A neurofibromatose tipo 1 ( NF1 NF1 Neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF1), also known as phakomatosis, is a neurocutaneous disorder that is most commonly of autosomal dominant inheritance due to mutations in the NF1 gene. Neurofibromatosis type 1 presents a range of clinical manifestations with the most prominent features being various pigmented skin lesions called café au lait macules (CALMs), neurofibromas, freckling of the inguinal and axillary regions, and iris hamartomas. Neurofibromatosis Type 1), também conhecida como facomatose, é uma doença neurocutânea que é mais MAIS Androgen Insensitivity Syndrome frequentemente de hereditariedade autossómica dominante devido a mutações no gene Gene A category of nucleic acid sequences that function as units of heredity and which code for the basic instructions for the development, reproduction, and maintenance of organisms. Basic Terms of Genetics NF1 NF1 Neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF1), also known as phakomatosis, is a neurocutaneous disorder that is most commonly of autosomal dominant inheritance due to mutations in the NF1 gene. Neurofibromatosis type 1 presents a range of clinical manifestations with the most prominent features being various pigmented skin lesions called café au lait macules (CALMs), neurofibromas, freckling of the inguinal and axillary regions, and iris hamartomas. Neurofibromatosis Type 1. A neurofibromatose tipo 1 apresenta uma variedade de manifestações clínicas, sendo as características mais MAIS Androgen Insensitivity Syndrome proeminentes as várias lesões cutâneas pigmentadas chamadas máculas de café com leite ( CALMs CALMs Light brown pigmented macules associated with neurofibromatosis and Albright's syndrome. Neurofibromatosis Type 1, pela sigla em inglês), tumores benignos da bainha nervosa chamados neurofibromas, sardas nas regiões inguinal e axilar e hamartomas da íris, referidos como nódulos de Lisch. Pelo menos metade dos indivíduos com NF1 NF1 Neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF1), also known as phakomatosis, is a neurocutaneous disorder that is most commonly of autosomal dominant inheritance due to mutations in the NF1 gene. Neurofibromatosis type 1 presents a range of clinical manifestations with the most prominent features being various pigmented skin lesions called café au lait macules (CALMs), neurofibromas, freckling of the inguinal and axillary regions, and iris hamartomas. Neurofibromatosis Type 1 tem dificuldades de aprendizagem. A neurofibromatose tipo 1 também pode causar osteodisplasia e transformação maligna de tumores. O diagnóstico é baseado na apresentação clínica típica e pode ser confirmado através de testes Testes Gonadal Hormones genéticos. O tratamento depende da apresentação clínica e pode variar desde a remoção cirúrgica até à quimioterapia/radioterapia de tumores, terapia ocupacional e fisioterapia se défices motores, tratamento com hormona do crescimento e órtese no caso de alterações ósseas.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
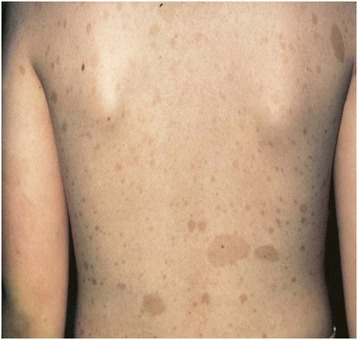
Máculas de café com leite (CALMs, pela sigla em inglês):
Imagem a demostrar CALMs bem circunscritos, castanho-claro e pigmentados que são frequentemente encontrados na população em geral. As máculas podem ter alguns milímetros a vários centímetros (> 20 cm) de tamanho e podem aparecer ao nascimento ou no início da vida. O desenvolvimento de múltiplos CALMs pode estar associado a síndromes genéticas como o neurofibroma tipo 1. As máculas podem ser tratadas com terapêutica com laser para fins estéticos.
