O pâncreas é um órgão composto que contém uma combinação distinta de linhagens celulares. O tecido exócrino compreende células acinares, que secretam enzimas digestivas no intestino. A função endócrina é realizada pelas ilhotas de Langerhans, que consistem em tipos celulares distintos que secretam 4 hormonas diferentes na circulação (células α, glucagon Glucagon A 29-amino acid pancreatic peptide derived from proglucagon which is also the precursor of intestinal glucagon-like peptides. Glucagon is secreted by pancreatic alpha cells and plays an important role in regulation of blood glucose concentration, ketone metabolism, and several other biochemical and physiological processes. Gastrointestinal Secretions; células β, insulina; células δ, somatostatina; e células γ, polipeptídeo pancreático). As hormonas endócrinas, bem como algumas enzimas exócrinas, podem ser medidas em fluidos corporais e fornecem informações diagnósticas importantes na doença pancreática aguda e crónica.
Last updated: Jan 11, 2024
O pâncreas é um órgão posicionado na face posterior do abdómen, atrás do estômago e tem 2 funções principais:
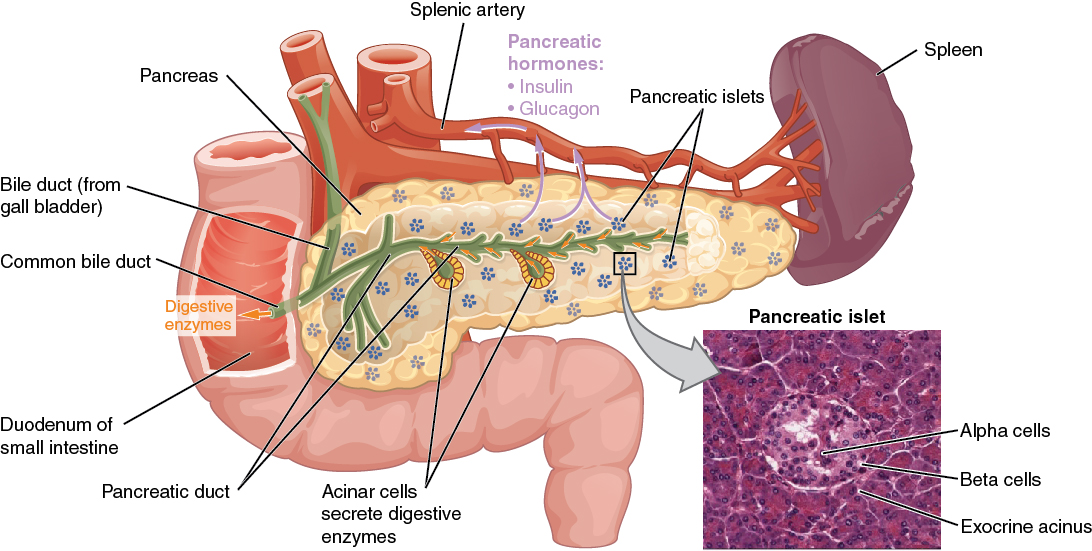
O pâncreas
Imagem: “The pancreas” por CDC. Licença: CC BY 3.0As ilhotas de Langerhans, espalhadas pelo pâncreas, possuem diferentes tipos de células, que correspondem às seguintes hormonas:
Funções e estímulos diferem com cada hormônio.
| Parâmetro | Testes Testes Gonadal Hormones associados | Situações clínicas |
|---|---|---|
| Insulina |
|
Aumentada em:
|
| Somatostatina | Somatostatina plasmática | Aumentada em:
|
| Glucagon Glucagon A 29-amino acid pancreatic peptide derived from proglucagon which is also the precursor of intestinal glucagon-like peptides. Glucagon is secreted by pancreatic alpha cells and plays an important role in regulation of blood glucose concentration, ketone metabolism, and several other biochemical and physiological processes. Gastrointestinal Secretions | Glucagon Glucagon A 29-amino acid pancreatic peptide derived from proglucagon which is also the precursor of intestinal glucagon-like peptides. Glucagon is secreted by pancreatic alpha cells and plays an important role in regulation of blood glucose concentration, ketone metabolism, and several other biochemical and physiological processes. Gastrointestinal Secretions plasmático | Aumentado em:
|
| Polipeptídeo pancreático | Polipeptídeo pancreático plasmático | Aumentado em:
|
| Amilase pancreática | Amilase sérica/plasmática | Aumentada em:
|
| Lipase Lipase An enzyme of the hydrolase class that catalyzes the reaction of triacylglycerol and water to yield diacylglycerol and a fatty acid anion. It is produced by glands on the tongue and by the pancreas and initiates the digestion of dietary fats. Malabsorption and Maldigestion pancreática | Lipase Lipase An enzyme of the hydrolase class that catalyzes the reaction of triacylglycerol and water to yield diacylglycerol and a fatty acid anion. It is produced by glands on the tongue and by the pancreas and initiates the digestion of dietary fats. Malabsorption and Maldigestion sérica | Aumentada em:
|
| Elastase Elastase A protease of broad specificity, obtained from dried pancreas. Molecular weight is approximately 25, 000. The enzyme breaks down elastin, the specific protein of elastic fibers, and digests other proteins such as fibrin, hemoglobin, and albumin. Proteins and Peptides pancreática | Elastase-1 Elastase-1 A protease of broad specificity, obtained from dried pancreas. Molecular weight is approximately 25, 000. The enzyme breaks down elastin, the specific protein of elastic fibers, and digests other proteins such as fibrin, hemoglobin, and albumin. Pancreatic Parameters (fezes) | Aumentada em: pancreatite aguda Diminuída em:
|
| Tripsinogénio | Tripsinogénio sérico | Aumentada em: pancreatite aguda |
| Quimotripsina | Quimotripsina (fezes) | Insuficiência pancreática: teste negativo |