A infertilidade é a incapacidade de engravidar na presença de relações sexuais regulares. Nas mulheres, as causas mais MAIS Androgen Insensitivity Syndrome comuns estão relacionadas com a disfunção ovulatória ou obstrução tubar, enquanto que, nos homens, uma causa comum são as alterações do esperma. O diagnóstico de infertilidade envolve a avaliação laboratorial da função ovulatória e uma histerossalpingografia para determinar a permeabilidade tubar em mulheres, nos homens, deve-se analisar o sémen. O tratamento envolve a abordagem da patologia subjacente quando possível e pode incluir indutores da ovulação com relações sexuais programadas ou inseminação intrauterina (IIU), fertilização in vitro (FIV) e gâmetas de dador, ou barrigas de aluguer ou adoção.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
A infertilidade define-se como a incapacidade de um casal conceber uma gravidez após 12 meses de relações sexuais regulares, nos casos de mulheres com < 35 anos, ou após 6 meses quando a mulher tem > 35 anos.
Para ocorrer uma gravidez, a mulher deve ovular e ter as trompas de falópio permeáveis, bem como um útero recetivo, enquanto o homem deve produzir espermatozoides capazes de fertilizar o oócito.
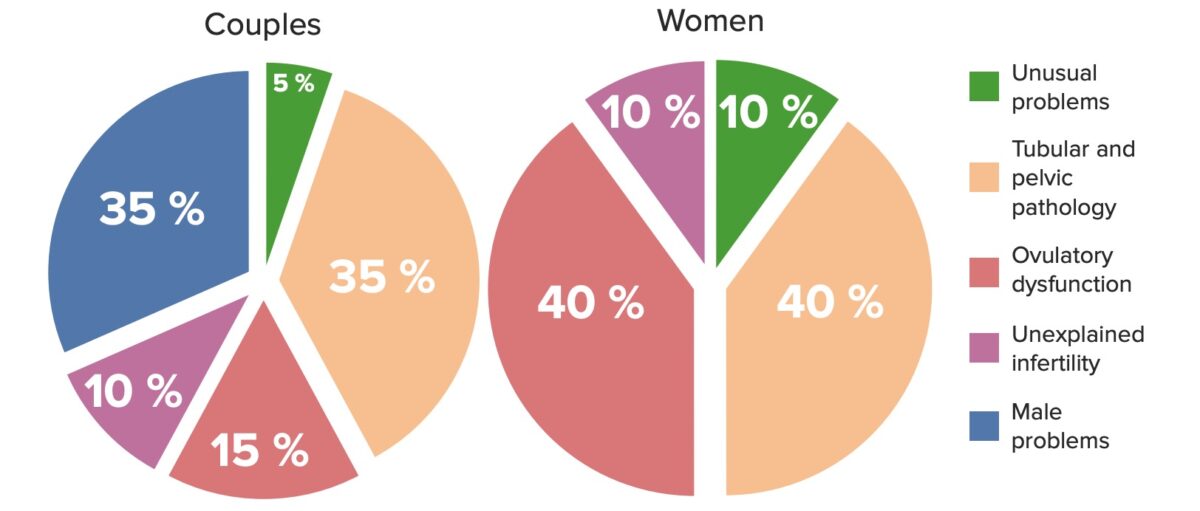
Etiologias de infertilidade em casais (esquerda) e em mulheres (direita)
Imagem por Lecturio. Licença: CC BY-NC-SA 4.0As causas de infertilidade feminina podem ser categorizadas em disfunção ovulatória, fatores tubários e fatores uterinos.
Revisão do eixo hipotálamo-hipófise-ovário (HPO, pela sigla em inglês):
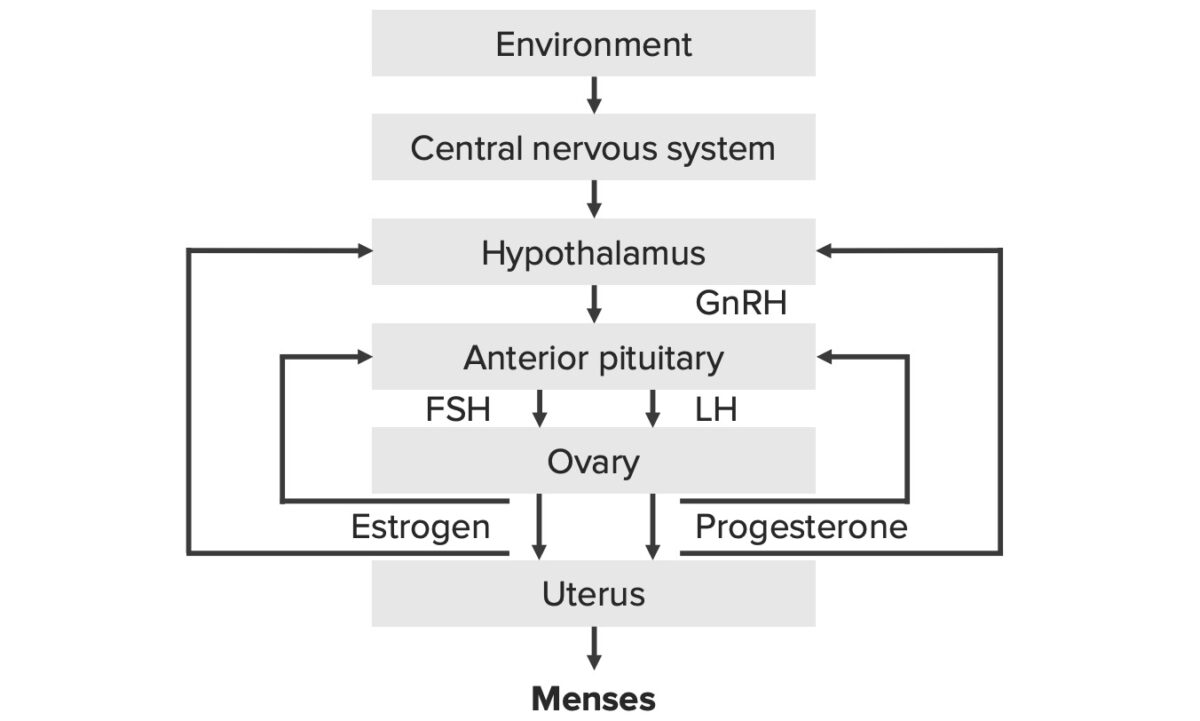
Eixo hipotálamo-hipófise-ovário (HPO, pela sigla em inglês)
GnRH: hormona libertadora de gonadotrofinas
FSH: hormona folículo-estimulante
LH: hormona luteinizante
Disfunção ovulatória:
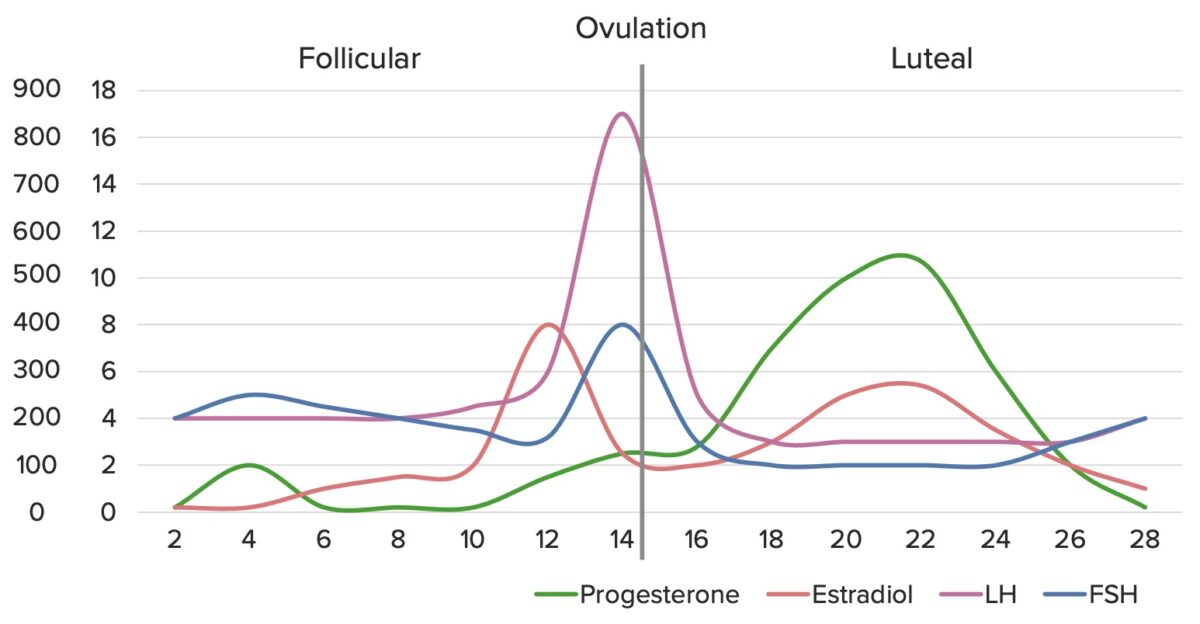
Flutuações hormonais normais ao longo do ciclo menstrual
Imagem por Lecturio. Licença: CC BY-NC-SA 4.0Fatores tubários:
Fatores uterinos:
Patologias endócrinas e sistémicas:
Defeitos testiculares na espermatogénese:
Patologias do transporte do esperma e disfunção sexual:
Clínica:
História menstrual minuciosa: ciclos regulares com mastodinia (dor mamária de forma cíclica e dor na ovulação) sugerem fortemente a ovulação.
Estudos laboratoriais:
Imagiologia:
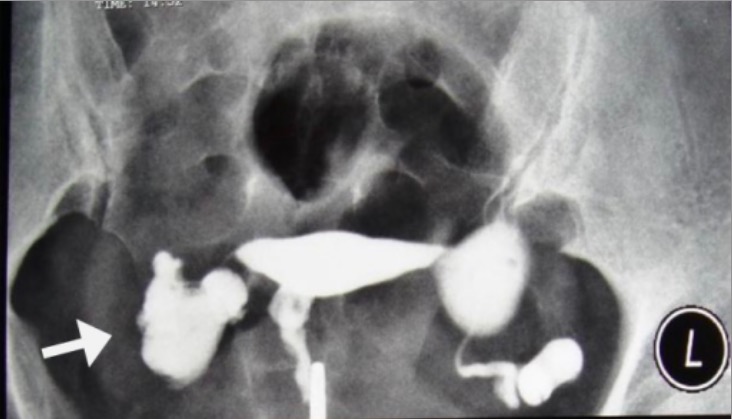
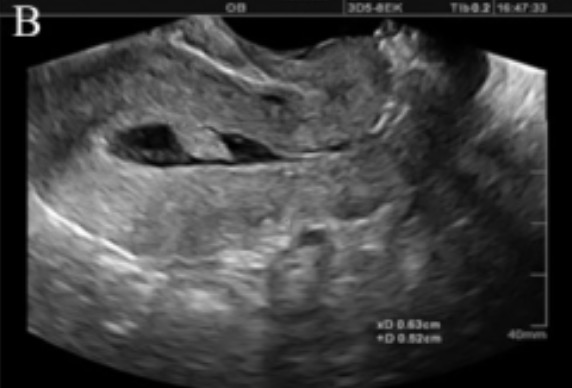
Uma mulher de 38 anos com tuberculose genital: na
histerossalpingografia observa-se uma saculação terminal e oclusão de ambas as trompas de falópio, causando hidrossalpingite (setas). A cavidade uterina tem uma aparência normal.
Histerossalpingografia com infusão salina onde se observa uma lesão pedunculada (provavelmente um pólipo) na cavidade uterina:
Numa ecografia transvaginal normal sem a infusão de solução salina, este achado apareceria apenas como uma área de revestimento endometrial espessado.
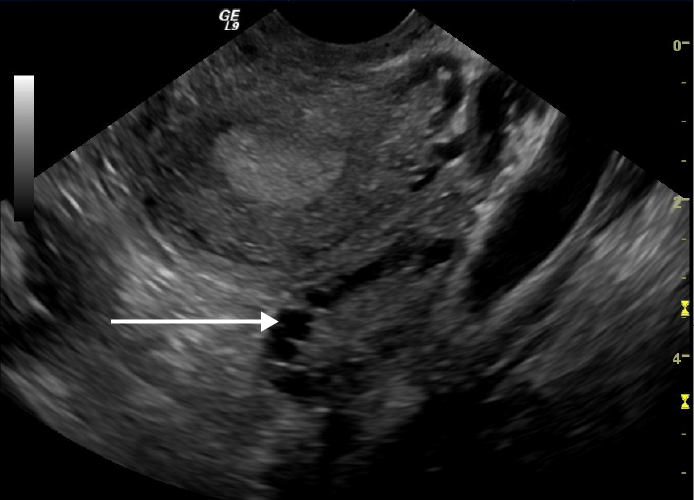
Ultrassonografia transvaginal apresenta um ovário poliquístico:
Observar os múltiplos quistos na periferia do ovário (seta branca)
Cirurgia:
Análise do sémen:
| Volume | 1,5-5,0 mL |
|---|---|
| pH pH The quantitative measurement of the acidity or basicity of a solution. Acid-Base Balance | > 7,2 |
| Viscosidade | < 3 |
| Sperm concentration | > 15 milhões/mL |
| Total sperm count | > 40 milhões/mL |
| Percentagem de espermatozoides móveis | > 40% |
| Motilidade progressiva | > 2 (baseado numa escala de 0 a 4) |
| Morfologia normal | > 4% normais |
| Células redondas | <1 milhão/mL |
| Aglutinação dos espermatozoides | <2 |
Avaliação laboratorial e imagiologia quando a análise do sémen é anormal:

Inseminação intra-uterina
Imagem : “Assisted reproductive technology process” por BruceBlaus. Licença: CC BY 3.0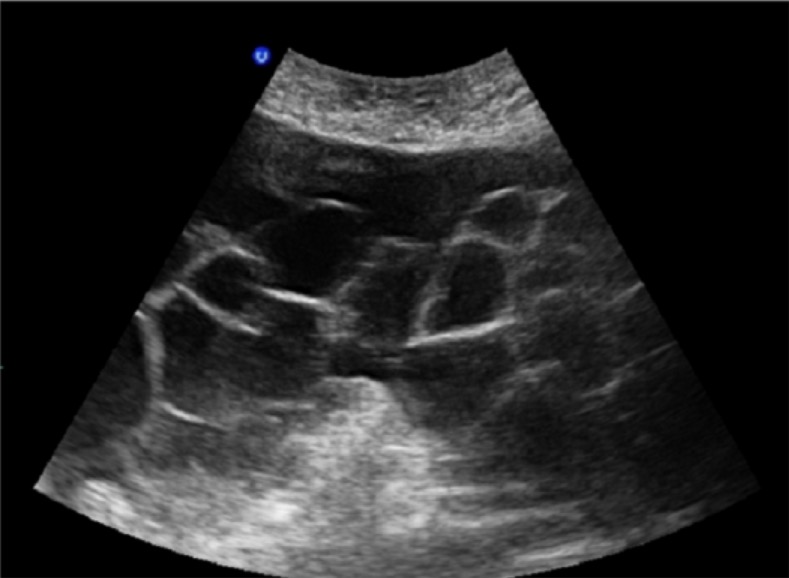
Massas quísticas multiloculares bilaterais numa doente com síndrome de hiperestimulação ovárica, numa gestação espontânea com mola invasiva
Imagem : “Bilateral multilocular cystic masses” pelo Myriam Rachad et al.Licença: CC BY 4.0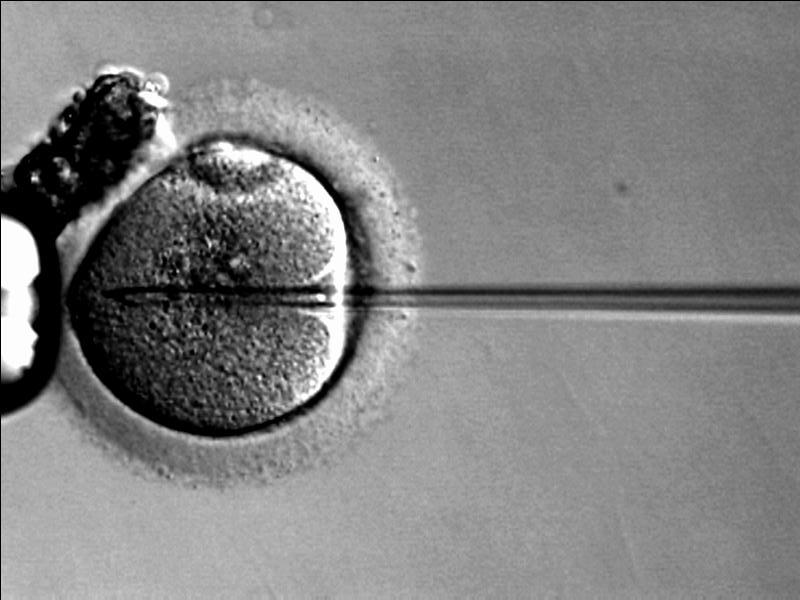
Injeção intracitoplasmática de espermatozoides (ICSI, pela sigla em inglês):
Técnica utilizada em casais que apresentam baixa motilidade na análise do sémen ou múltiplas tentativas fracassadas de fertilização in vitro