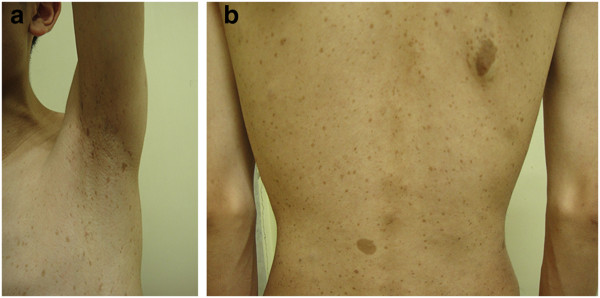
Sardas axilares (a) e vários CALMs (b) espalhando-se sobre a pele do tronco de um indivíduo com neurofibromatose tipo 1 (NF1)
Imagem: “The special signs of the patient. Axillary freckling (a) and multiple CALMs (b) spread over the skin of the trunk” por Duan, L. et al. Licença: CC BY 2.0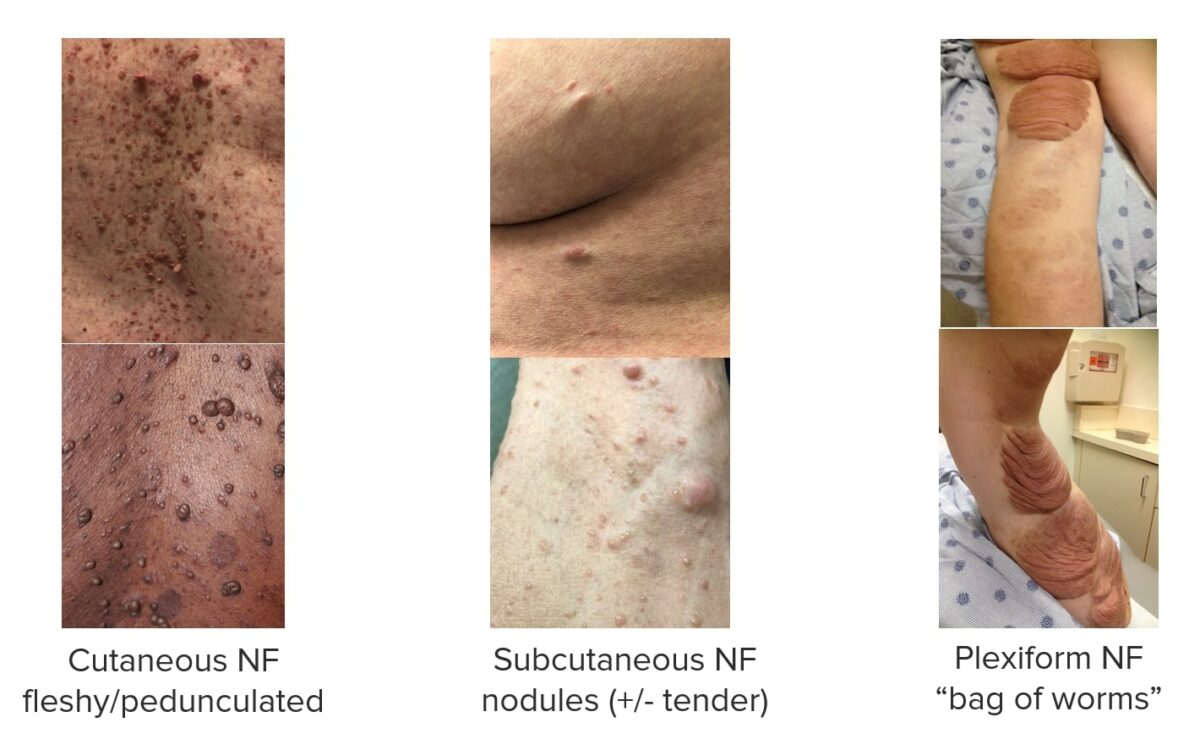
Neurofibromas (NF):
Imagens a mostrar diferentes tipos de neurofibromas associados à NF1.
