Los LOS Neisseria abscesos retrofaríngeos ocurren en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el espacio retrofaríngeo, el cual se extiende desde la base del cráneo hasta el mediastino posterior. Se producen debido a la extensión de infecciones locales, incluyendo infecciones de las vías respiratorias superiores o infecciones localizadas causadas por traumatismos, como los LOS Neisseria procedimientos dentales. Las infecciones son más frecuentes en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria niños. Las principales características clínicas son el trismo, la disfagia y la incapacidad de extender el cuello. El diagnóstico se confirma mediante una tomografía computarizada del cuello. El tratamiento es principalmente a través de antibióticos y drenaje quirúrgico. Las complicaciones incluyen compromiso de la vía aérea, mediastinitis Mediastinitis Mediastinitis refers to an infection or inflammation involving the mediastinum (a region in the thoracic cavity containing the heart, thymus gland, portions of the esophagus, and trachea). Acute mediastinitis can be caused by bacterial infection due to direct contamination, hematogenous or lymphatic spread, or extension of infection from nearby structures. Mediastinitis y trombosis de la vena yugular interna.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
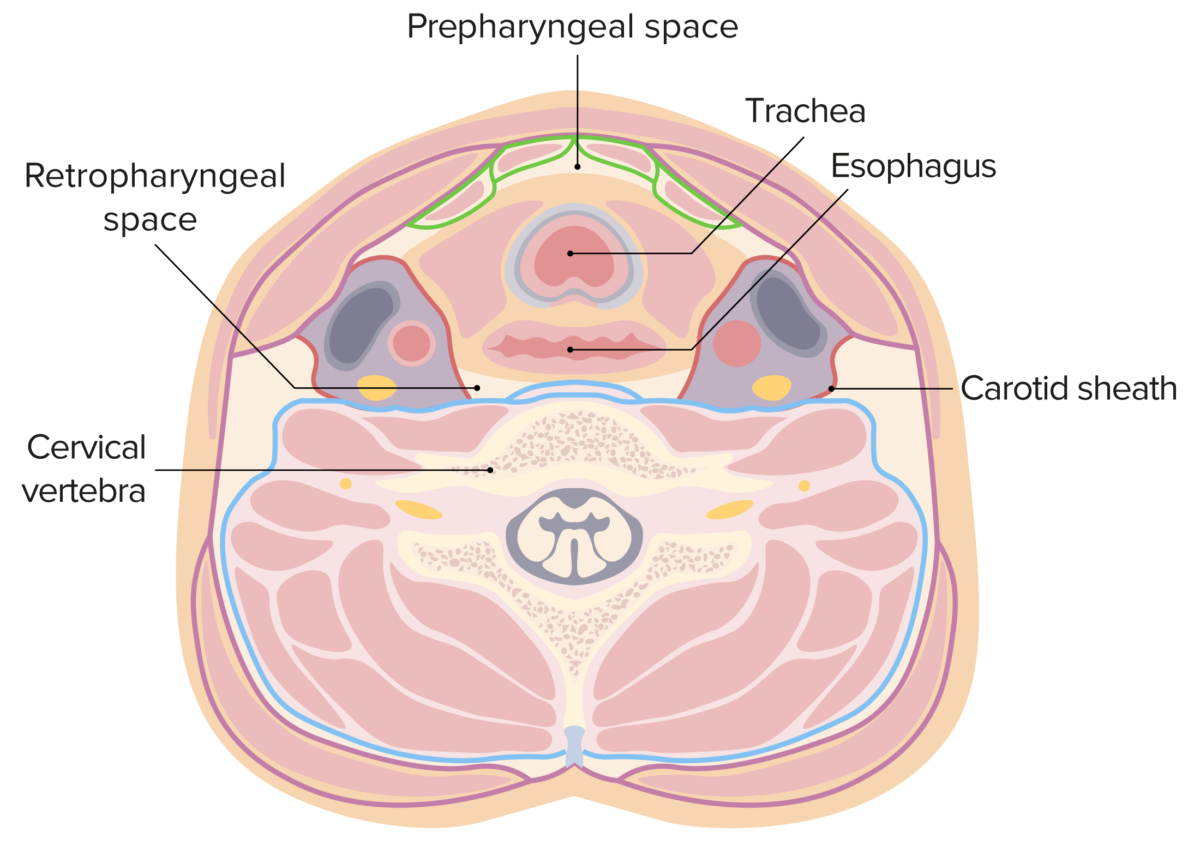
El espacio retrofaríngeo en esta figura se encuentra entre las líneas amarilla (fascia bucofaríngea) y azul (fascia prevertebral). Los bordes laterales están formados por la vaina carotídea (líneas rojas).
Imagen por Lecturio.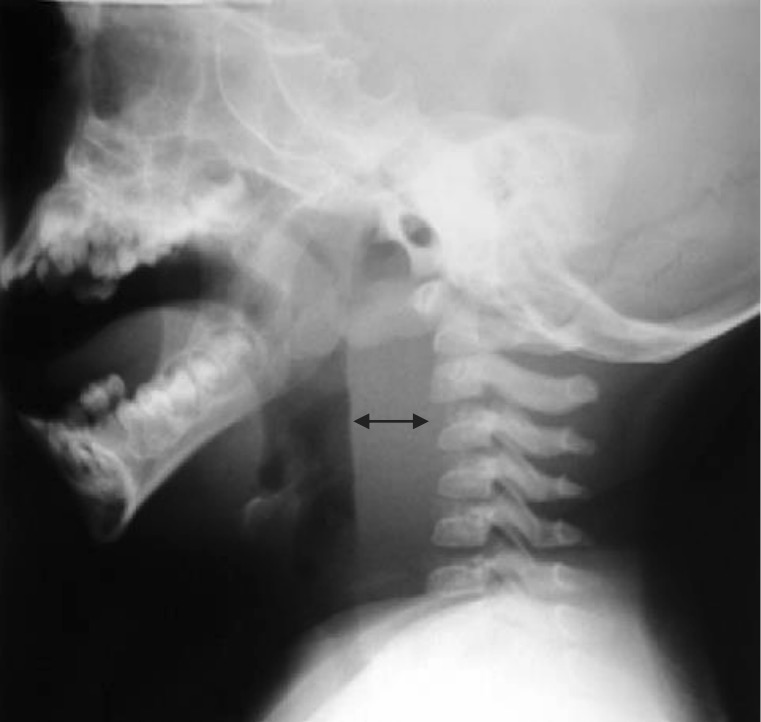
El engrosamiento del tejido blando entre el esófago y las vértebras cervicales es altamente predictivo de edema tisular y absceso en el espacio retrofaríngeo.
David Swenson; Widlus DM.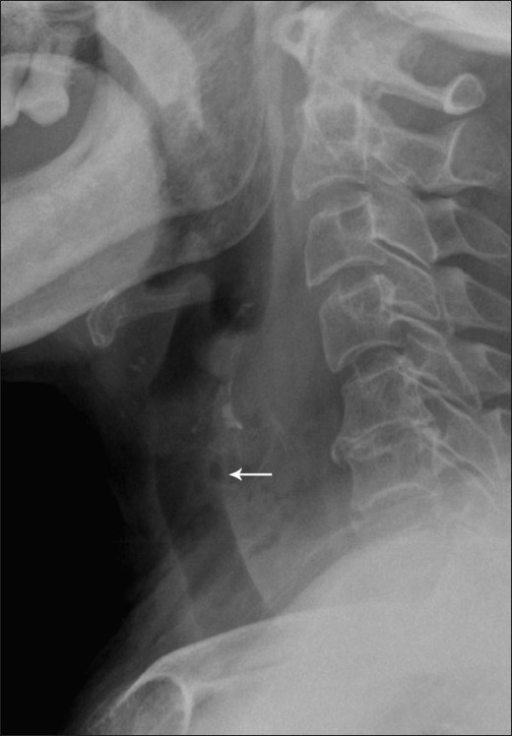
Radiografía lateral que muestra un ensanchamiento del espacio prevertebral con pequeños lóculos (flecha):
Los hallazgos son consistentes con un absceso retrofaríngeo. En este caso, el absceso fue causado por la ingestión de un cuerpo extraño.
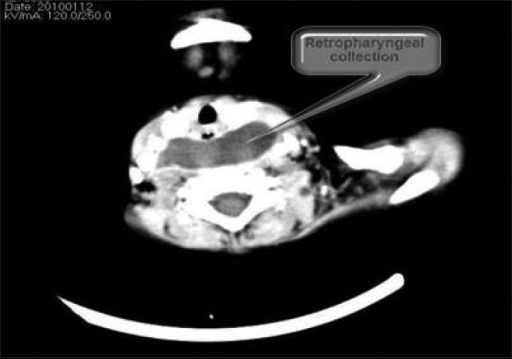
Absceso retrofaríngeo:
una TC del cuello que muestra una colección retrofaríngea que sugiere un absceso
Los LOS Neisseria abscesos retrofaríngeos se consideran la infección profunda del cuello más mortal.
Las complicaciones más comunes son: