A imunodeficiência combinada severa ( SCID SCID Severe combined immunodeficiency (SCID), also called "bubble boy disease," is a rare genetic disorder in which the development of functional B and T cells is disturbed due to several genetic mutations that result in reduced or absent immune function. Severe Combined Immunodeficiency (SCID), pela sigla em inglês), também denominada “doença do menino da bolha”, é um distúrbio genético raro no qual o desenvolvimento de células B e T funcionais é perturbado devido a várias mutações genéticas, que resultam na redução ou usência da função imunológica. É a forma mais MAIS Androgen Insensitivity Syndrome grave de imunodeficiência primária e é caracterizada por disfunção nas resposta imune humoral e mediada por células. Múltiplas mutações podem resultar em tipos heterogéneos de SCID SCID Severe combined immunodeficiency (SCID), also called "bubble boy disease," is a rare genetic disorder in which the development of functional B and T cells is disturbed due to several genetic mutations that result in reduced or absent immune function. Severe Combined Immunodeficiency (SCID). Os doentes apresentam infeções graves e recorrentes nos primeiros meses de vida. O tratamento inclui imunoglobulinas IV e transplante de medula óssea. Se não for tratada, a SCID SCID Severe combined immunodeficiency (SCID), also called "bubble boy disease," is a rare genetic disorder in which the development of functional B and T cells is disturbed due to several genetic mutations that result in reduced or absent immune function. Severe Combined Immunodeficiency (SCID) geralmente é fatal no primeiro ano de vida.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Pelo menos 12 genes Genes A category of nucleic acid sequences that function as units of heredity and which code for the basic instructions for the development, reproduction, and maintenance of organisms. DNA Types and Structure são conhecidos por causar imunodeficiência combinada grave ( SCID SCID Severe combined immunodeficiency (SCID), also called “bubble boy disease,” is a rare genetic disorder in which the development of functional B and T cells is disturbed due to several genetic mutations that result in reduced or absent immune function. Severe Combined Immunodeficiency (SCID), pela sigla em inglês) se mutados, incluindo aqueles que codificam para o seguinte:
O padrão de hereditariedade depende do tipo de mutação genética envolvida:
| Fenótipo | Defeito genético |
|---|---|
| T–B+NK– | γC, JAK3 JAK3 A janus kinase subtype that is predominantly expressed in hematopoietic cells. It is involved in signaling from a broad variety of cytokine receptors including ones that utilize the interleukin receptor common gamma subunit. Severe Combined Immunodeficiency (SCID) |
| T–B–NK+ | RAG-1, RAG-2, Artemis, DNA DNA A deoxyribonucleotide polymer that is the primary genetic material of all cells. Eukaryotic and prokaryotic organisms normally contain DNA in a double-stranded state, yet several important biological processes transiently involve single-stranded regions. DNA, which consists of a polysugar-phosphate backbone possessing projections of purines (adenine and guanine) and pyrimidines (thymine and cytosine), forms a double helix that is held together by hydrogen bonds between these purines and pyrimidines (adenine to thymine and guanine to cytosine). DNA Types and Structure ligase IV, Cernunnos, DNA DNA A deoxyribonucleotide polymer that is the primary genetic material of all cells. Eukaryotic and prokaryotic organisms normally contain DNA in a double-stranded state, yet several important biological processes transiently involve single-stranded regions. DNA, which consists of a polysugar-phosphate backbone possessing projections of purines (adenine and guanine) and pyrimidines (thymine and cytosine), forms a double helix that is held together by hydrogen bonds between these purines and pyrimidines (adenine to thymine and guanine to cytosine). DNA Types and Structure PKcs |
| T–B+NK+ | IL-7Rα, CD3δ, CD3ζ, Coronin-1A, ZAP-70, CD45 |
| T–B–NK– | ADA ADA An enzyme that catalyzes the hydrolysis of adenosine to inosine with the elimination of ammonia. Purine and Pyrimidine Metabolism, AK2 |
| Síndrome | Defeito |
|---|---|
| Imunodeficiência Combinada Severa Ligada ao X | Mutações no gene Gene A category of nucleic acid sequences that function as units of heredity and which code for the basic instructions for the development, reproduction, and maintenance of organisms. Basic Terms of Genetics que codifica a cadeia γ comum, uma proteína que é compartilhada pelos recetores das interleucinas IL-2, IL-4, IL-7 IL-7 A proinflammatory cytokine produced primarily by T-lymphocytes or their precursors. Several subtypes of interleukin-17 have been identified, each of which is a product of a unique gene. Severe Combined Immunodeficiency (SCID), IL-9, IL-15 e IL-21 |
| Deficiência da adenosina desaminase |
|
| Deficiência de nucleosídeo fosforilase de purina ( PNP PNP An enzyme that catalyzes the reaction between a purine nucleoside and orthophosphate to form a free purine plus ribose-5-phosphate. Purine and Pyrimidine Metabolism, pela sigla em inglês) | Doença autossómica recessiva que envolve mutações do gene Gene A category of nucleic acid sequences that function as units of heredity and which code for the basic instructions for the development, reproduction, and maintenance of organisms. Basic Terms of Genetics PNP PNP An enzyme that catalyzes the reaction between a purine nucleoside and orthophosphate to form a free purine plus ribose-5-phosphate. Purine and Pyrimidine Metabolism |
| Disgenesia reticular | Incapacidade dos precursores de granulócitos formarem grânulos secundários devido ao mau funcionamento da adenilato cinase 2 mitocondrial |
| Síndrome de Omenn |
|
| Síndrome do linfócito nu |
|
| JAK3 JAK3 A janus kinase subtype that is predominantly expressed in hematopoietic cells. It is involved in signaling from a broad variety of cytokine receptors including ones that utilize the interleukin receptor common gamma subunit. Severe Combined Immunodeficiency (SCID) | JAK3 JAK3 A janus kinase subtype that is predominantly expressed in hematopoietic cells. It is involved in signaling from a broad variety of cytokine receptors including ones that utilize the interleukin receptor common gamma subunit. Severe Combined Immunodeficiency (SCID) é uma enzima que medeia a transdução a jusante dos sinais γc. |
A doença geralmente apresenta-se na primeira infância (2-6 meses). Nos indivíduos afetados observam-se infeções oportunistas graves e recorrentes.
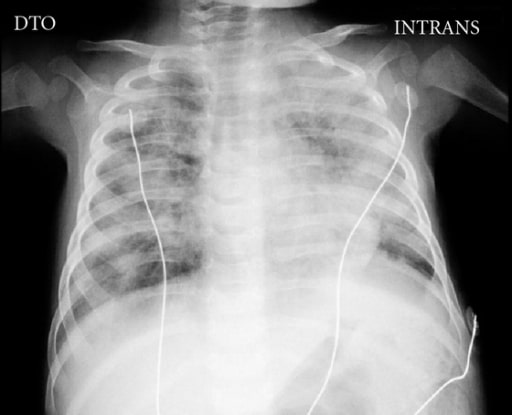
Radiografia de tórax de um menino de 5 meses com SCID complicada por doença disseminada pelo bacilo Calmette-Guérin (BCG) a demostrar a ausência de timo e áreas bilaterais de opacidades
Imagem: “Chest X-ray” por Pediatric Intensive Care Unit, Hospital Dona Estefânia, 1169-045 Lisboa, Portugal. Licença: CC BY 3.0
As seguintes condições são diagnósticos diferenciais de SCID SCID Severe combined immunodeficiency (SCID), also called “bubble boy disease,” is a rare genetic disorder in which the development of functional B and T cells is disturbed due to several genetic mutations that result in reduced or absent immune function. Severe Combined Immunodeficiency (SCID):