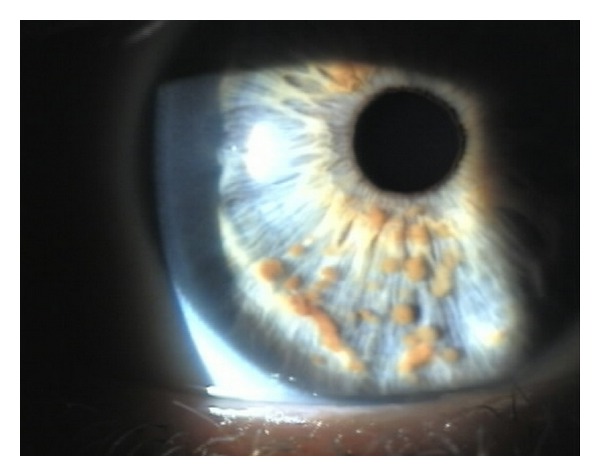
Nódulos de Lisch na íris:
Imagem a mostrar hamartomas pigmentados que derivam de melanócitos dendríticos
Imagem: “Várias pápulas pequenas, ovais, marrom-amareladas (nódulos de Lisch) na íris direita” por Adams, EG, et al. Licença: CC BY 3.0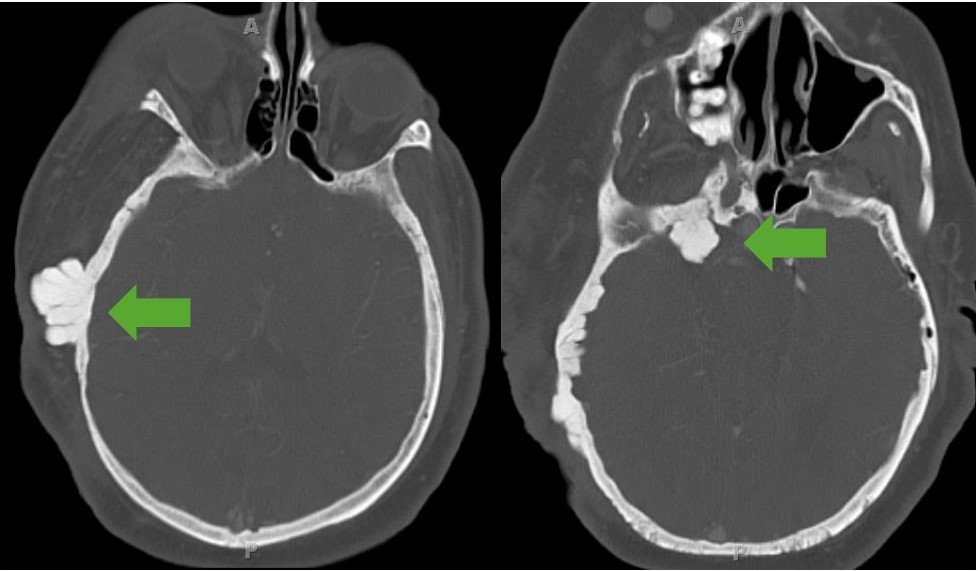
Displasia da asa do esfenóide:
Imagem de TC a demostrar displasia exofítica do osso esfenóide. Observar o envolvimento de tecidos moles visto como aumento de todo o lado direito da face do indivíduo.
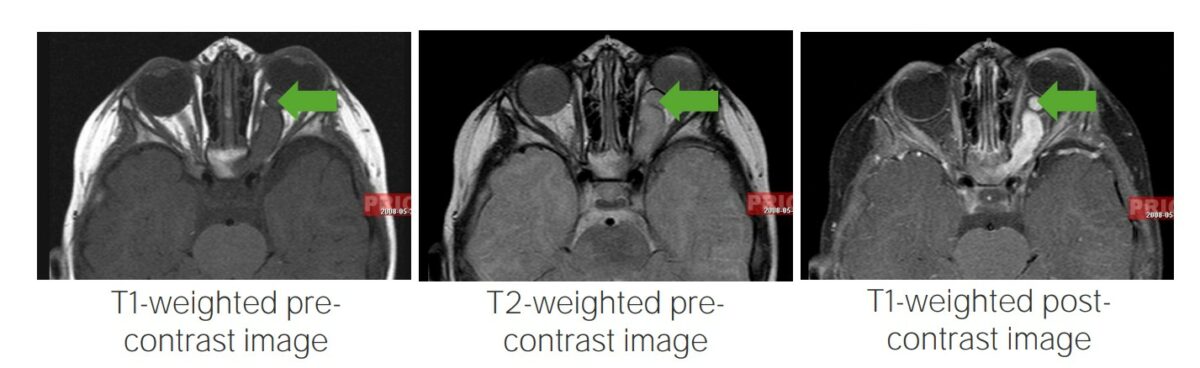
Glioma da via ótica:
Imagens de RMN a mostrar gliomas da via ótica, um achado típico em indivíduos com neurofibromatose tipo 1
O diagnóstico de NF1 NF1 Neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF1), also known as phakomatosis, is a neurocutaneous disorder that is most commonly of autosomal dominant inheritance due to mutations in the NF1 gene. Neurofibromatosis type 1 presents a range of clinical manifestations with the most prominent features being various pigmented skin lesions called café au lait macules (CALMs), neurofibromas, freckling of the inguinal and axillary regions, and iris hamartomas. Neurofibromatosis Type 1 geralmente é feito clinicamente com base na apresentação clínica típica e confirmado por testes Testes Gonadal Hormones genéticos.