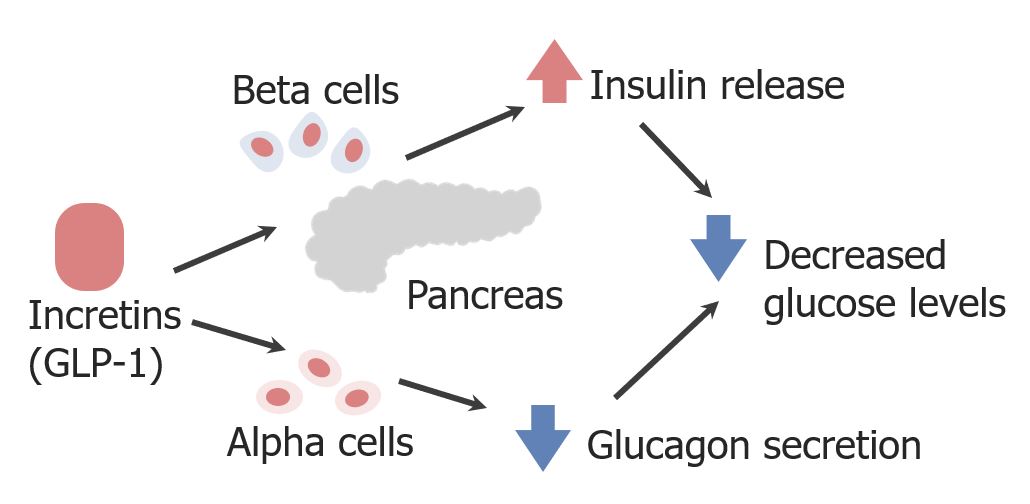
El mecanismo de acción del péptido similar al glucagón-1 (GLP-1, por sus siglas en inglés) y los miméticos
Imagen por Lecturio.
Función normal de la dipeptidil peptidasa-4 (DPP-4): la inhibición de la enzima evita la degradación del péptido similar al glucagón-1 (GLP-1, por sus siglas en inglés), lo que permite una mayor liberación de insulina y una menor secreción de glucagón.
Imagen por Lecturio.Los LOS Neisseria inhibidores de la dipeptidil peptidasa-4 tratan la diabetes Diabetes Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a metabolic disease characterized by hyperglycemia and dysfunction of the regulation of glucose metabolism by insulin. Type 1 DM is diagnosed mostly in children and young adults as the result of autoimmune destruction of β cells in the pancreas and the resulting lack of insulin. Type 2 DM has a significant association with obesity and is characterized by insulin resistance. Diabetes Mellitus mellitus tipo 2:
La siguiente tabla compara los LOS Neisseria medicamentos no insulínicos para la diabetes Diabetes Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a metabolic disease characterized by hyperglycemia and dysfunction of the regulation of glucose metabolism by insulin. Type 1 DM is diagnosed mostly in children and young adults as the result of autoimmune destruction of β cells in the pancreas and the resulting lack of insulin. Type 2 DM has a significant association with obesity and is characterized by insulin resistance. Diabetes Mellitus mellitus tipo 2:
| Medicamento | Mecanismo | Indicaciones | Efectos secundarios |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sulfonilureas |
|
|
|
| Meglitinidas |
|
|
|
| Agonistas del péptido similar al AL Amyloidosis glucagón-1 |
|
|
|
| Inhibidores de la dipeptidil peptidasa-4 |
|
Terapia complementaria |
|
| Biguanidas |
|
|
|
| Tiazolidinedionas |
|
|
|
| Inhibidores de alfa-glucosidasa |
|
|
|
| Inhibidores del cotransportador de sodio-glucosa 2 |
|
|
|
| Análogos de la amilina |
|
|
|
Los LOS Neisseria efectos de los LOS Neisseria medicamentos para la diabetes Diabetes Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a metabolic disease characterized by hyperglycemia and dysfunction of the regulation of glucose metabolism by insulin. Type 1 DM is diagnosed mostly in children and young adults as the result of autoimmune destruction of β cells in the pancreas and the resulting lack of insulin. Type 2 DM has a significant association with obesity and is characterized by insulin resistance. Diabetes Mellitus sobre el peso pueden ser un factor importante en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la elección de la terapia de un individuo: