A retinopatia de prematuridade (ROP) é uma situação clínica observada em recém-nascidos prematuros e com baixo peso que se caracteriza por uma neovascularização progressiva e excessiva. Nesta situação, a anormal proliferação de neovasos e do tecido fibrovascular por detrás do cristalino impede o desenvolvimento normal da retina. Pode levar a défices visuais graves ou mesmo a cegueira. O tratamento com fotocoagulação laser previne a perda de visão em 95% dos casos.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Os bebés prematuros de baixo peso à nascença correm o risco de desenvolver hiperóxia durante os seus cuidados; isto pode levar a:
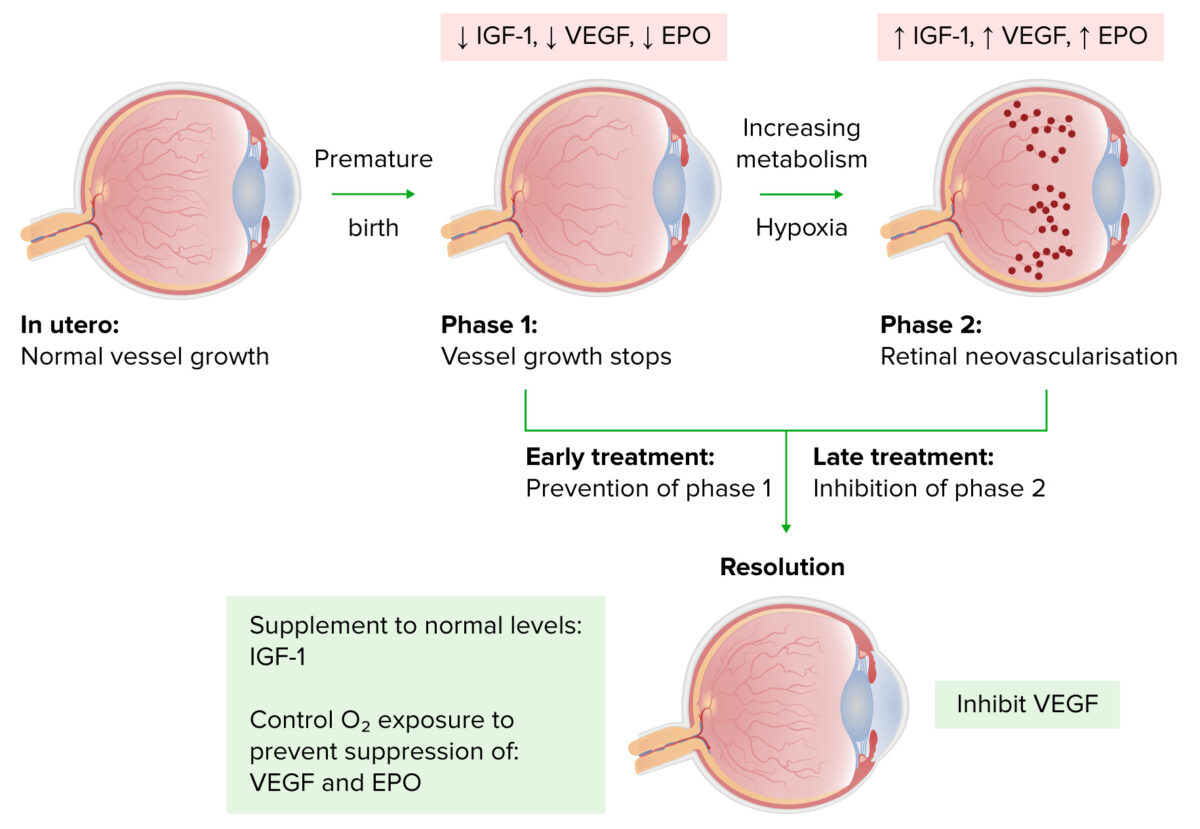
Progressão da retinopatia da prematuridade
Imagem de Lecturio.A classificação internacional da retinopatia da prematuridade utiliza uma série de parâmetros para descrever a situação clínica:
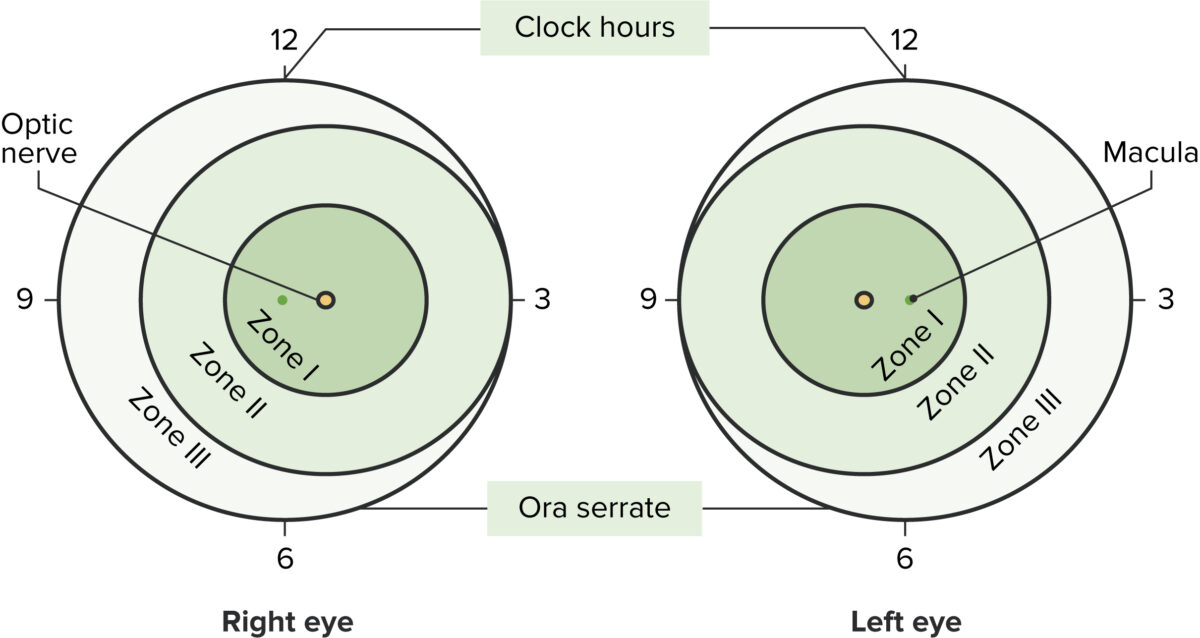
Representação da classificação da retinopatia da pré-maturidade
Imagem de Lecturio.| Estadios | Características |
|---|---|
| 1 | Linha de demarcação entre a retina Retina The ten-layered nervous tissue membrane of the eye. It is continuous with the optic nerve and receives images of external objects and transmits visual impulses to the brain. Its outer surface is in contact with the choroid and the inner surface with the vitreous body. The outermost layer is pigmented, whereas the inner nine layers are transparent. Eye: Anatomy vascular e a retina Retina The ten-layered nervous tissue membrane of the eye. It is continuous with the optic nerve and receives images of external objects and transmits visual impulses to the brain. Its outer surface is in contact with the choroid and the inner surface with the vitreous body. The outermost layer is pigmented, whereas the inner nine layers are transparent. Eye: Anatomy avascular Avascular Corneal Abrasions, Erosion, and Ulcers |
| 2 | A linha de demarcação cresce em volume formando uma prega acima do plano da retina Retina The ten-layered nervous tissue membrane of the eye. It is continuous with the optic nerve and receives images of external objects and transmits visual impulses to the brain. Its outer surface is in contact with the choroid and the inner surface with the vitreous body. The outermost layer is pigmented, whereas the inner nine layers are transparent. Eye: Anatomy que se projeta para o vítreo. |
| 3 |
|
| 4 | Descolamento da
retina
Retina
The ten-layered nervous tissue membrane of the eye. It is continuous with the optic nerve and receives images of external objects and transmits visual impulses to the brain. Its outer surface is in contact with the choroid and the inner surface with the vitreous body. The outermost layer is pigmented, whereas the inner nine layers are transparent.
Eye: Anatomy (parcial ou subtotal)
|
| 5 |
|
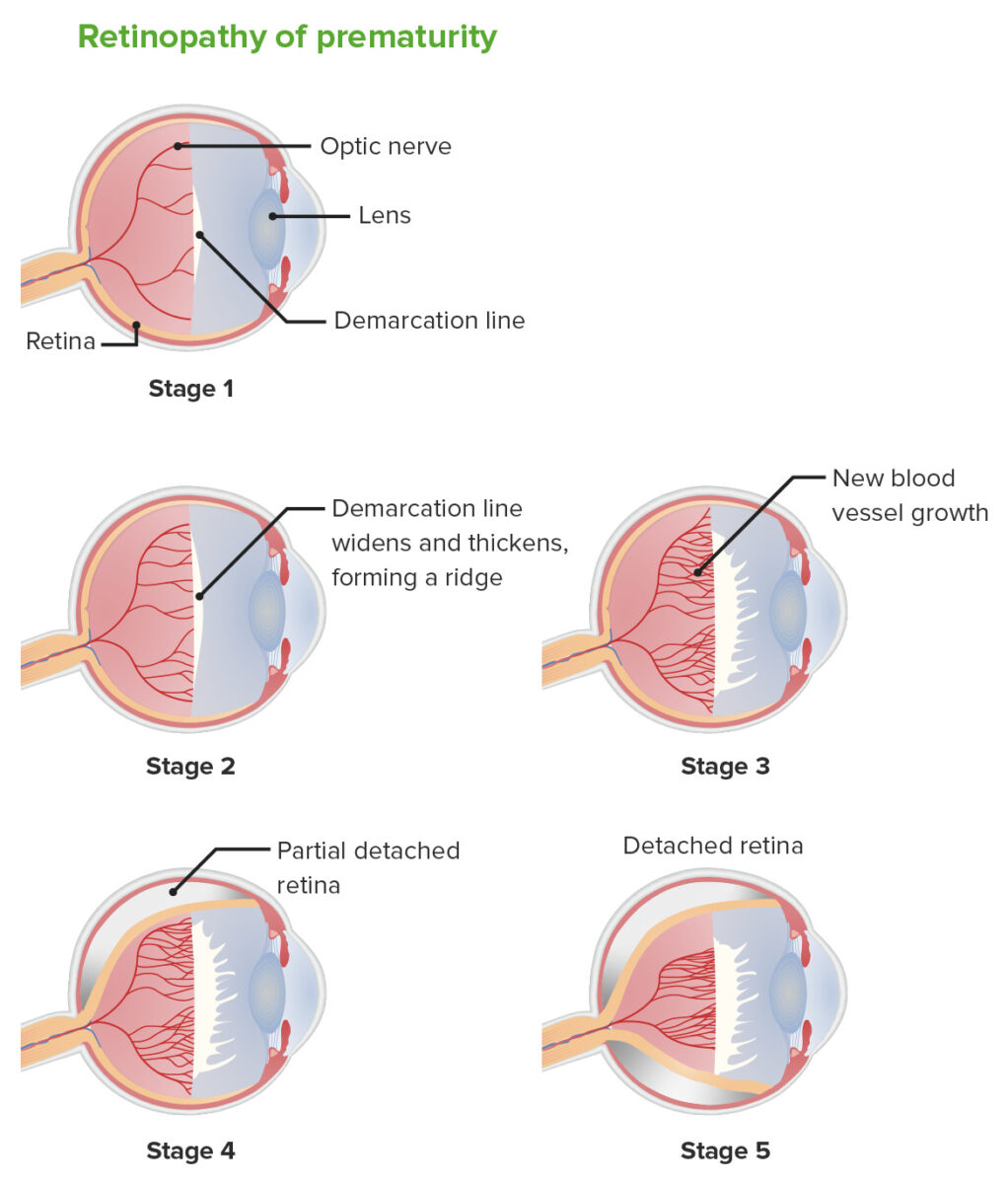
Retinopatia da prematuridade: etapas
Imagem de Lecturio.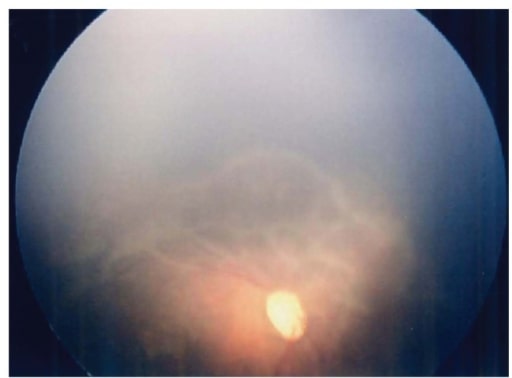
Fundoscopia ao olho direito após 57 dias do nascimento. Observe esta extensa retina avascular com alterações do tipo traccionais progressivas.
Imagem: “Fundus image of the right eye” por Department of Pediatrics, Hamamatsu University School of Medicine. Licença: CC BY 3.0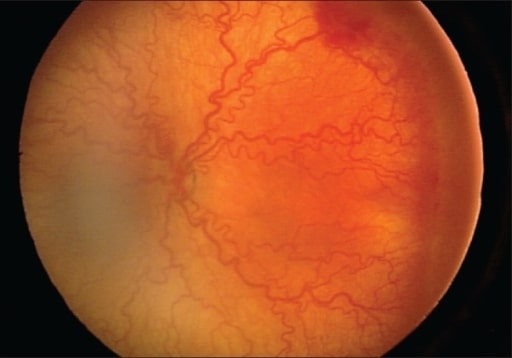
Retinopatia posterior severa e agressiva com doença plus, porém com mínimas alterações na periferia
Imagem: “Presence of severe aggressive posterior ROP” por Division of Pediatric Ophthalmology, King Khaled Eye Specialist Hospital, Riyadh, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia. Licença: CC BY 2.0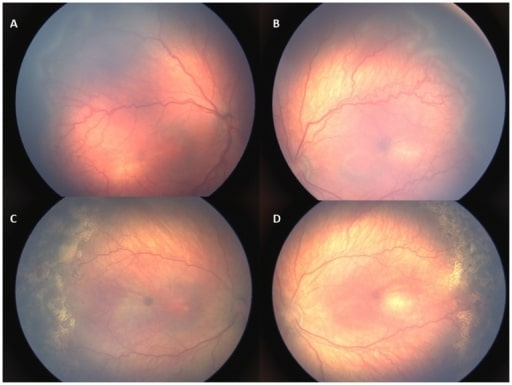
Imagens da retina de uma criança com retinopatia tipo 1. A, B: retinopatia de zona II, estadio 3 com sinais de doença plus antes de ser instituído qualquer tratamento. C, D: A doença plus e a retinopatia regrediram 1 semana após o tratamento com laser.
Imagem: “Retinal images of an infant with type 1 ROP” por US National Library of Medicine. Licença: CC BY 4.0As seguintes situações clínicas podem ser diagnósticos diferenciais no caso de cegueira pediátrica: